AHTG100 FINAL
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:33 AM on 4/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
1
New cards
What’s the difference between negative & positive liberty?
Negative: Freedom From
\-congress shall not (amendment)
\-limited gov & markets embodied in the works of John Locke & Adam Smith
Positive: Freedom to
\-congress shall… (13th-15th amendment)
\-congress shall not (amendment)
\-limited gov & markets embodied in the works of John Locke & Adam Smith
Positive: Freedom to
\-congress shall… (13th-15th amendment)
2
New cards
Recap: What was Adam Smith’s Free Market System? What are two broad advantages of the market system and according to Adam Smith, what happens when the Gov. gets involved?
Adam Smith’s Market: when everyone pursues their own self-interests w/in the constraints of social norms (so no murder), that’s what leads to the best outcome.
Advantages:
1. Incentives that improve social welfare
2. The invisible hand.
\
If Gov. tries to set prices or control production that reduces the welfare of society
Advantages:
1. Incentives that improve social welfare
2. The invisible hand.
\
If Gov. tries to set prices or control production that reduces the welfare of society
3
New cards
What are some roles government’s have in Markey Economy?
\-limit coercion or fraud
\-property rights
\-enforce contracts
\-facilitate exchange through $ & infrastructure
\-property rights
\-enforce contracts
\-facilitate exchange through $ & infrastructure
4
New cards
Who was William Lee and his invention, the stocking Frame?
Made an automatic machine for knitting, but had to get permission from Elizabeth 1st to manufacture them…and Elizabeth said no because it would put people out of a job
\*downfalls of command economies: less innovation
\*downfalls of command economies: less innovation
5
New cards
T or F: While in the long run both trade and innovation are what make society wealthy, in the short run, some people stand to lose-often a lot.
TRUE
6
New cards
With the increase in production after the Civil War, came an increase in income, what was a negative side effect of this?
\*Income more than quintuples
BUT there was more inequality among workers (owners & people who are replaced by factories)
BUT there was more inequality among workers (owners & people who are replaced by factories)
7
New cards
How did urbanization change post Civil War era?
5% in 1800-40% in 1900 lived in cities
8
New cards
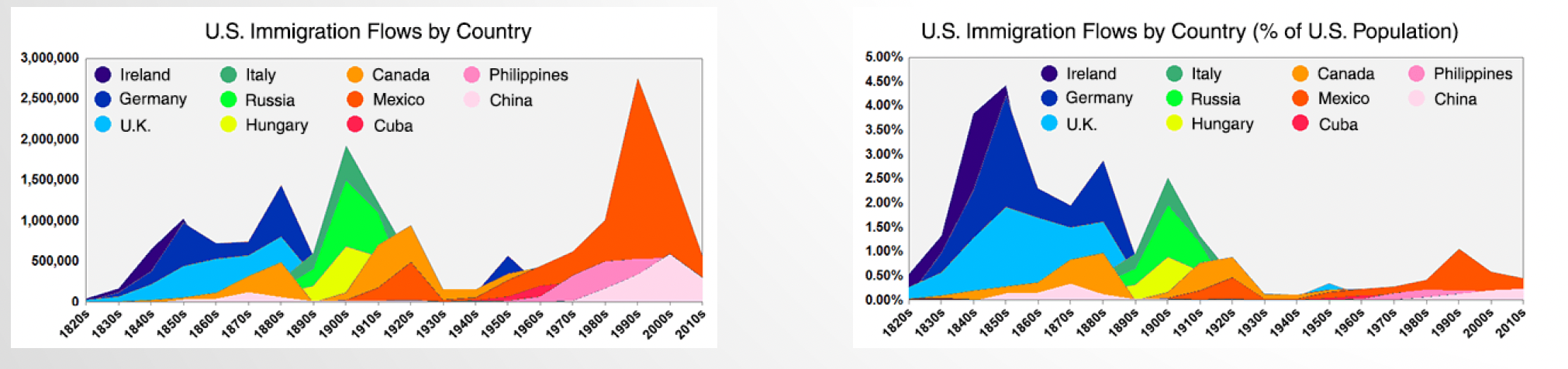
How much did population grow in the 19th century and what were three key causes of growth?
5million → 76 million
1. Longer Life Spans
2. High Birthrates
3. Immigration
1. Longer Life Spans
2. High Birthrates
3. Immigration
9
New cards
True of False: Gridlock is a key insurance against widespread poverty.
FALSE, Migration
10
New cards
How did the scale of institutions change post Civil war?
* Everything becomes larger, faster, & denser
* agriculture, workplaces,
* Room for new intermediating institutions ex. the union
* agriculture, workplaces,
* Room for new intermediating institutions ex. the union
11
New cards
What was the Gilded Age?
\*The concentration of wealth intermingled w/ extensive poverty
The Gilded Age was a period of rapid industrialization in America from 1865-1898. It was characterized by the extreme wealth of a few individuals, while many others lived in poverty. This era is often associated with political corruption and exploitation of immigrant labor.
The Gilded Age was a period of rapid industrialization in America from 1865-1898. It was characterized by the extreme wealth of a few individuals, while many others lived in poverty. This era is often associated with political corruption and exploitation of immigrant labor.
12
New cards
What were the Muckrakers? List the three examples given in class.
Investigative journalism that showed the neg. consequences of new urbanism & industrialization in order to expose businesses & cities
ex.
1. Jacob Riis’ *How the Other Half Lives* -sparks the concern over economic inequality & poverty
2. Ida Tarbell’s History of the Standard Oil Company-Rockefeller as a vicious monopolist
3. Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle-Chicago meatpacking industry
ex.
