Human Eye and Ear Anatomy: Functions and Structures
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
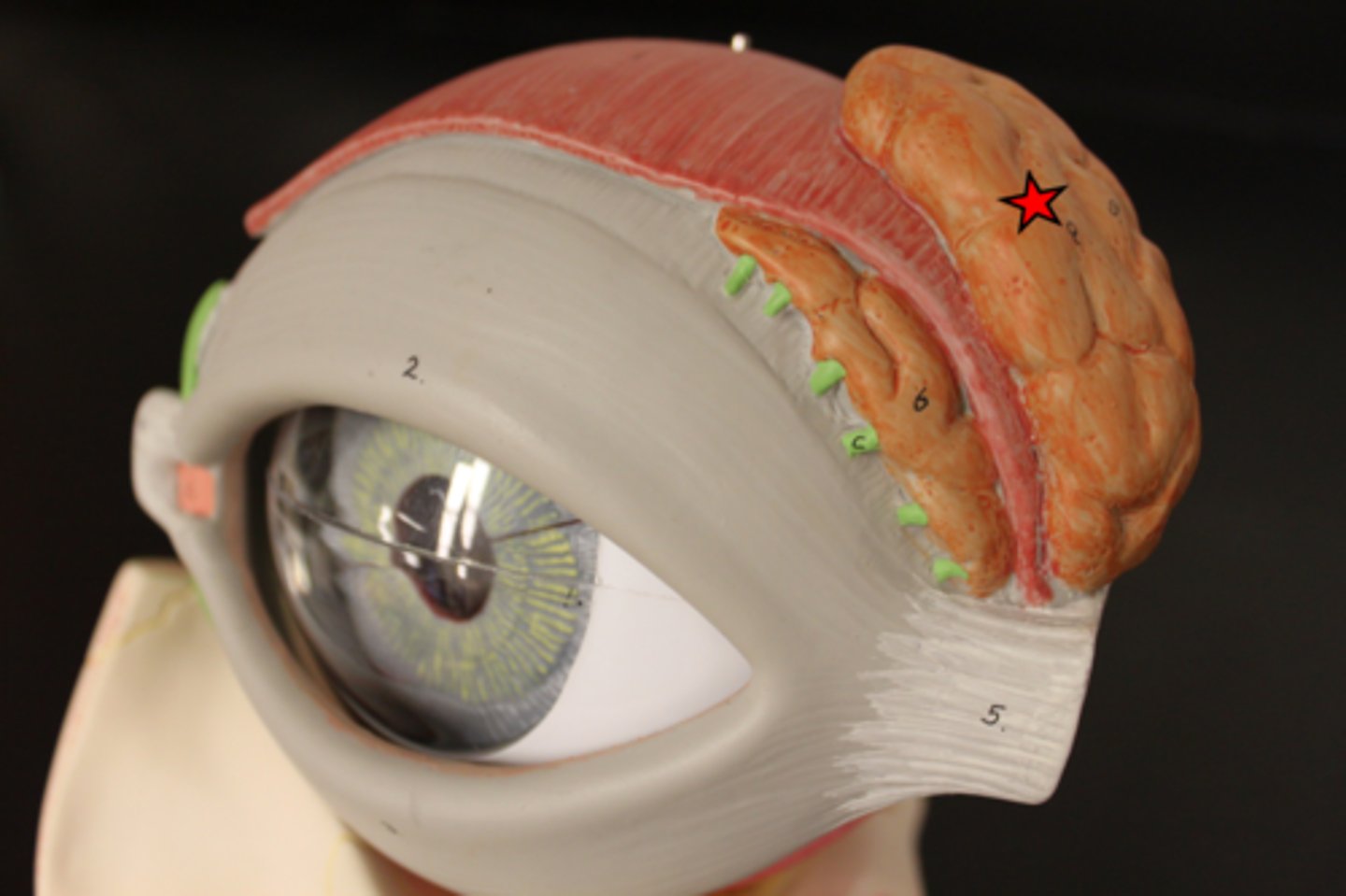
Eyebrow
Prevents sweat and debris from entering the eye
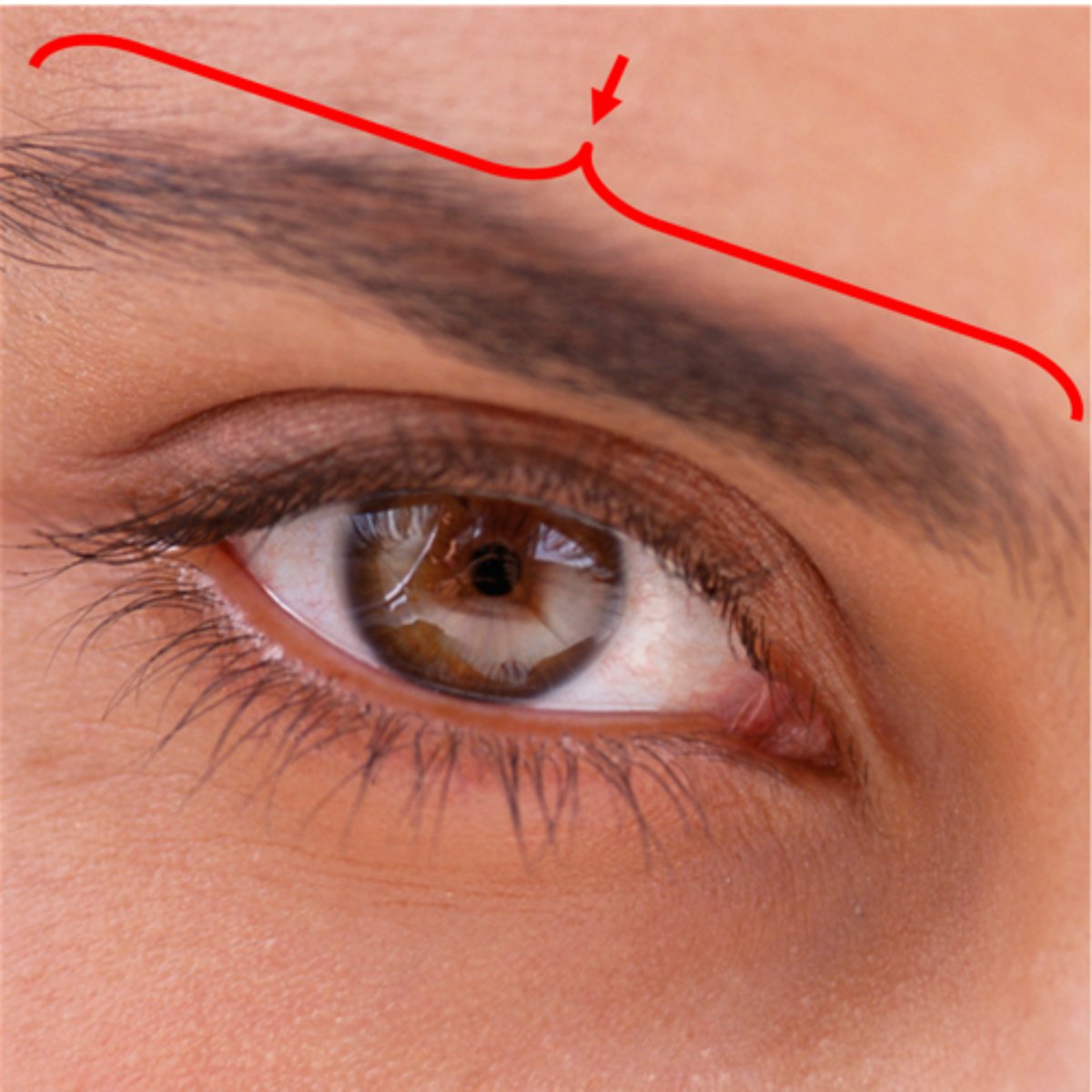
