Consciousness + Cell Bio - Psyc 211
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is consciousness?
the state or quality of awareness
What is cut in split brain surgery?
Corpus callosum
Left brain controls: (3 things)
1) Muscles on right half of body
2) Complex language comp + speech + writing
3) Processing right half of visual field
Right brain controls: (3 things)
1) Muscles on left half of body
2) Limited language (small ‘dictionary’)
3) Processing left half of visual field
The Left visual field is processed by the __ half of __ eye
Right; each
The Right visual field is processed by the __ half of __ eye
Left; each
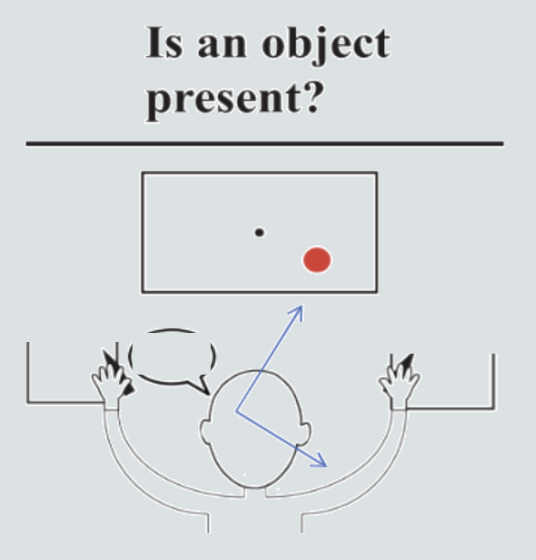
What will a split brain patient report:
1) Verbally?
2) Writing with the left hand?
3) Writing with the right hand?
1) Yes - left hemisphere sees the right side and the dot
2) No - Right hemisphere sees empty left side
3) Yes - left hemisphere sees right side and the dot
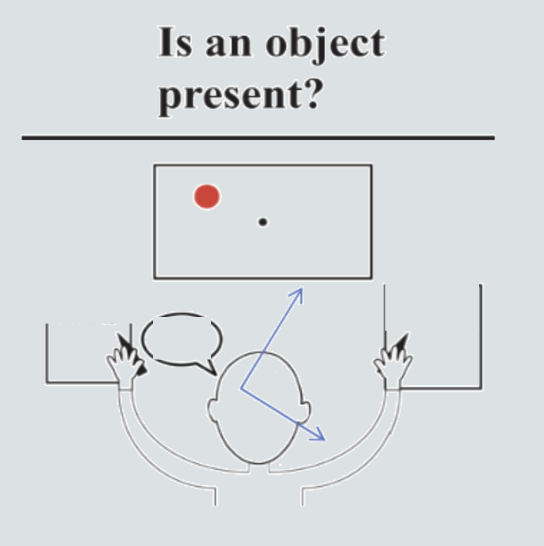
What will a split brain patient report:
1) Verbally?
2) Writing with the left hand?
3) Writing with the right hand?
1) No - left hemisphere sees empty right side
2) Yes - left side is controlled by right hemisphere which sees left visual field
3) No - left hemisphere sees empty right side
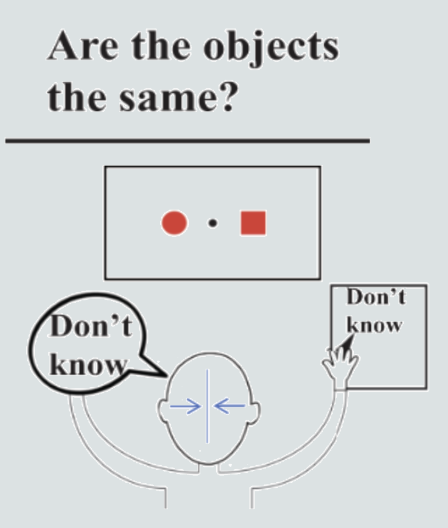
What will a split brain patient report:
1) Verbally?
2) Writing with the left hand?
3) Writing with the right hand?
1) Don’t know - the patient can’t compare because hemispheres can’t communicate
2) No answer - Left hand can’t process question / respond bc of limited language bank (right brain)
3) Don’t know - Right hand (left hem) doesn’t know what right hemisphere saw
What is Gazzaniga’s Interpreter Theory?
No free will - behaviour is out of our control
left brain develops meaningful narrative through which we can understand out experiences
What is the acronym for what the biological world is made up of?
CHNOPS
What are the CHNOPS?
Carbon - 11%
Hydrogen - 59%
Nitrogen - 4%
Oxygen - 24%
Phosphorus/Sulpher/Other - 2%
What are the 5 main molecules that CHNOPS form?