1. Jacob Riis’ *How the Other Half Lives* -sparks the concern over economic inequality & poverty
2. Ida Tarbell’s History of the Standard Oil Company-Rockefeller as a vicious monopolist
3. Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle-Chicago meatpacking industry
13
New cards
While there was mass progress in society, how did this new America fall short from what Jefferson envisioned it to be?
A large class of urban poor
14
New cards
What class and movement is born out of the Gilded age?
Non-rural middle class
The Progressive Movement: born from the middle class desire to solve social & economic problems= the Good Society
\*\*\*Progressives are NOT the poor, but well-off reformers
\*\*\*Saw Positive Liberty as a goal & the Gov. as a means to provide it.
\-their desire reflects deep idealism & religion
\-Go on to fight perceived market failures & social problems
The Progressive Movement: born from the middle class desire to solve social & economic problems= the Good Society
\*\*\*Progressives are NOT the poor, but well-off reformers
\*\*\*Saw Positive Liberty as a goal & the Gov. as a means to provide it.
\-their desire reflects deep idealism & religion
\-Go on to fight perceived market failures & social problems
15
New cards
Describe some key beliefs of the Progressives?
* Believe in scientific, innovation, & economic progress
* Everything is a product of society therefore…
* The progress of society promised by innovation is corrupted by bad institutions or ignorant people who are unaware of how to be better.
* The solution to above is professional, technical expertise as the tool & the gov. as it’s operator
* Everything is a product of society therefore…
* The progress of society promised by innovation is corrupted by bad institutions or ignorant people who are unaware of how to be better.
* The solution to above is professional, technical expertise as the tool & the gov. as it’s operator
16
New cards
Progressives hated: Trusts (too close to Monopolies), political machines (false voter results), corrupt lawmakers (not representative & not helping people), & city ills (the poor, living conditions, socioeconomic gap)…what THREE things did they do to fight what they hated?
1. State Legislature Reforms:
1. Initiative: allowed reformers to go around state leg by submitting new Leg directly on the ballot
2. Referendum:
3. Recall: voters right to remove public officials at a special election (How Arnold got elected)
2. Expanding Democracy (17th & 19th Amendment)
3. Use Experts to make gov. more scientific: FDA, Pure Food & drug, Land management, Federal Reserve, etc.
17
New cards
What are Market Failures/Weaknesses? EMPIRE (Know the difference between weaknesses/failures)
When Smith’s model doesn’t work the way it says it should.
FAILURES:
1. Externalities
2. Monopolies/Markey Power
3. Public Good
4. Inadequate Info
\
WEAKNESSES:
1. Recession
2. Economic Inequality
FAILURES:
1. Externalities
2. Monopolies/Markey Power
3. Public Good
4. Inadequate Info
\
WEAKNESSES:
1. Recession
2. Economic Inequality
18
New cards
What Market Failure term is defined below? Give an example:
The third party that is not directly involved in an exchange, but is still effected by it. Ex. pollution produced by factory
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
The third party that is not directly involved in an exchange, but is still effected by it. Ex. pollution produced by factory
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
c. Externalities
ex. Andrew Carnegie brought many jobs to Pittsburg but also brought horrific air pollution
\-classic externality where the effects of pollution are not reflected in the price of steel, or coal
\-no incentive to pollute less when pollution __does not cost__
\-Is considered a market failure because it’s not really factored into the price of things\*\*\*\*
ex. Andrew Carnegie brought many jobs to Pittsburg but also brought horrific air pollution
\-classic externality where the effects of pollution are not reflected in the price of steel, or coal
\-no incentive to pollute less when pollution __does not cost__
\-Is considered a market failure because it’s not really factored into the price of things\*\*\*\*
19
New cards
What’s the difference between Bad & Good externalities
Bad: External costs imposed such as air pollution, PDA haha
\-Markets tend to OVERPRODUCE goods w/ neg externalities
Good: External benefits received such as flu shots & TEMPLES
\-Markets tend to UNderproduce goods w/e pos externalities b/c we’re not really worried about other people.
\-Markets tend to OVERPRODUCE goods w/ neg externalities
Good: External benefits received such as flu shots & TEMPLES
\-Markets tend to UNderproduce goods w/e pos externalities b/c we’re not really worried about other people.
20
New cards
What’s the gov. response to externalities?
Try to reduce neg. externalities in the most cost-effective way possible:
1. Impose bans…many fail
2. Create mandates….not very effective
3. __**Tax or Subsidize**__
4. Market Approach: ASSIGN PROPERTY RIGHTS where people can use markets to co-ordinate & gives people incentives to reduce pollution cheaply
1. ex. emission permits
1. Impose bans…many fail
2. Create mandates….not very effective
3. __**Tax or Subsidize**__
4. Market Approach: ASSIGN PROPERTY RIGHTS where people can use markets to co-ordinate & gives people incentives to reduce pollution cheaply
1. ex. emission permits
21
New cards
What Market Failure term is defined below:
Limits consumer choices, imposes higher prices, & reduces the welfare of society & exchange
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
Limits consumer choices, imposes higher prices, & reduces the welfare of society & exchange
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
ex. Google, Apple, Disney, Meta, CARNAGEE STEEL
\*Note Market Power itself is the power to control and raise prices, which is what a cartel or monopoly does
Market Power=Higher Prices=too little exchange
SOLUTION: Break them up
ex. Google, Apple, Disney, Meta, CARNAGEE STEEL
\*Note Market Power itself is the power to control and raise prices, which is what a cartel or monopoly does
Market Power=Higher Prices=too little exchange
SOLUTION: Break them up
22
New cards
Poll: The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) restricts the production of oil by member countries, which increases its price. Which market weakness does this best illustrate?
