Fluid Therapy: Colloids - DONE
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is the most permeable part of the vascular system?
capillary beds
what is permeability?
intravascular space
-->conducting vessels are relatively impermeable: arteries, arterioles, venules, veins
capillaries = semipermebale membrane
-->water
-->small ions (Na, K, Cl)
-->small molecules
what is permeability of the intracellular space
phospholipid bilayer
-->semipermable: water and glucose
what are colloids?
colloids are fluids that contain large, insoluble molecules that do not freely cross a semipermable membrane
colloids act to "hold" water within the vascular space for a longer duration of crystalloid
why are colloids important?
directly realted to plasma volume expansion
-->saline approximately 20% of infused volume
-->colloid thereotically 100% of infused volume (varies by type of colloid)
starling forces equation
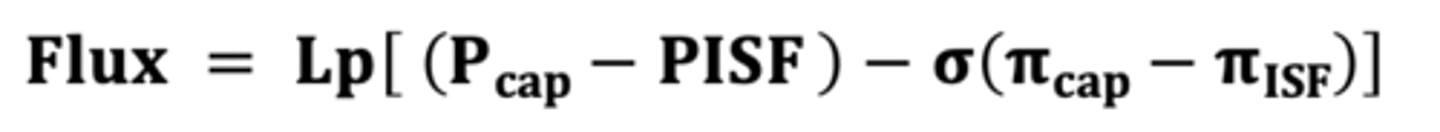
which value in the starling equation helps to explain why a severely hypoproteinemic P develops a pitting limb edema, but not pulmonary edema?
reflection coefficient
lungs pretty much let anything pass (coefficient of 0)
-->free passage of proteins so we don't see edema
when there is not free passage (limbs), we will see edema
what is transcapillary fluid flux?
net movement of fluid into interstitium
returned to systemic circulation by lymphatic system (series of tubes with one-way valves)
what is the filtration coefficient (K)
correlates to permeability of vessel
varies along circulatory system
arteries and veins less permeable than capillaries
what is the reflection coefficient (o)?
degree to which membrane prevents trasnfer of colloid molecules
value between 0 and 1
-->0 indicates free passage, 1 is no passage
the lower the value, the less effect colloid will have on fluid dynamics
wht do changes in the filtration and reflection coefficients make it difficult to predict?
the pharacokinetcis of colloids in vivo
what is collid osmotic p (COP)?
the pressure exerted by large molecules
because, in health, these molecules do not easily leave the vasculature, they hold water within the vascular space
how do you measure COP?
using a colloid osometer
measures a change in P created by adding colloid solution to one side of a semipermeable membrane
as water diffuses across the membrane, it creates hydraulic pressure that can be measured
what is the major contributor to COP in the intravascular space?
albumin
what is normal COP for dog? cats?
dog: 15.3-26.3 mmHg
cat: 17.6-33.1 mmHg
albumin generates 80% of COP in normal states
whole blood vs plasma COP
significant difference between whole blood and plasma COP in healthy dogs
however, clinically the difference is minot and either can be used
rec same sample type
what are some proposed benefits of colloids?
longer intravascular effects
smaller volume requirements for intravacasular expansion
less dilutional coagulopathies
decreased tissue edema formation
if charge of the molecules are not considered, would sodium or albumin contribute most to serum osmolality?
exaclty equal if you remove charge
the size of the particle is unimportant so that a single ion (sodium) contributes as much to the serum osmolality as a single large portein miolecule
large molecules persist in the circulation longer
what is the pharamcology of colloids?