Eyelid
Protects and moistens the eye
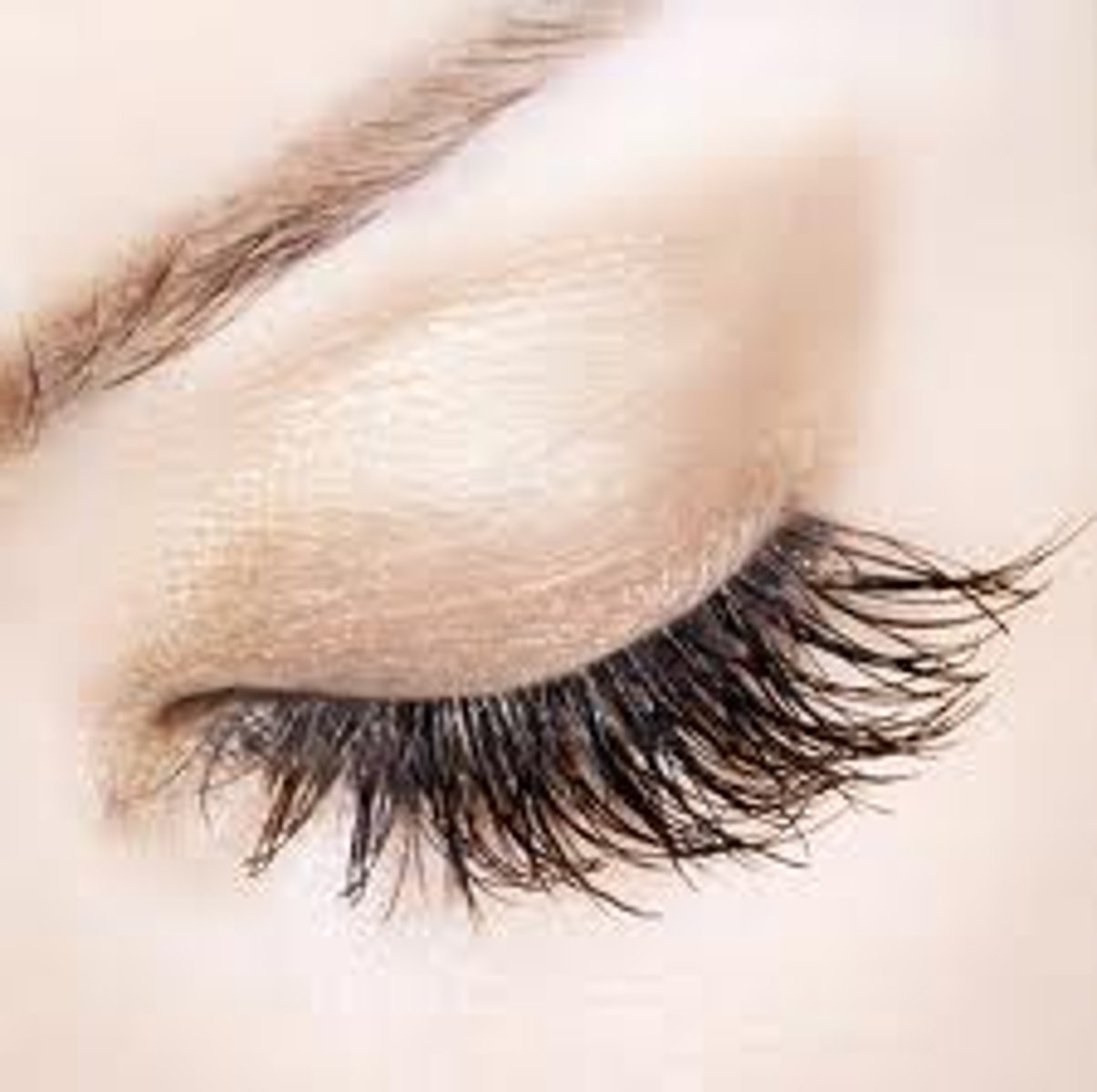
Eyelashes
Protect the eye from debris and trigger blink reflex

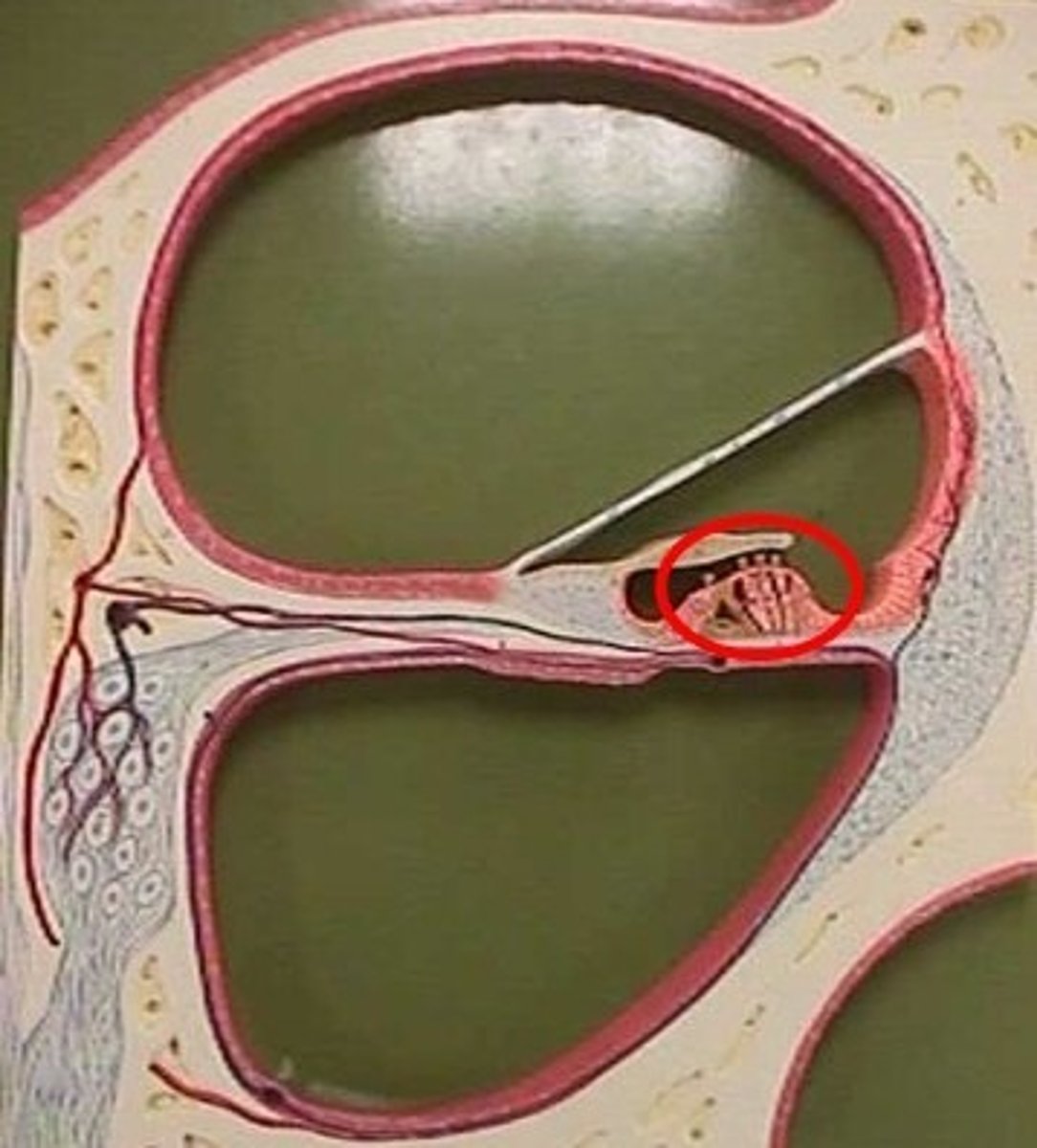
Lacrimal sac
Collects tears from lacrimal canaliculi
