Atoms, Molecules, Ions
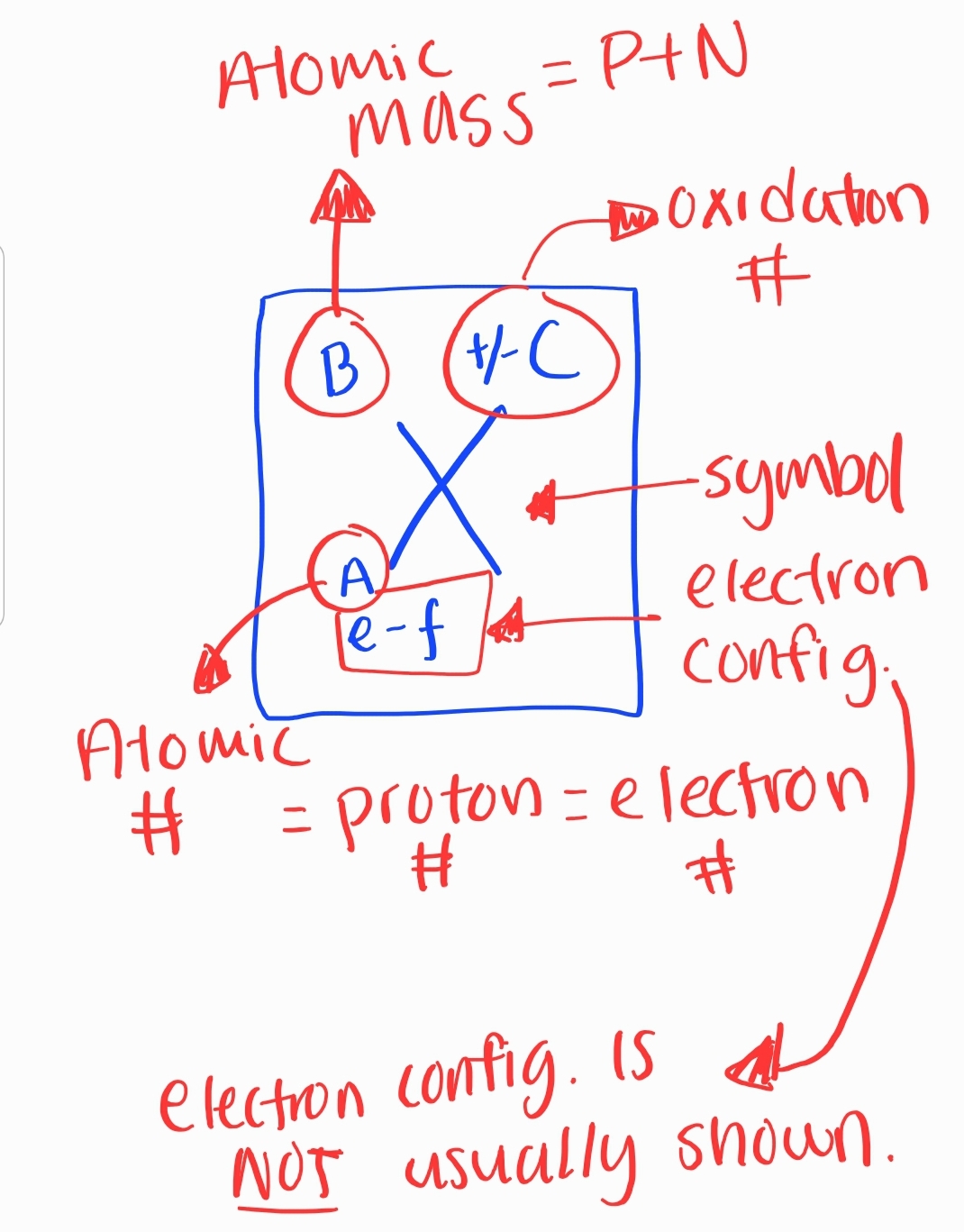
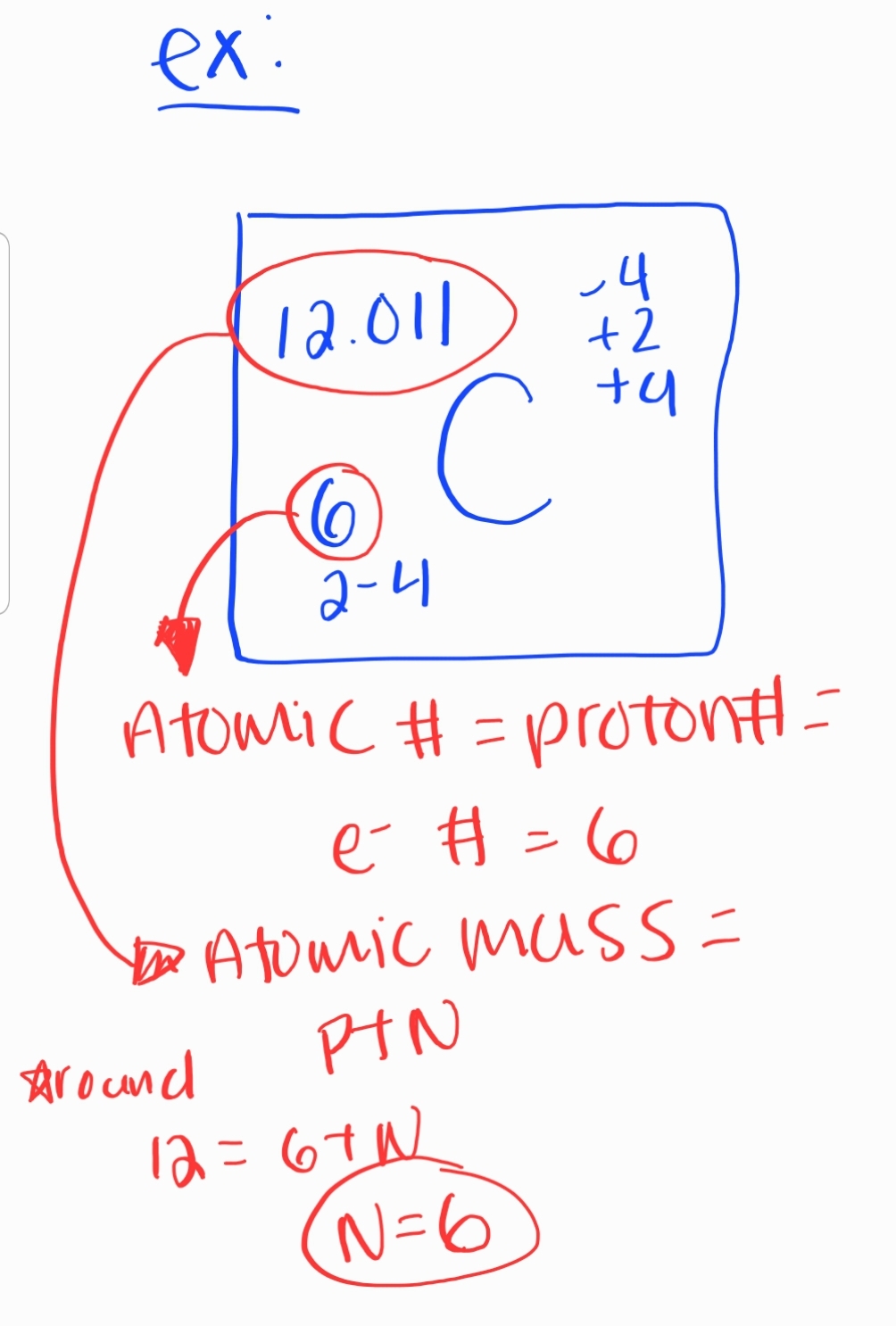
All atoms of an element must have the same ATOMIC #
Mind Map: Atoms, Molecules, Ions
Central Idea: Atoms
- Definition: Basic building blocks of matter
- Composed of: Protons, neutrons, and electrons
Main Branches
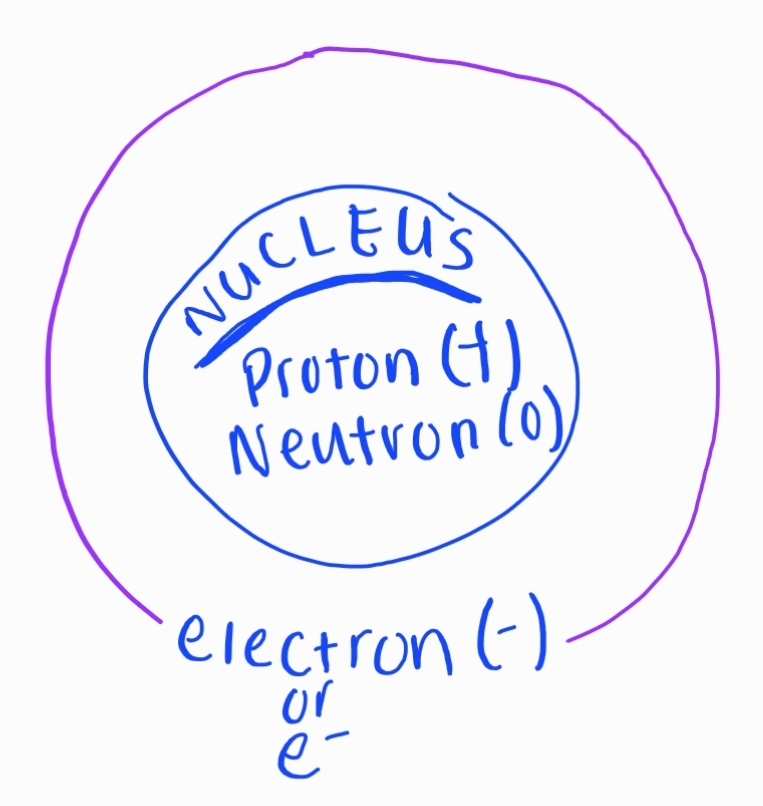
1. Atomic Structure
- Protons
- Positive charge
- Located in the nucleus
- Neutrons
- No charge
- Located in the nucleus
- Electrons
- Negative charge
- Orbit around the nucleus
2. Elements
- Definition: Pure substances made up of only one type of atom
- Examples: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon
3. Atomic Number and Mass
- Atomic Number
- Number of protons in an atom
