Ch. 2.2 Exploring the Relationship Between Two Categorical Variables
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What do you use to summarize the relationship between two categorical variables?
a contingency table
What do we use to describe the joint behaviour of both categorical variables?
contingency table
What is a contingency table?
It’s a two-way table listing frequencies for each combination of the two categorical variables.
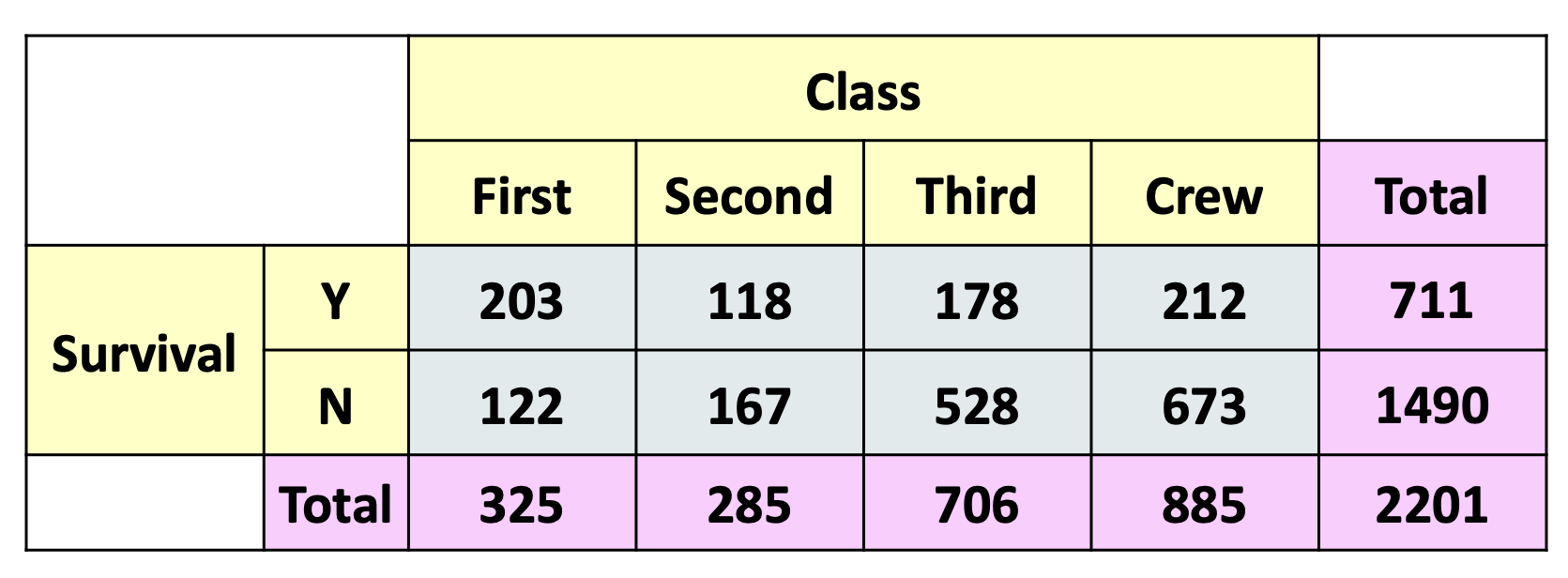
What kind of table would this be considered as?
a contingency table
What can a contingency table also report?
the relative frequencies as %
What would you use when you want to describe the joint distribution of the categorical variables?