A. Externalities
B. Imperfect Information
C. Market Power/Monopoly
D. Public Goods
A. Externalities
B. Imperfect Information
C. Market Power/Monopoly
D. Public Goods
C. Market Power
23
New cards
What Market Failure term is defined below:
When one or both parties aren’t adequately informed that leads to non-mutually beneficial exchanges
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
When one or both parties aren’t adequately informed that leads to non-mutually beneficial exchanges
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
b. Inadequate Information
\-progressives were concerned that firms were misrepresenting their products
ex. Upton’s Sinclair’s *The Jungle* exposed unsanitary practices in meat industry & appalling working conditions. ..Americans were appalled & sales of meat dropped
Other ex. canned foods, medicine, doctors smoking cigars, etc.
\-progressives were concerned that firms were misrepresenting their products
ex. Upton’s Sinclair’s *The Jungle* exposed unsanitary practices in meat industry & appalling working conditions. ..Americans were appalled & sales of meat dropped
Other ex. canned foods, medicine, doctors smoking cigars, etc.
24
New cards
What are some solutions to the market failure: inadequate information?
1. Different acts & institutions being created to monitor/ban companies from using “adulterated” ingredients:
* Pure Food & Drug Act, FDA creation, Food Drug & Cosmetic Act
2. Courts give damage recovery
3. Labeling, truth in marketing
4. Companies use reputation & feedback such as Carfax
5. Money back guarantees
25
New cards
What Market Failure term is defined below:
Consumed by one person w/out reducing the amount available for others ex. National defense & light house
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
Consumed by one person w/out reducing the amount available for others ex. National defense & light house
a. Monopoly or Cartel or Market Power
b. Inadequate Information
c. Externalities
d. Public Goods
d. Public Goods
26
New cards
When it comes to the market weakness: public goods, what is the difference of the two public good concepts non-rival and non-excludable? Give examples. What is a Common Pool resource?
Non-rival: consumed by one person w/out reducing the amount available for others.
ex. flood control measures
Non-excludable: Very difficult to exclude non-payers from consuming the good.
ex. national defense, lighthouse
\*Common Pool resources are public goods that are RIVAL, BUT non-excludable such as a park
ex. flood control measures
Non-excludable: Very difficult to exclude non-payers from consuming the good.
ex. national defense, lighthouse
\*Common Pool resources are public goods that are RIVAL, BUT non-excludable such as a park
27
New cards
Public Good example problems: decide if they are non-rival and/or non-excludable
Fishing ground
Dish Network
Park
Fishing ground
Dish Network
Park
Non-excludable, meaning anyone can fish, but they ARE RIVAL, because if someone is taking my favorite spot, then I’m competing with them.
Dish Network: Non-Rival (don’t have to compete with service) but it IS EXCLUDABLE because you have to buy a satellite dish, so if you’re too poor, you can’t get it.
Park: Again, non-excludable, b/c everyone can go but IS RIVAL b/c you might have to fight someone for a chance on the swings
Dish Network: Non-Rival (don’t have to compete with service) but it IS EXCLUDABLE because you have to buy a satellite dish, so if you’re too poor, you can’t get it.
Park: Again, non-excludable, b/c everyone can go but IS RIVAL b/c you might have to fight someone for a chance on the swings
28
New cards
What is the Free Rider Problem
Everyone has an incentive to consume the good w/out paying or providing the good & therefore…
Good will be UNDERPRODUCED so…
Gov produces it itself & forces people to contribute through taxes & funds or provide the good
Good will be UNDERPRODUCED so…
Gov produces it itself & forces people to contribute through taxes & funds or provide the good
29
New cards
What are Trusts and what are some examples of men who held these trusts?
* Trusts are the organization of several businesses in the same industry and by joining forces, the trust controls production and distribution of a product or service, thereby limiting competition. (vs. Monopolies are businesses that have total control over a sector of the economy, including prices.)
* Examples:
• John Rockefeller – Standard Oil
• Andrew Carnegie – U.S. Steel
• Cornelius Vanderbilt – Eastern Railroads
• J.P. Morgan – Banking
* Examples:
• John Rockefeller – Standard Oil
• Andrew Carnegie – U.S. Steel
• Cornelius Vanderbilt – Eastern Railroads
• J.P. Morgan – Banking
30
New cards
What is the true issue of Monopolies?
They exercise political power & some things should NOT be allocated by money
31
New cards
How did the Government respond to Trusts?
1. Progressive Antitrust laws:
* **Sherman Act:** outlaws "every contract, combination, or conspiracy in restraint of trade," and any "monopolization, attempted monopolization, or conspiracy or combination to monopolize."
* \*It does NOT outlaw being a monopoly
* Clayton Act: outlaws price fixing
* Federal Trade Commissions Act: looks at mergers
2. Gov. may break up large firms that have too much market power ex. Rockefeller’s standard oil
3. Gov. regulate economically powerful firms
1. ex. Interstate Commerce Act regulates railroads & other transport.
2. can also force firms to behave like competitive firms
32
New cards
While the gov. can intervene in trusts or firms that have too much market power, what are some key issues with this process?
1. Too slow
2. monopolists have the ability to persuade regulators
3. It’s hard to define monopoly power in tech
33
New cards
What is the true worry of the progressives?
Public power (monopolies using their market power to control public power/politics)
34
New cards
What is a Common Pool resource?
A PUBLIC GOOD that is Rival, But is NON-EXCLUDABLE
Example: Parks
Non excludable (anyone can come to the park), BUT they are rival b/c if one person is using the swing, it takes away form me.