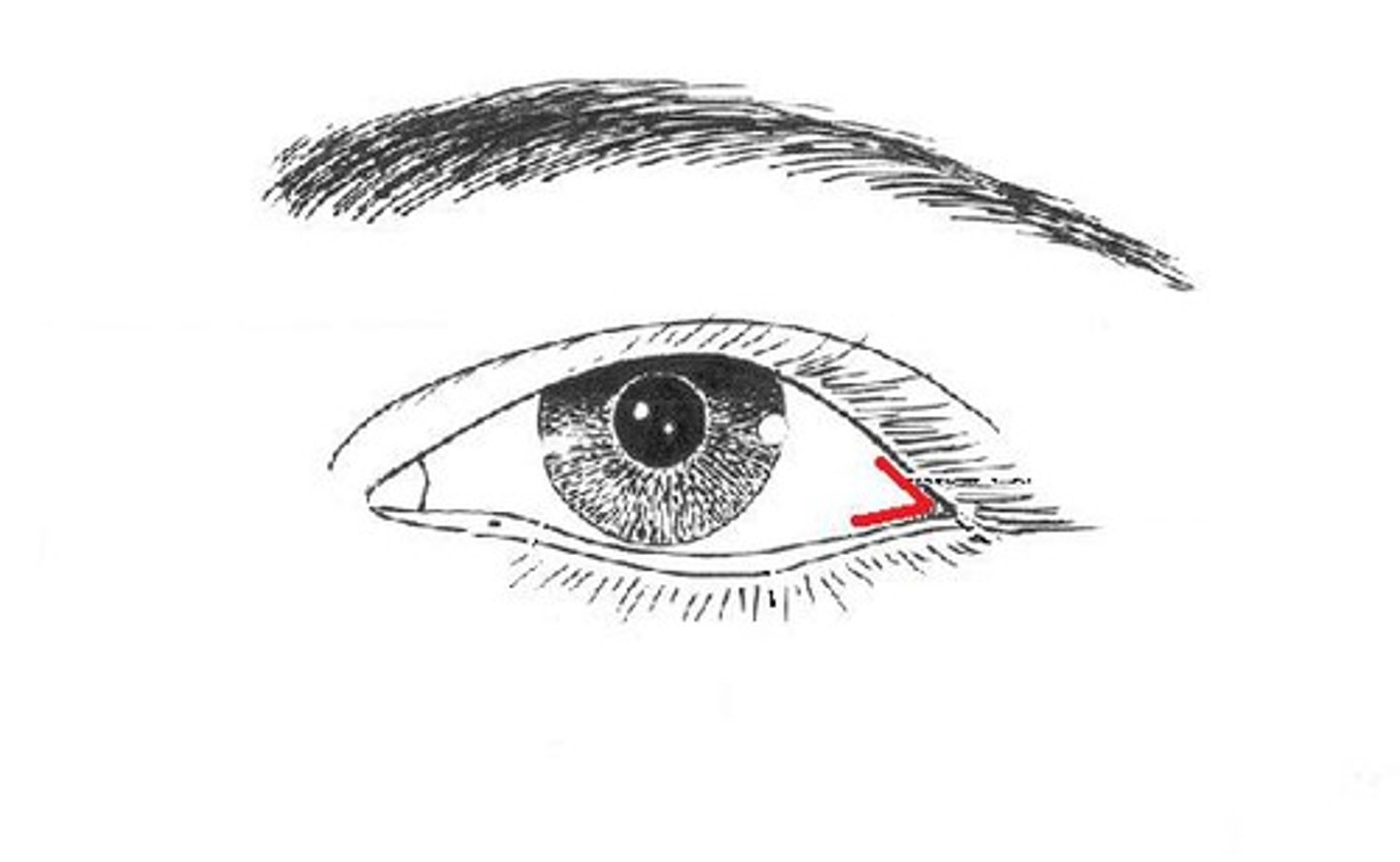
Medial commissure
Corner of the eye near the nose where eyelids meet
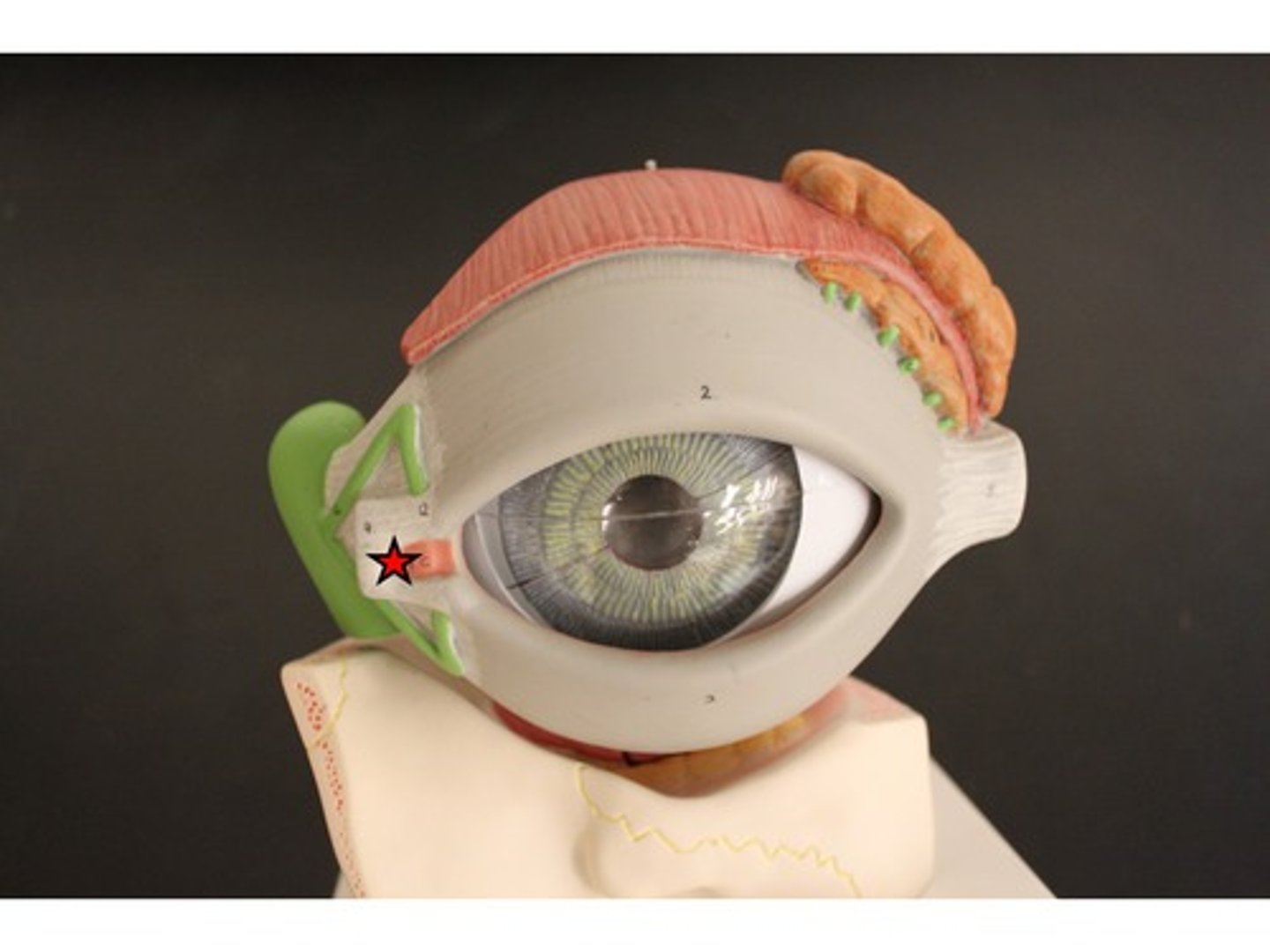

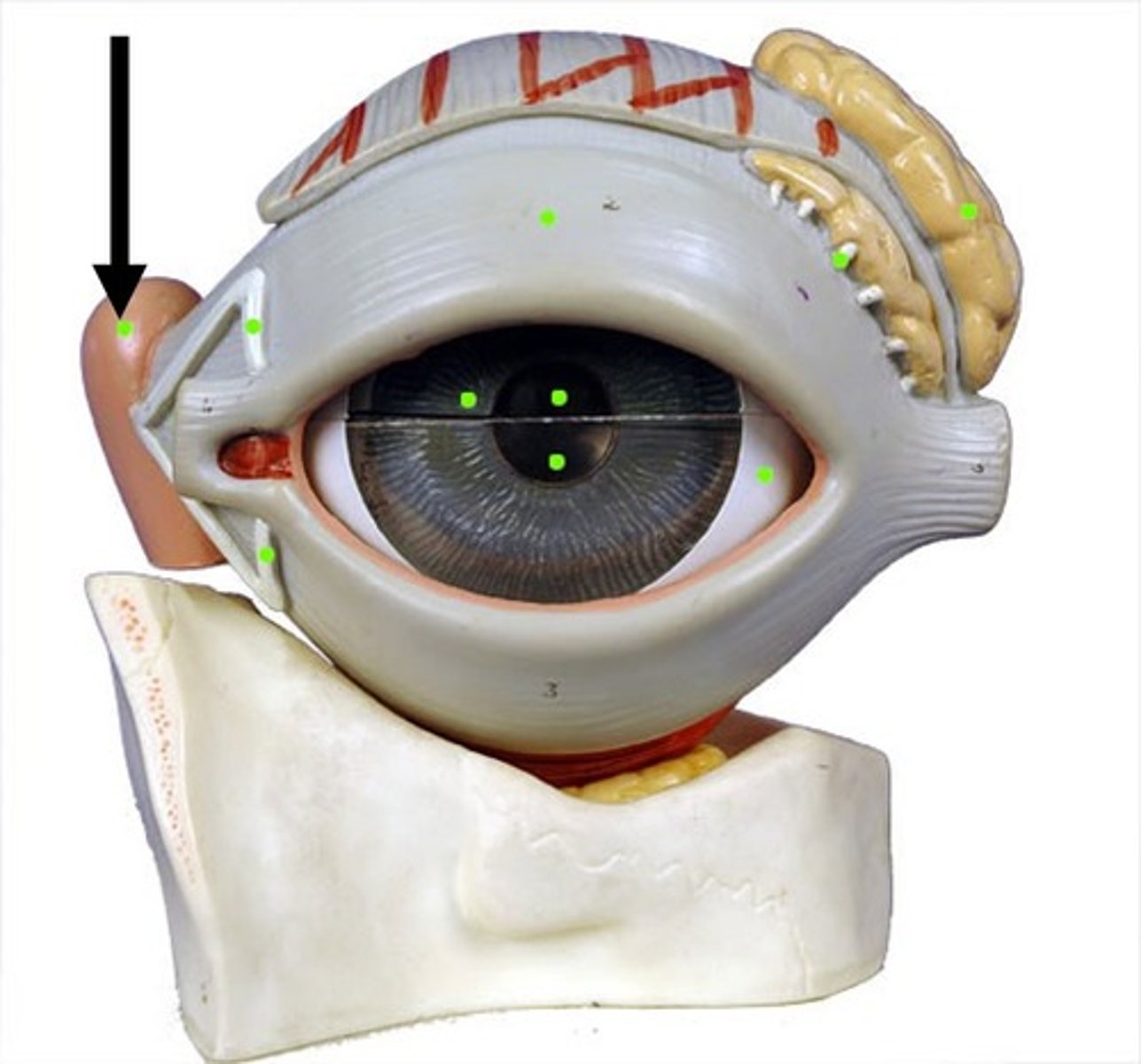
Lacrimal caruncle
