Biology - Structures and Functions of Cells
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
Cell
- the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of known organisms
-the smallest unit of life or the "building blocks of life"
-the smallest unit of life or the "building blocks of life"
2
New cards
Cytology
- study of cells
3
New cards
surface area to volume ratio
- as a cell's size increases, its volume increases much more rapidly than its surface area
- when this happens, the cell must divide into smaller cells with favorable ratios
- the reason why cells are small
- when this happens, the cell must divide into smaller cells with favorable ratios
- the reason why cells are small
4
New cards
Robert Hooke(1665)
- named the basic structure of all living things as a cell and observed cork cells & cells walls under a microscope
- he named them "cells" as they reminded him of the cells or rooms in monasteries
- he named them "cells" as they reminded him of the cells or rooms in monasteries
5
New cards
Anton van Leeuwenheok
- discovered "bacteria" from looking at dental scrapings on his teeth using hi own microscope
- named bacteria "Animalcules" because they looked like little animals
- named bacteria "Animalcules" because they looked like little animals
6
New cards
light micoscope (LM)
- visible light is passed through the specimen, through glass lenses, and is bent through the lens allowing you to see a magnified image of a specimen
7
New cards
Bright-field microscope
- illumination light is transmitted through the sample and the contrast is generated by the absorption of light in dense areas of the specimen.
- light then gets transmitted through the specimen and appears against an illuminated background.
- best used by fixed stained specimens to improve contrast
- light then gets transmitted through the specimen and appears against an illuminated background.
- best used by fixed stained specimens to improve contrast
8
New cards
dark-field microscope
- Light is directed at an angle toward the specimen
-A microscope that only shows light that was reflected off the sample due to a condenser lens.
- ideally used to illuminate unstained samples causing them to appear brightly lit against a dark background
-A microscope that only shows light that was reflected off the sample due to a condenser lens.
- ideally used to illuminate unstained samples causing them to appear brightly lit against a dark background
9
New cards
phase-contrast microscope
- its components bring light waves out of phases and produces differences in image contrast and brightness when the light waves recombine.
- internal details and organelles of live, unstained organisms can be seen and called phase objects
- internal details and organelles of live, unstained organisms can be seen and called phase objects
10
New cards
differential-interference-contrast microscope
- splits polarized light into to beams that have slightly different paths through the sample.
- combining these two beams produces greater contrast, producing a pseudo 3D-effect
- combining these two beams produces greater contrast, producing a pseudo 3D-effect
11
New cards
fluorescence microscope
- its stains absorb light at one wavelength, then emit it at another.
- It filters only the emitted light
- used to image specific features of small specimens such us the genetic material within a cell
- It filters only the emitted light
- used to image specific features of small specimens such us the genetic material within a cell
12
New cards
confocal microscope
- designed to reject background from matter outside the focal plane and therefore allowing images of different sections of a specimen to be obtained.
- produces a point source of light and rejects out of focus light, providing 3D reconstructions of imaged samples
- produces a point source of light and rejects out of focus light, providing 3D reconstructions of imaged samples
13
New cards
Electron Microscope(1950)
- rather than focusing light, focuses a beam of electrons through the specimen or onto its surface
14
New cards
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
- focuses a beam of electrons onto the surface of a specimen, providing images that look 3D
15
New cards
transmission electron microscope
- focuses a beam of electrons through a specimen
16
New cards
Cell Fractionation
- takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from one another
- enable scientist to determine the functions of organelles
- enable scientist to determine the functions of organelles
17
New cards
Ultracentrifuge
- fractionate cells into their component parts
18
New cards
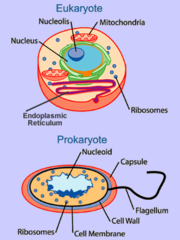
Prokaryotes
- simplest organisms
- most of its genetic material lies in a single circular molecule of DNA that resides in the NUCLEOID, but the area is not segregated from the rest of the cell's interior
- most of its genetic material lies in a single circular molecule of DNA that resides in the NUCLEOID, but the area is not segregated from the rest of the cell's interior
19
New cards
Eukaryotes
- complex organisms
- its DNA is contained in the NUCLEUS surrounded by a double-membrane structure called the Nuclear Envelope
- its DNA is contained in the NUCLEUS surrounded by a double-membrane structure called the Nuclear Envelope
20
New cards
Cytoplasm
- a common feature among all types of cells
- a semifluid matrix that fills the interior of the cell
- contains all of the sugars, amino acids, and proteins the cell uses to carry out its everyday activities.