a contingency table that reports relative frequencies as %
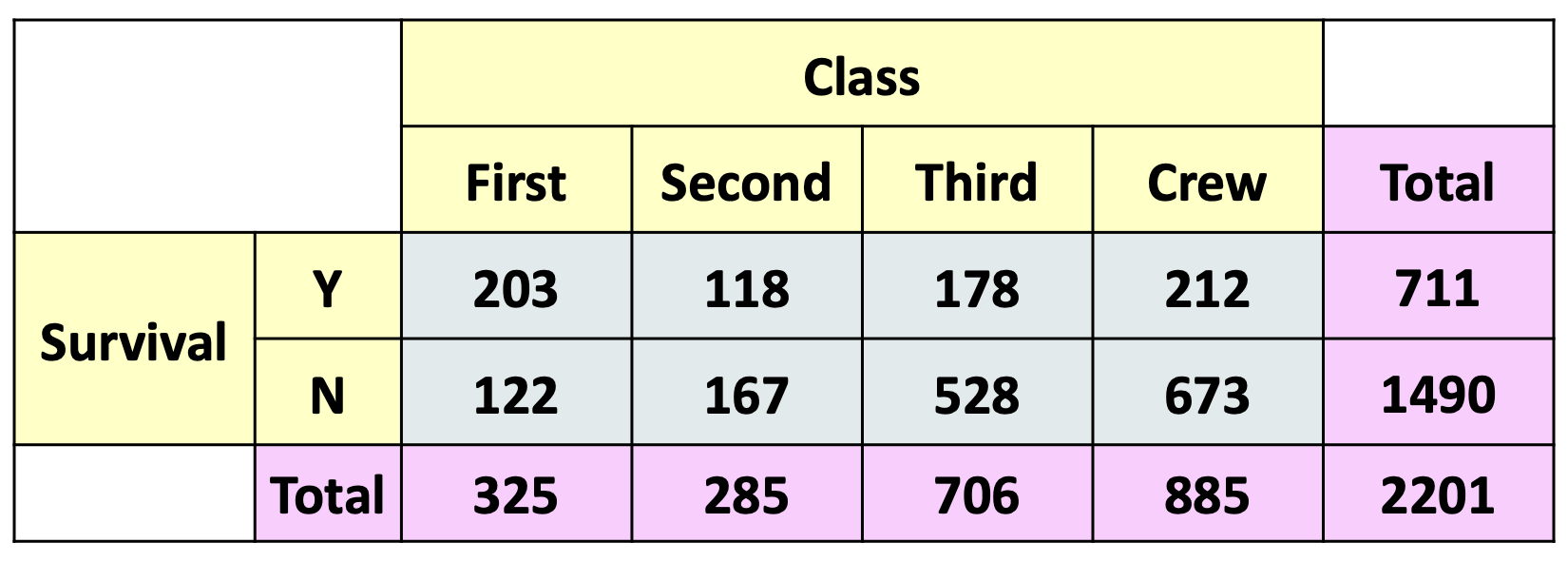
In this image, adding all the grey cells would give you what % value?
100%

Solve the question in the image.
6.3%
What gives distributions of each categorical variable separately in contingency table?
