APES - Soil Conservation and Cycles
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What are the major causes of soil degredation?
Erosion
Compaction
Nutrient Imbalance
Pollution
Acidification
Water Logging
Loss of Soil Biodiversity
Increased Salinity
Deforestation
Tilling
Mnemonic:
Everyday Carla Needs Pickles And Water Literally In Demand Today
Why is soil important?
store water
recycle nutrients
storing carbon
What does grasses and perennial crops do to help restore topsoil?
longer, thicker roots hold soil and water in place
they don’t die each year
they don’t need to be replanted
reduces the need for tilling, less weeds grow, and there is less erosion
What are Prarie Strips?
small parts of fields planted with native perennial grass and plants that help conserve soil
they reduce sediment loss from runoff, retain more nitrogen, and provide habitat for pollinators
What is CROP ROTATION?
crops are altered in a field each season
What is an advantage(s) for crop rotation?
reduces the amount of fertilizer needed
What is a disadvantage(s) for crop rotation?
requires knowledge in plant interactions
can be expensive
What is TERRACING
converting steep sloped land into broad level steps
What is an advantage(s) for terracing?
retains water
reduces topsoil erosion by controlling runoff
What is a disadvantage(s) of terracing?
costly
labor intensive
What are SHELTER BELTS/WIND BREAKS?
planting trees around the fields to stop wind erosion
What is an advantage(s) of shelter belts/wind breaks?
reduces wind erosion
provides habitats for birds and insects
What is a disadvantage(s) of shelter belts/wind breaks?
initial cost of planting trees is expensive
What is CONTOUR PLOWING?
plowing and harvesting is done parallel to the countours of the land
What is an advantage(s) of countour plowing?
conserves soil
prevents erosion by water
What is a disadvantage of contour plowing?
labor intensive
costly
What is INTERCROPPING?
2 or more crop species are planted in the same field to promote a positive interaction between them
What are advantage(s) of intercropping?
reduces the amount of fertilizer required
What is a disadvantage(s) of intercropping?
requires knowledge of plant interactions
can be labor intensive
What is NO TILL FARMING?
soil is not turned over/plowed between season to reduce topsoil erosion
What is an advantage(s) of no till farming?
reduces topsoil erosion
reduces CO2 emissions
What is an disadvantage(s) of no till farming?
farmers may need to use herbicides (chemical that kill weeds/ plants) before and after planting crops
Where is Nitrogen gas stored?
in the atmosphere (78%)
What can nitrogen NOT be used for?
cannot be used as a GAS by PLANTS and ANIMALS
limiting factor for plant growth
What is Nitrogen essential for?
proteins
DNA
RNA
What is FNAAD?
Fixation
Nitrification
Assimilation
Ammonification
Denitrification
What is ANPAN?
Ammonia
Nitrates, Nitrites
Proteins
Ammonia
Nitrogen Gas
Which is the process and which is the products?
FNAAD = processes
ANPAN = products
Human Impacts of the Nitrogen Cycle
burning fossil fuels gives off NOx - can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone
burning fossil fuels releases NO - contributes to the formation of acid rain
agriculture use of fertilizer/manure and sewage (and waste water from treatment plants) can add excess nitrogen to water causing eutrophication
clear cutting, harvesting crops, and irrigation can remove/wash away nitrogen from topsoil
breakdown of fertilizers can release nitrogen oxide (N2O), a GHG, into the atmosphere
What is ammonification? (NC)
bacteria converts detrius material into ammonia
What is assimilation? (NC)
plants abosorb nitrogen from soil, animals get it by eating plants
it is used to make protein
What is Nitrogen Fixation>
makes N2 gas usable, done by bacteria in soil or lightning strike, forms ammonia (NH4)
What is Nitrification>
bacteria in soil converts ammonia (NH4) into nitrates NO2 then into nitrites NO3Wha
What is Denitrification?