-contains the organelles and cytosol
- a semifluid matrix that fills the interior of the cell
- contains all of the sugars, amino acids, and proteins the cell uses to carry out its everyday activities.
-contains the organelles and cytosol
21
New cards
Organelle
- any discrete macromolecular structure the cytoplasm specialized for a particular function
22
New cards
Cytosol
- part of the cytoplasm that contains organic molecules and ions in solution to distinguish it from larger organelles suspended in its fluid
23
New cards
Plasma membrane
- a common feature among all types of cells
- encloses a cell and separates its contents from its surroundings
- it is a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER about 5 to 10 nm thick, with proteins embedded in it.
- encloses a cell and separates its contents from its surroundings
- it is a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER about 5 to 10 nm thick, with proteins embedded in it.
24
New cards
Ribosomes
- a common feature among all types of cells
- particles made of ribosomal RNA and protein
- carry out protein synthesis
- made up of different subunits
- particles made of ribosomal RNA and protein
- carry out protein synthesis
- made up of different subunits
25
New cards
Svedberg unit(S)
- sedimentation coefficient
- not additive
- determines how fast a particle/organelles pellet out during centrifugation
- not additive
- determines how fast a particle/organelles pellet out during centrifugation
26
New cards
- 5S RNA, 23S RNA, 16S RNA
- 50S large subunit + 30S small subunit
- 50S large subunit + 30S small subunit
Subunit of prokaryote
27
New cards
- 5S RNA, 5.8S, 28S RNA, 18S RNA
- 60S large subunit + 40S small subunit
- 60S large subunit + 40S small subunit
Subunit of eukaryote
28
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
- cells without a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
- -pro(before) + -karyon(nucleus)
- consists of bacteria and archaea
- -pro(before) + -karyon(nucleus)
- consists of bacteria and archaea
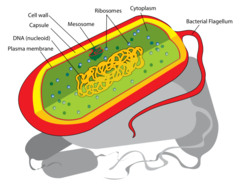
29
New cards
nucleoid/nuclear region
- part of a prokaryote
- contains the DNA
- contains the DNA
30
New cards
plasmid
- part of a prokaryote
- the extrachromosomal source of DNA that can replicate independently
- the extrachromosomal source of DNA that can replicate independently
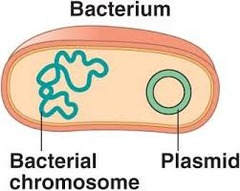
31
New cards
plasma/cell membrane
- part of a prokaryote
- made up of phospholipids and proteins, semi-permeable
- made up of phospholipids and proteins, semi-permeable
32
New cards
ribosomes
- part of a prokaryote
-site of protein synthesis
-site of protein synthesis
33
New cards
Cell wall
- part of a prokaryote
- made of peptidoglycan, structural support
- made of peptidoglycan, structural support
34
New cards
Peptidoglycan
- A protein-carbohydrate compound that makes the cell walls of the prokaryotic cell
35
New cards
Gram Staining method
- can use cell wall composition to classify bacteria into either Gram + (purple) or Gram - (pink)
36
New cards
Flagellum
- part of a prokaryote
- for locomotion
- for locomotion
37
New cards
Pilus
- part of a prokaryote
- for conjugal(reproduction) exchange & locomotion
- for conjugal(reproduction) exchange & locomotion
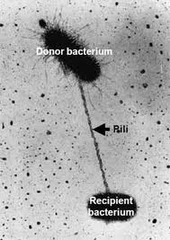
38
New cards
Capsule
- part of a prokaryote
- extra layer made of glycolipids for protection
- extra layer made of glycolipids for protection
39
New cards
Endospore
- part of a prokaryote
- dormant, tough, non-reproductive structure for protection against severe environment stresses
- dormant, tough, non-reproductive structure for protection against severe environment stresses
40
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells
- cells that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
- -eu(true) + -karyon(nucleus)
-consists of plants, animals, fungi, and protists
- -eu(true) + -karyon(nucleus)
-consists of plants, animals, fungi, and protists
41
New cards
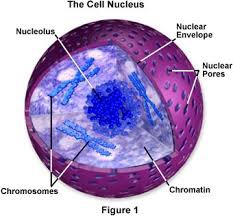
Nucleus
- part of a eukaryote
- contains most of the cell's genes and is usually the most conspicuous organelle
- the DNA and proteins inside it form a genetic material called CHROMATIN
- contains most of the cell's genes and is usually the most conspicuous organelle