margins
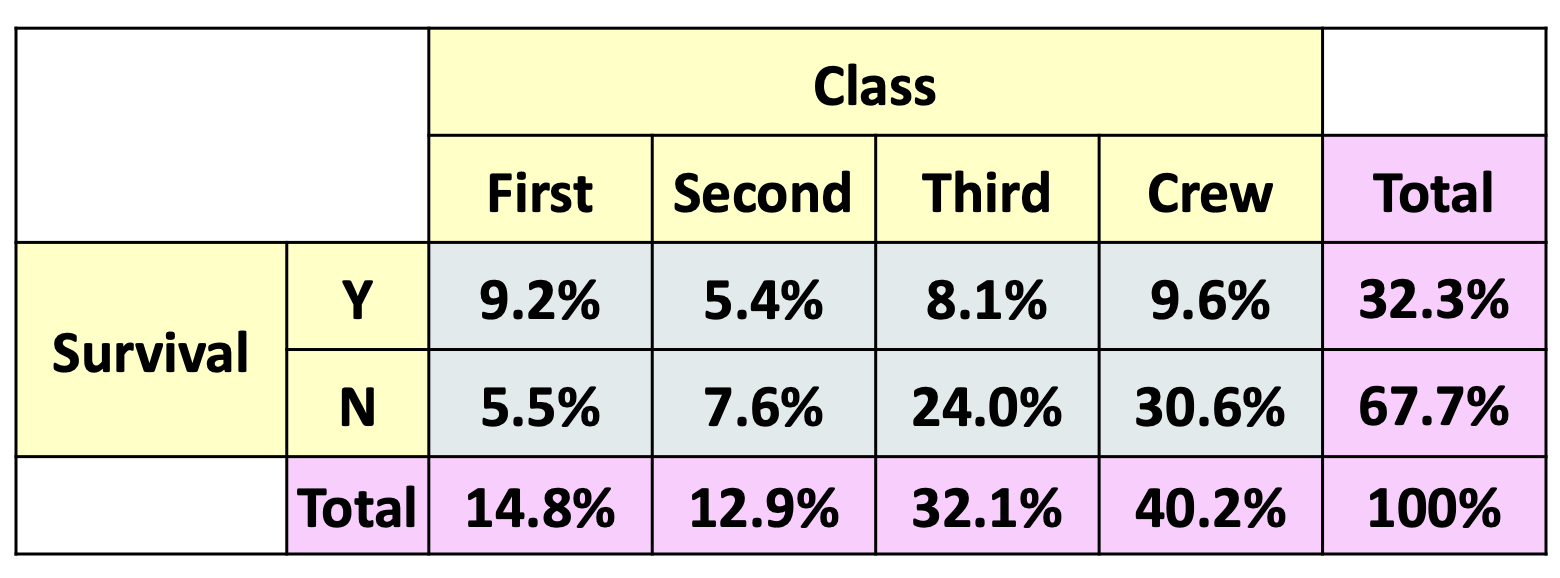
What kind of distribution is shown in the grey cells found in the contingency table?
joint distribution - as adding all the cells makes 100%
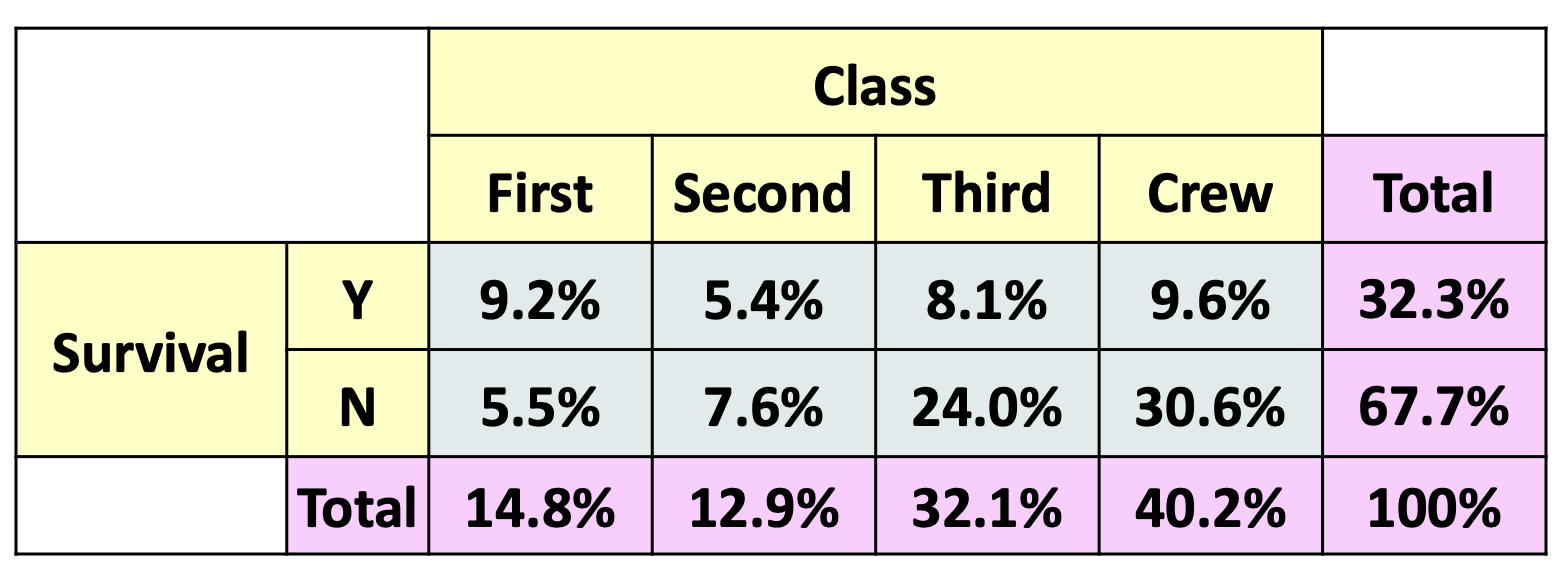
What kind of distibution do the pink cells display in this contingency table?
