Genetics E2- Review
1/147
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What is the federal law that protects against discrimination by health insurers and employers based on genetic information?
*ex- illegal for employer to use genetic info to hire/fire someone
GINA
What does GINA not apply to?
Life insurance, disability insurance, or long-term care insurance
What federal law classifies genetic information as protected health information (PHI) to protect patient privacy?
HIPAA
_______ protects the privacy of your genetic data, while ________ protects you from discrimination based on it.
HIPAA ; GINA
42 y/o male recently diagnosed with Lynch syndrome based on genetic testing wants to increase his life insurance policy to protect his family in case something happens, but he is also worried his boss will see him as a liability and fire him. Which of the following statements most accurately addresses the patient's concerns regarding his employment and life insurance application?
GINA protects him from employment discrimination, but its rules do not apply when seeking life insurance.
According to GINA, can a life insurance provider legally ask about genetic testing results and use that information to determine eligibility and set premium rates?
Yes
What term refers to the high frequency of a gene in a new population founded by a few individuals?
Founder effect
What are examples of the founder effect?
BRCA1/2 mutations MC among Ashkenazi Jews; ARVC can be MC in specific populations
Who has a survival benefit against malaria?
Sickle cell carriers (1 normal hgb gene, 1 sickle cell gene)
*heterozygous advantage
An individual affected by a mutant gene from the founder effect acquired the disorder by which of the following mechanisms?
Their ancestors passed the trait down to them
What kind of mutation occurs when a new genetic alteration arises in an individual without being inherited from either parent, which can then be passed on to subsequent generations?
De novo mutation
What are examples of de novo mutations?
Achondroplasia, NF1, Marfan syndrome
What is the MC form of skeletal dysplasia which leads to disproportionate short stature & rhizomelic?
Achondroplasia
What gene is involved in achondroplasia?
*80% of cases are de novo
Gain-of-function mutation in FGFR3 gene causes protein (which acts as a “brake” on bone formation) to become overly active, excessively slowing down bone growth
The risk of de novo mutation increases with _______
Advanced paternal age
What term refers to short digits?
Brachydactyly
What term refers to flattening of the nasal bridge in association with midface hypoplasia?
Saddle nose deformity
What term refers to shortening of proximal long bones (humeri, femora)?
Rhizomelic
What term refers to deformities of the knees with outward deviation due to bowing and/or joint laxity?
Varus
What are monogenic disorders?
Conditions that result from a mutation in a single gene
What term refers to a disorder being attributable to a mutation in just one gene in an individual case, though mutations in a variety of genes could cause the condition?
Locus heterogeneity
What neurocutaneous monogenic disorder is caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes for neurofibromin protein (a tumor suppressor) on chromosome 17q11.2?
NF1
What neurocutaneous monogenic disorder is caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes for merlin protein (a tumor suppressor) on chromosome 22q12.2?
NF2-SWN
What signs & symptoms would you see with NF1?
Growth of neurofibromas, cafe-au-lait macules, Crowe sign (axillary/inguinal freckling), lisch nodules
What signs & symptoms would see you with NF2-SWN?
BL vestibular schwannomas from CN VIII (hallmark) → progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, balance issues
17 y/o male stumbles into exam room. Inspection reveals >6 hypopigmented macules on the neck, shoulder, chest, and back. The lesions are absent from the axillae. They are itchy & transient, usually appear in the summer. His MRI results demonstrate BL acoustic nerve sheath tumors. What type of disorder does he most likely have?
NF2-SWN
What autosomal dominant condition is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder that typically onsets between 30-60 years of age & there is no current cure?
*HTT gene affected
Huntington’s Chorea
What mutation is involved in Huntington’s disease (Huntingtons chorea)?
≥ 40 CAG repeats in HTT gene (normally 6-26) → huntingtin protein misfiles & aggregates → cellular toxicity & neuronal cell death
What autosomal recessive condition is a progressive ataxia of all limbs associated with neurological dysfunction, cardiomyopathy, & DM?
*MC hereditary ataxia
Friedreich ataxia
What causes friedreich ataxia?