- the DNA and proteins inside it form a genetic material called CHROMATIN
42
New cards
Nuclear membrane
- part of a eukaryote's nucleus
- a double membrane each consists a lipid bilayer
- its pores regulate the entry and exit of molecules from the nucleus
- a double membrane each consists a lipid bilayer
- its pores regulate the entry and exit of molecules from the nucleus
43
New cards
nuclear lamina
- part of a eukaryote's nucleus
- maintains the shape of the nucleus
- composed of protein
- maintains the shape of the nucleus
- composed of protein
44
New cards
nucleolus
- part of a eukaryote's nucleus
- located within the nucleus
- is the site of ribosomal RNA(rRNA) synthesis
- located within the nucleus
- is the site of ribosomal RNA(rRNA) synthesis
45
New cards
Endomembrane System
- part of a eukaryote
- has 6 components
- its components are either continuous or connected via transfer by vesicles
- modifies, packages, and transports lipids and proteins
- has 6 components
- its components are either continuous or connected via transfer by vesicles
- modifies, packages, and transports lipids and proteins
46
New cards
Nuclear envelope
- component of the endomembrane system
- encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm
- encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm
47
New cards
Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER)
- component of the endomembrane system
- accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
- continuous with the nuclear envelope
- has 2 distinct regions: smooth ER & rough ER
- accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
- continuous with the nuclear envelope
- has 2 distinct regions: smooth ER & rough ER
48
New cards
Smooth ER
- component of the endomembrane system
- lacks ribosomes
- synthesizes lipids
- metabolizes carbohydrates
- detoxifies poison
- stores calcium
- lacks ribosomes
- synthesizes lipids
- metabolizes carbohydrates
- detoxifies poison
- stores calcium
49
New cards
Rough ER
- component of the endomembrane system
- has bound ribosomes which secrete GLYCOPROTEINS(protein covalently bonded to carbohydrates)
- distributes transport vesicles, proteins surrounded by membranes
- a membrane factory for the cell
- has bound ribosomes which secrete GLYCOPROTEINS(protein covalently bonded to carbohydrates)
- distributes transport vesicles, proteins surrounded by membranes
- a membrane factory for the cell
50
New cards
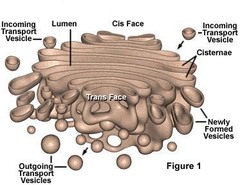
Golgi Apparatus
- component of the endomembrane system
- consists of flattened membranous sacs call CISTERNAE
- modifies products of the ER
- manufactures certain macromolecules
- sorts and packages materials intro transport vesicles
- consists of flattened membranous sacs call CISTERNAE
- modifies products of the ER
- manufactures certain macromolecules
- sorts and packages materials intro transport vesicles
51
New cards
Cisternae
- what the Golgi apparatus consists of
- has two types:
cis face" receiving" and transface "shipping"
- has two types:
cis face" receiving" and transface "shipping"
52
New cards
Lysosome
- component of the endomembrane system
- membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
- its enzymes can hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides and nucleic acids
- membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
- its enzymes can hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides and nucleic acids
53
New cards
Phagocytosis
- a process in which some types of cell can engulf another cell forming a food vacuole
- the food vacuole created fuses with LYSOSOME and digests the molecules
- the food vacuole created fuses with LYSOSOME and digests the molecules
54
New cards
Autophagy
- a process in which lysosomes uses enzymes to recycle the cell's own organelles and macrimolecules
55
New cards
Vacuole
- component of the endomembrane system
- a eukaryotic cell may have one or several
- help in the storage and disposal of various substances
- has 3 kinds
- a eukaryotic cell may have one or several
- help in the storage and disposal of various substances
- has 3 kinds
56
New cards
Food vacuole
- temporarily stores food
- formed by phagocytosis
- formed by phagocytosis
57
New cards
contractile vacuole
- found in many freshwater protists
- pump excess water out of cells