bacteria converts ammonia/nitrates back into N2 gas and it is released into the atmosphere
What is Ingestion? (NC)
animals consumer plants/animals to absorb nitrogen into their bodies
What is Excretion? (NC)
animals get rid of waste containing nitrogen in the form of ammonia
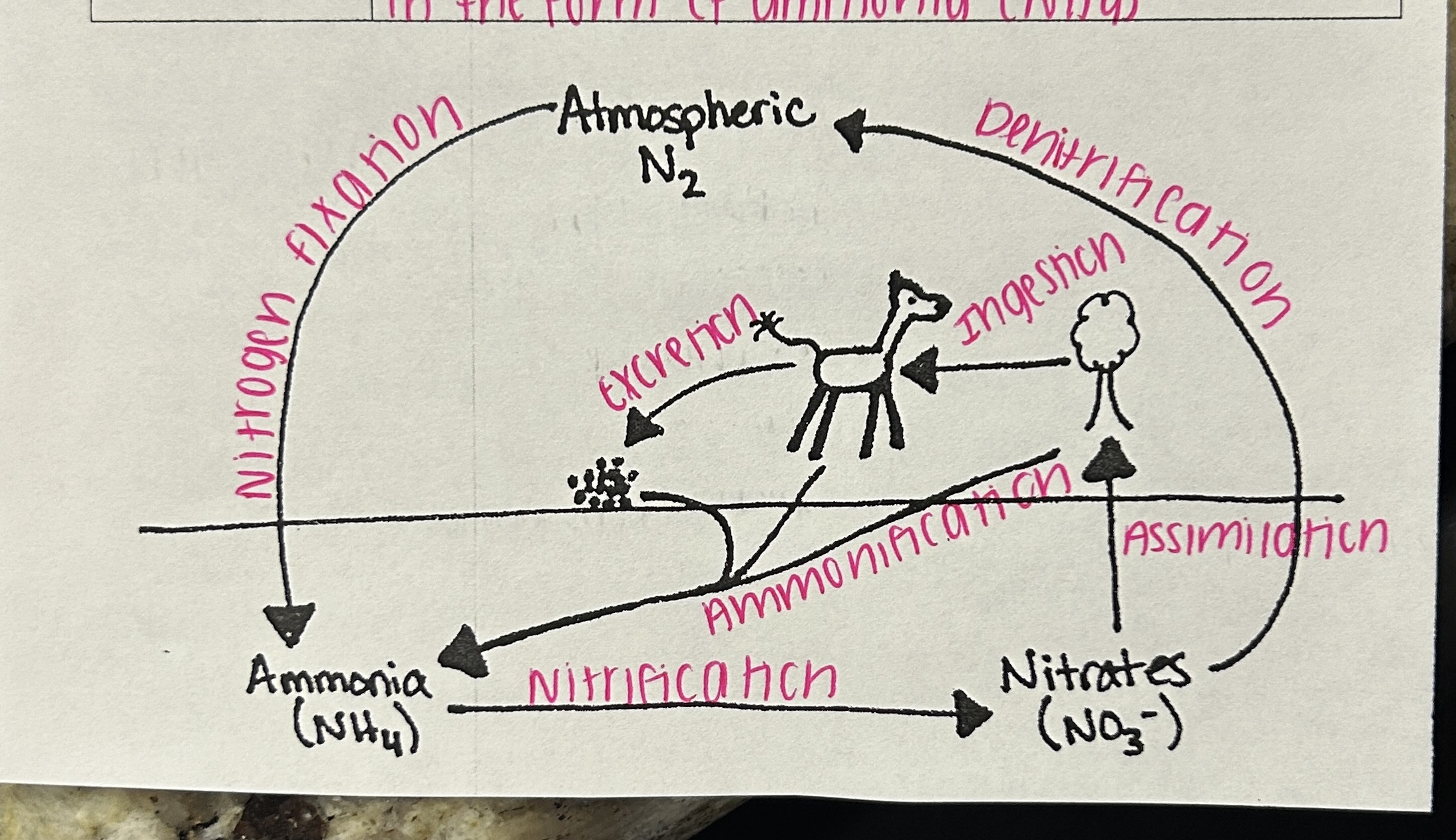
Which cycle is this?
Nitrogen Cycle
Which cycle is the slowest?