Water, Sugar, Fat (lipids), Nucleic Acids, Amino Acids
What are Ribozymes
A subGroup of RNA that can catalyze chemical reactions
RNA vs DNA
RNA - Single stranded chain of nucleic acids; fragile; prob gave life to first life on earth
DNA - Double stranded chain of nucleic acids; stable; primary storage of genetic info
What is the cell membrane made of (specify the two parts also)
Phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic phosphate head
hydrophobic lipid tail
The ___ bilayer makes diffusion across the cell membrane ___.
Phospholipid bilayer; difficult
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells (3 pt)
Prokaryotic:
single cell organisms
cell membrane filled with cytoplasm
DNA/RNA/Ribosomes free floating inside
Eukaryotic:
Single OR Multi-cell organisms
Contains organelles (like mitochondria and nucleus)
Can store DNA + create energy
What is cytoplasm?
Salty nutrient filled liquid inside all cells - everything inside the cell nucleus
What are the 4 steps of protein synthesis?
Segment of DNA in the nucleus is unraveled and a complementary strand of RNA is created (mRNA)
mRNA leaves the nucleus
Ribosome latches onto mRNA and recruits tRNA to bring in complementary amino acids
Amino acids are added to a growing chain that eventually breaks off and folds into a protein
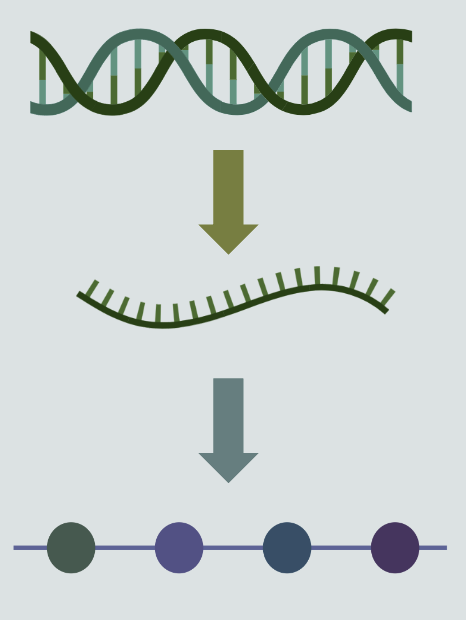
mRNA vs tRNA and what process are they found in?
Found in Protein Synthesis
mRNA - Messenger - carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes
tRNA - Transfer - brings specific amino acids to ribosome
Proteins are chains of what?
Amino acids!
Jobs of a protein (6 listed)
Scaffolding; transporting molecules; channels; receptors; enzymes; cellular repair
4 Parts of a neuron
Soma - cell body
Dendrites - loading docks (receive chem/sensory input)
Axon - relay system- electrical signals sent down length
Axon terminals - send off point - where action potential triggers release of neurotransmitter
What is Cytosol
Salty water-like solution inside neuron/cell - filled with potassium (K+), chloride (Cl-), and sodium (Na+)
What makes a cell specialized
What part of the DNA it reads
neurons are filled w/ proteins that determine a cell’s role
What are the two ways Neurons communicate?
Electrically - within a cell - action potential
Chemically - between cells - neurotransmitter release
Cations vs Anions
Cations - Pos charge (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg+)
Anions - Neg charge (Cl-)
Potassium (K+) is more abundant (inside/outside) cell and wants to (leave/enter) the cell
Inside; leave
Sodium (Na+) is more abundant (inside/outside) cell and wants to (leave/enter) the cell
Outside; Enter
What does the Sodium Potassium pump do?
Sets the concentration gradient; sends Na+ out of cell and K+ into cell
What’s the concentration gradient?
The difference in the amount of an ion present in one area vs another
What are determines where ions want to go? (2 things)
Diffusion and Electrostatic force
How does Diffusion determine Ion movement?
Ions want to be spread out from other similar ions
if many of the same ion are close together - there’s a pressure to spread away
Ex: K+ within the cell → wants to leave
How does Electrostatic Force determine Ion movement?
Ions want to be spread out from similarly charged ions
opposites attract, similar charges repulse
Mom analogy
Lee and Laura are very much opposites (but they are still attracted to each other)
Lee = K+
inside circle - always trying venture out and meet more ppl
Laura = Na+
feels like she’s on the outside and wants to get in to the more extroverted people on the inside
Equilibrium potential of K+ is?
-90 mV
Resting membrane potential inside neuron?
-70mV
What does the Potassium Leak Channel do?
Allows K+ to move freely in/out cell; K+ leaking sets/maintains cell’s resting membrane potential (making it negative)
What starts an action potential? (3 things)
we have a negatively charged cell → pos ions want to come in bc of electrostatic pressure
Sodium wants to come in to lower the concentration gradient
A depolarizing stimulus
Ex: neurotransmitters released from another cell → sensory stimulus
Ex: Receptor binding opens ion channels which allows initial influx of Na+
Membrane potential goes from __ to __ when action potential is initiated?