- pump excess water out of cells
58
New cards
central vacuole
- found in many mature plant cells
- hold organic compounds and water
- hold organic compounds and water
59
New cards
plasma membrane
- part of a endomembrane system
- a double layer of lipids that separates the cell interior from the outside environment
- a double layer of lipids that separates the cell interior from the outside environment
60
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
- a theory that eukaryotic cells formed from symbiosis among several different prokaryotic organisms
61
New cards
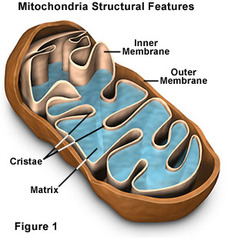
Mitochondria
- nearly in all eukaryotic cells
- have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded in CRISTAE
- have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded in CRISTAE
62
New cards
mitchondrial matrix
- catalyzes some metabolic steps in cellular respiration
- a compartment created by the inner membrane along with the intermembrane space
- a compartment created by the inner membrane along with the intermembrane space
63
New cards
Cristae
- present a large surface area for enzymes that synthesize ATP
- folds the inner membrane of mitochondria
- folds the inner membrane of mitochondria
64
New cards
Chloroplasts
- part of a eukaryote
- a member of a family of organelles called PLASTIDS
- contain the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis
- found in leaves and other green organs and in algae
- a member of a family of organelles called PLASTIDS
- contain the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis
- found in leaves and other green organs and in algae
65
New cards
Thyakoids
- structure of chloroplasts
- membranous sacs stacked to form a GRANUM
- membranous sacs stacked to form a GRANUM
66
New cards
Stroma
- structure of chloroplasts
- the internal fluid
- the internal fluid
67
New cards
mitochondria & chloroplasts
- not part of the endomembrane system
- a member of a family of organelles
- the site of cellular respiration, a metabolic process that generates ATP
- have a double membrane
-have proteins made by free ribosomes
- contain their own DNA
- a member of a family of organelles
- the site of cellular respiration, a metabolic process that generates ATP
- have a double membrane
-have proteins made by free ribosomes
- contain their own DNA
68
New cards
Peroxisomes
- part of a eukaryote
- specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane
- produce hydrogen peroxide and convert it to water
- uses oxygen to break down different types of molecules
- specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane
- produce hydrogen peroxide and convert it to water
- uses oxygen to break down different types of molecules
69
New cards
Cytoskeleton
- a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm
- organizes the cell's structures and activities, anchoring many organelles
- helps support the cell and maintain its shape
- interacts with MOTOR PROTEINS to produce motility
- provides "monorails" that vesicles can travel along in the cell
- may help regulate biochemical activities
- organizes the cell's structures and activities, anchoring many organelles
- helps support the cell and maintain its shape
- interacts with MOTOR PROTEINS to produce motility
- provides "monorails" that vesicles can travel along in the cell
- may help regulate biochemical activities
70
New cards
Microtubules
- a type of fiber that makes up the cytoskeleton
- the thickest of the three components of the cytoskeleton
- function for intracellular trasnport
- the thickest of the three components of the cytoskeleton
- function for intracellular trasnport
71
New cards
Microfilaments
- type of fiber that make up the cytoskeleton
-also called actin filaments
- the thinnest components
-also called actin filaments
- the thinnest components
72
New cards
Intermediate filaments
- type of fiber that make up the cytoskeleton
- fibers with diameter in a middle range
- fibers with diameter in a middle range
73
New cards
Centrosome
- where microtubules grow
- a "microtubule-organizing center"
- a "microtubule-organizing center"
74
New cards
centrioles
- in animal cells, the centrosome has a pair of ________, each with nine triplets of microtubules arranged in a ring
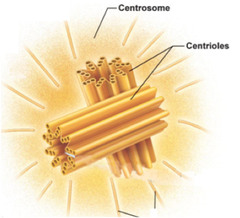
75
New cards