marginal distribution of survival & marginal distribution of ticket class
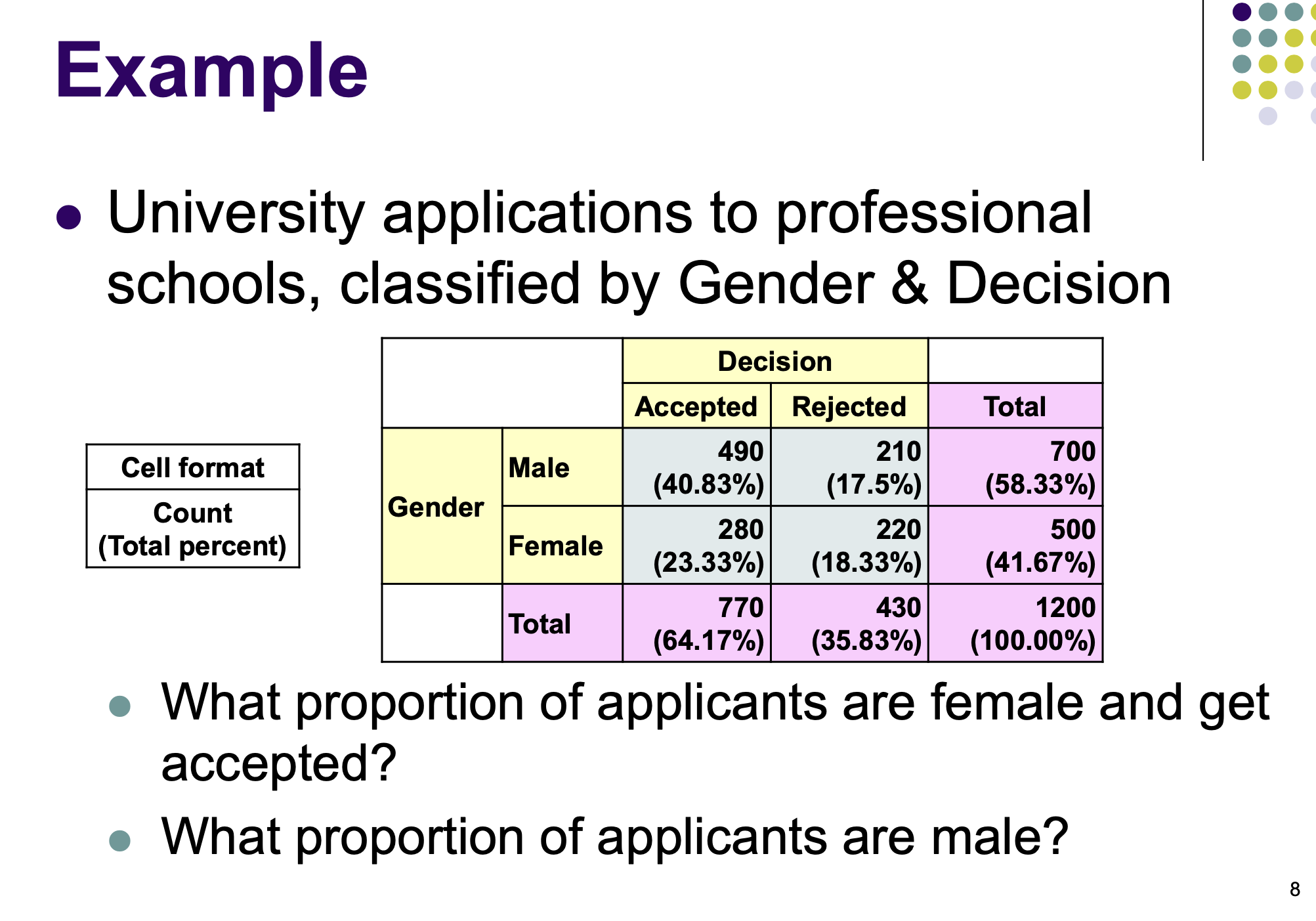
Answer the following questions.