Phophorus
What is NOT a reservoir for the Phophorus cycle?
the atmosphere
What is the Phophorus Cycle’s largest reservoir?
sedimentary rock
What is Phosphorus?
a limiting nutrient for terrestrial and aquatic plants
Where is phosphorus located?
nucleic acids
ADP
ATP
bones
teeth
Human Impacts (PC)
mined to ADD to artificial fertilizer
excess fertilizer runoff causes eutrophication
clear cutting forests causes phosphates to wash away with soil erosion
What is Phosphate Mining?
phosphates are mined for fertilizer and other products, some phosphate enters runoff
What is Decomposition? (PS)
dead plants and animals are broken down, releasing phosphorus into the soil
What is Excretion? (PC)
animals get rid of waste that can contain phosphorus
What is Geological Uplift? (PC)
phosphorus in sedimentary rock is pushed to the surface
What is Burial and Compaction? (PC)
phosphorus is trapped in sediment layers and compacted into sedimentary rock
What is Erosion? (PC)
weathering releases phosphorus and it is moved by wind and water
What is Ingestion? (PC)
animals consume plants/animals and abosorb phosphorus in their body
What is Absorption? (PC)
phosphorus is abosorbed into plants by their roots
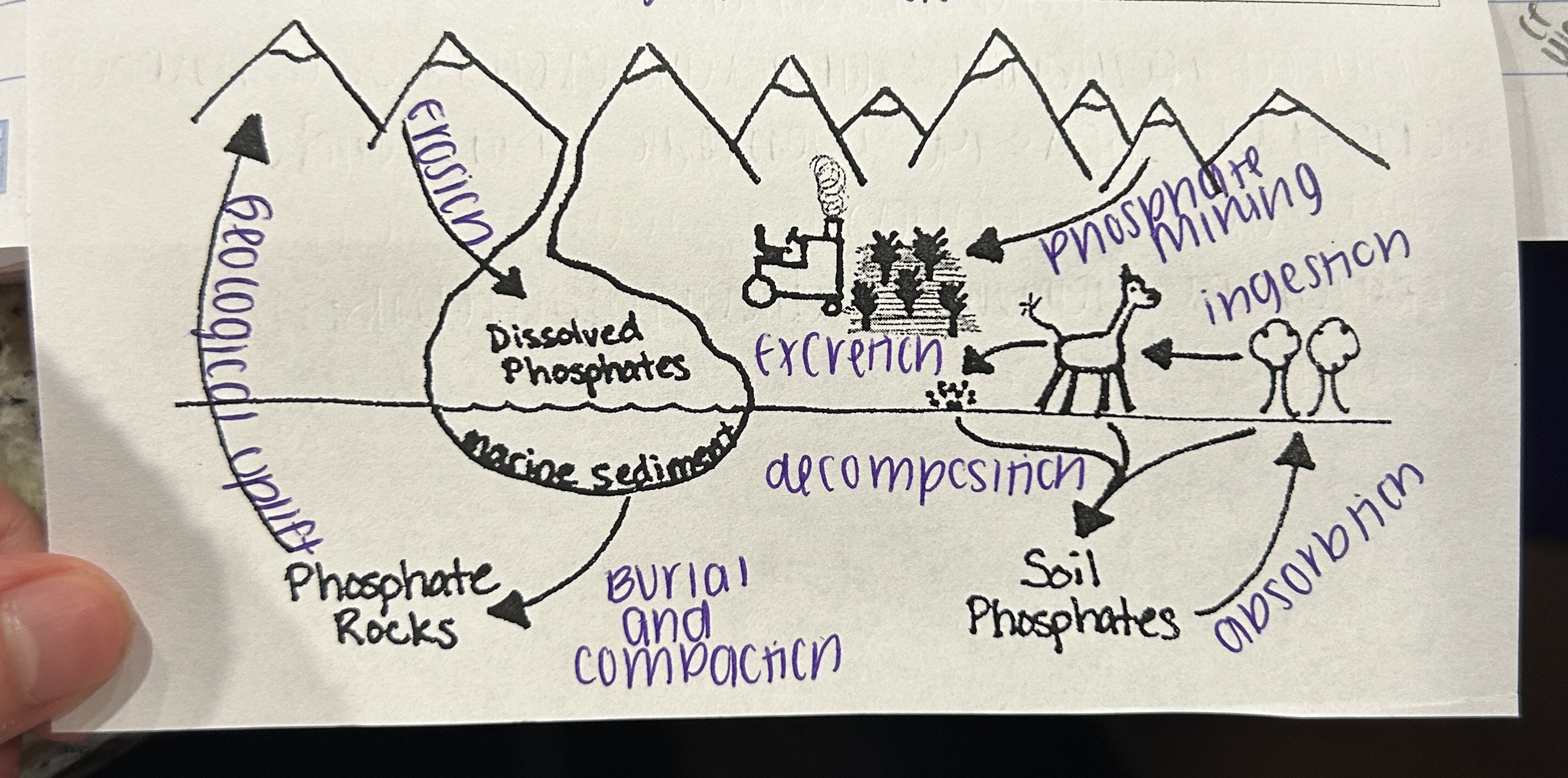
Which cycle is this?