* everyone wants to defect & take as much as they can b/c they know if they don’t others will & they’ll be left w/ nothing
SOLUTION: Gov. manage resource to ensure it’s best use &..
__sometimes we can solve it on our own__ IF it’s on a smaller scale
\*Public Goods can only be solved by GOV!
Example: Parks
Non excludable (anyone can come to the park), BUT they are rival b/c if one person is using the swing, it takes away form me.
* everyone wants to defect & take as much as they can b/c they know if they don’t others will & they’ll be left w/ nothing
SOLUTION: Gov. manage resource to ensure it’s best use &..
__sometimes we can solve it on our own__ IF it’s on a smaller scale
\*Public Goods can only be solved by GOV!
35
New cards
What market WEAKNESS is defined below:
When GDP is declining for a certain amount of time, aka we make a lot less stuff than what we have resources to make
When GDP is declining for a certain amount of time, aka we make a lot less stuff than what we have resources to make
Recession
36
New cards
What market weakness is described below: Give the three
the unequal distribution of income and opportunity between different groups in society
the unequal distribution of income and opportunity between different groups in society
Income Inequality
37
New cards
What is the difference between these three economic inequality concepts: Equal Opportunity, Equality of Result, & Proportionally Fairness?
__**Equal Opportunity**__**:** Everyone is at the same starting line
* ex. everyone has the opportunity to vote, if there’s a gender wage gap, this is a violation of equal opportunity
__**Equality of Result**__: Equal finishing line (similar outcomes for everyone regardless of input
* not common in America
* Ex. SS
__**Proportionally Fairness:**__ You get out what you put in (individualistic-you figure it out)
* ex. everyone has the opportunity to vote, if there’s a gender wage gap, this is a violation of equal opportunity
__**Equality of Result**__: Equal finishing line (similar outcomes for everyone regardless of input
* not common in America
* Ex. SS
__**Proportionally Fairness:**__ You get out what you put in (individualistic-you figure it out)
38
New cards
39
New cards
What other economic reforms did progressives work hard for?
* Tenement Laws
* Regulation of working conditions: workman’s comp, unemployment, minimum wages, max. hours, etc.
* 16th Amendment: Income tax
* Federal Reserve System: manages large banks to ensure stable financial system
* Regulation of working conditions: workman’s comp, unemployment, minimum wages, max. hours, etc.
* 16th Amendment: Income tax
* Federal Reserve System: manages large banks to ensure stable financial system
40
New cards
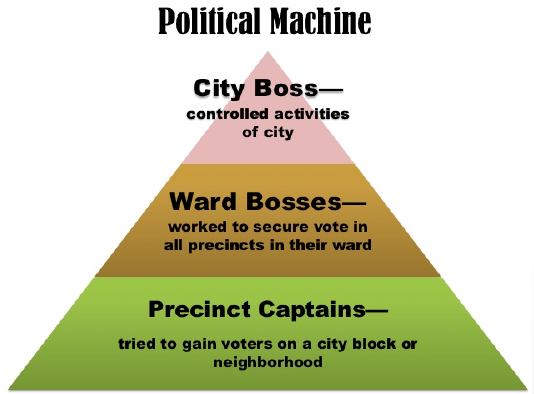
What is the political Machine & how do political machines use immigrants?
Bosses provide things for people who are poor & ask the immigrants to vote for their “friends”
\-by attending to the poor’s needs, they control a large block of votes
\-by attending to the poor’s needs, they control a large block of votes
41
New cards
Who was one of the most powerful city bosses? Why are the middle class worried about him and others?
William Tweed
Remember, middle class are the progressives who had a deep concern over municipal & state gov. corruption and wanted to create a good society
Remember, middle class are the progressives who had a deep concern over municipal & state gov. corruption and wanted to create a good society
42
New cards
Progressives generally believe that Human nature is ______ constructed. What are their two solutions?
Socially constructed & therefore all problems can be solved through social reforms:
1. Science can be used to improve society
2. Political power & democratic reform can also improve society
1. Science can be used to improve society
2. Political power & democratic reform can also improve society
43
New cards
What is the Social Reform aka the Social Gospel? What things were created because of it?
A movement w/in Protestantism that aims to apply Christian ethics to social problems aka a move to achieve salvation w/out a second coming
ex. Alcohol , poverty, child labor, etc.
Created:
1. Child Labor Laws & Compulsory schooling
2. Private Foundations ex. RED CROSS
3. Local Family assistance programs
4. Forest Service & National Parks
5. 18th Amendment (ratified 1919, repealed 1933)
ex. Alcohol , poverty, child labor, etc.
Created:
1. Child Labor Laws & Compulsory schooling
2. Private Foundations ex. RED CROSS
3. Local Family assistance programs
4. Forest Service & National Parks
5. 18th Amendment (ratified 1919, repealed 1933)
44
New cards
Who was Jane Addams?
Created settlement movement & Hull House & brings middle class volunteers to live with immigrants & the poor to:
1. To extend democracy beyond the ballot box.
2. Idealism: to bring as much social energy & the accumulation of civilization to those portions of the race which have little
1. “the wish to right wrong & alleviate suffering, haunts them \[young people\] daily
3. To make religion a social expression
1. To extend democracy beyond the ballot box.
2. Idealism: to bring as much social energy & the accumulation of civilization to those portions of the race which have little
1. “the wish to right wrong & alleviate suffering, haunts them \[young people\] daily
3. To make religion a social expression
45
New cards
What was the Women’s Christian Union (WCTU)?
Group of women who worked towards the prohibition of alcohol b/c alcohol was at the roots of many problems (domestic violence, hold jobs, etc)
Carrie Nation: Women w/ a hatchet
Carrie Nation: Women w/ a hatchet
46
New cards
How does Henry Ford affect the Prohibition movement?