23.33% (280/1200 × 100%)
58.33% (700/1200 × 100%)
What is a conditional distribution?
It’s a distribution seen in a contingency table where you have a fixed value of one variable & look at the distribution of the other for that value only.
Fill in the blanks.
Often need the distribution of ____________ for a particular value of the other.
one variable
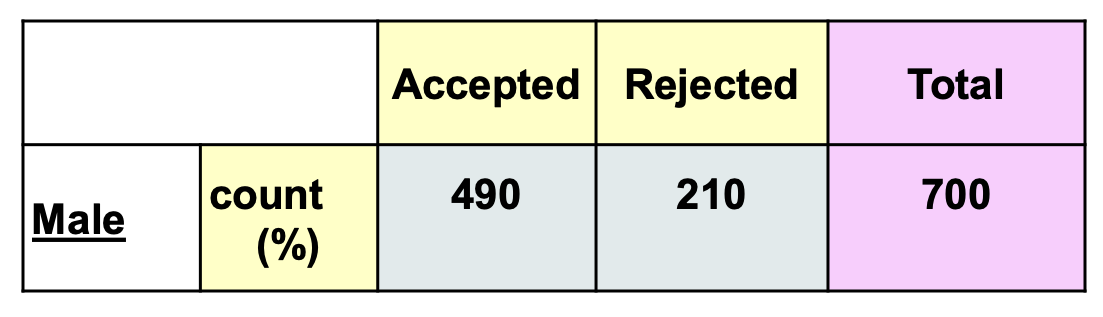
Looking at this table, Fill in the blanks.
The table shows a conditional distribution of ______________ conditional on _____=_________.
decision, gender = male (row%)
True or False.
Conditional distribution can condition only on one variable of contingency table.
False.
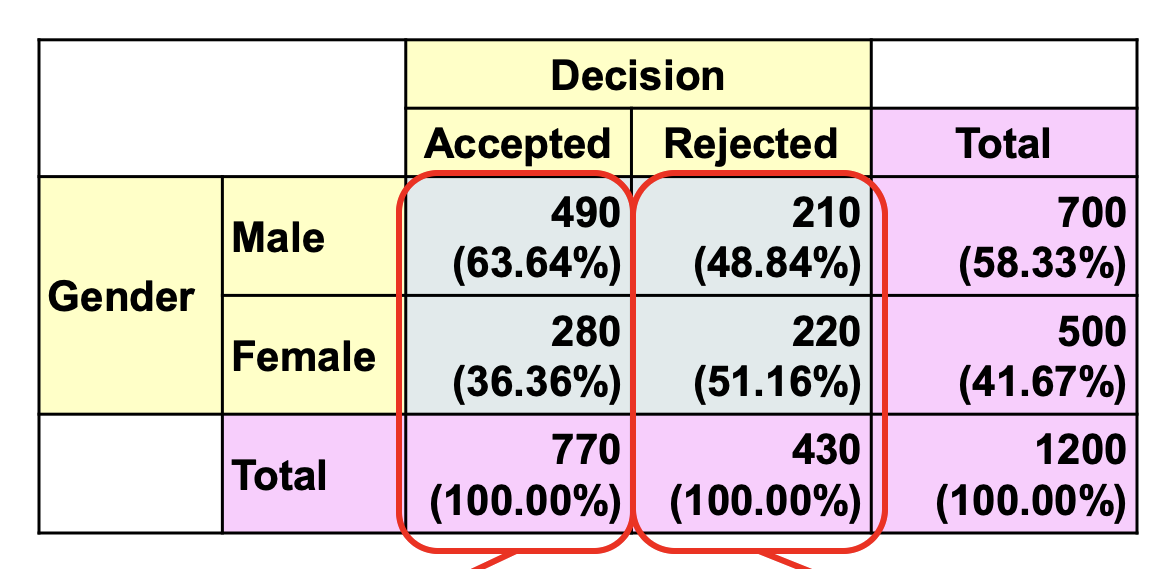
Looking at this table, Fill in the blanks.
