Topic 6 Cities
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Site factors
location based on environmental factors
Situation Factors
Location factors related to the transportation of materials into and from a factory.
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.
Borchert's epochs
According to the geographer John R. Borchert, American cities have undergone five major epochs, or periods, of development shaped by the dominant forms of transportation and communication at the time. These include sail-wagon epoch (1790-1830), iron horse epoch (1830-1870), steel rail epoch (1870-1920), auto-air-amenity epoch (1920-1970), and satellite-electronic-jet propulsion and high-technology epoch (1970-present).
The Sail wagon epoch
Period of expansion with primitive overland and waterway circulation - leading cities northeastern ports heavily oriented to European overseas trade - Hinterlands barely accessible.
The Iron Horse Epoch
Period dominated by steam-powered railroad, provided nation-wide transportation system, New York primate city by 1850.
The Steel Rail Epoch
Period with full establishment of national metropolitan system, increasing scale of manufacturing, rise of steel and automobile industries.
Auto-Air Amenity Epoch
Period of maturation of national urban hierarchy, key elements were airplane and automobile, expansion of white-collar services jobs, growing pull of amenities (pleasant environments) stimulating urbanization of the suburbs.
Trade networks
a system of people in different lands who trade goods
Rural-urban migration
the movement of people from the countryside to the city