He pays workers a lot more, but in return he wanted more control over their social lives
\-ex. he wanted them to be sober so he had people go into their homes to check in on them to make sure they were spending money wisely
\-ex. he wanted them to be sober so he had people go into their homes to check in on them to make sure they were spending money wisely
47
New cards
What were the effects of Prohibition of Alcohol? Do people actually follow it?
* It only lasts a decade
* Reduced Alcohol consumption but didn’t stop it (Congress)
* Large part of society ignores it…do is it really a law?
* Reduced Alcohol consumption but didn’t stop it (Congress)
* Large part of society ignores it…do is it really a law?
48
New cards
What was the Election Reform during the Progressive Era?
* Secret Ballots aka Australian Ballots (b/c it started there) instead of tickets
* 17th Amendment: Direct election of Senators
* More direct Democracy
* 17th Amendment: Direct election of Senators
* More direct Democracy
49
New cards
What’s the issue with too much democracy?
It looks like you give power back to the people, but in reality, the people don’t really have the time & attention to vote on every little thing…that’s why we’re a republic!
50
New cards
What was the Women’s Suffrage movement?
Grows out of the abolition movement and fights over the 15th Amendment (right to vote for men)
\-Reinvigorated from the progressive Era due to rise of middle class women who are politically active
\-The west is the most receptive
\-Reinvigorated from the progressive Era due to rise of middle class women who are politically active
\-The west is the most receptive
51
New cards
What was the turning point of the Women’s Suffrage Movement?
1. Wilson’s Administration
2. The women’s role in the war
3. They get sympathetic publicity (the parade)
52
New cards
What is the 19th Amendment?
Ratified in 1920, gives women the right to vote
\*The most important political accomplishment of the progressive Era
\*The most important political accomplishment of the progressive Era
53
New cards
How did Progressives view the Constitution? What were some other problems Progressives faced?
1. Outdated & standing in the way of scientific progress
* hence all the amendments
2. Science is not omniscient (all-knowing)…detours into pseudoscience which saps the movement
3. WWI-other concerns competed for attention
54
New cards
What was the dark side of the Progressives?
Their drive for purity and a perfect society led many to embrace:
* Racism & Eugenics
* Anti-Immigration (mostly on racial grounds)
* Restricted women’s’ economic opportunity in weirdly paternalistic way…they argued for minimum wage/max hours rules for women only.
* Racism & Eugenics
* Anti-Immigration (mostly on racial grounds)
* Restricted women’s’ economic opportunity in weirdly paternalistic way…they argued for minimum wage/max hours rules for women only.
55
New cards
What were the Progressives Legacy?
They changed liberalism as a model of government
Citizen activism & Private civic organizations
Citizen activism & Private civic organizations
56
New cards
What is the general trend of economic growth cycles?
They “wiggle”
57
New cards
What is the difference between a recession and a depression?
Recession: when we actually produce much less stuff than we have the resources to make
Depression: a severe, prolonged recession
Depression: a severe, prolonged recession
58
New cards
Why do recessions happen? (Three main reasons)
1. During the good times people delay change, invest poorly, etc. and then the economy is hit by a…
2. SHOCK-such as the stock market crashes, theirs bank panic, etc. & b/c some people are afraid, they spend less $=less demand=less stuff being produced.
3. Propagation (wildly spreading an idea/info)-recession spreads to other areas of the economy such as institutions
59
New cards
What are some primary effects of an Economy Shock?
* Businesses fail or contract
* resources are unemployed
* People become fearful
* resources are unemployed
* People become fearful
60
New cards
What happens after a recession?
Most are short, 18month or less…
* as wages & prices fall, opportunities are created
* people/businesses start spending again
* as wages & prices fall, opportunities are created
* people/businesses start spending again
61
New cards
How was the Great Depression Unique?
The Perfect Storm: GDP (stuff a nation produces) went down 30% HUGE!!
1. The Stock market crashes & many are ruined
2. Bank Run/Crisis: Everyone shows up to w/draw their $
1. 9000 Banks fail, $140 Billion lost in deposits
3. Weather Crisis: climate in the midwest created the DUST BOWL
1. drought & ignorance creates conditions for massive windstorms to blow away the topsoil
2. 1/3 of American farmers experience foreclosure
1. The Stock market crashes & many are ruined
2. Bank Run/Crisis: Everyone shows up to w/draw their $
1. 9000 Banks fail, $140 Billion lost in deposits
3. Weather Crisis: climate in the midwest created the DUST BOWL
1. drought & ignorance creates conditions for massive windstorms to blow away the topsoil
2. 1/3 of American farmers experience foreclosure
62
New cards
How did the Great Depression cause a moral & political crisis?
1. Moral Crisis: Self-reliant country of optimism…now people are becoming ruined everywhere.
1. Suicide, family abandonment, & alcoholism on the rise
2. national demoralization, private charities overwhelmed
2. Political Crisis: severe hardship & misery strains political system
1. loss of faith in politics & economics in the U.S.
2. Increased protests, sick of Republicans
63
New cards
How did Franklin Delano Roosevelt save the day during the Great Depression? How does he effect the role of gov. in society?
* FDR dramatically inc. the role of the gov. in society
* Unlike Horrible Hoover, FDR believes inaction of the gov. makes things worse!
* Admits he doesn’t know the answer, but experiments and finds one.
* “Bold persistent experimentation”
* Enacted many programs and took what worked
* Restored confidence in the banking system:
* Fireside chats (let’s the people through radio know whats going on)
* Does a Bank Holiday
* When banks open, they will be backed by the U.S. gov. $ insured by the FDIC
* Unlike Horrible Hoover, FDR believes inaction of the gov. makes things worse!
