VS331: Module 39: Ovaries
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
1. Ovaries
2. Uterine tubes (oviducts, fallopian tubes)
3. Uterus (Body, horns, & cervix)
4. Vagina
5. External genitalia (labia, clitoris, vestibule)
6. Placenta
7. Mammary glands
List the organs of the female reproductive system
1. Gametogenesis - also called oogenesis
2. Steroid hormone production - Estrogens & progestogens
List the functions of the ovaries
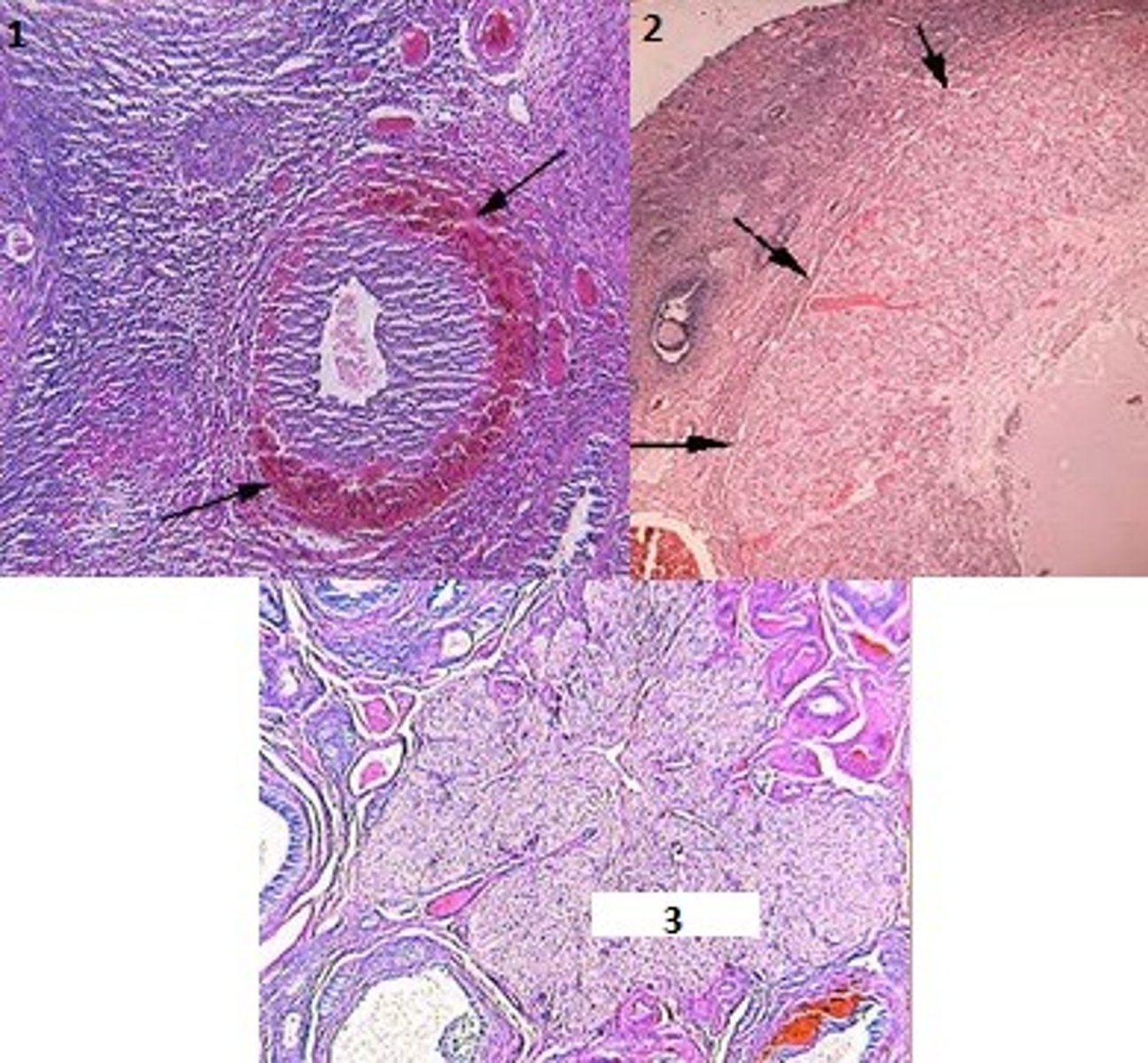
Ovary
2. Cortex - Contains developing ova & corpora lutea
1. Medulla - Has blood vessels, CT, lymphatic vessels & nerves
Identify the organ, & what is indicated by #1 & 2.