Squatter Settlements
a lower income housing development that fails to provide basic functions
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
Urban Sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land.
Suburbs
residential areas surrounding a city
Edge Cities
A large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area.
Boomburbs
Rapidly growing suburb cities
Exurbs
Prosperous residential districts beyond the suburbs.
World Cities
A group of cities that form an interconnected, internationally dominant system of global control of finance and commerce
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements according to their size and economic functions.
Rank Size Rule
In a model urban hierarchy, the idea that the population of a city or town will be inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchy.
Primate City
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
The Gravity Model
A mathematical formula that describes the level of interaction between two places, based on the size of their populations and their distance from each other.
Central Place Theory
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
High-Order Goods and Services
relatively costly; larger range EX: an arena, hospital
Low-Order Goods and Services
less costly, smaller range ex: McDonalds
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
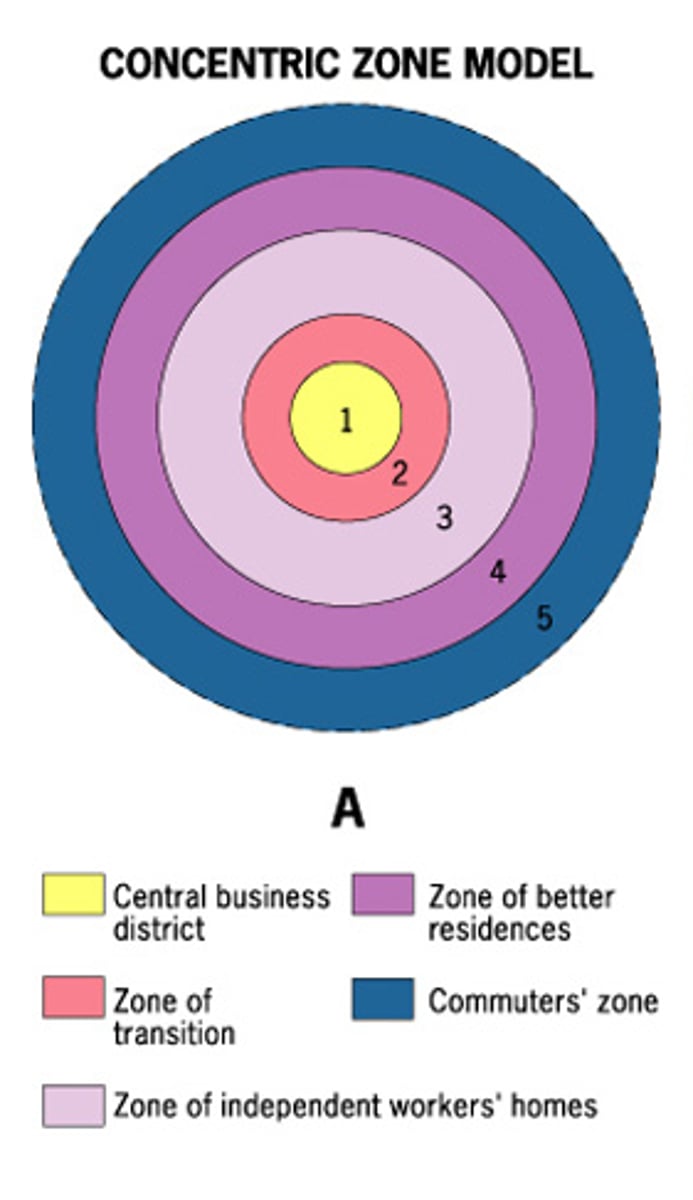
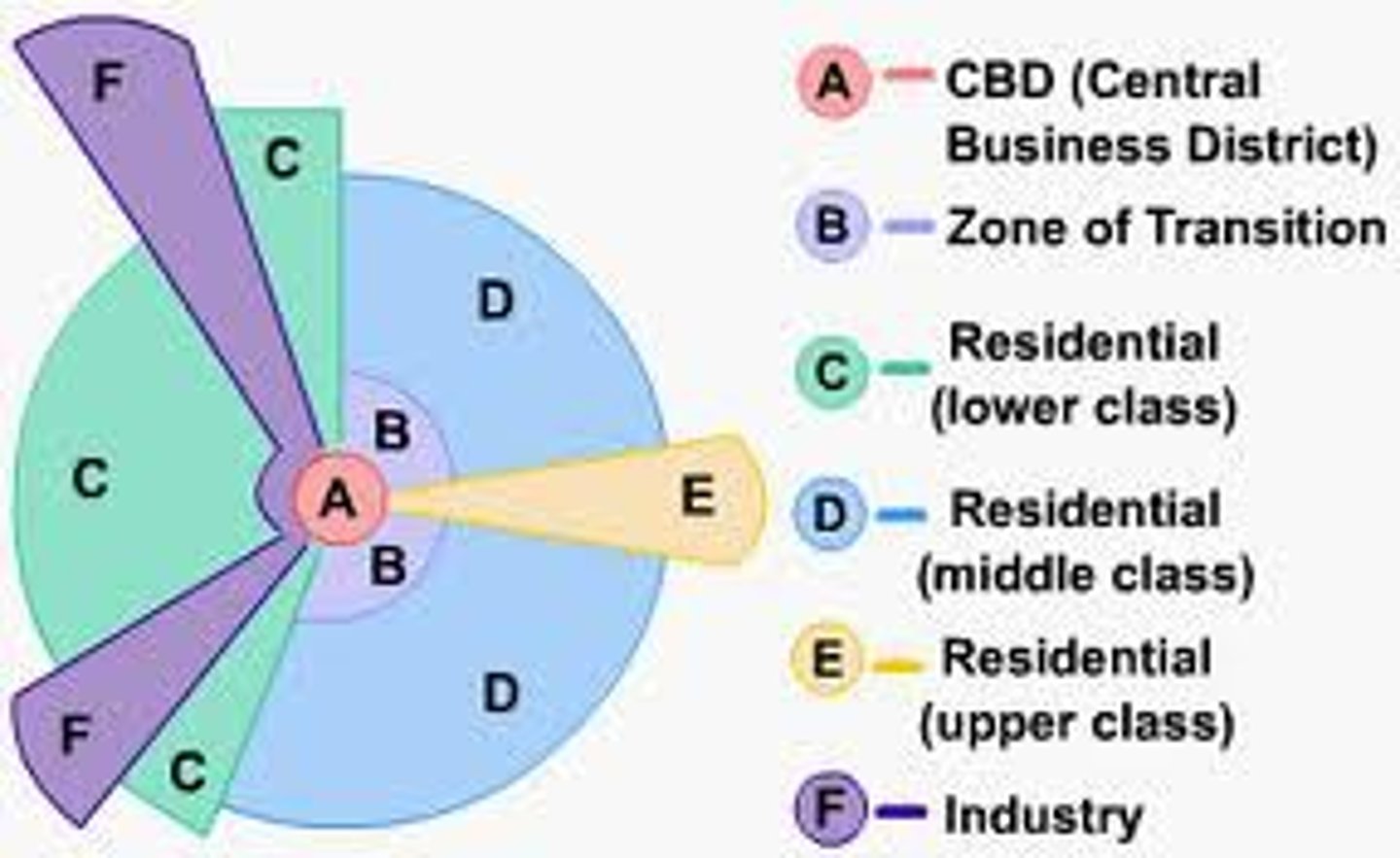
Hoyt Sector Model
the theory of urban structure that a city develops in a series of certain sectors, instead of rings.
