ap psych unit 1
1/65
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
three roadblocks to critical thinking
hindsight bias, overconfidence, perceiving patterns in random events
hindsight bias
believing you could have predicted an outcome after learning it
overconfidence
the tendency to think we know more than we do
three elements of the scientific attitude
curiosity, skepticism, humility
curiosity
a desire to explore and understand, need evidence based on real observations
skepticism
doubting + questioning w/o judgement
humility
admitting that your wrong if evidence doesn’t match your own ideas
critical thinking
does not accept arguments + conclusions blindly, asks questions
scientific method
theory —> hypothesis —> research + observations
theory
a statement of fact
hypothesis
an ‘if. . . then . . .’ statement
operational definition
statement of exact procedure used in a research study
replication
repeating a study
three scientific methods
descriptive, correlational, experimental
three descriptive methods
case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys/interviews
case study
a person or small group studied in depth to reveal underlying behavioral principles
clinical study
a kind of case study; therapists investigate problem associated w/ client
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior w/o controlling situation
survey
technique for obtaining self-reported attitudes, opinions, behaviors, done by questioning random people
cannot determine cause and effect
wording effect
wording of a question can change the results of a survey
false consensus effect
a tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors
cohort effect
group w/ shared experience = similar interpretations
response bias
people give answers they believe the researchers want to hear
non-response bias
people don’t respond at all
population
all individuals in a group being studied
sample
subset of the population being studied
random sample
represents a population w/o bias, each member has an equal chance of inclusion
sampling bias
sampling so results will go in one direction or the other
representative sample
same distribution of demographic qualities as the population
variable
any attribute of a person or animal being studied
quantitative variable
a numerical value; counts or measurements
qualitative variable
a categorical variable that divides the individuals into distinct groups; can be numerical
correlational method
looks at relationship btwn two things — cause & effect
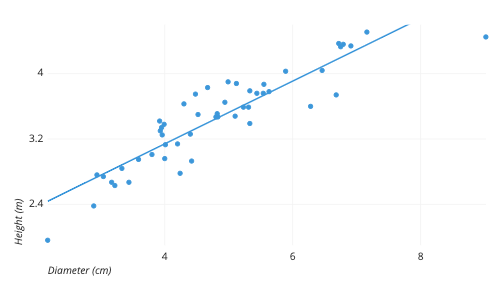
scatterplot
a graph composed of points generated by 2 quantitative variables
correlation coefficient
a statistical measure of the relationship btwn 2 variables
closer to 0 = weaker
can be positive or negative
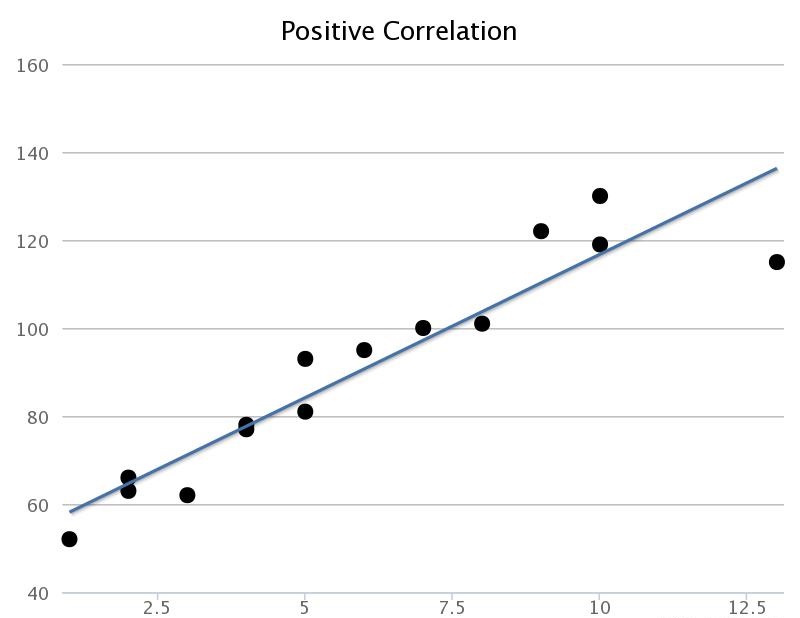
positive correlation
variables increase or decrease together
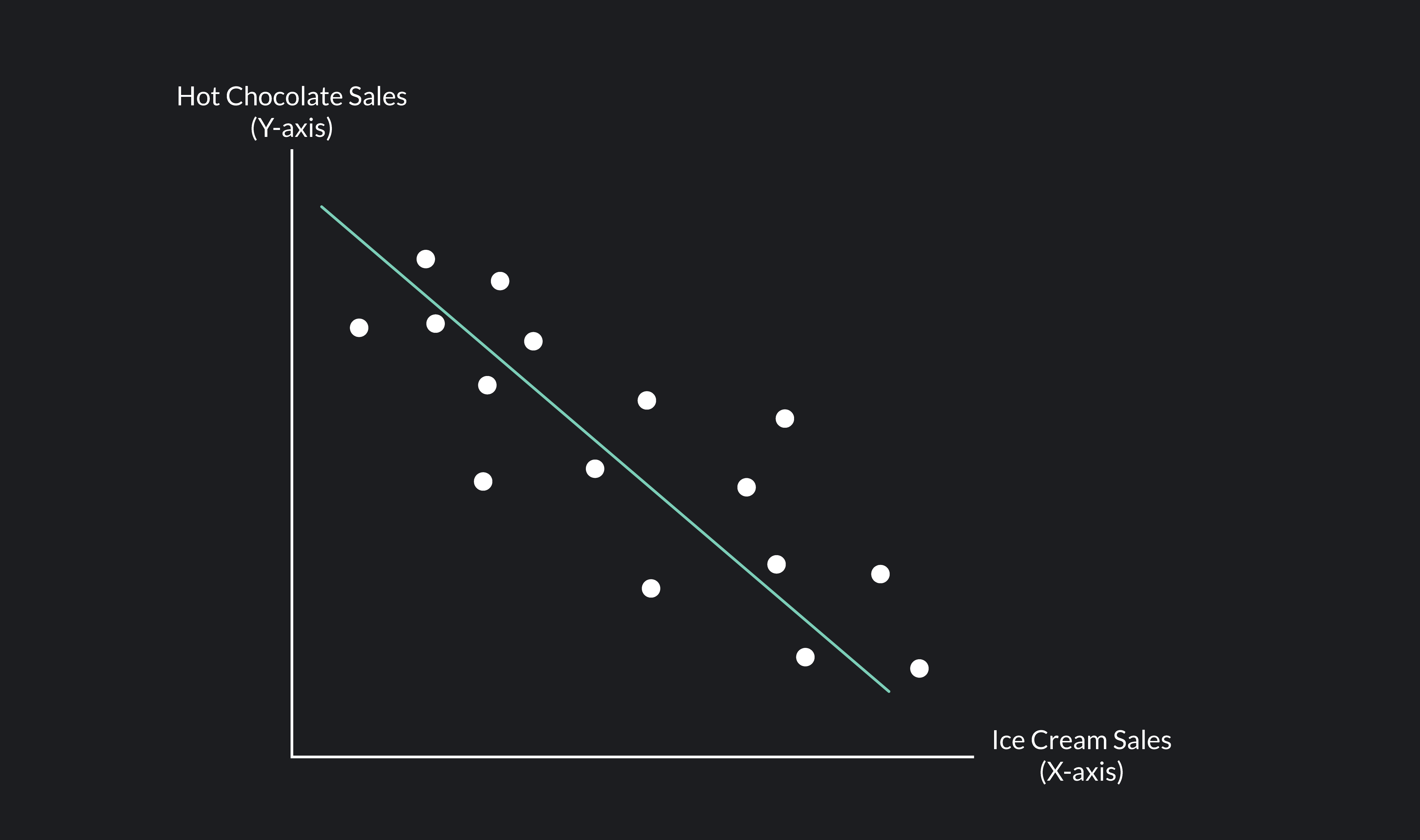
negative correlation
as one variable decreases, the other increases
no correlation
as one variable increases or decreases, the other increases or decreases randomly
correlation and causation
correlation does not imply causation
third variable problem
a type of confounding variable where a factor leads to a mistaken causal relationship btwn 2 variables in a study