The table shows a conditional distribution of ______________ for _____=_________.
gender, decision = accepted/rejected (column %)
Fill in the blanks.
If conditional distributions of one variable are the same for every value of the other, we say the two variables are _____________.
independent
What do we use to compare conditional distributions visually?
side-by-side bar plot
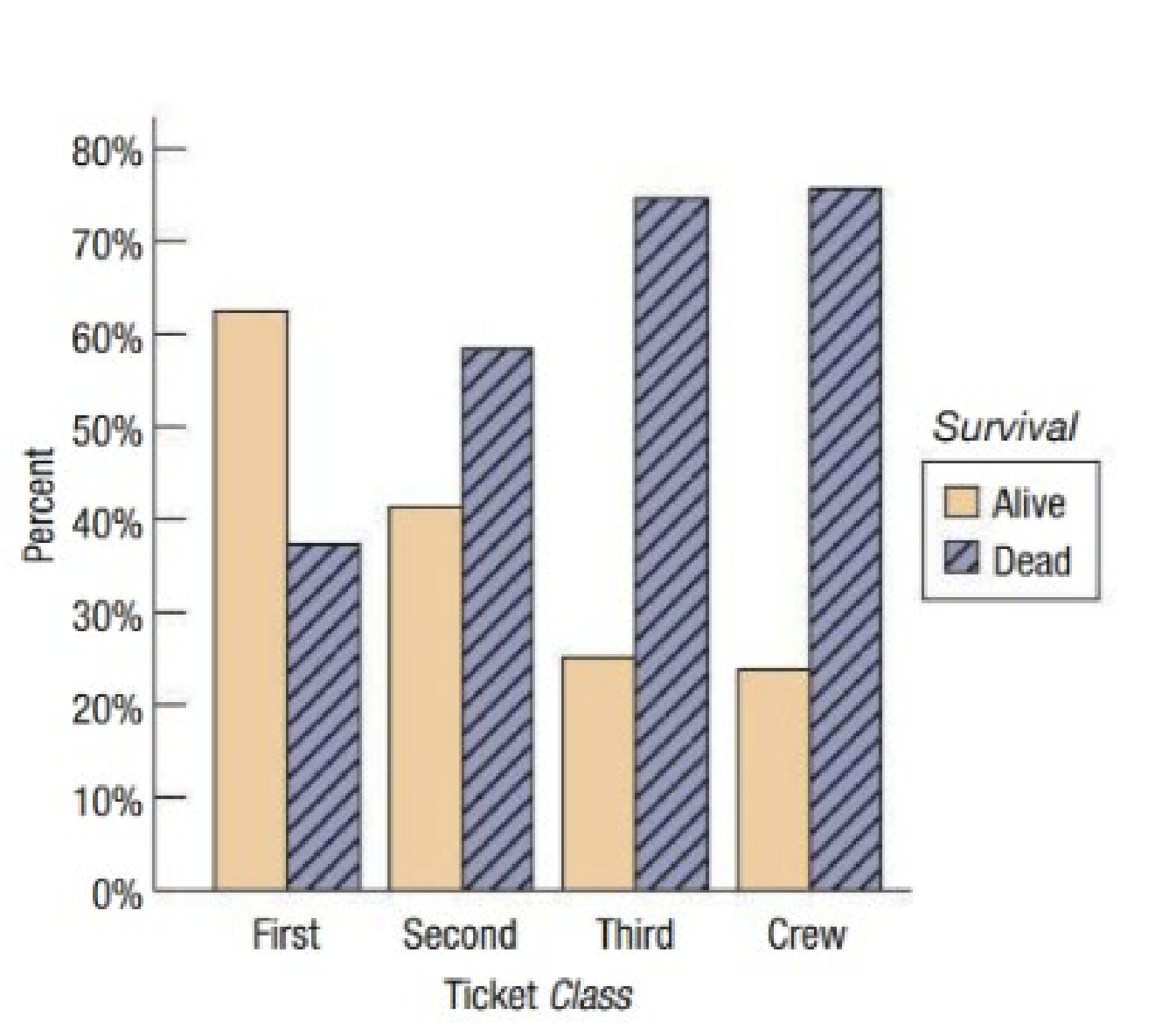
What do you call this type of plot in this image?