Small pink nodule at medial commissure containing sweat and sebaceous glands
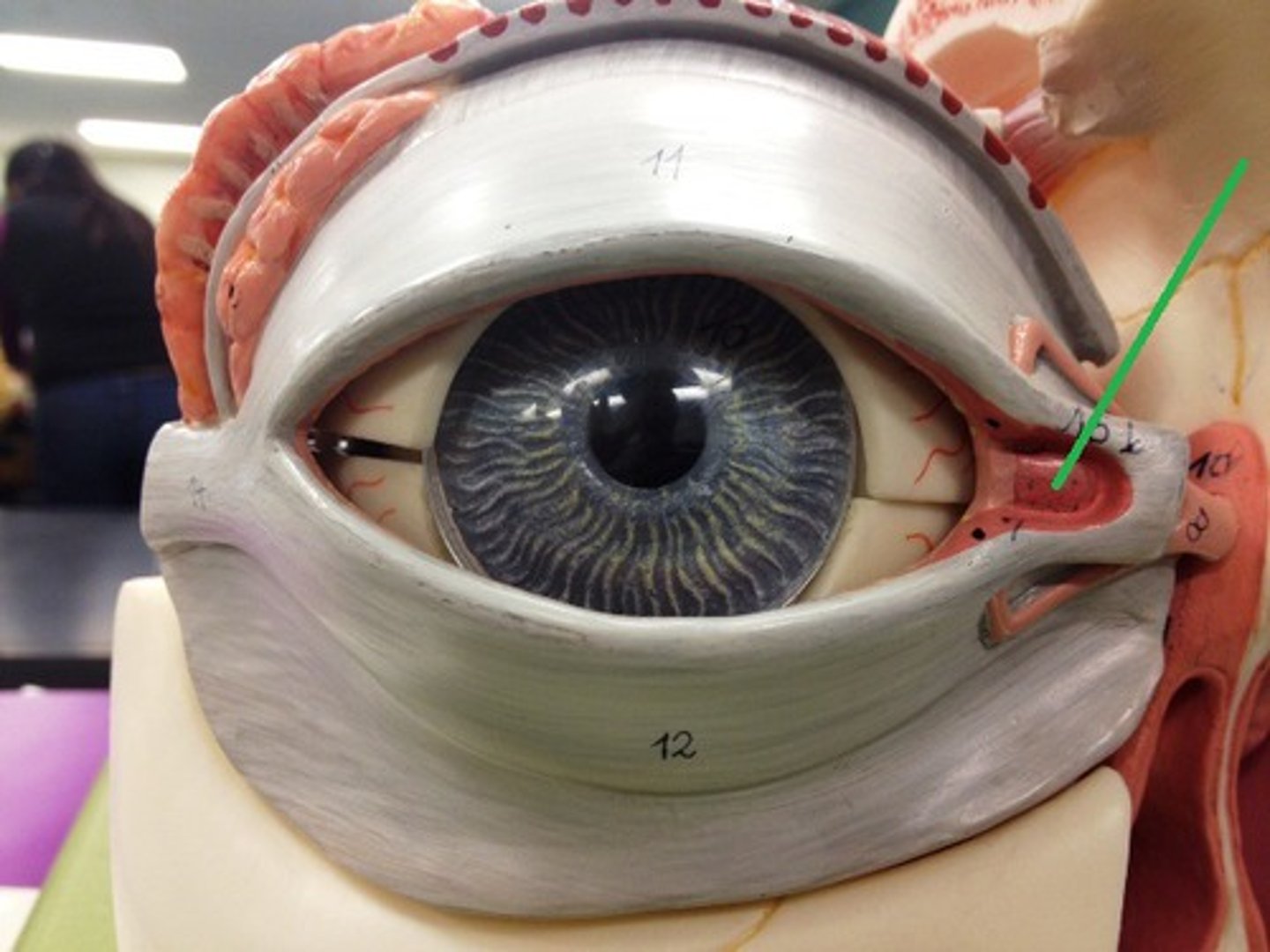
Lacrimal gland
Produces tears
Lateral commissure
Outer corner of the eye where eyelids meet
Lacrimal canaliculus