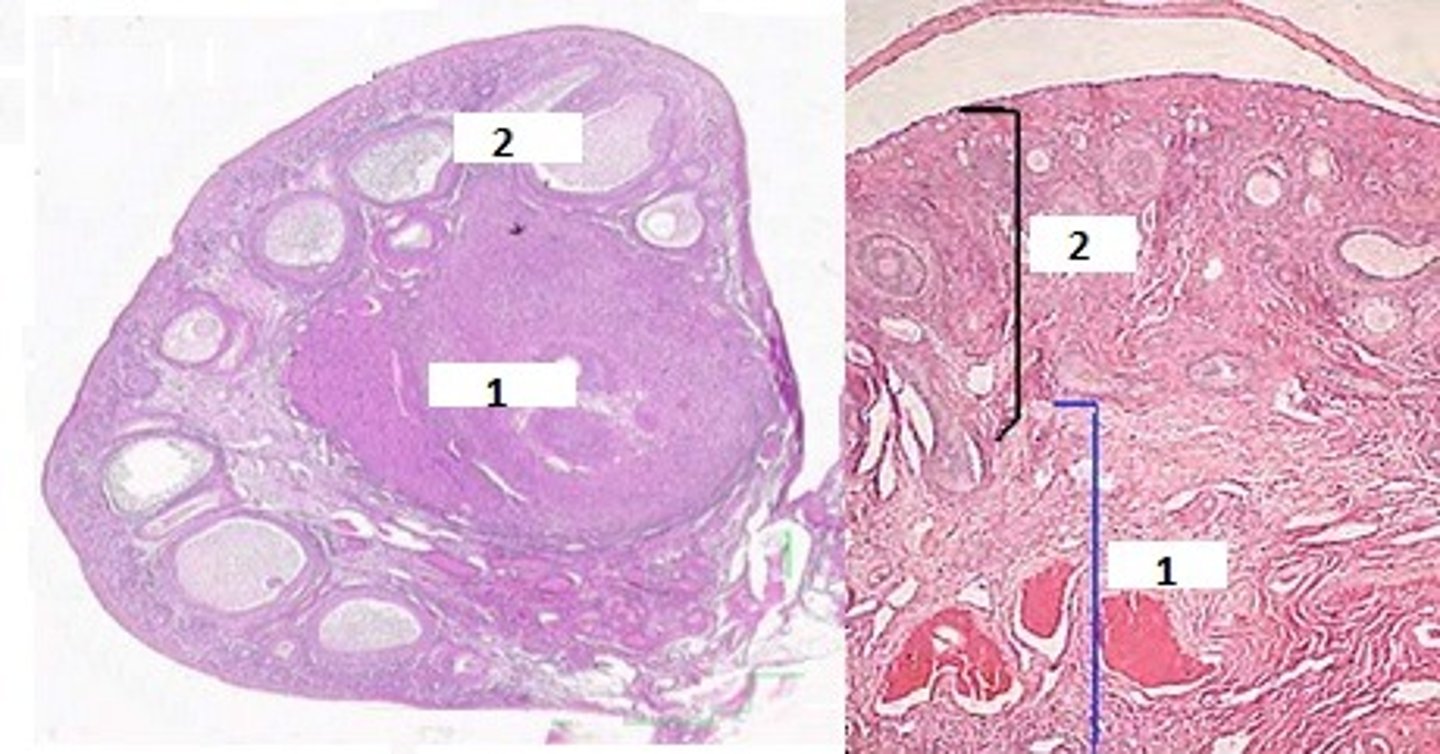
1. Primordial follicles - Contains primary oocyte, Has single layer of granulosa cells
2. Secondary (Antral) Follicle - Granulosa cells become secretory. Produces liquor folliculi and follicular antrum.
3. Mature/Graafian follicle - Forms cumulus oophorus & corona radiata
Identify the 3 follicles & their characteristics seen in oogenesis
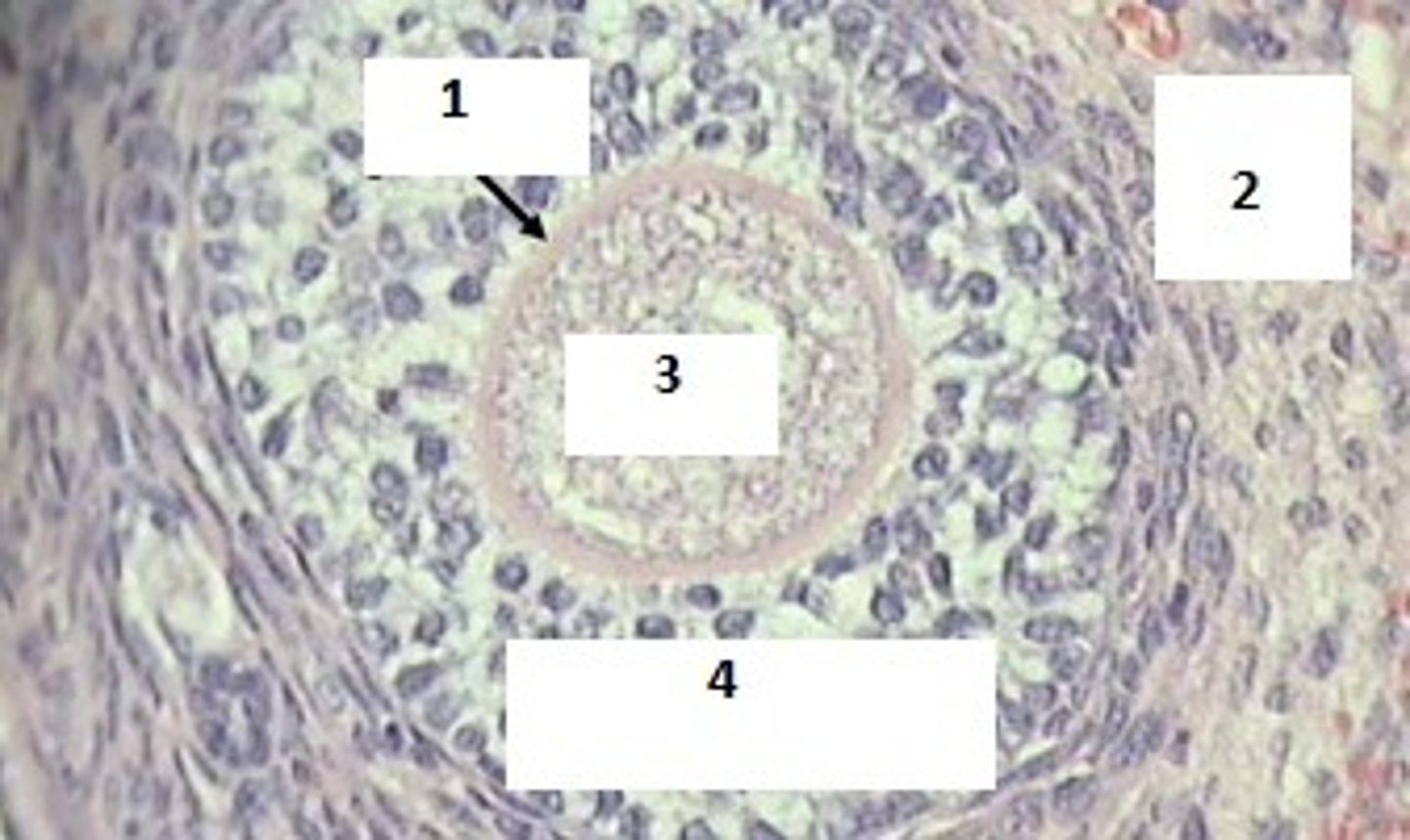
Developing follicle
1. Zona pellucida
2. Theca interna cells
3. Primary oocyte