Loss-of-function mutation in FXN gene on chromosome 9q13 (GAA repeat expansion) → deficiency of frataxin protein
What clinical features are associated with Friedrich’s ataxia?
Unsteady wide based gait, progressive ataxia of all limbs, nystagmus, dysarthria, cardiomyopathy, DM
What is an umbrella term that covers many specific types of distinct, inherited peripheral neuropathies due to mutations that affect the structure and function of peripheral nerves?
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
What clinical features would you see with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease?
Slowly progressive distal muscle weakness and atrophy, stork legs, foot drop, pes caves, hammer toes
A 25-year-old man presents with complaints of gradual worsening of coordination that began in their late teens. He has a progressively unsteady, wide-based gait, leading to frequent falls. The patient also experiences dysarthria. PE is significant for nystagmus, motor incoordination, and challenges with fine motor tasks. Which gene mutation is most likely to be implicated?
Frataxin (FXN)
What motor neuron disease is characterized by progressive muscle paralysis due to degeneration and death of motor neurons from the brain all the way down to the muscle?
*sporadic in 90% of cases (not inherited)
ALS
What LMN signs can be seen in ALS?
Weakness / flaccid paralysis, fasciculations, muscular atrophy, hyporeflexia
What UMN signs can be seen in ALS?
Weakness of large muscle groups, spasticity, babinski sign, hyperreflexia
What genes are involved in familial ALS cases?
C9ORF72, SOD1
What autosomal dominant condition is a microangiopathy affecting mainly the brain that is caused by a mutation in the NOTCH3 gene?
*dx w/ skin bx → ultrastructural deposits in small blood vessels
CADASIL
What is the MC inherited cause of stroke & vascular dementia?
CADASIL
What clinical features are seen with CADASIL?
Ischemic episodes, migraine w/ aura, cognitive impairment & dementia, psychiatric disturbances, gait disturbances (occurs later)
What autosomal dominant condition is caused by mutations in PSEN1, APP, or PSEN2?
*accounts for < 1% of Alzheimer’s disease
Familial early-onset AD
What clinical features are seen with familial early-onset AD?
Memory impairment, poor judgement, agitation, confusion, language difficulties; occasionally parkinsonian features & seizures
48 y/o male presents with 2 yr history of unpredictable, irregular, involuntary movements of limbs & face. Spouse reports notable decline in ability to manage daily tasks, increasing irritability, and unexplained emotional outbursts. +Fhx in parent & grandparent. Brain MRI shows generalized cerebral atrophy. Which of the following monogenic disorders is the most likely diagnosis?
Huntington’s Chorea
What X-linked recessive condition results from a frame shift mutation of DMD gene at Xp21.2 involving a near-complete absence of functional dystrophin protein, which causes severe progressive muscle weakness?
DMD
What X-linked recessive condition results from an in-frame mutation of DMD gene at Xp21.2 involving a reduced / partially functional dystrophin protein, which causes less severe progressive muscle weakness?
BMD
What autosomal recessive condition is due to a defect in the CFTR gene which causes thick secretions & affects multiple organ systems?
pulm: chronic infx, bronchiectasis
pancreatic: insufficiency, DM
repro: >96% of men infertile (absent vas deferens)
Cystic Fibrosis
How do you diagnose CF?
Sweat chloride test & newborn screening
What is the treatment for CF?
CFTR modulators & supportive care
What condition is characterized by LVH with preserved systolic function, due to affected sarcomeric proteins (MYH7, MYBPC3)?
*leading cause of SCD in young athletes
HCM
What condition is characterized by fibro-fatty replacement of RV myocardium, due to affected desmosomal proteins (PKP2, DSP)?
ARVC
How would arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) appear on an EKG?