"the whole is greater than the sum of its parts"
molecular weight does not effect osmolality
charge is important
-->gibbs-donnan effect
what is the gibbs=donnan effect?
electroneutrality must be maintained
large proteins such as albumin are negatively charged and non-diffusable across semipermeable membrane
draws positive ions (Na) across membraen, pulling water with them
it inc COP by 7-8 mmHg
what are the natural colloids?
albumin
-->human albumin 5% and 25%
-->lyophilized canine albumin
blood products
-->fresh forzen plasma
-->whole blood
what are the synthetic colloids?
hydroxyethyl starch
gelatin
dextran
what is characteristic of albumin?
albumin has a unifom size
-->greater than 95% of particles have molecular weight of 69 kDa
-->the only monodisperse colloid known
highly preserved across species
accounts for 80% of colloid osmotic P in health
what are the roles of albumin?
carrier molecule
-->divalent cations (Ca and Zn)
-->hormones
-->drugs
maintain oncotic P
coagulation/inflammation
role in healing
what is lyophilized canine albumin?
purified canine albumin
sold as 5g vials
adverse reactions less frequent and less severe than human albumin in dogs
limited availability
what is human albumin?
human albumin 5% and 25%
may be used in critically ill Ps
adverse reactions
-->anaphylaxis
-->delayed hypersensitivity reactions
-->death
NEVER ADMINISTER TO A HEALTHY PATIENT OR A P THAT HAS RECEIVED HUMAN ALBUMIN IN THE PAST
what are the blood products?
fresh frozen plasma
whole blood
weak colloids
used primarily for replacement of clotting factors in Ps with coagulopathies
what is albumin deficit?
calculation to estimate amount of an albumin containing product is required to inc the albumin to a desired level
Alb dft = 10 [ALBdesired - ALBpatient] BW * 0.3
alb deficit = grams
ALBdes = g/dL
BW = kg
what are the synthetic collloids?
starches
-->hetastarch (hetastarch, hespan)
-->pentastarch
-->tetrastarch (voluven)
gelatins
dextrans (70 and 40)
what are some possible adverse effects of synthetic colloids?
acute renal failure
anaphylaxis
volume overload
coagulopathy
immunosuppression
what is hydroxyethyl starch?
primary synthetic colloid used in vet med
polydisperse solutions
-->made up of many size particles
-->reported molecular weight is a calculated value based on different particles sizes and distribution
described by molecular weight and degree of substiuton
degree of substitution is the proportion of glucose moieties that have been substituted with hydroxyethyl groups
-->ranges from 0 to 1
what are the types of hydroxyethyl starch?
6% hetastarch in 0.9% saline
-->molecule weight: 670 kDa
-->DS = 0.75
10% pentastarch
-->molecule weight: 200 kDa
--> DS = 0.5
6% tetrastarch (voluven)
-->molecular weight: 130 kDa
-->DS = 0.4
what are theadverse effecrs of hydroxyethyl starch?
acute renal failure
anaphylaxis
volume overload
coagulopathy
immunosuppression
which has a greater correlation with negative effects on coagulation
A: degree of substitution
B: molecular weigth
A
how does degree of substiution affect hydroxyethyl starches and coagulation?
higher degree of sibsitutuion correlates to greater negative effect on coagulation
interferes with factor VIII and vwF leading to platelet dysfunction
may also be incorporated into fibrin clot, weakening clot
how is hetastarch used in practice?
670/0.75
higher degree of substituotion so greater adverse effects on coagulation
daily rec maximum dosage is 20 mL/kg
larger molecules persist in the vasculature longer
-->however, minimal effect due to much fewe numbers of large molecules
administered as 2-5 mL/kg IV boluses
common practice is to use as CRI
how is voluven used in practive?
130/0.4
lesser degree of substitution so minimal effect on coagultion
daily rec maximum dosage is 40 mL/kg
shorter half life than hetastarch (16 vs 46 hours)
administered as 2-5 mL IV boluses
what is the COP of hetastarch 6%? voluven? human albumin 5%/25%? canine fresh frozen plasma?
hetastarch: 32%
voluvenL 37%
human albumin: 23%
canine fresh forzen plasma: 17%
how do you monitor colloid therapy?
refractometeric readings of total solids
-->COP should be used to monitor therapy bc of the minimal effects of synthetic colloids on TS
what is the effect of HES (670/0.75) on USG and osmolality in the dog?
dogs were administered 20 mL/kg HES
urine osmolality and speciifc gravity were measured
usually correlate, except in the presence of large molecules
urine specific gravity overestimated osmolality after administration of HES****** ON EXAM
the majority og the effect was within 2=3 houts after administration