4. Granulosa cells - Estrogen secretors
Identify the follicle & #1-4
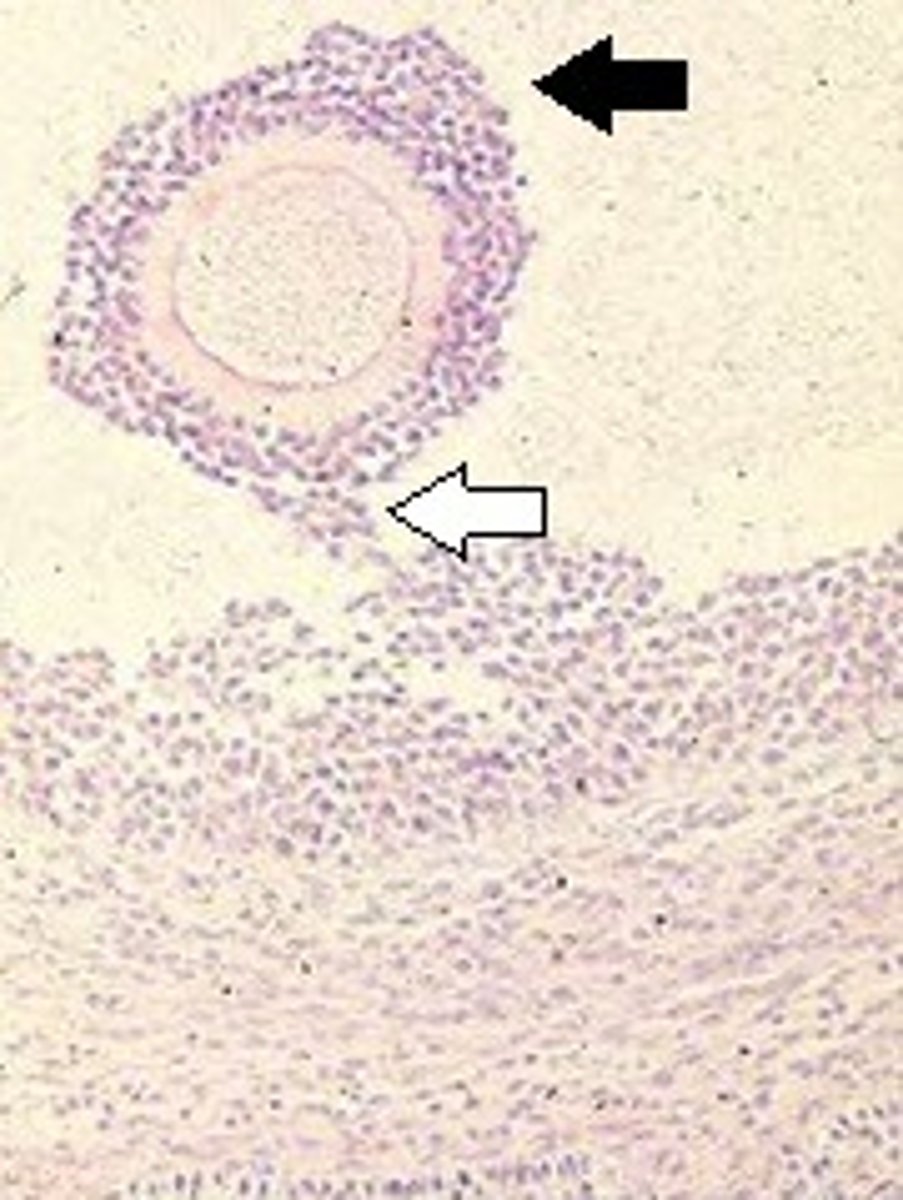
Mature or Graafian Follicle
Black arrow = Corona radiata
White arrow = Cumulus oophorus
What follicle has these characteristics and what is indicated by the black & white arrows
Rupture of a follicle & release of the secondary oocyte from a Graafian follicle
Define ovulation
When sperm binds to sperm receptor on the zona pellucida allowing it to penetrate & enter the secondary oocyte
Define fertilization
Follicles that develop but fail to ovulate result in a temporary scar called a corpus atreticum
Define follicular atresia
1. Initally after ovulation, bleeding into the follicular lumen to form corpus hemorrhagicum
2. Granulose cells & theca interna cells proliferate to form corpus luteum
3. Corpus luteum - produces progesterone & estrogens
- will be retained if pregnancy occurs, becomes corpus albicans and dissolves if not
Identify the step 1 - 3 that occur after ovulation