* Admits he doesn’t know the answer, but experiments and finds one.
* “Bold persistent experimentation”
* Enacted many programs and took what worked
* Restored confidence in the banking system:
* Fireside chats (let’s the people through radio know whats going on)
* Does a Bank Holiday
* When banks open, they will be backed by the U.S. gov. $ insured by the FDIC
64
New cards
What was Keynesianism by John Keynes?
John Keynes was a polymath that said if the recession is caused by too little demand, the gov. can act in recessions to boost demand & make recession less harmful.
65
New cards
What is defined below:
Gov. spends money (creates jobs) and cut __taxes__
a. Fiscal Policy
b. Monetary Policy
Gov. spends money (creates jobs) and cut __taxes__
a. Fiscal Policy
b. Monetary Policy
a. Fiscal Policy
ex. stimulus checks, WPA (Gov. hired citizens to create roads, bridges, trails, etc.), CCC
\-What FDR used during the Great Depression
ex. stimulus checks, WPA (Gov. hired citizens to create roads, bridges, trails, etc.), CCC
\-What FDR used during the Great Depression
66
New cards
What is defined below:
Controlled by the Federal Reserve system, inc. the __$ supply__ __& lowers interest rates__ to reduce attractiveness of saving
a. Fiscal Policy
b. Monetary Policy
Controlled by the Federal Reserve system, inc. the __$ supply__ __& lowers interest rates__ to reduce attractiveness of saving
a. Fiscal Policy
b. Monetary Policy
b. Monetary Policy
67
New cards
What is the NRA (NOT the national rifle ass)? Where did it come from?
NRA (National Recovery Administration),
* wanted to keep trying to raise real prices
* wanted the gov. to play a larger role in planning what the economy should do (Rex Tugwell)
* Supreme Court shut them down!
* wanted to keep trying to raise real prices
* wanted the gov. to play a larger role in planning what the economy should do (Rex Tugwell)
* Supreme Court shut them down!
68
New cards
What were RD Roosevelt’s Four Freedoms? SWWF! What was his Second Bill of Rights?
Freedom of: 1. Speech, 2. Worship, from 3. Want, from 4. Fear
__2nd Bill of Rights__: ALL POSITIVE LIBERTIES (freedom to DO something instead of FROM something)
* Gov. must provide economic security-new role
* Decent housing
* Medical care & education
* Protection from old age
__2nd Bill of Rights__: ALL POSITIVE LIBERTIES (freedom to DO something instead of FROM something)
* Gov. must provide economic security-new role
* Decent housing
* Medical care & education
* Protection from old age
69
New cards
What were the legacies of the NEW DEAL?
1. Political coalition (alliance for combined action)
2. End of a philosophy of American economic individualism
3. Idea that gov. has a positive duty to promote economic security
1. permanent expansion in size of gov. to meet this role.
70
New cards
How has Judicial Review expanded?
* Marbury v. Madison
* Dred Scott v. Sanford
* As time passes judicial review becomes more common:
* Clinton 225, G.W Bush 148, Obama 175
* Dred Scott v. Sanford
* As time passes judicial review becomes more common:
* Clinton 225, G.W Bush 148, Obama 175
71
New cards
What are some concerns for the judicial review expanding?
Courts are not democratic- insulated from consent
Unelected
Lifetime appointments
\*this is by design though b/c its hard to protect the rights against the “tyranny of the majority” if the majority can fire you. -does this remove accountability though?
Hamilton: “Neither force nor will, but merely judgement”
Unelected
Lifetime appointments
\*this is by design though b/c its hard to protect the rights against the “tyranny of the majority” if the majority can fire you. -does this remove accountability though?
Hamilton: “Neither force nor will, but merely judgement”
72
New cards
What are some examples of judicial reviews that have maybe gone too far?
__**KELO v. NEW LONDON:**__ Supreme court ruled they could take Kelo’s home for a mall→public outrage→states respond by passing anti-Kelo laws.
__**Affordable Care Act**__: Can’t fine you for not getting it, but they can add extra taxes if you don’t
__**PLESSEY V. FERGUSON**__: SC backed the Louisiana state law for separate but equal spaces for blacks & whites
__**Affordable Care Act**__: Can’t fine you for not getting it, but they can add extra taxes if you don’t
__**PLESSEY V. FERGUSON**__: SC backed the Louisiana state law for separate but equal spaces for blacks & whites
73
New cards
How does the Supreme Court facilitate the Jim Crow segregation regime through Judicial review?
__**Plessey v. Ferguson:**__
1892 Homer Adolph Plessey took a seat in the “whites only” car and was arrested-claimed the 14th amendment should prohibit such practices BUT….SC disagrees:
Claim a diff b/w political equality & social equality
?Should the SC lead or follow moral consensus?
1892 Homer Adolph Plessey took a seat in the “whites only” car and was arrested-claimed the 14th amendment should prohibit such practices BUT….SC disagrees:
Claim a diff b/w political equality & social equality
?Should the SC lead or follow moral consensus?
74
New cards
John Marshall Harlan’s Famous Dissent, Justice Harlan said “Our constitution is color-blind….The law regards man as man, and takes no account of his surroundings or of his color.”
Even if the Supreme Court had followed Harlan, would issues would they have faced?
Even if the Supreme Court had followed Harlan, would issues would they have faced?
Can the Supreme Court __enforce__ it’s own decisions??
“John Marshall has made his decision; now let him enforce it”
“John Marshall has made his decision; now let him enforce it”
75
New cards
What did Hamilton say about the three branches of gov.(who holds the sword, the purse, and has no influence over the sword or the purse)?