illusory correlation
perception of a relationship where none exists / a stronger-than-actual relationship
regression to the mean
extreme scores / events fall back toward the average
experiments
backbone of psychology research
isolate causes and their effects
manipulate / control factors
treatment
a specific condition applied to the individuals in the experiment
experimental group
subjects receive the treatment
control group
subjects do not receive the treatment or receive a dummy treatment
random assignment
each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group
independent variable
factor manipulated by experimenter
dependent variable
the outcome that will be measured
confounding variables
extraneous factors that might influence the study’s results
present in 1 group, not the other
experimenter bias
a researcher’s expectations/preferences about the outcome of the study influence the result
placebo effect
a response to treatment based off expectations of the procedure/treatment
single blind procedure
participants are uninformed about the treatment (if any) that they are receiving
double blind procedure
participants and researcher are uniformed about which group receives the treatment and which does not
controls for experimenter bias and placebo
differences between samples are least likely to be statistically significant if
he samples are large and the standard deviations of the samples are small
Random samples provide __________ estimates of population averages if the samples have small __________.
good, standard deviations
In an experimental study of the extent to which mental alertness is inhibited by sleep deprivation, alertness would be the:
dependent variable
A correlation of +0.70 between children's physical height and their popularity among their peers indicates that:
higher levels of popularity are associated w/ greater physical height in children
Every twenty-fifth person who ordered a subscription to a weekly news magazine was contacted by market researchers to complete a survey of opinions regarding the magazine's contents. The researchers were most clearly employing a technique known as:
systematic sampling
What statistical technique would be appropriate for a researcher to use in trying to determine how consistent intelligence scores are over time?
standard deviation (1)
In an experimental study of the effects of dieting on weight loss, dieting would be the:
independent variable
A tendency to notice and remember instances in which our premonitions of disaster are subsequently followed by harmful events is most likely to contribute to:
illusory correlations
Stacey suggests that because children are more impulsive than adults, they will have more difficulty controlling their anger. Stacey's prediction regarding anger management exemplifies:
a hypothesis
In order to test the potential effect of hunger on taste sensitivity, groups of research participants are deprived of food for differing lengths of time before they engage in a taste-sensitivity test. This research is an example of:
correlational research
Which research technique is most directly useful for avoiding the thinking error known as the false consensus effect?
random sampling (1)
the __ is a measure of _
standard deviation, variation