Unit 1 BACE Exam Review
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMPs)
System for ensuring that regulated healthcare products are consitently produced anf controlled accoring to quality standards. - covers all aspects of production
- ensures safety, identify, potency, purity, and quality that they claim to have.
Early Drug Discovery
-Target identification & Validation
-Hit discovery
-Assay Development & screening
-High Throughput Screening
-Hit to Lead
-Lead Optimization
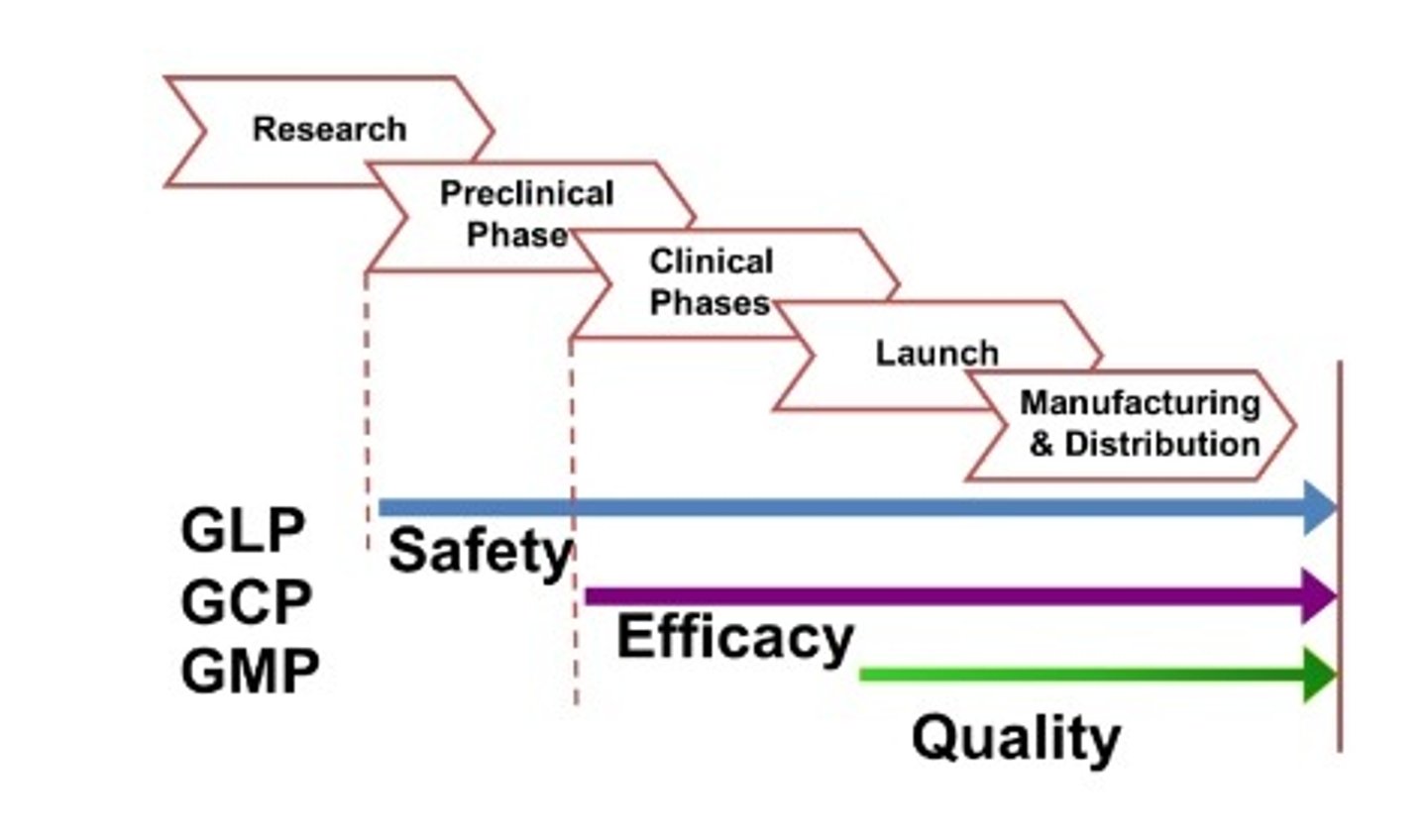
Preclinical Studies
- In Vivo, In Vitro & Ex Vivo Assays
- ADME
-Proof of Concept
-Drug Delivery
- Formulation Optimization & Bioavailability
- Dose Range Finding
- IND-enabling Studies
- IND Application
Clinical Development
- Phase 1- Healthy Volunteer Study
- Phase 2 and Phase 3: Studies in Patient Population
- Dose Escalation, Single Ascending & Multiple Dose Studies
- Safety & Efficacy
- Pharmacokinetic Analysis
- Bioanalytical Method Development and Validation
FDA Review
- NDA/ANDA/BLA Application
- FDA Approval
- Drug Registration
Post-Market Monitoring
- FDA Adverse Event Reporting System(FAERS)
Step 1: Discovery and Development- Research for a new drug begins in the laboratory
- Design product to stop or reverse the effects of a disease
- tests of molecular compounds for possible beneficial effects against diseases
- treatments that heave unanticipated effects
- New technology
Step 2: Preclinical Research
- Drugs undergo laboratory and animal testing to answer basic questions about safety
- Testing Toxicity
- In vitro and In Vivo
GLP
Good Laboratory Practices asserts the minimum basic requirements for study conduct, personnel, facilities, equipment, written protocols, operating procedures, study reports, and the system of quality assurance oversight to help assure product safety.