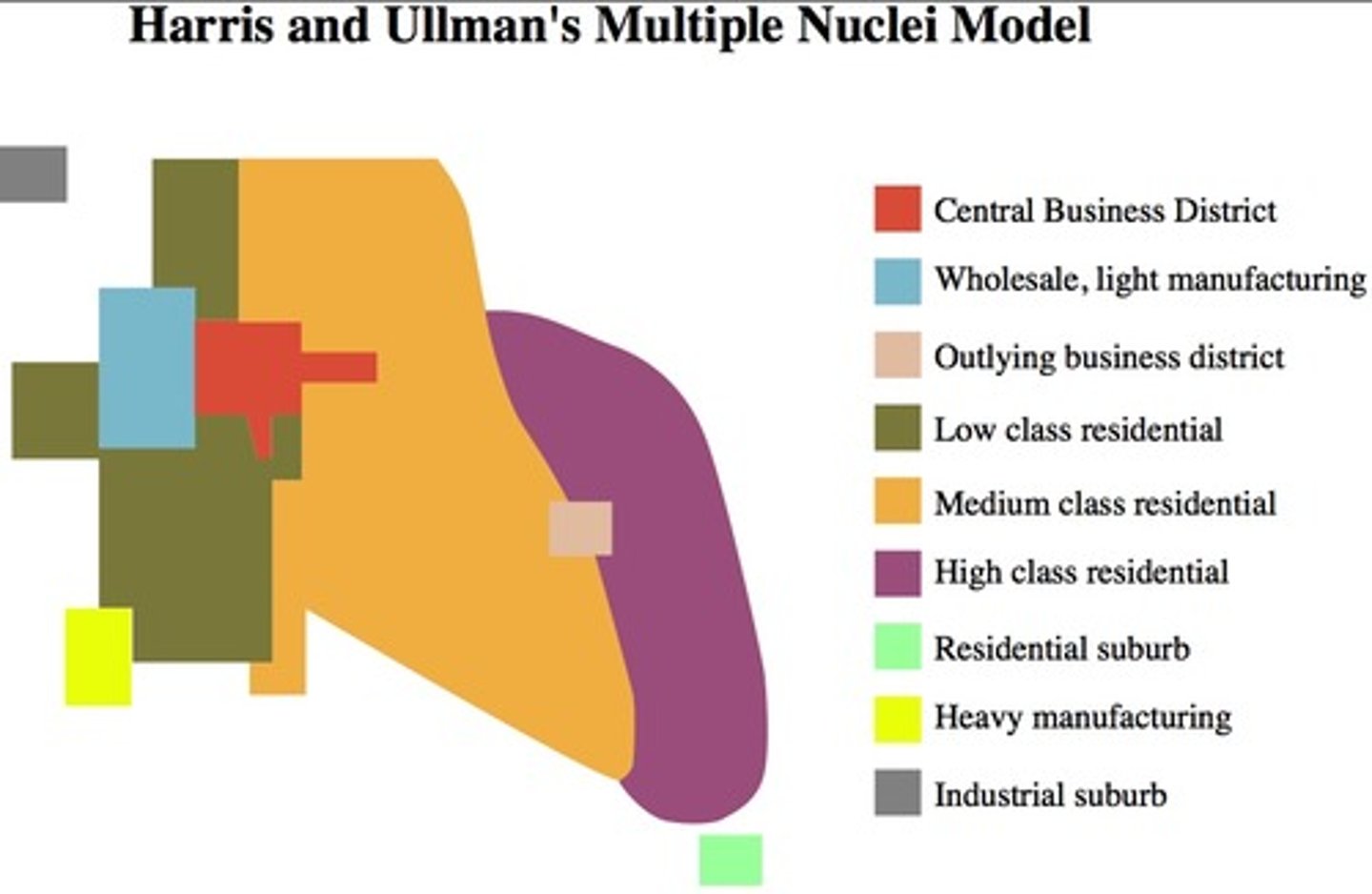
Harris and Ullman Multiple Nucleu Model
model where there are multiple CBDs
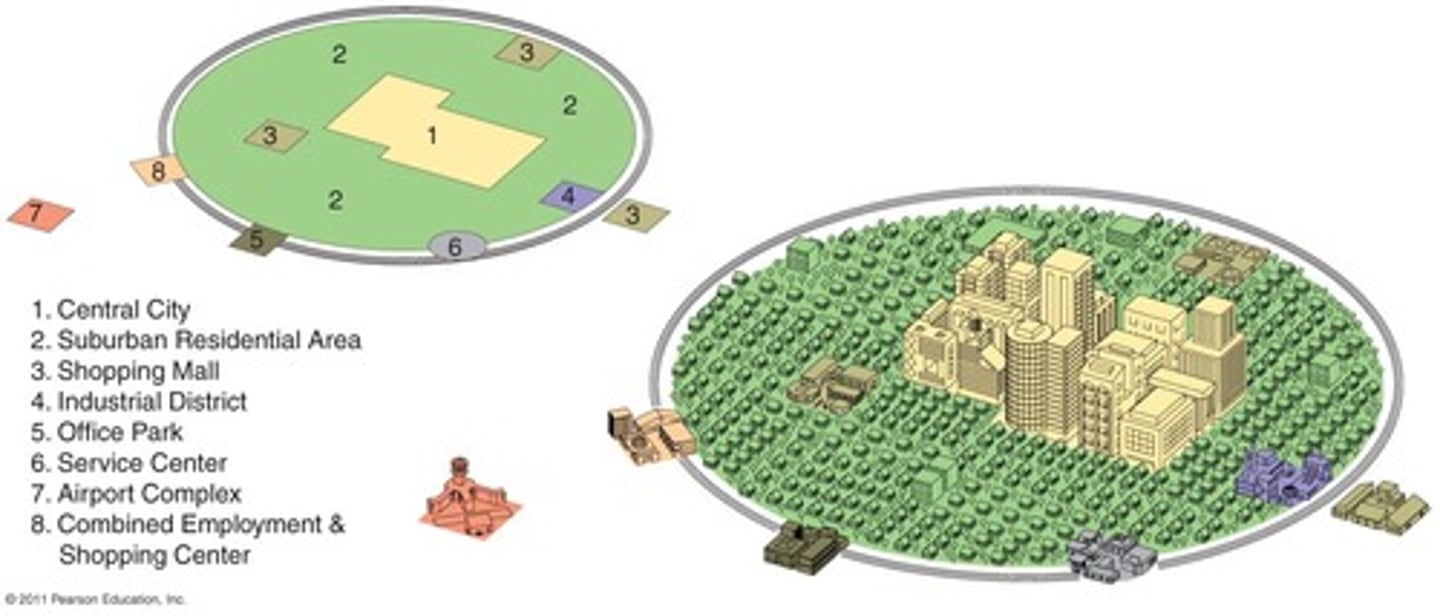
Galactic City Model
represents the post-industrial city with its several, dispersed