Executive: holds the sword of the community
Legislature: Commands the purse
Judiciary: no influence over either the sword or the purse & can take no active resolution whatever
Legislature: Commands the purse
Judiciary: no influence over either the sword or the purse & can take no active resolution whatever
76
New cards
During the Jim Crow regime, how did states resist change and/or get around the 14th & 15th amendment?
Did different ways of doing the same thing:
* instead of can’t vote b/c of skin color, you can’t vote if you’re illiterate or if you can’t sign your name.
\
Other were just blatant disregard for the law:
* Segregation in facilities
* Intimidation
* Disenfranchisement
* Physical violence: 4000 lynchings →Migrations of millions to the North
* instead of can’t vote b/c of skin color, you can’t vote if you’re illiterate or if you can’t sign your name.
\
Other were just blatant disregard for the law:
* Segregation in facilities
* Intimidation
* Disenfranchisement
* Physical violence: 4000 lynchings →Migrations of millions to the North
77
New cards
While many Blacks fled northward b/c of the Jim Crow regime, what struggles did they face there?
Segregation: the redlining, real estate rules
78
New cards
How did Collective Action for Social Change happen in this case of the Civil Right’s movement?
Considerations:
* War: black military officers
* Technology: televised media
* Political Entrepreneurs
* Change in the Supreme Court
* War: black military officers
* Technology: televised media
* Political Entrepreneurs
* Change in the Supreme Court
79
New cards
What was BROWN V. BOARD OF EDUCATION?
Can schools be segregated by race?
Thurgood Marshall-evidence shows facilities were inferior & social scientific evidence showed that separation was harmful
__**The LITTLE ROCK 9:**__ The Courage of Individuals!!
* 9black students enter the high school
* Arkanas govenor defies courts
* Eisenhower sends the 101st ariborne
Thurgood Marshall-evidence shows facilities were inferior & social scientific evidence showed that separation was harmful
__**The LITTLE ROCK 9:**__ The Courage of Individuals!!
* 9black students enter the high school
* Arkanas govenor defies courts
* Eisenhower sends the 101st ariborne
80
New cards
T or F: Martin Luther King Jr. encompassed John Brown’s ideals when facing the Civil Rights Movement?
FALSE; he took BOTH John Brown & Lincoln’s ways and combines them into a third way:
NONVIOLENT protest + Civil Disobedience aka break the law and accept the punishment to demonstrate the unfairness of the law
* Take immediate action BUT non-violent
* Takes his ideas from Gandhi+ New Testament: change w/ LOVE
\*Civil Rights movement provided a template & now we like to March for everything…
NONVIOLENT protest + Civil Disobedience aka break the law and accept the punishment to demonstrate the unfairness of the law
* Take immediate action BUT non-violent
* Takes his ideas from Gandhi+ New Testament: change w/ LOVE
\*Civil Rights movement provided a template & now we like to March for everything…
81
New cards
What are Just Laws vs. Unjust laws according to MLK jr.?
__Unjust__: Majority enacts them on the minority, but then doesn’t follow them themselves, degrades human personality
\-When a law is Unjust, we have the responsibility of CIVIL DISOBEDIENCE: disagree
__Just laws:__ Majority enforces & follows, God given, laws that uplift everyone
\-When a law is Unjust, we have the responsibility of CIVIL DISOBEDIENCE: disagree
__Just laws:__ Majority enforces & follows, God given, laws that uplift everyone
82
New cards
What Civil Right’s leader (Black) disagreed with Luther’s methods?
Abolitionist John Brown & Malcolm X: The Ballot or the Bullet
“Today it’s time to stop singing & start swinging”
“An old woman can sit. An old man can sit. A chump can sit. A coward can sit. Anything can sit. Well, you and I been sitting long enough, and it’s time today for us to start doing some standing, and some fighting to back that up.”
“Today it’s time to stop singing & start swinging”
“An old woman can sit. An old man can sit. A chump can sit. A coward can sit. Anything can sit. Well, you and I been sitting long enough, and it’s time today for us to start doing some standing, and some fighting to back that up.”
83
New cards
What other Institutional changes (ACTS) came after the Civil Rights Act of 1964?
• 1965 Voting Rights Act
• 1968 Fair Housing Act
• 1965 Elementary and Secondary Education Act – Title I (created funding for poor areas)
• 1968 Fair Housing Act
• 1965 Elementary and Secondary Education Act – Title I (created funding for poor areas)
84
New cards
Why does Judicial review matter, what institutions do we use to drive change?
* Congress: has to compromise & reflect consent of the governed
* Supreme Court: decides winners & are insulated from consent
\*Wouldn’t we all like to win rather than compromise?
BUT are we relying too much on the SC to force Social Change? Roe v. Wade?
* Supreme Court: decides winners & are insulated from consent
\*Wouldn’t we all like to win rather than compromise?
BUT are we relying too much on the SC to force Social Change? Roe v. Wade?
85
New cards
Economic Injustice occurs when the distribution of income is inconsistent w/ a commonly held sense of_____
Fairness
86
New cards
What’s the difference between __fairness__ as a procedure & fairness as an outcome (proportionality & equality)
Procedure: institutions that treat all people impartially
Outcome: (2)
* Proportionality: benefits of society should flow to those who have earned it through hard work/effort
* Equality: Economic outcomes are similar for groups & individuals.
\*most people believe in some combination of the two
Outcome: (2)
* Proportionality: benefits of society should flow to those who have earned it through hard work/effort
* Equality: Economic outcomes are similar for groups & individuals.
\*most people believe in some combination of the two
87
New cards
What are the two different viewpoints of poverty: Absolute phenomenon & relative phenomenon?