-70mV → -40mV
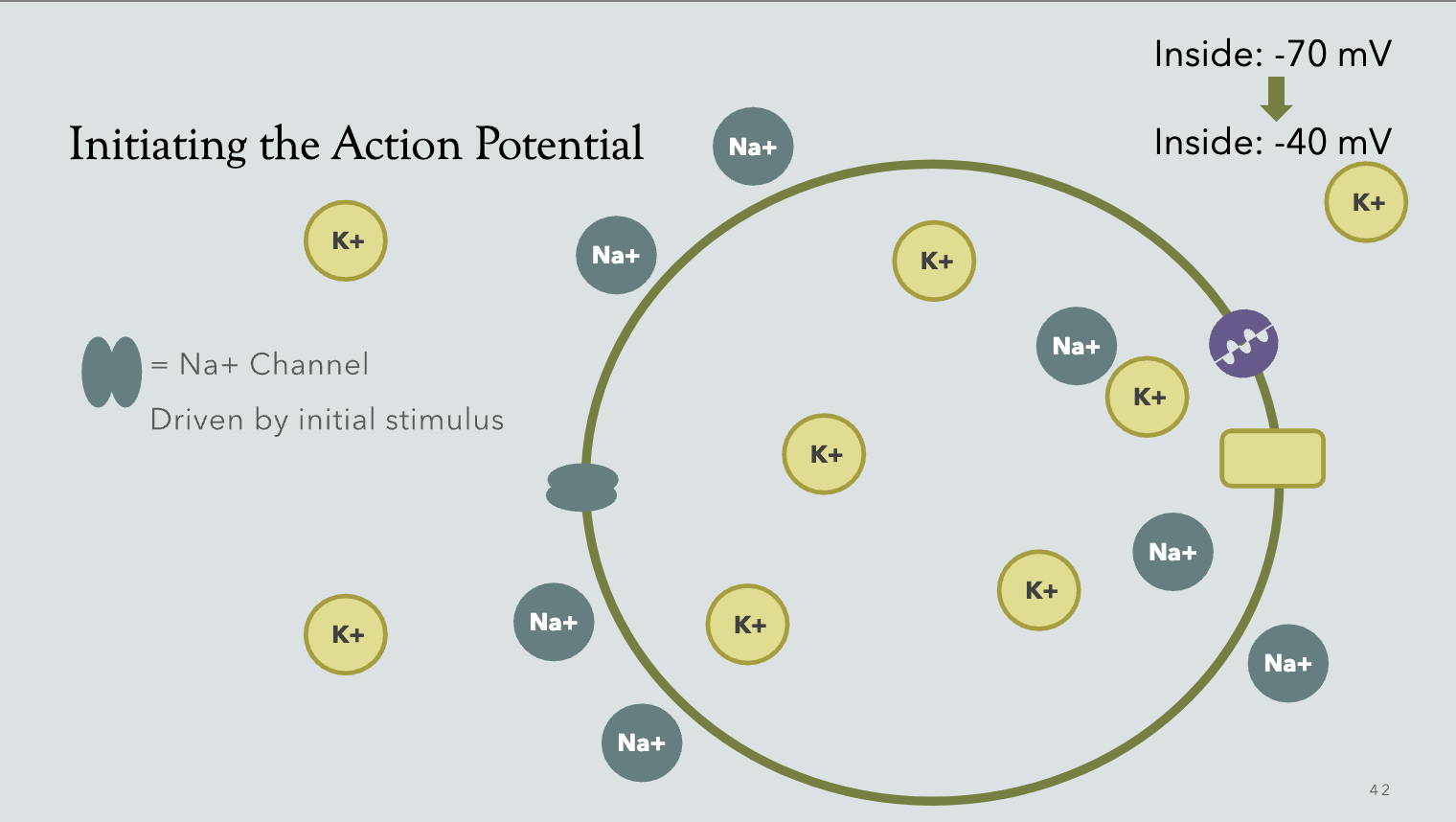
When Sodium (Na+) rushes in during action potential, what is the membrane potential change?