business districts. This model represents a distinct decentralization of the commercial urban landscape
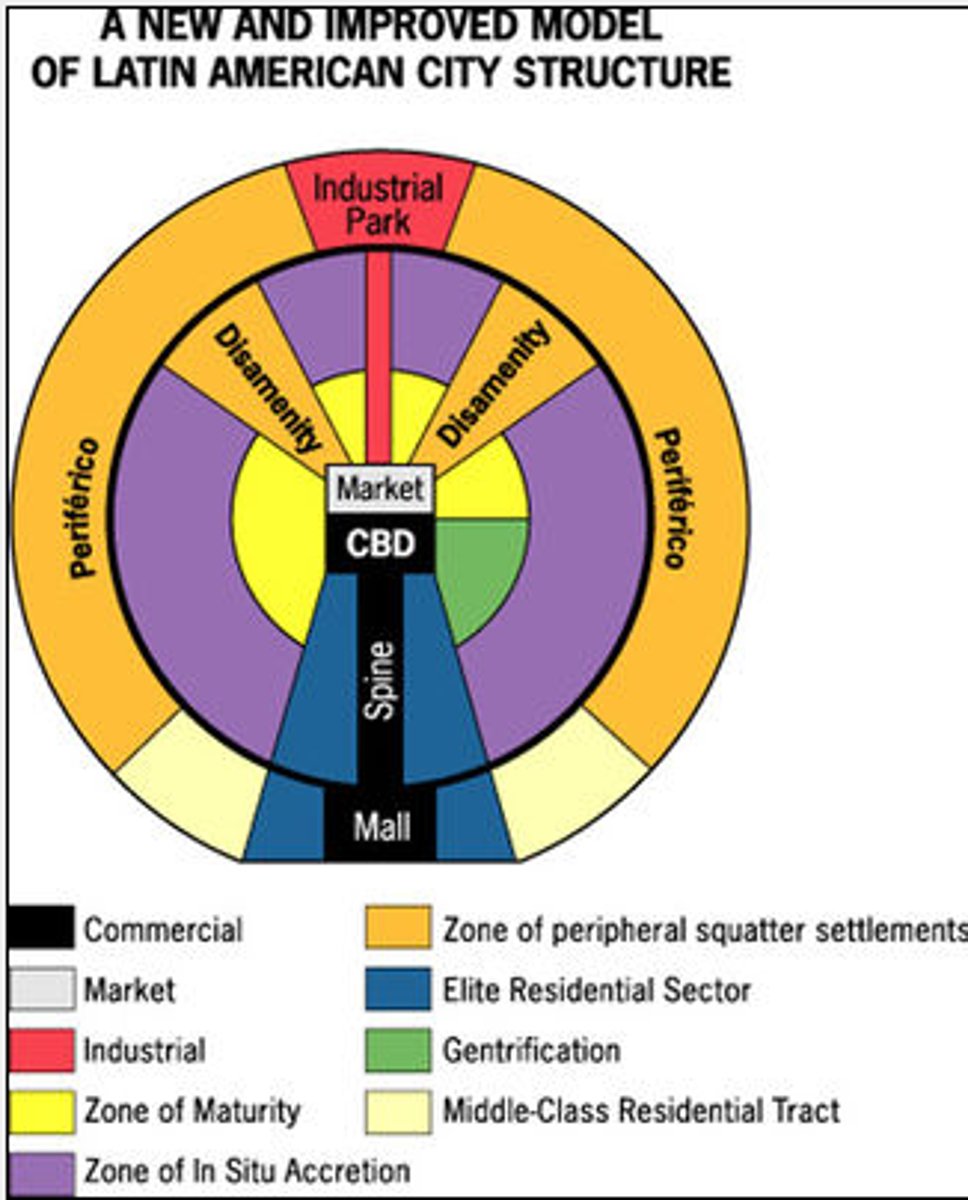
Latin American City Model
Combines elements of Latin American Culture and globalization by combining radial sectors and concentric zones. Includes a thriving CBD with a commercial spine. The quality of houses decreases as one moves outward away from the CBD, and the areas of worse housing occurs in the Disamenity sectors.
