Chapter 9 - Savings, Interest Rates and the Market for Loanable Funds
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
loanable funds market
The market where savers supply funds for loans to borrowers, including institutions like stock exchanges, investment banks, mutual funds, and commercial banks.
role of loanable funds market
A bridge between savers and borrowers that helps firms invest in resources and enables economic growth by efficiently channeling funds.
interest rate
The price of loanable funds, expressed as a percentage of the original loan amount.
Interest rate as a reward for saving
higher interest rates incentivize saving by increasing the return on funds supplied
interest rate as a cost of borrowing
firms borrow only if the expected return on investment exceeds the interest rate on the loan
supply of loanable funds
Comes from households, foreign entities, and institutions that save money, which banks then lend out.
Demand for Loanable Funds
Comes from borrowers, primarily firms looking to invest in capital to produce future output.
real interest rate
The interest rate corrected for inflation, representing the actual change in purchasing power.
nominal interest rate
The stated interest rate before adjusting for inflation.
fisher equation
Real Interest Rate=Nominal Interest Rate−Inflation Rate
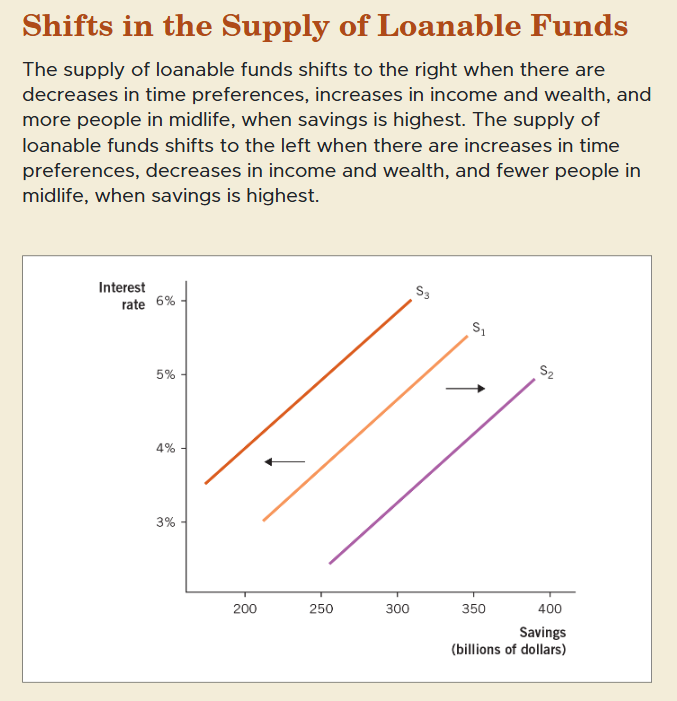
Factors Shifting Supply of Loanable Funds
Income and Wealth – Higher income and wealth lead to more savings, increasing supply.
Time Preferences – People who prefer future consumption save more, increasing supply.
Consumption Smoothing – Individuals save during working years and dissave during retirement, affecting supply.
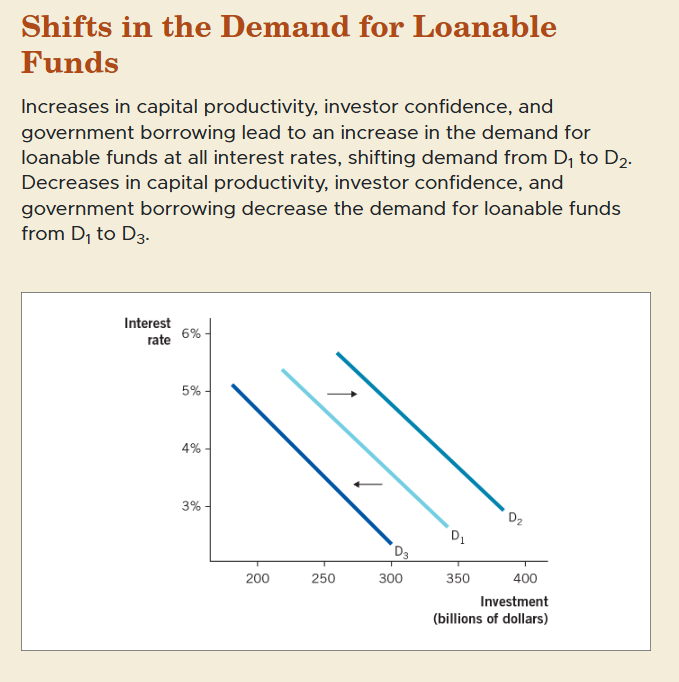
factors shifting demand for loanable funds
Productivity of Capital – More productive capital increases demand for loans.
Investor Confidence – Higher confidence leads to greater borrowing for investment.
Government Borrowing – Higher government borrowing increases demand for loanable funds.
consumption smoothing
The tendency of individuals to maintain stable consumption over time by saving during high-income years and dissaving during low-income years.
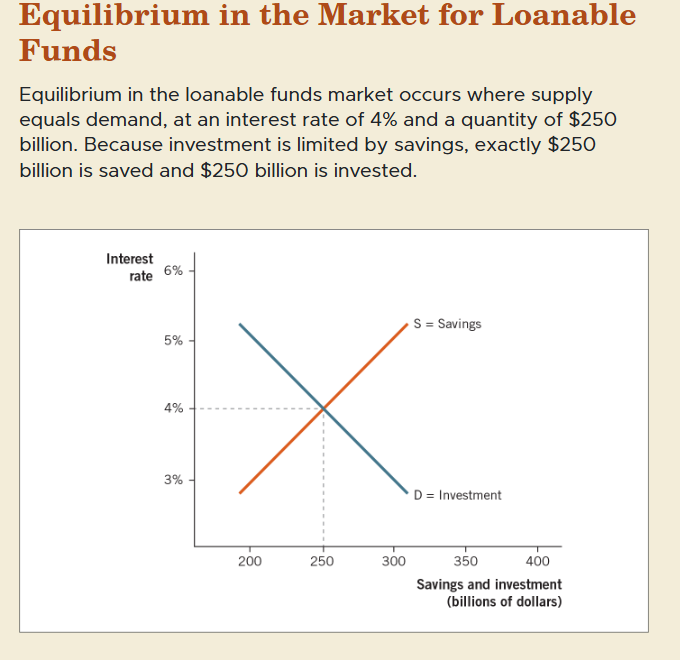
equilibrium in loanable funds market
Occurs when the quantity of savings supplied equals the quantity of funds demanded for investment.
Effect of Economic Downturn on Loanable Funds Market
Firms reduce investment due to lower expected sales, decreasing the demand for loanable funds.
shift in the supply of loanable funds
shifts in the demand for loanable funds
equilibrium in the market for loanable funds