Step 3: Clinical Research
-Drugs are tested on people to make sure they are safe and effective.
- Refers to studies, or trials, that are done in people; studies the way the drug will react in the human body.
Step 3: Phase 1
- Less than one year
- 20 to 100 participants who may be healthy or have disease
Goal of Step 3 Phase 1
- Learn how the treatment works in the human body
- Understand the best dose (amount) of the treatment
Step 3 Phase 2
- A few months to 2 years
- About 300 participants who have the disease
Goal of Step 3 Phase 2
Learn more about how safe the treatment is for people to use
Step 3 Phase 3
- 1-3 years
- 300- 3000 participants who have the disease
Goal of Step 3 Phase 3
-Learn if the treatment works to prevent , diagnose or treat the disease
- Learn more about safety and possible side effects
Step 3 Phase 4
- Many Years
- Thousands of participants who have the disease
Goal of Step 3 Phase 4
- After the FDA approves the treatment for use with the public, researchers continue to look at: the treatment's benefits, side effects, the best way to use it.
Step 4: FDA Review
Review teams thoroughly examine all of the submitted data related to the drug or device and make a decision to approve or not to approve it.
Step 5: FDA Post-Market Safety monitoring
FDA monitors all drug and device safety once products are available for use by the public
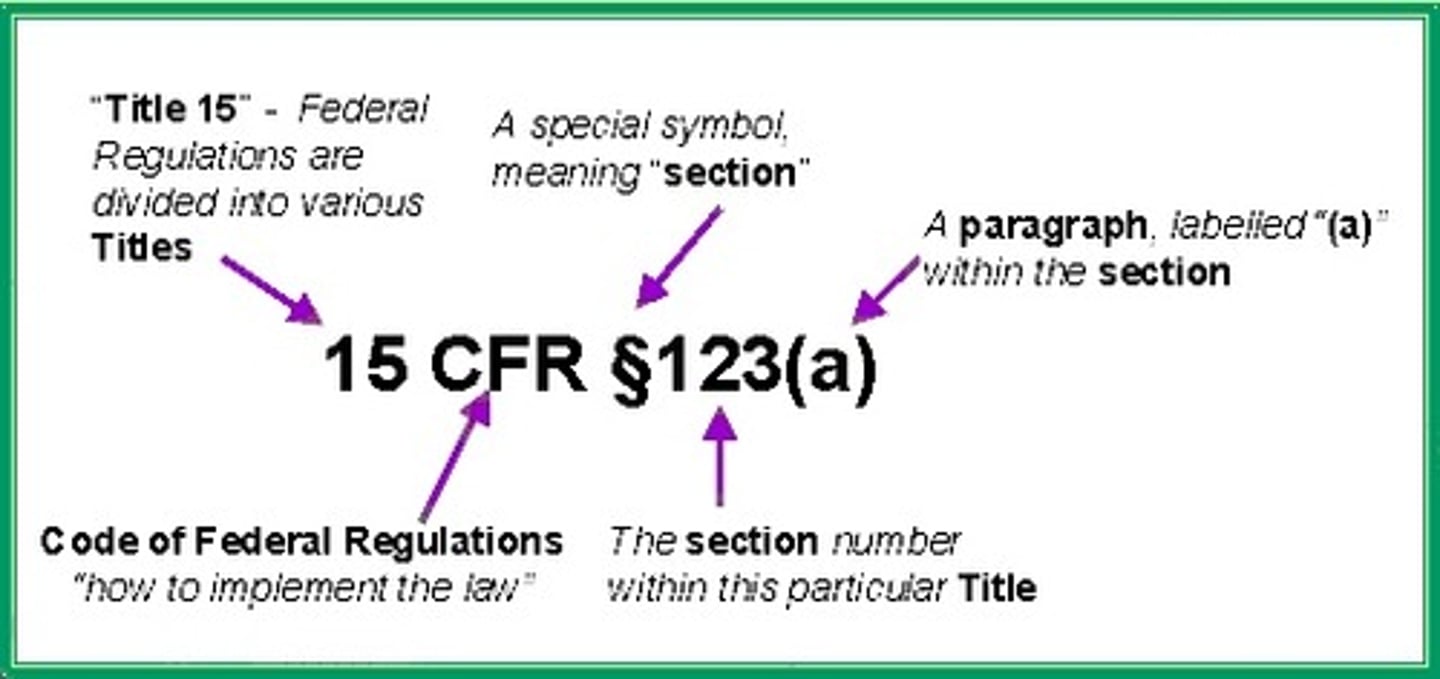
CFR (Code of Federal Regulations)
FDA, EPA, IRS, DHS
Research and Development
Responsible for discovering/developing a product with commercial value.
Manufacturing
Responsible for making the product
Quality Control (QC)
Responsible for testing the product to ensure its identity, safety, purity, and stability(smaller bubble in big QA bubble).
Quality Assurance(QA)/Regulatory Affairs
Responsible for ensuring compliance with CGMP(Current Good Manufacturing Processes). (Oversight, big bubble)
Records: Batch Records(BR's) and Test Records (TR's)
Directs operators on how to make or test the product
Logs: Equipment Cleaning and Use Log
Written record of major equipment cleaning, maintenance & use
Standard Operating Procedures(SOP)
Primary documents of Process Control; detailed and specific instructions for carrying out routine tasks
Reports
report on "events" (new materials, cleaning, ex...)
Specifications
a range of acceptable values established by QA and tested by QC
Document Control