Drains tears from eye surface to lacrimal sac
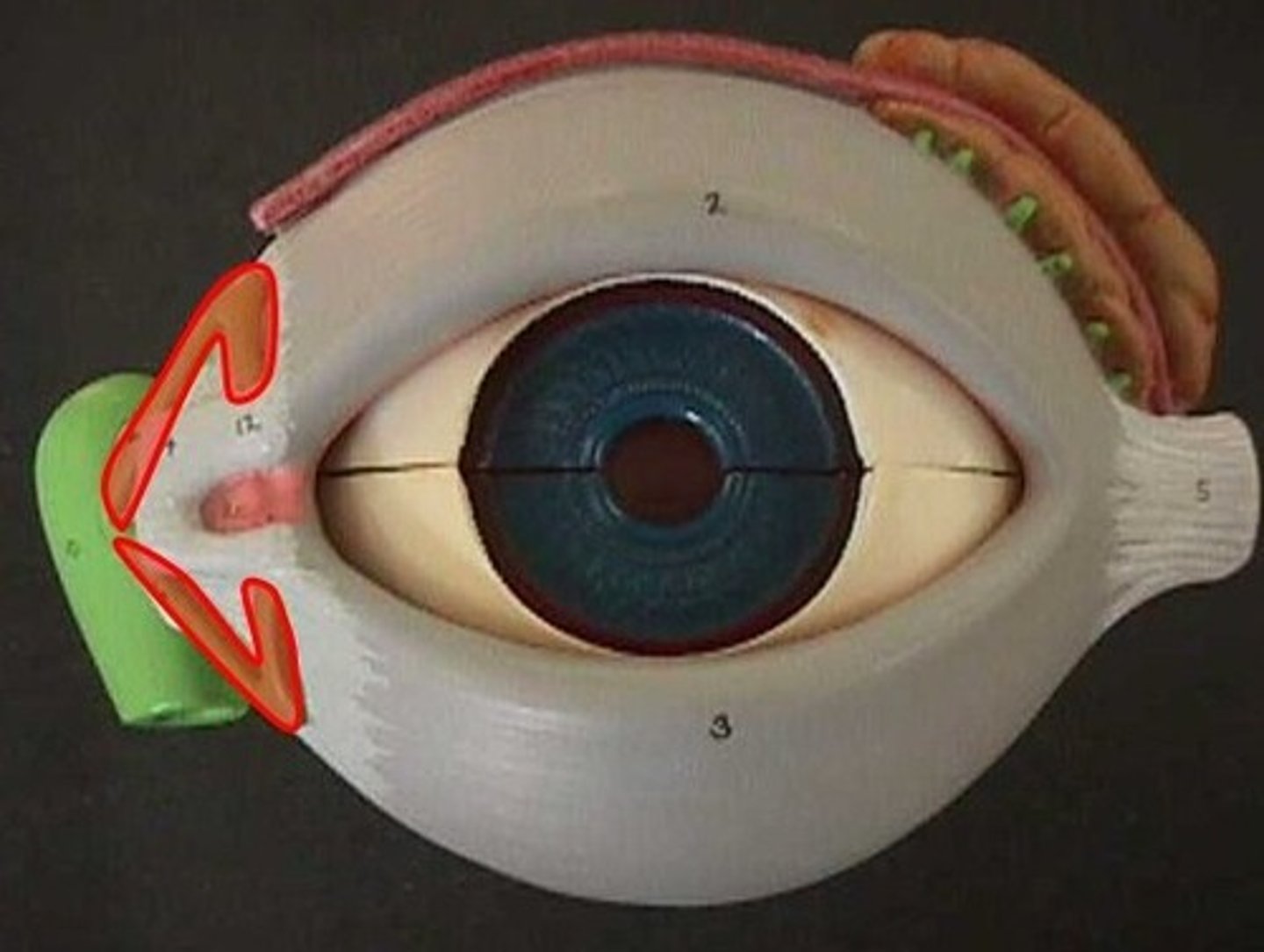
Nasolacrimal duct
Carries tears from lacrimal sac into nasal cavity
Superior oblique muscle
Rotates eye downward and laterally
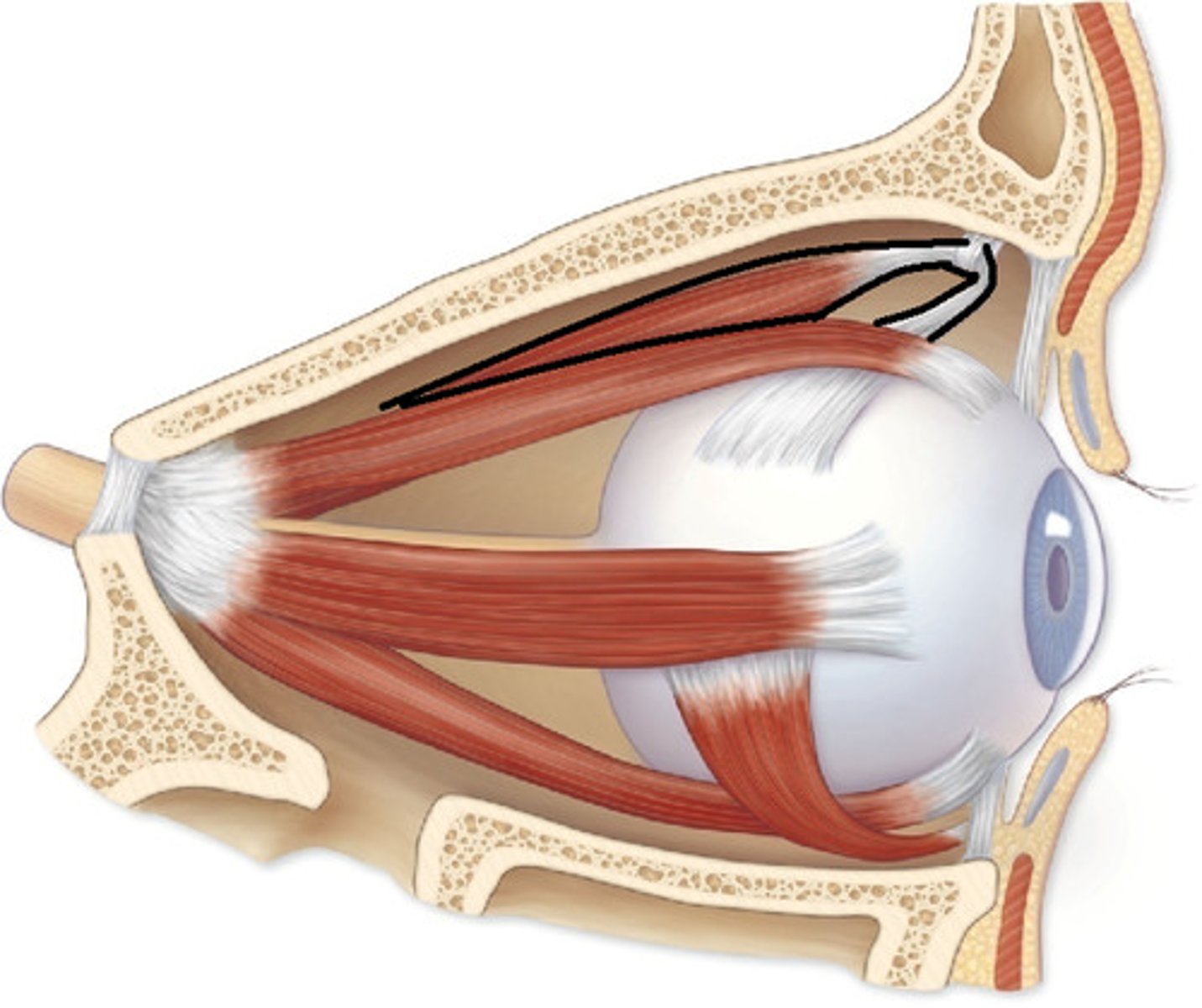