Phosphorus Cycle
What is the water cycle powered by?
the sun
What is the water cycles essential for?
maintaining the Earth’s temperature
T/F: Water vapor is a GHG?
True
What happens during transpiration?
more than 75% of moisture in thickly vegetated ecosystems (like the rainforest) passes through plants during transpiration
Human Impacts (WC)
overuse (use faster than can be replenished)
increase of pollutants in runoff
reduced inflitration - hard paved surfaces prevent recharging of groundwater
accelerates top soil erosion
increase risk of flooding - by draining/filling wetlands for farming or urban development
alters weather - deforestation reduces transpiration which is the primary source of rainfall in a rainforest
reduced shade evaporates water before it can permeate the soil
What is Infiltration? (WC)
water soaks into the ground to become groundwater
What is Runoff? (WC)
precipitation that flows over land and goes into streams, rivers, lakes, ocean
What is Transpiration? (WC)
water vapor released from plant leaves into the atmosphere
What is Evaporation? (WC)
sun’s heat turns water into water vapor
What is Precipitation? (WC)
rain, snow, sleet, or hail
What is Condensation? (WC)
water vapor cools and condenses into clounds
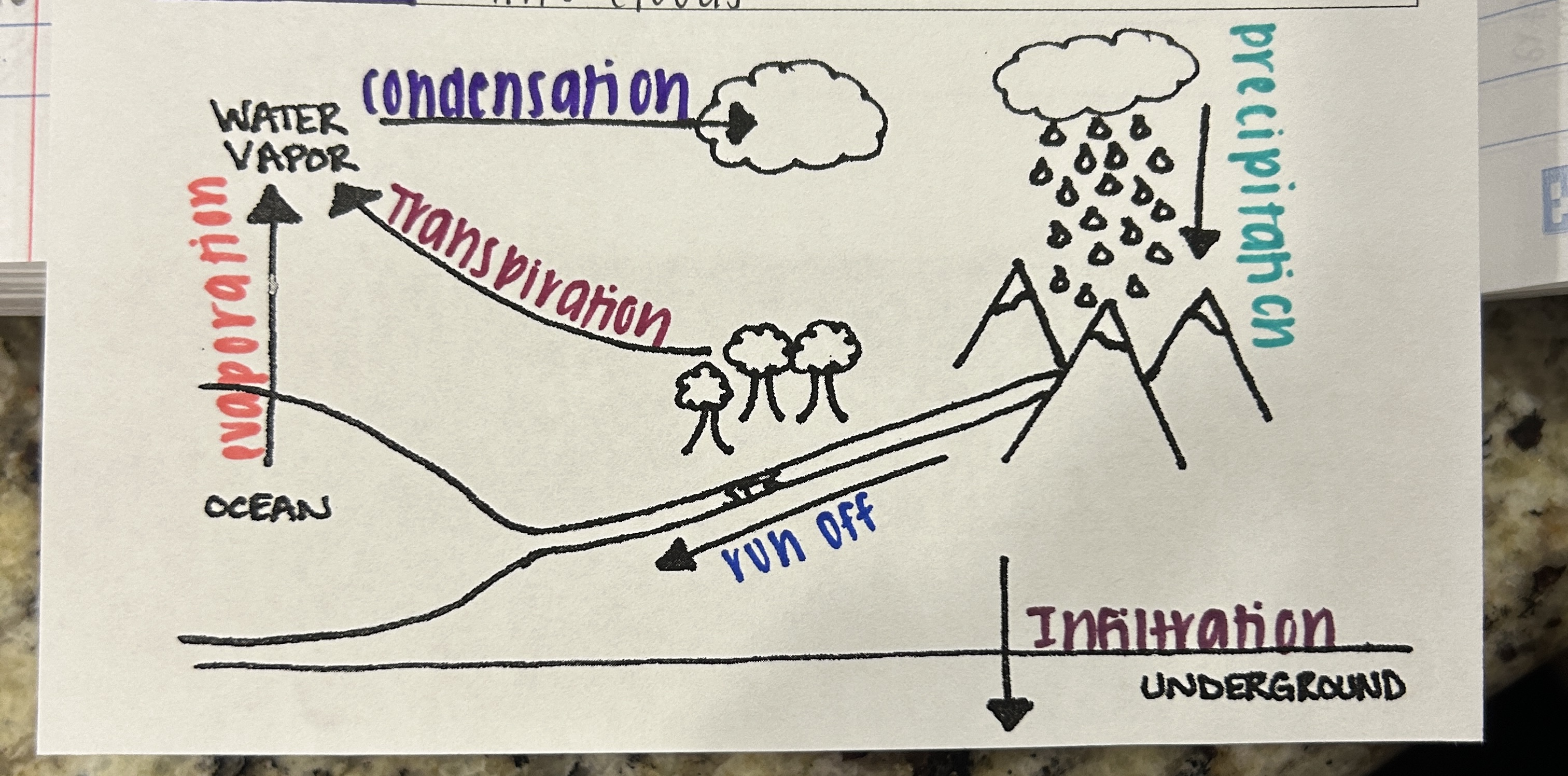
Which cycle is this?
Water Cycle
What is sulfur essential for?
an essential nutrient for:
amino acids
proteins
Where is sulfur found?
the Earth’s crust
How does sulfur enter the atmosphere?
volcanic eruptions
combustion of fossil fuels
sea spray (dimethyl sulfide - DMS) in the ocean
Human Impacts (SC)
DMS emissions from paper manufacturings can effect cloud cover and climate
DMS and fossil fuel emissions can contribute to formation of acid rain
Metals like copper, lead, and zinc are extracted from sulfur containing compounds in rocks
What is erosion? (SC)
sulfur stored in sediments is weathered and released/transported
What is Decomposition? (SC)
decomposers break down dead organisms and release sulfur into soil
What is Hydrogen sulfide? (SC)
(H2S) released from burning fossil fuels like coal and oil
What is Deposition? (SC)
sulfur is depositied into the Earth’s surface by precipitation