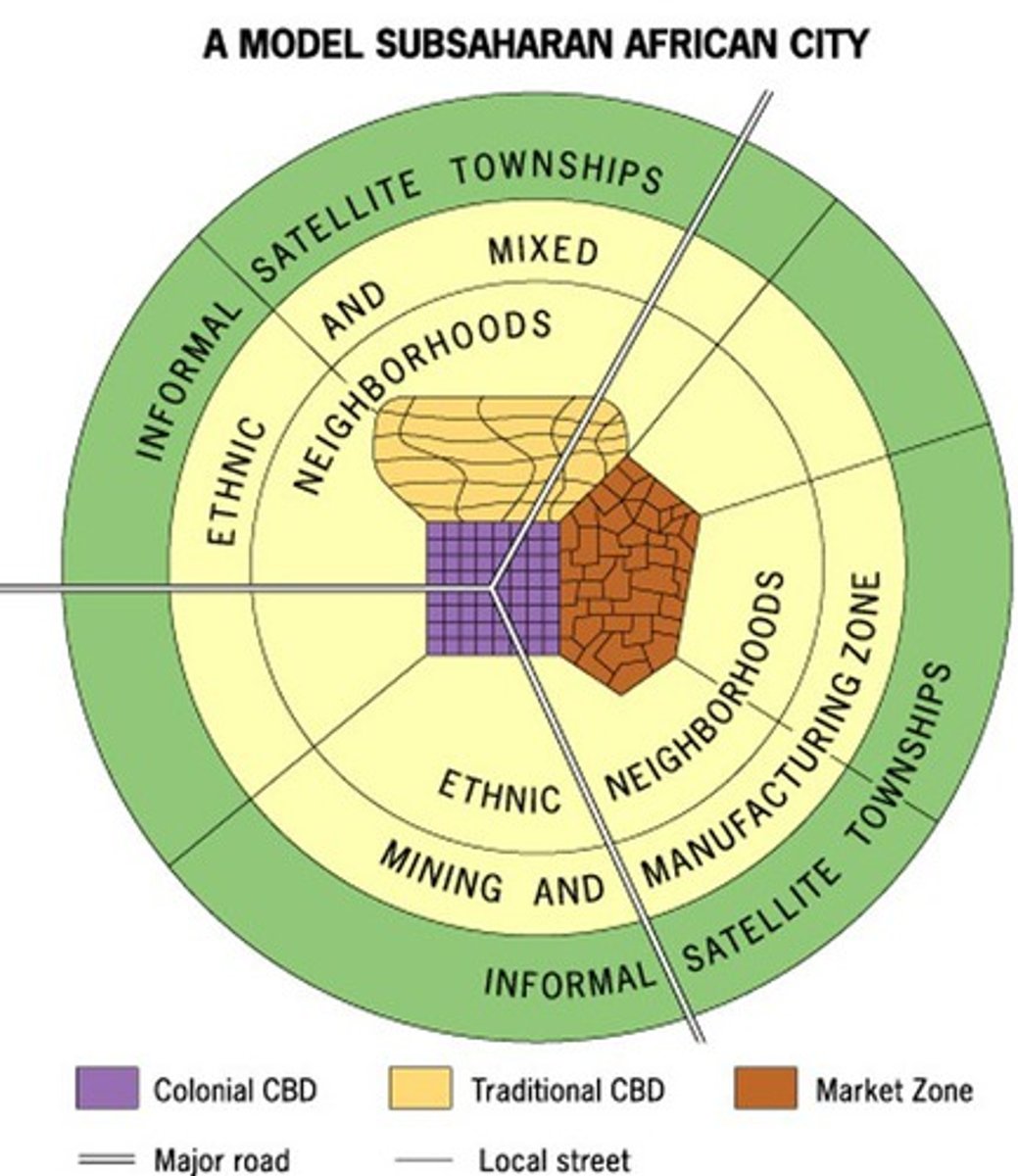
African City Model
model that suggests that African cities have more than one CBD, which is a remanence of colonialism
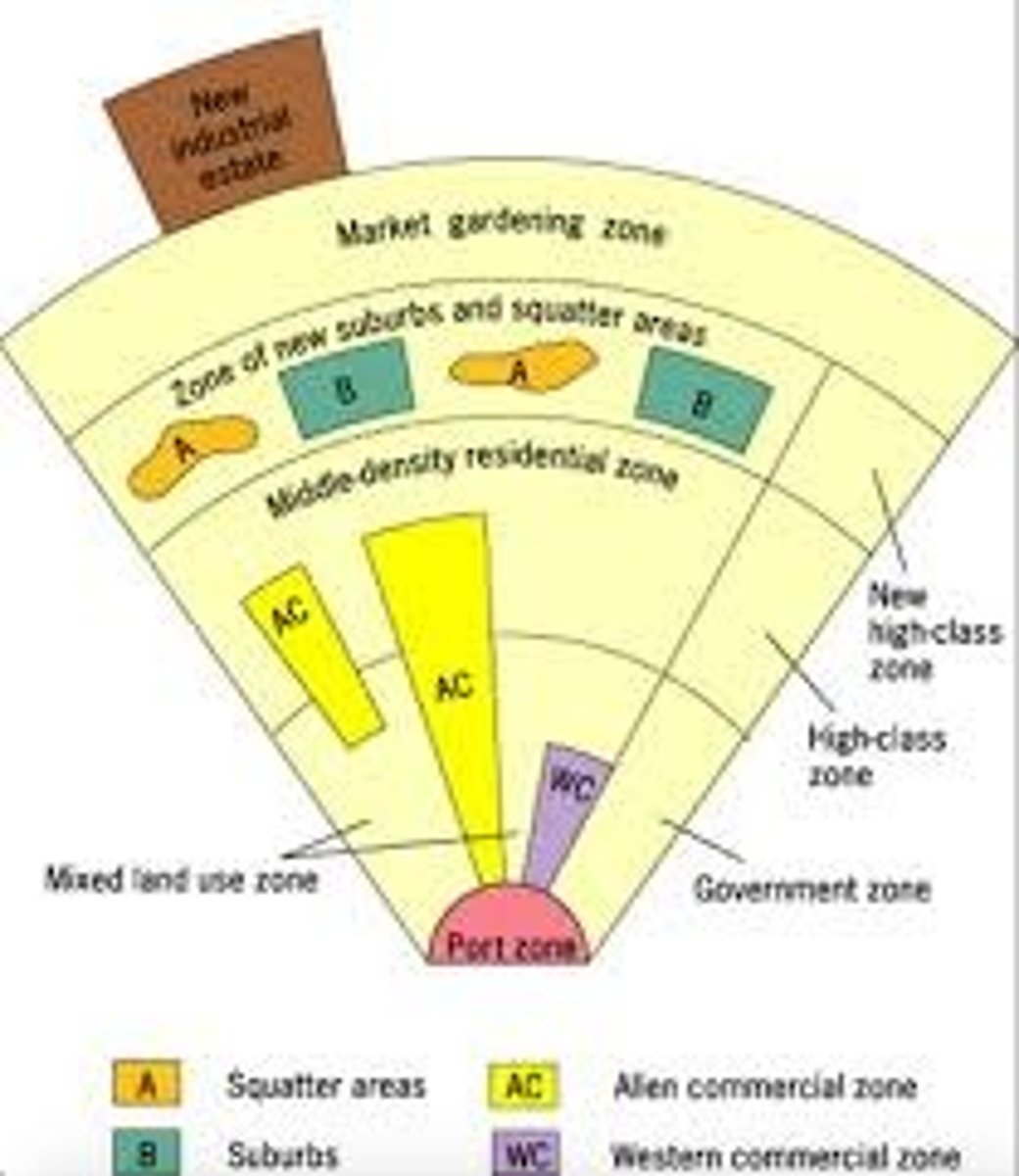
Southeast Asian City Model
a spatial city model that includes an old colonial port zone that is the focal point of the city reflecting a city oriented around exports, and radiating outward from the port zone are the Western commercial zone and Alien commercial zone
Zoning
dividing an area into zones or sections reserved for different purposes such as residence and business and manufacturing etc
Infilling
The process by which population density in an urban centre is increased by people using an old abandoned building to create apartments
Infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (e.g., buildings, roads, and power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise.
Urban Sustainability
The goal of improving the social and economic conditions of an increasingly urbanized population while maintaining environmental quality
Smart Growth and New Urbanism
planned economic and community development that attempts to curb urban sprawl and worsening environmental conditions.
mixed-use development
An approach to urban design that combines different types of land use within a particular neighborhood or district
Walkability
A measure of how friendly an area is to walking.
Greenbelts
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
Slow Growth Cities
urban communities where the planners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse affects of sprawl
Redlining
A process by which banks draw lines on a map and refuse to lend money to purchase or improve property within the boundaries.
Blockbusting
A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood
Food Deserts
Areas where it is difficult to find affordable, healthy food options. More common in highly populated low-income urban neighborhoods where there are fewer grocery stores/transportation options to seek out other food choices. Contribute to obesity in these areas bc people resort to buying cheap, highly caloric foods
Disamenity Zones
The very poorest parts of cities that in extreme cases are not connected to regular city services and are controlled by gangs and drug lords.
Inclusionary Zoning
zoning regulations that create incentives or requirements for affordable housing development
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area.
Suburban Sprawl
- spread of suburbs away from the core city
Brownfields
contaminated industrial or commercial sites that may require environmental cleanup before they can be redeveloped or expanded
Urban Growth Boundaries
place restrictions on development outside a designated area