Completed by QA, established organized system for documents
Document Numbering System
number system for documents
GLP
Good Laboratory Practices
GCP
Good Clinical Practices
GMP
Good Manufacturing Practices
CGMP in a Nutshell
- Know what to do before actually doing it
- Document everything; "if it isn't documented, it didn't happen"-FDA
- Consistency and control over all processes
- Have independent group make final decision on a product to avoid bias.
Fundamental of CGMP: Training-Subpart B: Organization of Personnel
-Employees must have education and experience necessary to perform role
- Employees must be trained in tasks and CGMP specific to role
- documented record of training
Fundamental of CGMP: Documentation and Recordkeeping- Subpart J: Record and Reports
Provides an "easy-to-follow" trail from the product, its components, equipment, and process at any point in time.
Fundamental of CGMP: Written Procedures - Subpart J: Records anf Reports
Documents and records required by the pharmaceutical CGMP
Required Written Procedures
Standard Operating Procedures
Batch Records
Test Records
Specification Forms
Deviation Forms
Equipment Cleaning & Maintenance Records
Fundamental of CGMP: Control and Identification of Materials - Subpart E: Control of Components, Drug Product Containers, and Closures
- Knowledge of receipt, origin, identity, status, location, storage, and distribution of materials.
Fundamental of CGMP: Communication - Subpart B: Organization of Personnel
Good communication system(all personnel notified of changes to SOPs)
Fundamental of CGMP: Label Controls - Subpart. G: Packaging and Label Control
All aspects of the label(nutrition facts, manufacturing, dosage) hold high importance, thus are subsequent to frequent inspection.
Fundamental of CGMP: Contamination Controls - Subpart F: Production and Process Controls
Requirements in place to help assure the quality, purity, and safety of the product.
Fundamental of CGMP: Change Control - Subpart I: Industry Practices
Any changes must be reported, evaluated, approved, implemented, and monitored
Fundamental of CGMP: Maintenance and Calibration - Subparts C and D: Buildings and Facilities, and Equipment
- Processes can only be controlled by equipment that is properly maintained and functioning.
Fundamental of CGMP: Validation - Subpart I: Industry Practices
- Documented evidence that a process does what it is supposed to do.
CFR citation