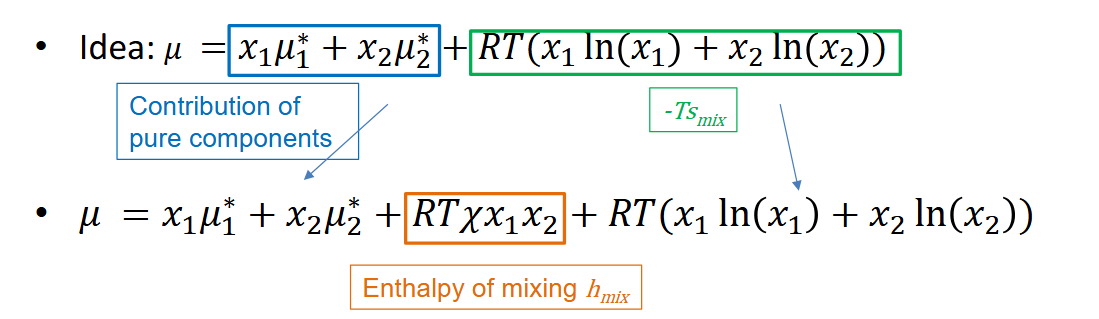Lecture 4 - Mixtures
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Entropy of mixing
When component 1 and 2 mix, they create additional microstates
Not equal to sum of entropies of both components.
Ideal mixture and chemical potential
No interactions between two components
Contribution of individual components as if they were unmixed and pure
𝜇1* and 𝜇2* are the chemical potential of pure systems
x1 and x2 are mole fractions
→ 𝜇 = x1𝜇1* + x2𝜇2*
Unrealistic situation where no mixing interactions occur
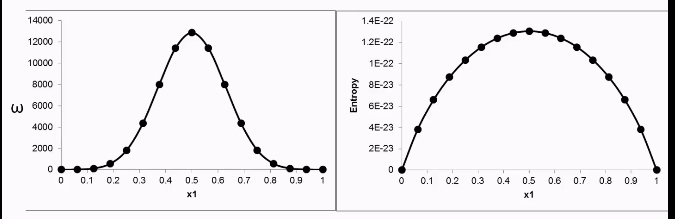
Number of possibilities for N1 and N2

Curve for system with no interactions (ideal mixture)
Graph microstates vs. x1
The graph shows a bell-shaped curve centered around x1=0.5X1, indicating that the maximum number of microstates (Ω) occurs when the system is most balanced — i.e., when half the particles are in state 1 and the other half are in state 2.
Entropy of mixing formula
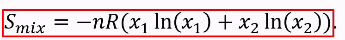
Formula chemical potential
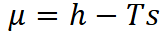
Mixing entropy for an ideal mixtures
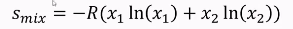
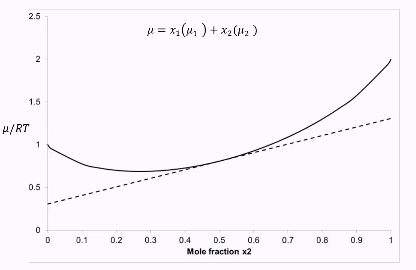
How to find chemical potential from a graph?
