Ch. 8: Assessment Techniques and Safety in the Clinical Setting
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What's the role of the examiner?
introduce yourself, state purpose of exam, ask if room is up to their standards, ensure patient is dressed properly/has privacy, and wash hands in front of patient
How can you keep a clean field?
wipe everything down before and after your patient
What's the general approach to assessing your patient?
wash hands, use gloves if needed, take basic measurements, build trust, document as you go from head to toe, and keep patient warm
How do you build trust with patient?
start by working with hands
What are the four major assessment techniques? What order are they done in?
inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation (in that order)
What do you do during the inspection portion?
carefully watch the patient, compare right to left, inspect each body system, START WITH HANDS!!
What do you do during the palpation portion?
use your hands to feel the body and confirm what you saw during inspection
What should you use your fingertips for during palpation?
feeling for texture, swelling, and lumps
What should you use your fingers and thumbs for during palpation?
check organs/masses shape, consistency, and position
What should you use your back of the hand for during palpation?
feeling temperature
What should you use your base of the hand for during palpation?
best for feeling vibration
What do you do during the percussion portion?
tapping the skin to make sounds that tells you whats underneath
What is amplitude?
intensity
What is pitch?
number of vibrations per second
What is quality?
difference between sounds
What is duration?
the length of time the note lingers
If there is abdominal issues what order would IPPA go in?
auscultation goes first
If there is a baby what order would IPPA go in?
auscultation, percussion, palpation, and inspection (GO BACKWARDS)
What does resonant sound like?
- hollow, low pitch, medium amp, moderate length
- found over normal lung tissue
What does hyper-resonant sound like?
- booming, lower pitch, louder amp, long length
- found over child's lung
What does tympany sound like?
- drumlike, high pitch, loud amp, longest in length
- found at stomach or the intestine
What does dull sound like?
- muffled thud, high pitch, soft amp, short length
- found in liver or spleen
What do you do during the auscultation portion?
listening to body sounds with a stethoscope
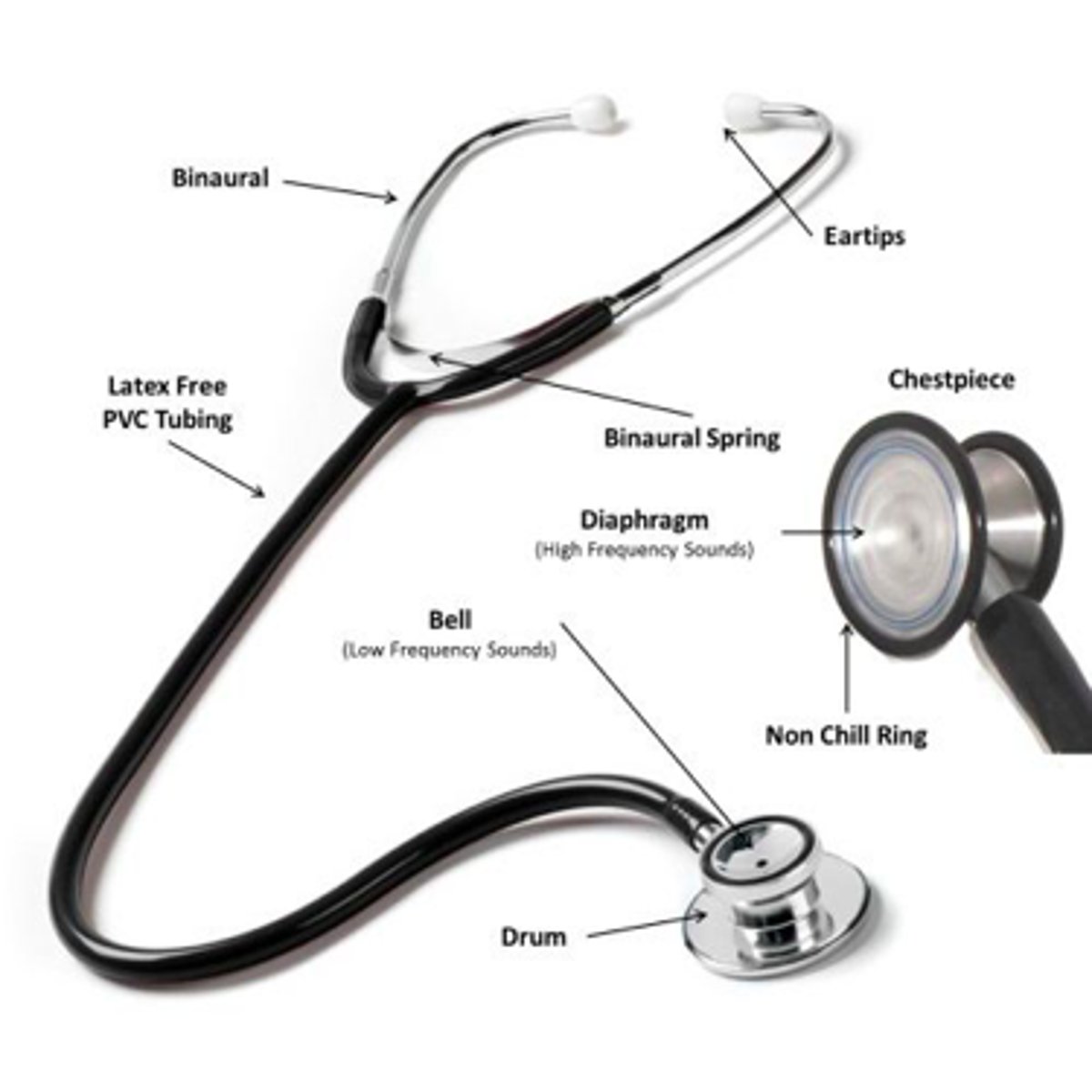
What are the parts of a stethoschope?
ear tips, ear tubes, tubing, diaphragm, (big part), and bell (small part)
What's an otoscope used for?
looking into ear canal
What's an ophthalmoscope used for?
looking at eyes
What is high fowler seating?
patient sitting with legs dangling
What is the lithotomy position?
Lying flat on the table with feet on stirrups, and legs apart
What is the semi fowler position?
The head of the bed is at 30 degrees and knees are flat
How do you assess an infant?
place baby on table (mom can hold when baby reaches 6 months), keep tools warm, do head, ears, eyes, nose, then throat
When should the baby be fed for a doctors appointment?
exam be 2 hours after fed
How do you assess a toddler?
allow to sit on parent, sit knee to knee, temp and ears won't go well, get info from parent, ask parent to undress when needed
How do you assess a preschooler?
they can answer questions, let them undress, leave underwear on, allow parents to undress, explain whats going to happen and let them examine tools
How do you assess a school age child?
sit on table, allow privacy, use small talk, demo tools before use, use head to toe sequence
How do you assess an adolescent?
privacy, they want to be normal, aware of body image, communicate abt hygiene, and assess emotional state
How do you assess a aging adult?
allow rest periods, physical touch is important, do not mistake diminished vision or hearing for confusion, be aware they have more life stressors