side-by-side bar plot
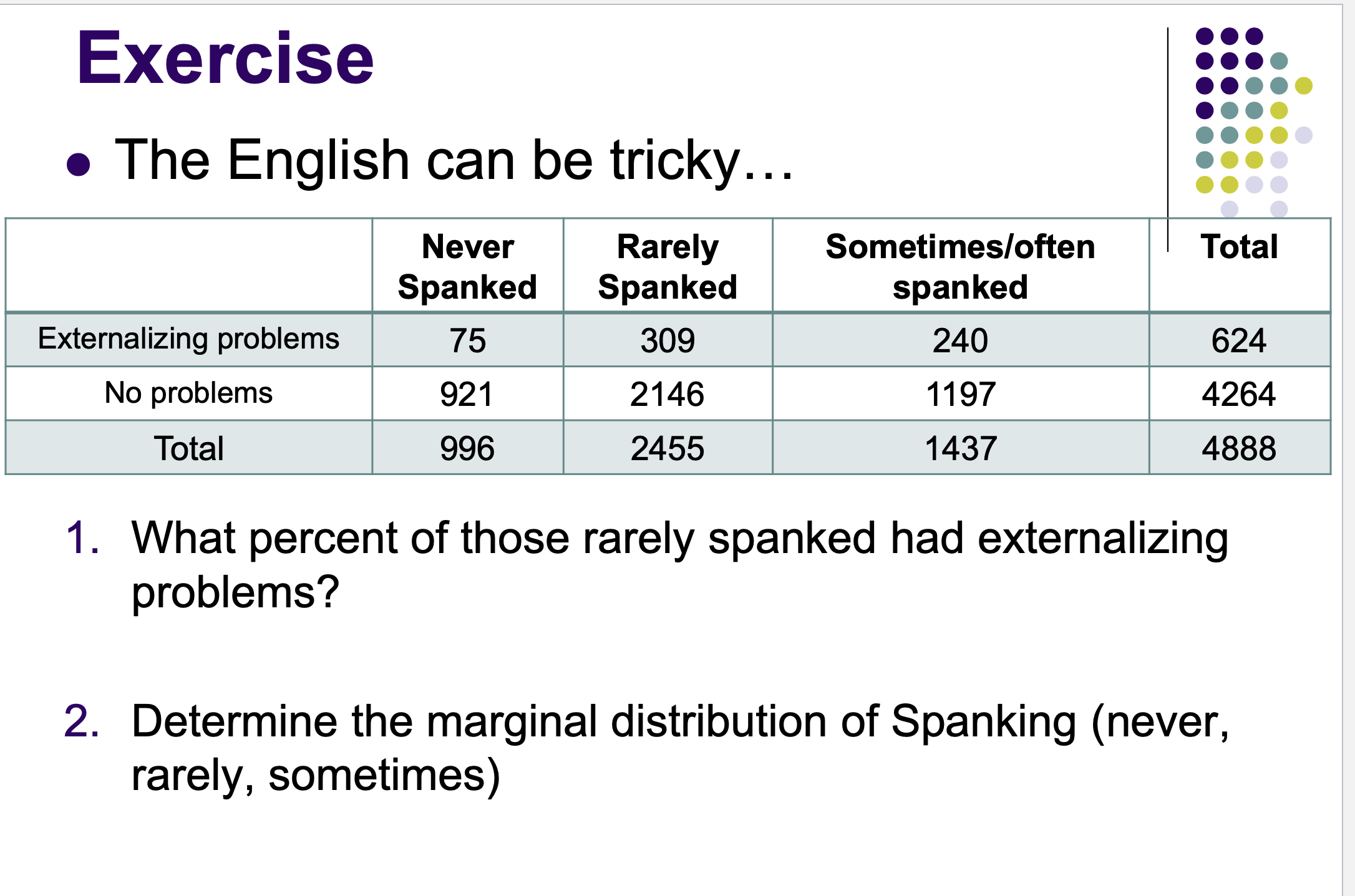
Answer the following questions provided in the image: Using 1. …. answer … format
309/2455 × 100% = 12.6%
Never : 996/4888 × 100% = 20.4% , Rarely : 2455/4888 × 100% = 50.2% Sometimes : 1437/4888 × 100% = 29.4%

Answer the following questions provided in the image: Using 1. …. answer … format

What is Simpson’s Paradox?