Absolute Phenomenon: lack of financial resources to get human needs (shelter/food/water)
Relative Phenomenon: unable to consume a meaningful fraction of the things those around you??? day 25 slide 7
Relative Phenomenon: unable to consume a meaningful fraction of the things those around you??? day 25 slide 7
88
New cards
How has income inequality changed over time? Why?
Was high, then fell sharply amidst the depression & the war, then in the mid to late 70’s it grew a lot!
Why?: The SCALE of success has changed
ex. a heart surgeon can only perform so many surgeries a year, but Taylor Swift can sell her songs to Billion of people each year. These people go into competitive areas & come out on top.
Why?: The SCALE of success has changed
ex. a heart surgeon can only perform so many surgeries a year, but Taylor Swift can sell her songs to Billion of people each year. These people go into competitive areas & come out on top.
89
New cards
What reasons have caused the top 10% to diverge so much from the bottom 25% (economic inequality)?
1. creative destruction-skill based technical change
2. Trade w/ 4 ex. China & that creates competition
3. Decline of Unions
*Manufacturing output hasn’t declined!! but employment has!!*\*\*\*\*\*
90
New cards
Many Americans believe that economic mobility is a key part of the American Dream. What is economic mobility & what are some characteristics?
MOBILITY: people able to increase their economic status-become greater than your parents-over time
* was high then it has declined\*\*
* Still high for children of immigrants though
* U.S. has much LESS economic mobility than other developed nations
* People tend to OVERESTIMATE their mobility
* was high then it has declined\*\*
* Still high for children of immigrants though
* U.S. has much LESS economic mobility than other developed nations
* People tend to OVERESTIMATE their mobility
91
New cards
T or F: Inequality in Consumption, lifespan, health, and leisure has risen over the years and stayed high.
FALSE; it has fallen and stayed lower.
92
New cards
What’s an example when it comes to Relative Rankings (wealth is subjective & depends on your circumstances) in economic inequality.
Ex. Richest person in the worlds in the 1800's couldn't treat blood poisoning and died, where as NOW the chances of survival is 95%, but back then he valued that treatment and would have payed ANYTHING to survive. Things are relative.
93
New cards
What are the two issues of fairness?
1\. Do we care more about absolutes (poverty) or relative measures?
2\. Do we care more about process or outcomes?
\*Answer depends on what sort of gov. you support.
ex. GI BILL\*: Gave WWII veterans college tuition subsidies & helped them to buy a house
* doubles the % of population w/ a college degree
* explosion in the middle class
2\. Do we care more about process or outcomes?
\*Answer depends on what sort of gov. you support.
ex. GI BILL\*: Gave WWII veterans college tuition subsidies & helped them to buy a house
* doubles the % of population w/ a college degree
* explosion in the middle class
94
New cards
What was Johnson’s *War on Poverty*? What are the downsides to these gov. programs?
Domestic expansion of government aid was programs to transfer money to single mothers, the disabled and other people with high poverty rates.
Downsides: translate into few meaningful future income gains for the recipients or their children.
WHY? If your mom stays married throughout your childhood, your chances of getting to Q5 is 20%!!!
Social Institutions such as the family MATTER! Economic mobility is tied to your mother’s marital status!!!
Downsides: translate into few meaningful future income gains for the recipients or their children.
WHY? If your mom stays married throughout your childhood, your chances of getting to Q5 is 20%!!!
Social Institutions such as the family MATTER! Economic mobility is tied to your mother’s marital status!!!
95
New cards
What did the Coleman Report say about what economic bracket you’d end up and your parents? 1966
* Most gov. policies considered at the time don’t improve economic opportunity by more than a little
* The most important thing YOU could do to have more economic opportunity is to have had better parents!
…this news isn’t very helpful
* The most important thing YOU could do to have more economic opportunity is to have had better parents!
…this news isn’t very helpful
96
New cards
What is one way, involving money, that the gov. can promote equality of result?
TAXES: tax and then redistribute either income or services
97
New cards
What are the differences between these three types of taxes? Which one best describes our federal income tax? Which best describes our overall tax system?
a. Progressive Tax
b. Regressive Tax
c. Proportional Tax
a. Progressive Tax
b. Regressive Tax
c. Proportional Tax
a. Progressive tax – Taxes increase as a percentage of income= the more $, the more you’re taxed
* Federal Income tax is very progressive
b. Regressive tax – Taxes decrease as a percentage of income= the less $, the more you’re taxed
c. Proportional tax – taxes are roughly proportional to income = FLAT RATE, taxed the same no matter how much you make ex. Tithing
\
Depends on what state you live in. Mostly slightly progressive, but close to proportional.
* Federal Income tax is very progressive
b. Regressive tax – Taxes decrease as a percentage of income= the less $, the more you’re taxed
c. Proportional tax – taxes are roughly proportional to income = FLAT RATE, taxed the same no matter how much you make ex. Tithing
\
Depends on what state you live in. Mostly slightly progressive, but close to proportional.
98
New cards
What are some examples of policies that redistribute Income & services?
Income: SS, Unemployment
Services: Food Stamps, Medicaid
Services: Food Stamps, Medicaid
99
New cards
What’s the metaphor of the Leaky Bucket?
We’re always going to lose some water “$” in the process of redistribution because;
IF YOU TAX SOMETHING, YOU GET LESS OF IT! \*key
…you also have to pay to implement the program!
IF YOU TAX SOMETHING, YOU GET LESS OF IT! \*key
…you also have to pay to implement the program!
100
New cards
T or F: Americans work more hours, have higher incomes, and lower tax rates than other countries.
TRUE