Epsilon wave, ventricular arrhythmias
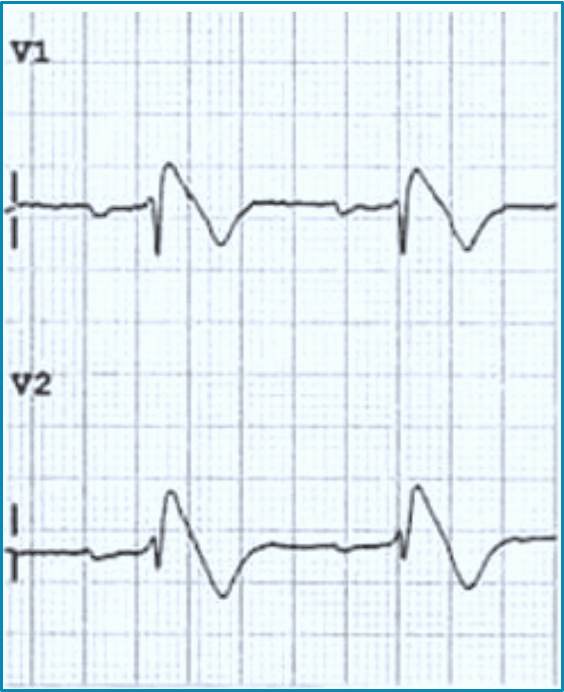
What autosomal dominant condition is usually diagnosed in 5th decade (40s) & associated with an increased risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmias & sudden cardiac death?
*down sloping ST elevation in V1 & V2
Brugada Syndrome
How does brugada syndrome appear on an EKG?
Down sloping ST elevation in V1 & V2
What genes are affected in brugada syndrome?
SCN5A (15-30%) or SCN10A (17%)
What triggers should be avoided in long QT syndrome?
Macrolides, FQs, SSRIs, antipsychotics
What is the treatment for long QT syndrome?
Nonselective BBs, consider ICD
What condition is characterized by a reproducible stress-induced VT but the heart is structurally normal & EKG at rest is normal?
*sx onset ~ 12 y/o
CPVT
What is the MC affected gene in catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT)?
RYR2
22 y/o woman presents with generalized joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, & atrophic scarring. Pt also reports that old scares sometimes split open with minimal trauma. What is the most likely diagnosis?
*atrophic scars represent weak points prone to dehiscence w/ minimal trauma
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
What autosomal dominant condition is associated with aortic root dilation & dissection, a tall, thin body habits w/ disproportionately long limbs, pectus excavatum or carinatum, scoliosis, & ectopia lentis?
Marfan syndrome
What gene is affected in Marfan syndrome?
FBN1 (codes for fibrillin-1 protein)
What autosomal dominant, non-syndromic disorder is associated with a fhx of aortic aneurysms or sudden unexplained death; and is often asymptomatic until an acute dissection occurs?
Familial TAAD
What imaging studies would you get for familial TAAD?
CT/MRI confirms aneurysm or dissection, CXR shows widened mediastinum
32 y/o male presents for sudden onset of severe chest pain that radiates down his back. PE reveals a tall and thin habitus, pectus excavatum, and scoliosis. Radiography shows widened mediastinum concerning for an aortic dissection. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Marfan syndrome
What is a dislocation of the ocular lens, and is a common feature of Marfan syndrome?
Ectopia lentis
ADPKD OR ARPKD: adult disease that slowly progresses over decades
ADPKD
ADPKD OR ARPKD: severe pediatric condition that can be life-threatening from birth
ARPKD
What genetic disorders cause cysts throughout the kidneys, with a high risk of ESRD?
*tx: hemodialysis / peritoneal dialysis; kidney transplant
Polycystic kidney disease (AD & AR)
ADPKD OR ARPKD: key genes affected are PKD1 (more severe) & PKD2 (milder)
ADPKD
ADPKD OR ARPKD: key genes affected are PKHD1 (primary), DZIP1L, an CYS1
ARPKD
ADPKD OR ARPKD: intracranial aneurysms, hepatic cysts, MVP; 50% of pts progress to ESRD by age 60
ADPKD
ADPKD OR ARPKD: hepatobiliary disease, hepatosplenomegaly, portal HTN; 50% of patients reach ESRD within the first decade
ARPKD
18 month old boy presents with swollen, painful knee (hemarthrosis) after a minor fall. Labs show prolonged PTT and normal PT. Genetic testing confirms mutation in the F9 gene. What is the specific diagnosis?
Hemophilia B
What X-linked recessive bleeding disorder is a deficiency of factor VIII caused by an F8 mutation that occurs primarily in males?