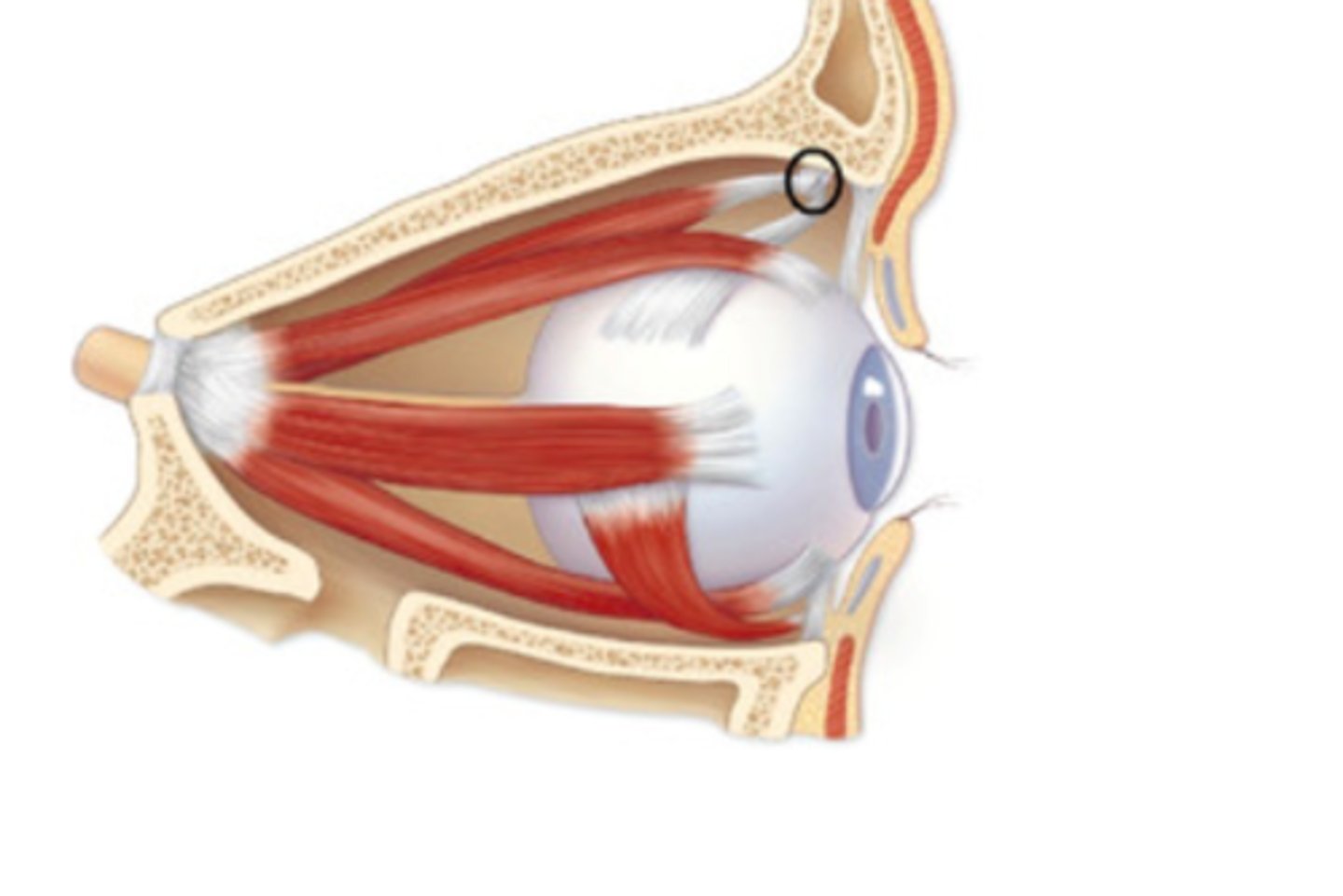
Trochlea
Pulley-like structure for superior oblique muscle tendon
Superior rectus muscle
Moves eye upward
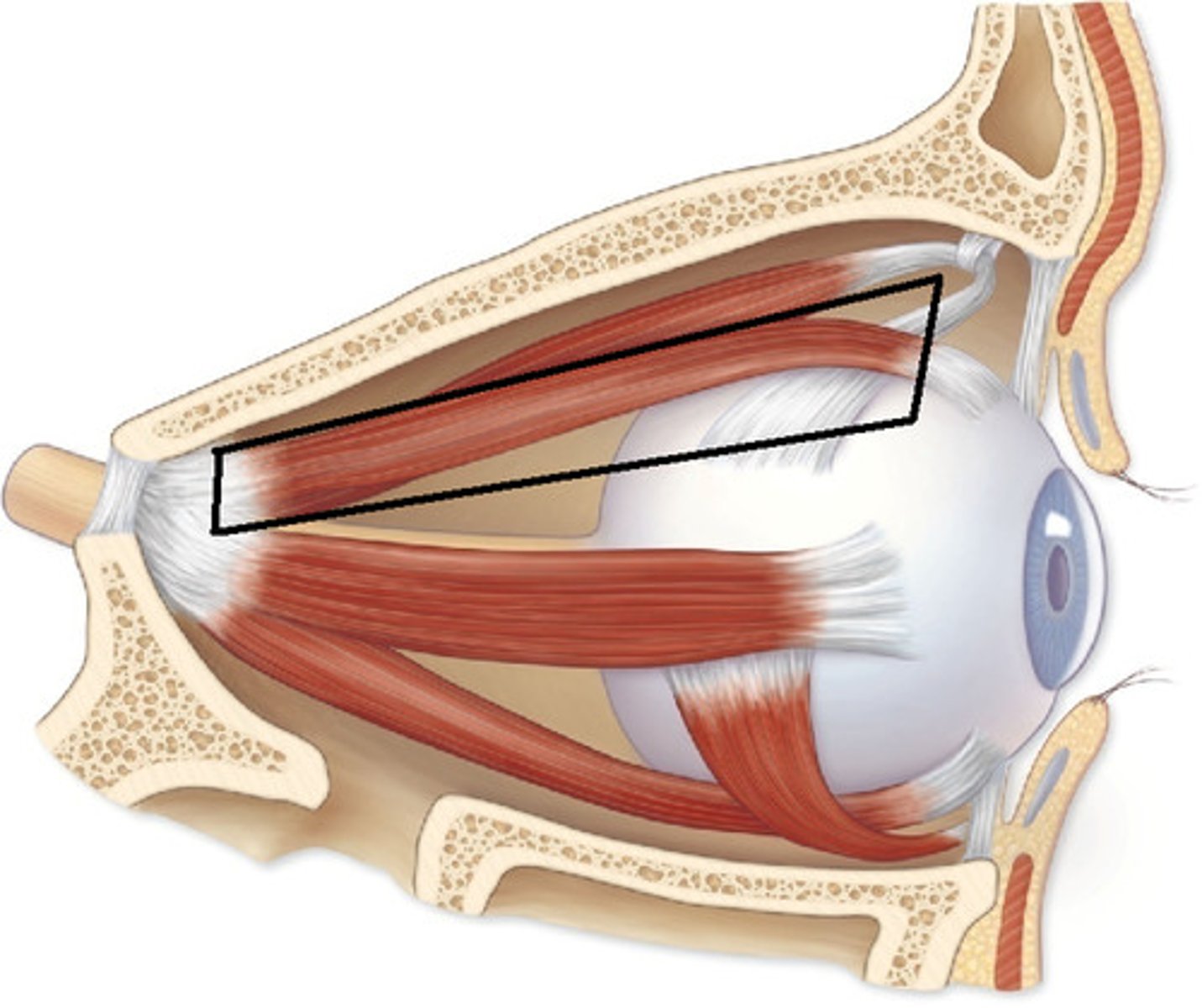
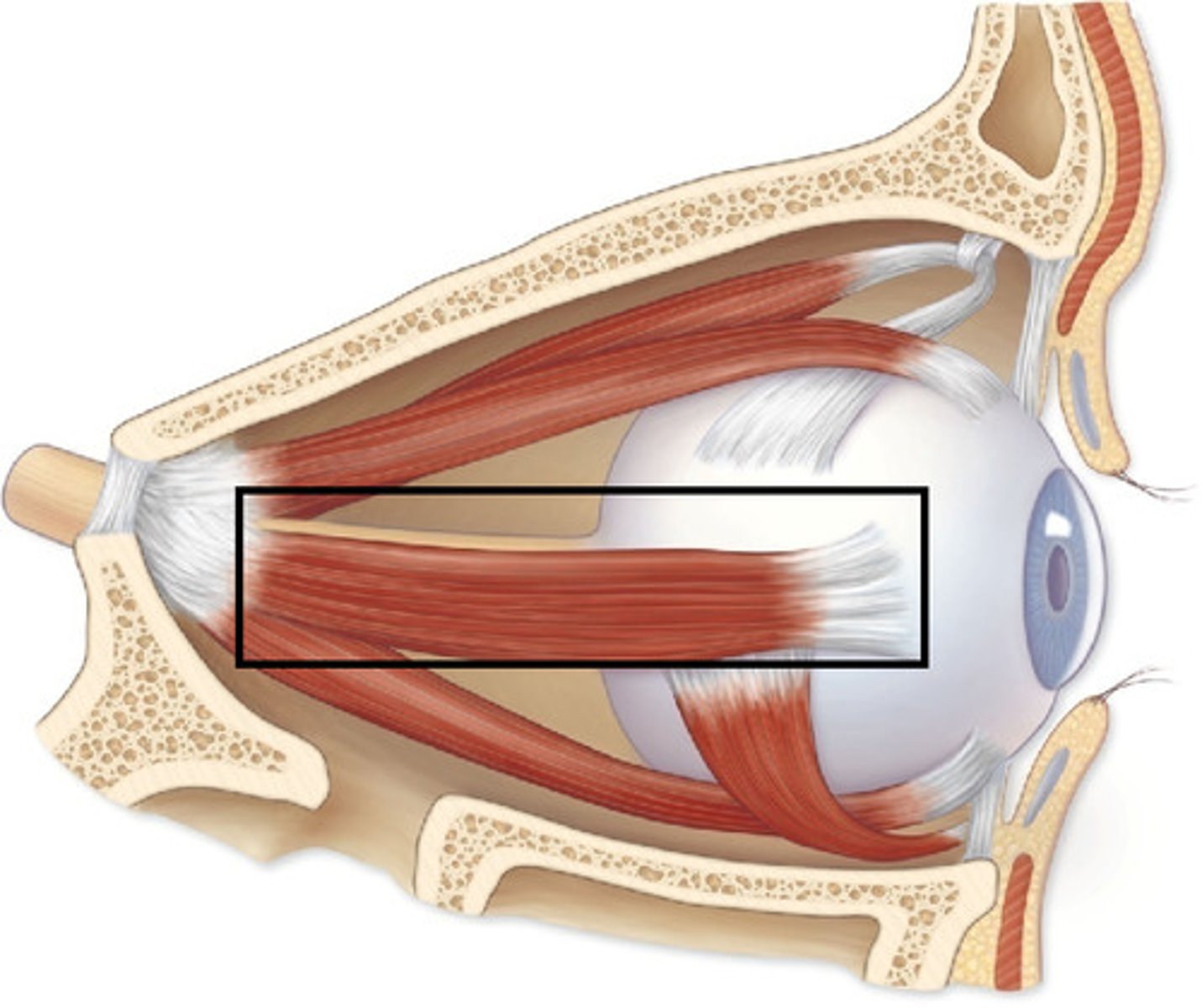