This only works if χ is more than two
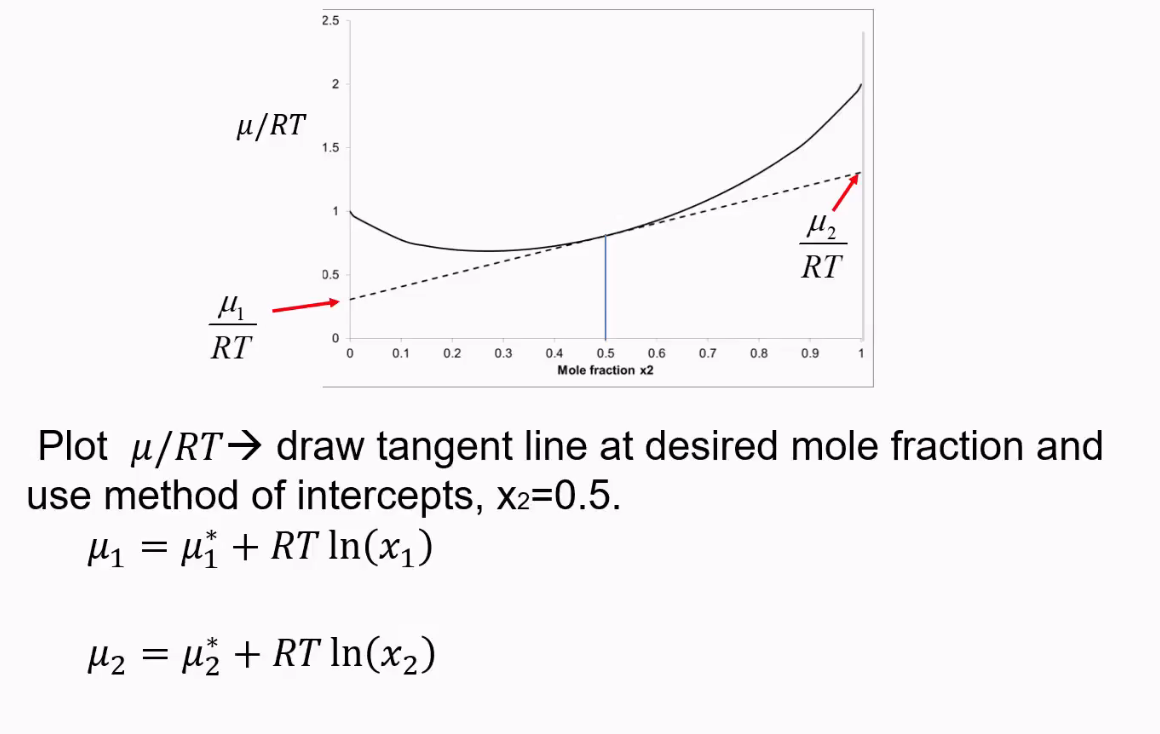
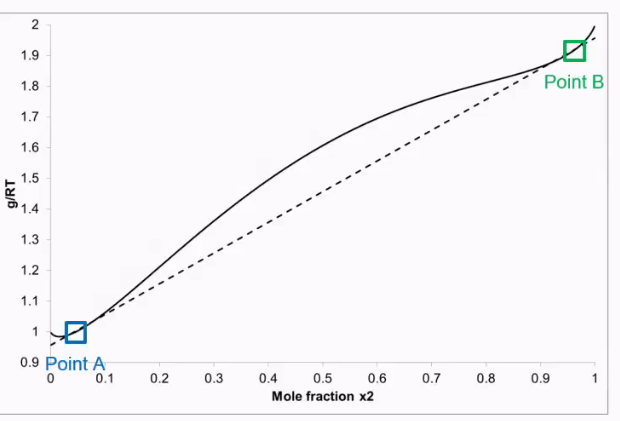
How to find chemical potential of regular mixes when χ is larger than two.
Connect point A and point B.
Point A and B are both in different phases. Because χ is larger than two.
Therefore each point has mew 1 and mew 2.
Interaction energy for different microstates. (Mole fraction 1/16)
Depending on where the orange ball is, it will have more or less bordering molecules
The more molecules that it borders with, the more interactions it will have.
One of these interactions is called KT.
This only occurs in non-ideal mixtures because in ideal mixtures there are no interactions.
As seen in the picture, the left has 2 KT, the middle 3 KT and the right 4 KT.
The state with the least energy is most probable, so the situation on the left is most probable.
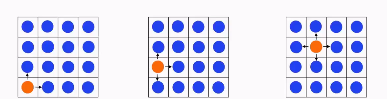
How does the interaction energy change when the mole fraction is 2/16?
To minimize the Gibbs free energy, and the interaction energy, particles will cluster as they don’t have interaction energy with each other.
If they spread out, the KT will be higher.