What is Sulfur dioxide? (SC)
(SO2) released from burning fossil fuels like coal
What is Dimethyl sulfide? (SC)
(DMS) produced by marine phytoplankton and transferred into the atmosphere
What is Sulfuric acid? (SC)
(H2SO4) secondary pollutants forms in atmosphere and causes acid rain
What is Combustion? (SC)
burning fossil fuels like coal releases sulfurA
What is Absorption? (SC)
Plants/microorganisms take up sulfur from soil
What is Infiltration? (SC)
water soaks into ground taking sulfur with it
What is Bacterial Decay? (SC)
decomposers release sulfur into the atmosphere during process of decomposition
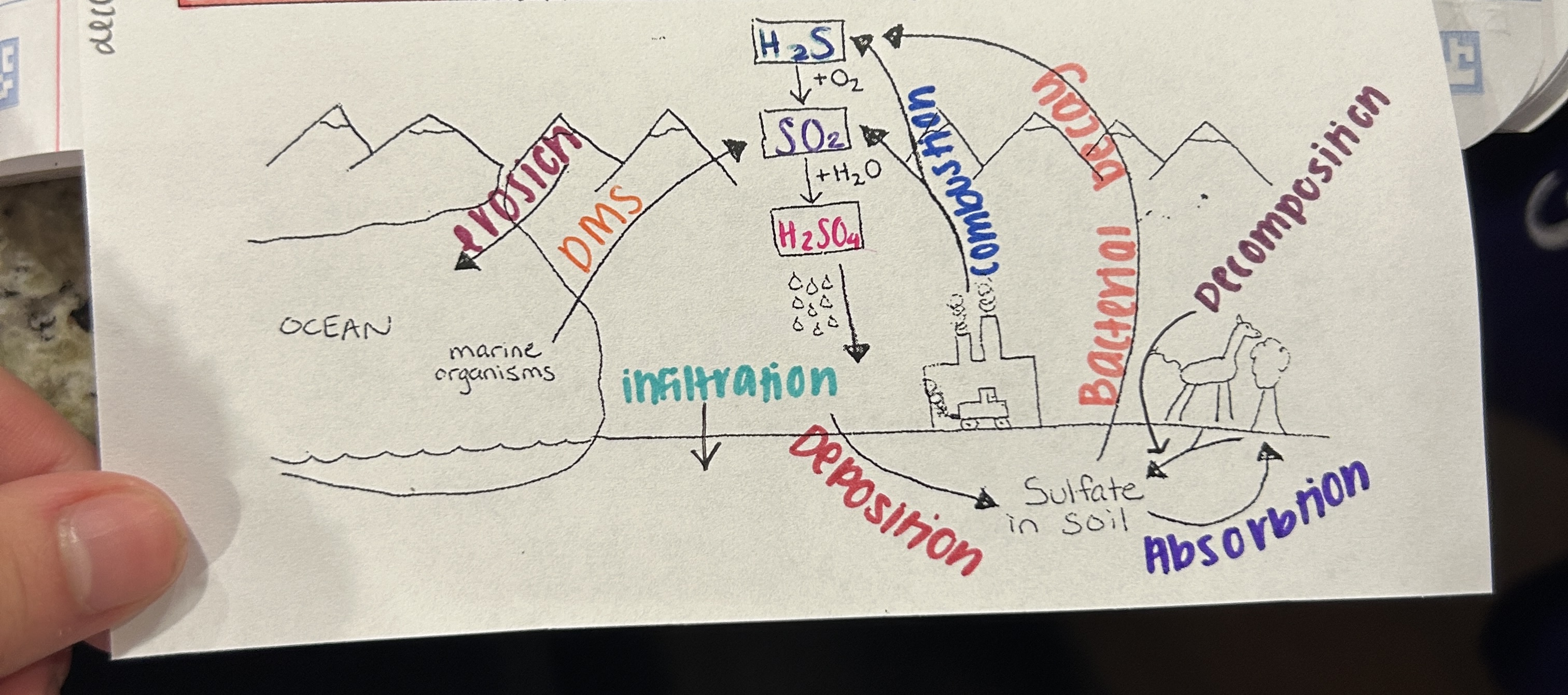
Which cycle is this?
Sulfur Cycle
What is carbon essential for?
carbs
lipids
proteins
DNA
other important organic molecules
What is Carbon Dioxide (CO2) essential for?
GHG
essential for maintaining Earth’s temperature
BUT too much can be bad
Where is carbon stored?
ocean
shells
marine sedimanet
limestone rock
fossil fuels
forest
plants
atmosphere
living organizms
What is one place carbon is stored?