Lateral rectus muscle
Moves eye laterally (abduction)
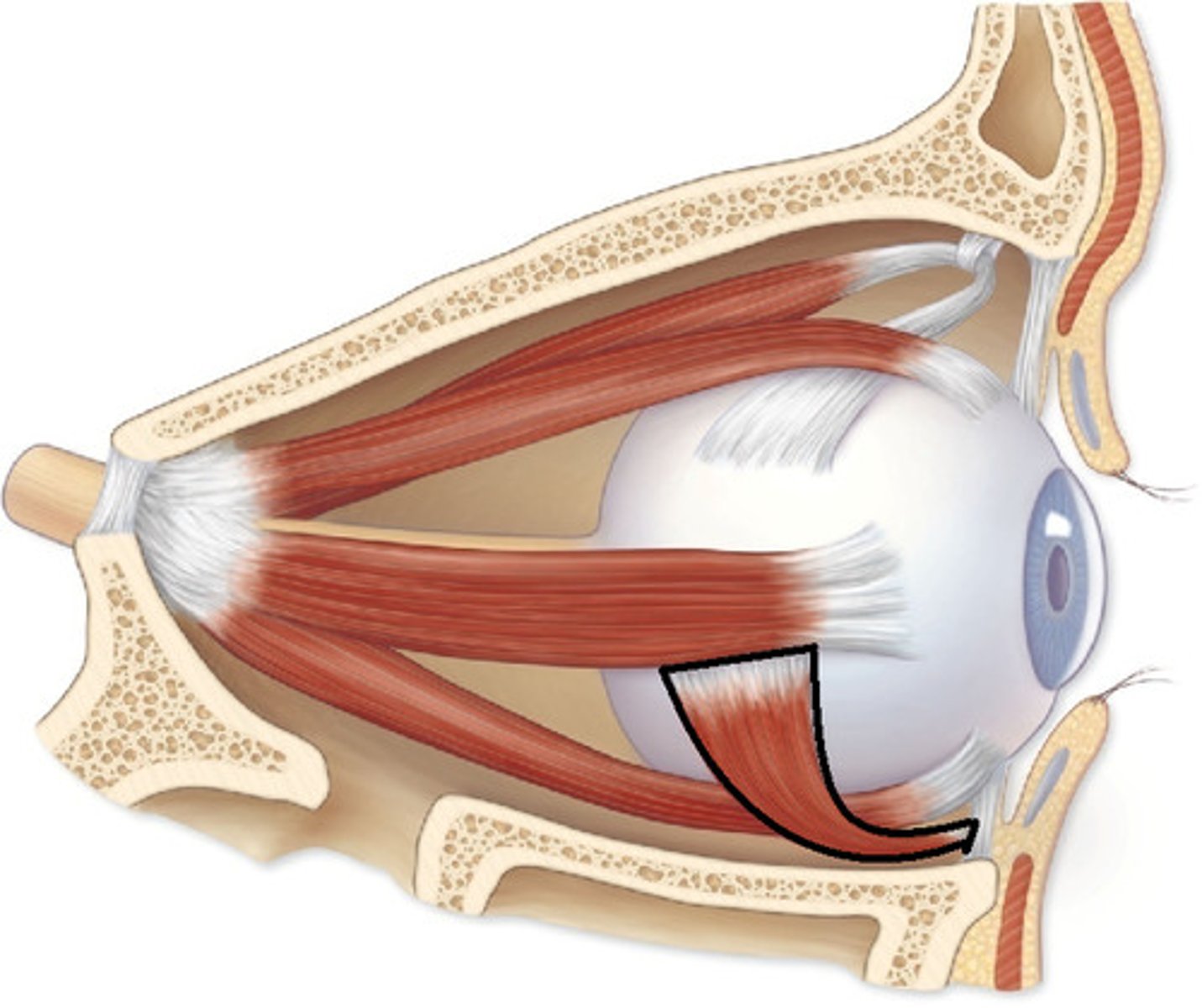
Inferior oblique muscle
Rotates eye upward and laterally
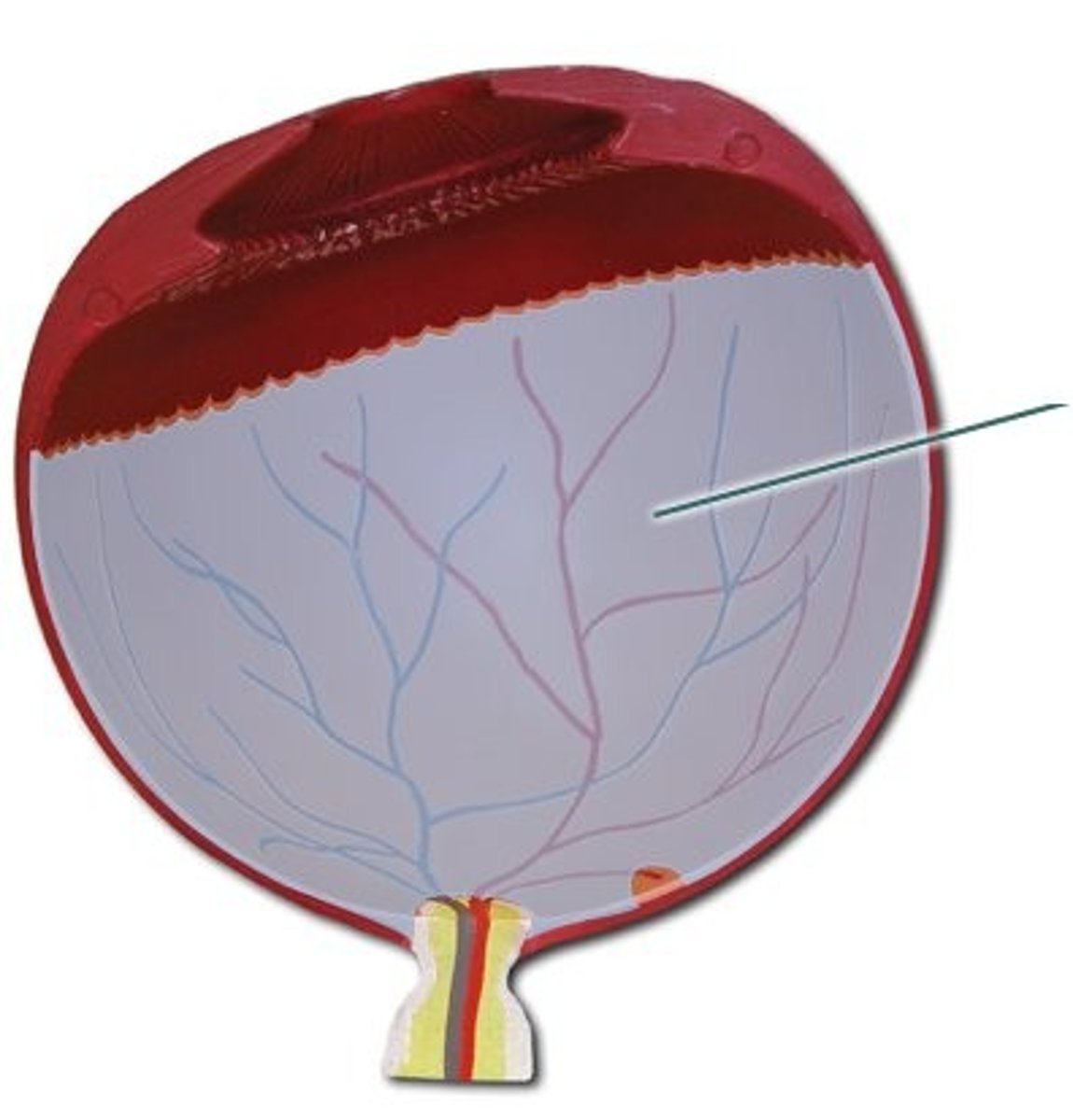
Retina