-40mV → +40mV
Voltage Gated Sodium channel (3 pts)
Opens when cell is slightly depolarized (aprox -40mV)
Ball and chain system blocks pore
Inactivates channel after opening
What ion channel aids in the return to baseline membrane potential (end of action potential)
Voltage-Gated Potassium (K+) channel
Voltage-Gated Potassium (K+) channel (2 pts)
Opens during upswing of action potential (aprox 0mV)
Responsible for return to baseline membrane potential
Hyperpolarization of membrane potential - action potential
(think refractory period)
Some VG K+ channels are still open so K+ leaves, sends Vm more negative then baseline
7 Stages of the Action Potential (AP) & their Vm:
Baseline: -70mV
Stimulus: -40mV
Upswing: increasing towards peak
Peak: +40mV
Downswing: decreasing towards hyper-polarization
Hyper-polarization: abt -80mV
Return to baseline: -70mV
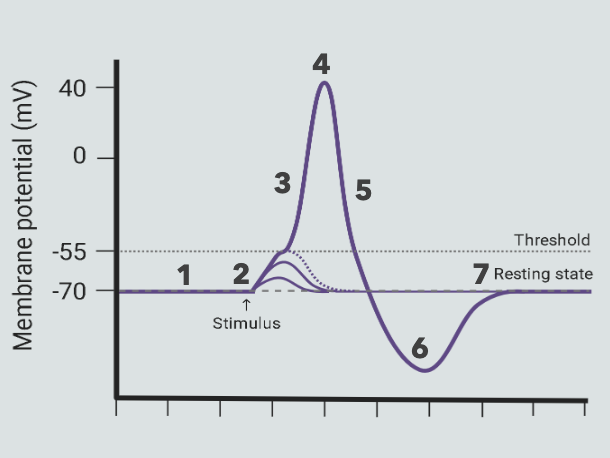
What’s happening during AP stage 1? (Baseline)
Na+/K+ pump changes ion concentrations; K+ leak channel brings K+ out
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: Na+ wants in
What’s happening during AP stage 2? (Stimulus)
External input depolarizes cell → a few VG Na+ channels open
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: Na+ wants in
What’s happening during AP stage 3? (Upswing)
Tons of VG Na+ channels open; VG K+ channels start to open
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
What’s happening during AP stage 4? (Peak)
VG Na+ channels are plugged by ball & chain mechanism; VG K+ channels still opening
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: K+ wants out
What’s happening during AP stage 5? (Downswing)
VG K+ channels open
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: K+ wants out
What’s happening during AP stage 6? (Hyper-Polarization)
Some VG K+ channels still open, K+ leaves → sends Vm more negative then baseline
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: Na+ wants in
What’s happening during AP stage 7? (Return to Baseline)
VG K+ channels close; Vm set by Na+/K+ pump and K+ leak channel
Diffusion: Na+ wants in; K+ wants out
Electrostatic Force: Na+ wants in
Does the force of diffusion ever change? Why?
No - the relative concentrations never change
Voltage-Gated (VG) Calcium Channel
Ca2+ into cell triggers neurotransmitter release
What (2) ion channels set the resting potential?
Sodium Potassium Pump (Na+/K+) & Potassium leak channel (K+)
What (2) ion channels open/close during action potential (AP)?
VG sodium channel (Na+) & VG potassium channel (K+)
What ion channel opens/closes at the axon terminal?
VG calcium channel (Ca2+)
Can an action potential ever go backwards?
Yes but only in experimental situations - never naturally.
Why doesn’t the action potential travel backwards?
AP involves influx of pos charge ions into cell which push other pos ions away (down the concentration gradient)
Previously active VG Na+ are in refractory period (ball clogging pore) → influx of pos ions can’t reopen them
What makes propagation of the action potential more efficient/faster
Myelination!
What is myelination?
An insulating layer of fat around segments of the axon (like the plastic around wires which speeds up their conductivity)
What are Glia Cells?
Crucial non-neuron cells in nervous system that provide support/protection/nourishment to neurons
4 types of Glia cells?
Astrocytes - janitors of cell
break down and clean up waste
provide scaffolding for other cellular functions
Microglia - nurses
provide immune support
regulate cell development + injury response
Oligodendrocytes - contractors
Create myelin + wrap it around nearby axons
can provide sheath for 50 axons
*Schwann cells = equivalent in peripheral nervous system
Ependymal Cells - soldiers
line the ventricles
Circulate CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
What’s the effect of insulated sections of the axon on the ions inside?
The ions are insensitive to charge differences outside
What is saltatory conduction?
the propagation of action potentials along myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next
What are Nodes of Ranvier?
Unmylinated segments of membrane where the AP is re-propagated
How many main types of receptors are there & what are they?
The 2 main types are Ionotropic receptors and metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic receptors (3 pts)
Ion channels (in the name)
Direct/fast effect on (next) cell’s potential
EPSP or IPSP
Metabotropic receptors (3 pts)
G-protein coupled receptors
Can act indirectly on ion channels
Slower modification of cell excitability
EPSP
Excitatory postsynaptic potential - NA+ permeable - doesn’t always induce AP
IPSP
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential - Cl- permeable - doesn’t always prevent AP
How do Neurotransmitters get removed? (3 things)
Re-uptake
re-uptake proteins transport NT bac kacross membrane of presynaptic cell
nt can then be repackaged into vesicle for next round of release
Enzymatic deactivation
enzymes break down NT in synapse
Diffusion
Released NT moves down its concentration gradient away from initial release site
What does the effect of a metabotropic receptor depend on?
The receptor itself & the signalling cascade its activation causes