calcium carbonate
makes up shells
in limestone
Human Impacts (CS)
burning fossil fuels - releases CO2
Clearcutting forests and releasing carbon
releasing GHG’s like CO2 and CH4 (methane) contributes to global warming
What is Decomposition? (CS)
decomposers (like bacteria) break down dead organisms and release CO2
What is combustion (natural and human) (CS)
burning wood or fossil fuels, releasing CO2
What is Cellular Respiration? (CS)
using glucose as fuel for cells and tissues, releasing CO2 and H2O
What is Photosynthesis? (CS)
uses the sun’s energy, CO2, and water to produce glucose and release O2
What is Erosion? (CS)
carbon stored in sediments is weathered and released/transported
What is Burial and Compaction? (CS)
carbon is stored in Earth’s crust and buried over time in rocks/sediments
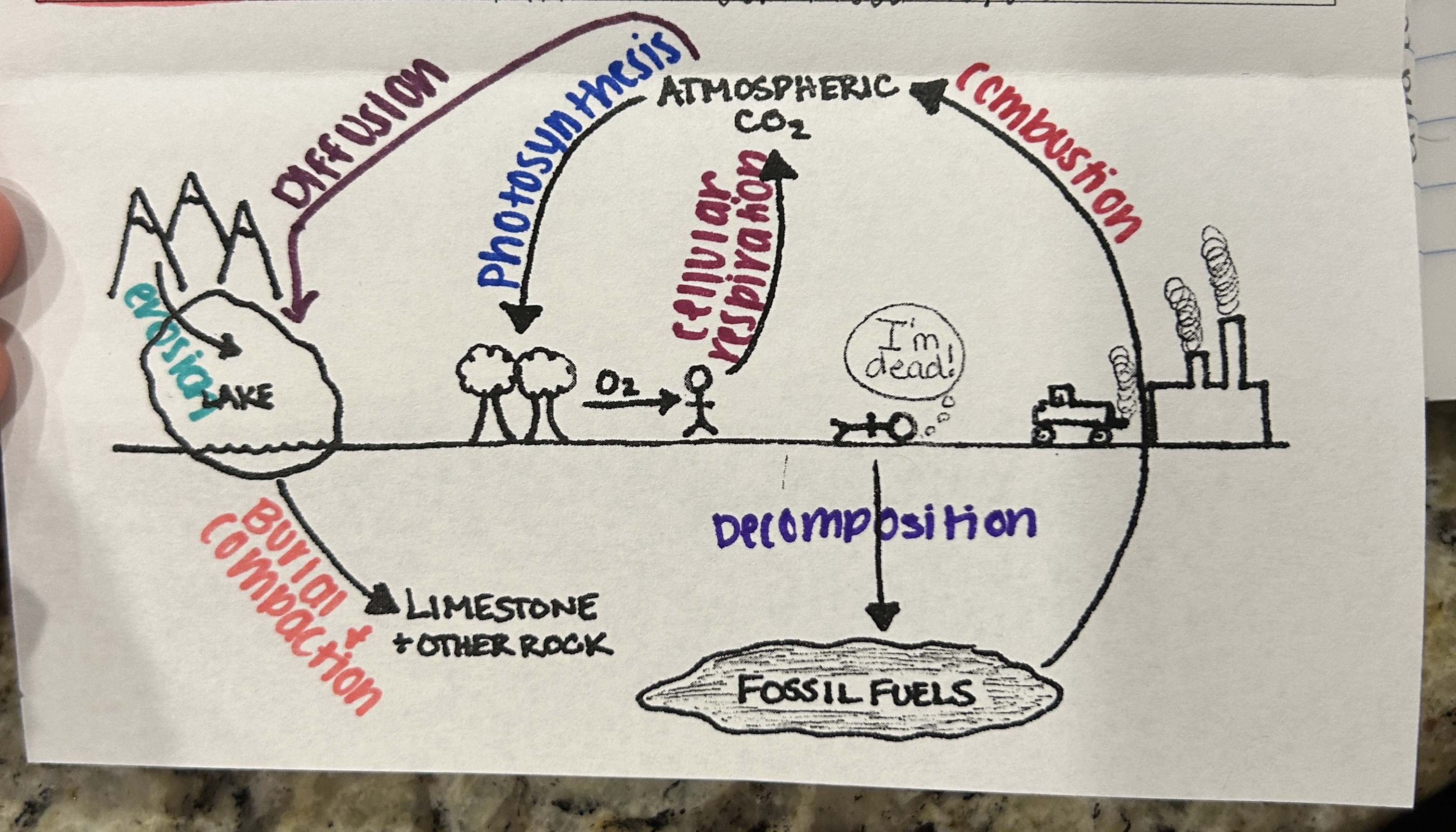
Which cycle is this?
Carbon Cycle