If half the solution is one chemical and half the other, the solution will spread half-and-half.
Enthalpy when mixing with interactions (so not ideal)
Is non-zero
Known as enthalpy of mixing
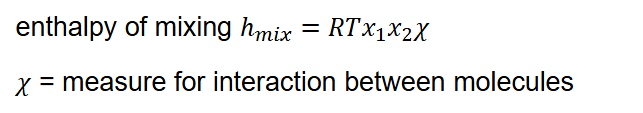
What does χ signify?
Electronegativity
This is the tendency to attract atoms towards itself.
Higher electronegativity means that an atoms holds onto its electrons.
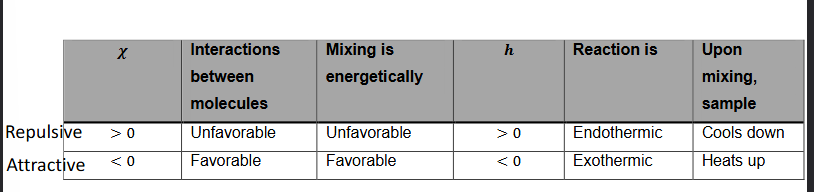
χ and enthalpy
When χ is positive, there is repulsion between two molecules. Therefore, the reaction is unfavorable, mixing is energetically unfavorable, enthalpy is positive.
If enthalpy is positive, you need to give energy to the system = endothermic
When mixing → system cools down
When χ is negative, molecules attract each other. Therefore, the reaction is favorable, mixing is energetically favorable, enthalpy is negative.
If enthalpy is negative, energy is released from the system = exothermic
When mixing → system heats up
What happens if χ is between 0 and 2?
χ is positive but not very strong.
So when a system is mixed, entropy increases and will compensate for the positive χ.
Therefore, the mixture is able to cool down and reactions can happen.
But when χ is larger than two, entropy can not compensate for this anymore.
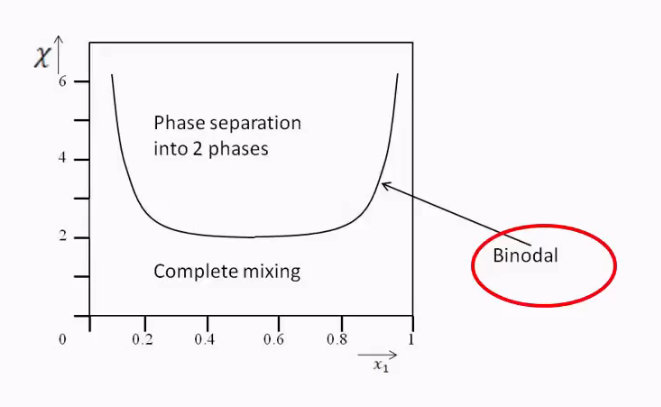
Phase separation
Only happens when χ is larger than two as we said, because entropy no longer compensates.
Can be seen in graph
You can see that when x1 is very small that you can still mix the oil and water.
We can use the lever rule to find the amounts of each of the two phases.
This is known as binodal curve.
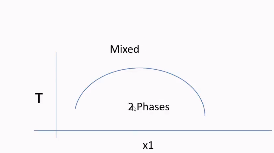
How is χ dependent on temperature?
Some mixtures are completely mixed above a certain temperature and phase separate below a certain temperature
N-hexane and nitro-benzene may phase separate below a certain temperature.
That curve seen in the picture can also be flipped depending on the molecules being mixed.
Good solvent vs. bad solvent
Good:
Interactions between polymer and solvent stronger than interactions between polymer segments
polymer segments prefer to be surrounded by solvent molecules instead of neighboring polymer segments.
Bad:
Interactions between polymer and solvent weaker than interactions between polymer segments
Polymer segments prefer to be surrounded by polymer segments instead of solvent molecules.
Formula for determining chemical potential in water or oil phase.
Mew of solute in oil should be the same as mew of solute in water, as they are in thermodynamic equilibrium

What is the meaning of each component in the molar Gibbs free energy of a regular mixture