- Determines the element
- Atomic Mass
- Sum of protons and neutrons in an atom
- Measured in atomic mass units (amu)
Sub-Branches
1. Molecules
- Definition: Two or more atoms chemically bonded together
- Types of Bonds
- Covalent Bonds
- Sharing of electrons between atoms
- Examples: H2, O2, CO2
- Ionic Bonds
- Transfer of electrons between atoms
- Examples: NaCl, MgO
2. Ions
- Definition: Charged particles formed by gaining or losing electrons
- Cations
- Positively charged ions (more protons than electrons)
- Formed by losing electrons
- Anions
- Negatively charged ions (more protons than electrons)
- Formed by gaining electrons
- Polyatomic Ion: electrically charged particle w 2+ atoms linked together so it behaves as a unit instead of separate atoms
- charge belongs to the ion as a WHOLE
3. Compound
- Definition: 2+ diff elements chemically bonded together
- Examples: Water (H2O), Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
4. Chemical Reactions
- Definition: Process where atoms are rearranged to form new substances
- Reactants
- Substances present before the reaction
- Products
- Substances formed after the reaction
5. Isotopes
- Definition: Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
- Ex: Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14
6. Atomic Models
- Dalton's Model
- Thomson's Model
- Rutherford's Model
- Bohr's Model
- Quantum Mechanical Model
7. Periodic Table
- Organizes elements in an increasing atomic #