*hallmark bleeding: deep joint / hemarthrosis & muscle
Hemophilia A
What X-linked recessive bleeding disorder is a deficiency of factor IX caused by an F9 mutation that occurs primarily in males?
*hallmark bleeding: deep joint / hemarthrosis & muscle
Hemophilia B
What autosomal dominant bleeding disorder is a deficiency of vWF protein, affecting males & females equally and often presents with normal PTT & PT?
*hallmark bleeding: mucosal bleeding (epistaxis, dental), easy bruising
VWD
What is the MC inherited bleeding disorder?
VWD
27-year-old man presents with a history of prolonged nosebleeds and easy bruising. He recently had a dental extraction that bled for two days. His father has a similar history. Lab work shows a normal PT and a normal PTT. Dx?
VWD
What autosomal recessive condition caused by a point mutation in the HBB gene, resulting in an abnormal hemoglobin (HbS) that causes RBCs to sickle, leading to vaso-occlusion & hemolysis?
*causes severe pain, tissue damage, & chronic anemia
Sickle Cell Disease
What are the treatment options for sickle cell disease?
Mainstay: Hydroxyurea → inc HbF to reduce sickling & pain crises
Prophylaxis: PCN in kids to prevent sepsis
Curative: Stem cell transplant, gene therapies (Casgevy, Lyfgenia)
19 y/o male is being evaluated for elevated liver enzymes. Slit lamp examination of his eyes reveals golden-brown rings at the corneal margins. This finding is a hallmark sign of a disorder caused by toxic accumulation of which substance?
Copper
What autosomal recessive condition is caused by mutation in the ATP7B gene, leading to a toxic accumulation of copper in the body?
Wilson’s disease
What are key findings of Wilson’s disease?
Kayser-fleischer rings (golden-brown rings in cornea), low ceruloplasmin, high urinary copper
What is the treatment for Wilsons disease?
Chelation therapy (D-penicillamine)
What autosomal recessive condition is due to an HFE gene mutation that leads to the toxic accumulation of iron?
Hereditary hemochromatosis
What are key findings of hereditary hemochromatosis?
“Bronze diabetes”- hyperpigmentation & insulin resistance, high transferrin saturation & ferritin
What is the treatment for hereditary hemochromatosis?
Therapeutic phlebotomy
What autosomal dominant condition is due to a mutation in the LDLR gene which leads to impaired clearance & markedly elevated LDL cholesterol levels from birth?
Familial hypercholesterolemia
What clinical features are associated with familial hypercholesterolemia?
Tendon xanthomas, xanthelasmata, arcus corneus, inc risk of premature CAD
What is the treatment for familial hypercholesterolemia?
High-intensity statin therapy
What typically autosomal dominant condition is caused by mutations in the COL1A1 or COL1A2 genes, leading to abnormal type I collagen structure which causes skeletal fragility & fractures?
Osteogenesis imperfecta
What clinical features are associated with osteogenesis imperfect (OI)?
Blue sclera, short stature, skeletal fragility, fractures, dentinogenesis imperfecta
What are key extra-skeletal findings of achondroplasia?
Saddle nose deformity & macrocephaly
What autosomal dominant condition is caused by BRCA1/2 mutations & associated with early onset breast cancer (< 50 y/o), triple negative breast cancer, history of both breast & ovarian cancer in the same family or individual, & male breast cancer (mc BRCA2)?
HBOC
A 38-year-old woman with a pathogenic BRCA1 mutation has completed childbearing. She asks about the most effective way to reduce her risk of developing ovarian cancer. What is the primary risk-reducing recommendation for managing her ovarian cancer risk?
RRSO
What condition affects the APC gene & is characterized by the development of hundreds to thousands of colonic polyps & near 100% lifetime risk of CRC if untreated?
FAP
What is the standard of care to prevent cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)?
Prophylactic colectomy
What age should screening colonoscopies start in patients with FAP?
10-15
What condition is associated with MLH, MSH, PMS, & EPCAM genes and is characterized by few, if any, polyps that progress to cancer much more rapidly?
Lynch syndrome