It's when a conclusion you get from looking at the total data is the exact opposite of the conclusion you get when you look at the data broken down into separate groups.
The reversal happens because you're ignoring a hidden factor that is unevenly spread across those groups. When you combine everything, that hidden factor makes the overall result misleading.
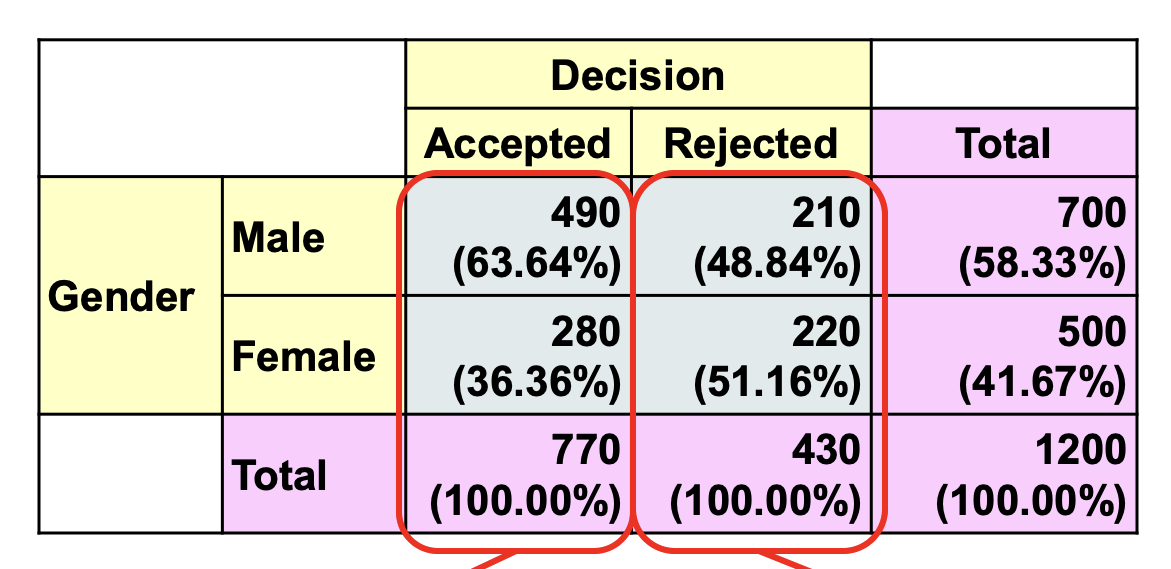
What type of distribution is shown in the image?
conditional distribution