Cilia and Flagella
- their beating is controlled by microtubules
- locomotor appendages of some cells
- compared to each other, they differ in beating patterns
- locomotor appendages of some cells
- compared to each other, they differ in beating patterns
76
New cards
muscle contraction
- is microfilaments that function in cellular motility that contain the protein MYOSIN in addition to ACTIN
- in muscle cells, thousands of actin filaments are arranged parallel to one another
- thicker filaments composed of myosin interdigitate(interlock) with the thinner actin fibers
- in muscle cells, thousands of actin filaments are arranged parallel to one another
- thicker filaments composed of myosin interdigitate(interlock) with the thinner actin fibers
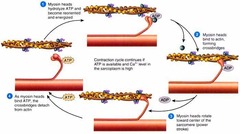
77
New cards
Ctyoplasmic Streaming
- a circular flow of cytoplasm within cells
- speeds distribution of materials within the cell
- driven by actin-myosin interactions in plant cells
- speeds distribution of materials within the cell
- driven by actin-myosin interactions in plant cells
78
New cards
Amoeboid movement (pseudopodia)
- localized contraction brought about by actin and myosin
- Pseudopodia (cellular extensions)
extend and contract through the
reversible assembly and contraction
of actin subunits into microfilaments
- Actin flexibility allows the structural
change in the pseudopods of
Amoeba, allowing it to move.
- Pseudopodia (cellular extensions)
extend and contract through the
reversible assembly and contraction
of actin subunits into microfilaments
- Actin flexibility allows the structural
change in the pseudopods of
Amoeba, allowing it to move.
79
New cards
Cell Wall
- an extracellular structure that distinguishes plant cells from animals cells
- plant cell walls are made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and protein
- prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists also have them
- plant cell walls are made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and protein
- prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists also have them
80
New cards
(1) Primary cell wall
(2) Middle lamella
(3) Secondary cell wall
(2) Middle lamella
(3) Secondary cell wall
- the three layers of Plant cell walls
- (1) relatively thin and flexible
- (2) thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells
- (3) in some cells; added between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall
- (1) relatively thin and flexible
- (2) thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells
- (3) in some cells; added between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall
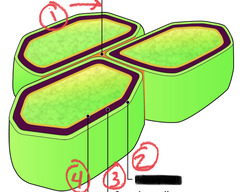
81
New cards
extracellular matrix (ECM)
- its functions: support, adhesion, movement & regulation
- what animal cells are covered by instead of cell walls
- what animal cells are covered by instead of cell walls
82
New cards
collagen, proteoglycans and fibronectin
The ECM is made up of glycoproteins such as _______, _____________, and ______________.
83
New cards
integrins
ECM proteins bind to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane called _________
84
New cards
intercellular junctions
- facilitate the adherance, interaction communication through direct physical contact of neighboring cells in tissues, organs or organ systems
85
New cards
Plasmodesmata
- a type of intercellular junction
- channels between adjacent plant cells
- through this, water and small solutes(and sometimes proteins and RNA) can pass from cell to cell
- channels between adjacent plant cells
- through this, water and small solutes(and sometimes proteins and RNA) can pass from cell to cell
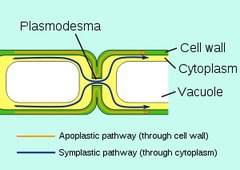
86
New cards
Tight junctions
- a type of intercellular junction
- membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
- membranes of neighboring cells are pressed together, preventing leakage of extracellular fluid
87
New cards
Desmosomes (anchoring junctions)
- a type of intercellular junction
- fasten cells together into strong sheets
- fasten cells together into strong sheets
88
New cards
Gap junctions (communicating junctions)
- a type of intercellular junction
- provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells
- provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent cells