Inner layer of the eye containing photoreceptors
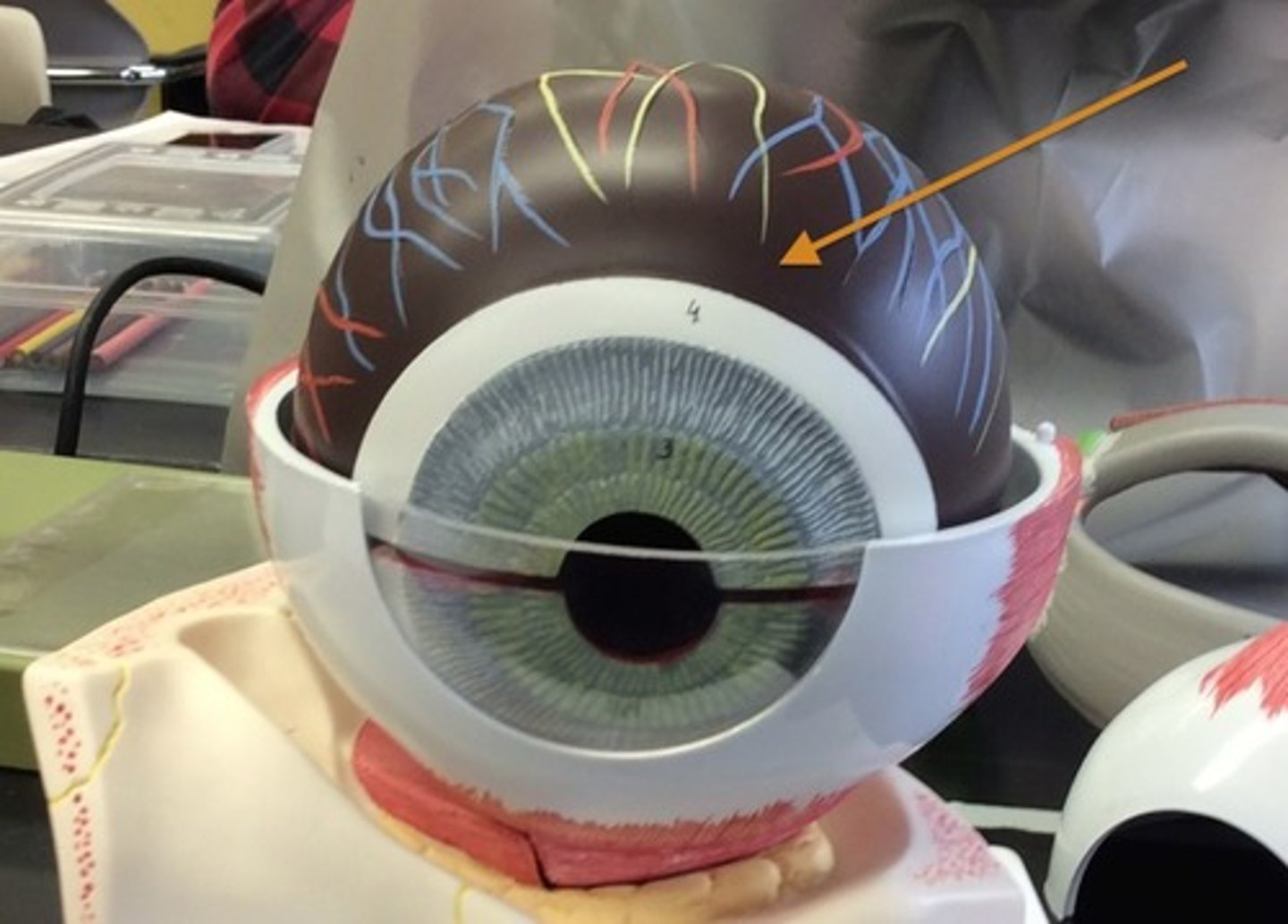
Choroid
Middle vascular layer providing blood supply to retina
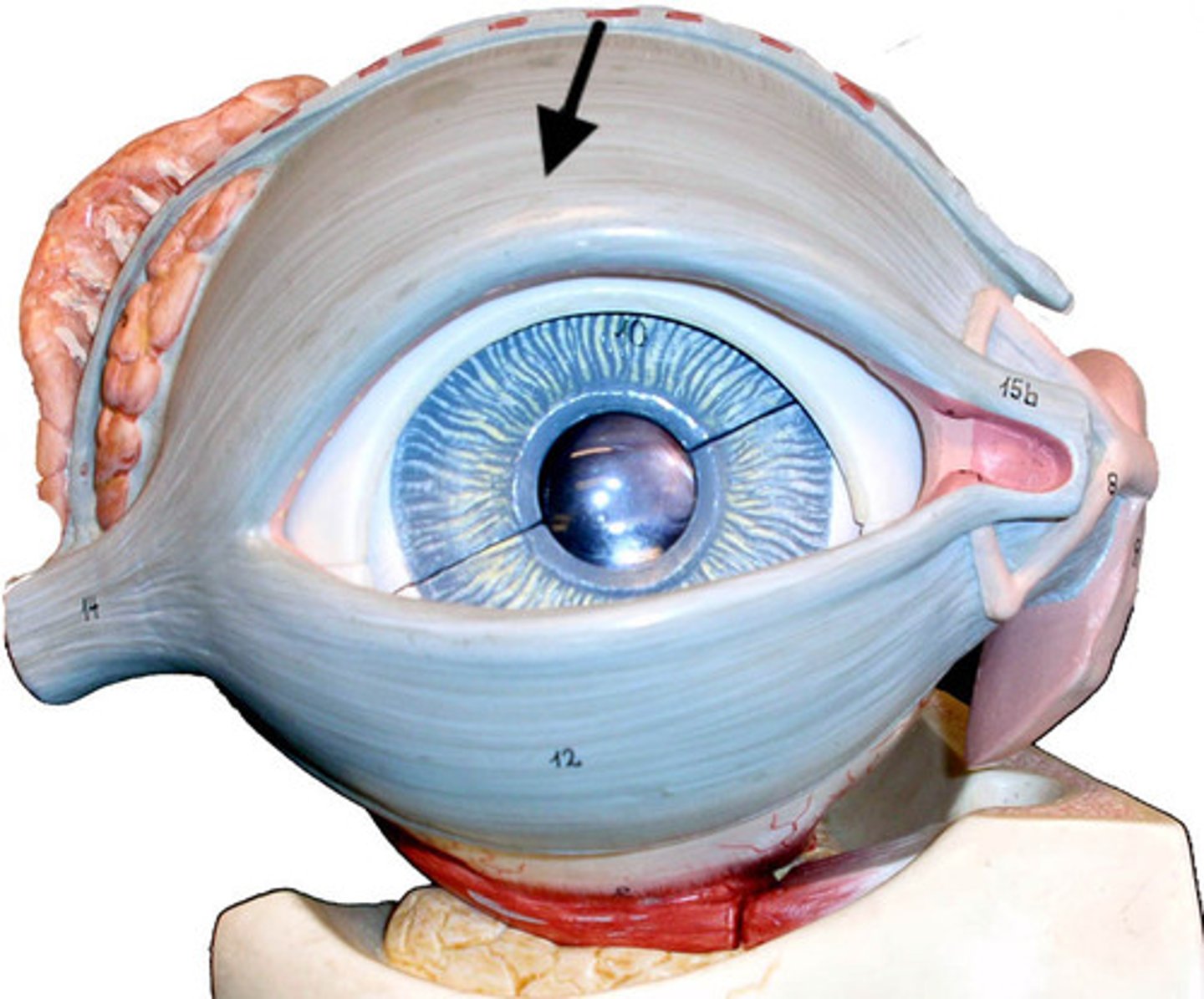
Sclera
White outer fibrous layer protecting the eye
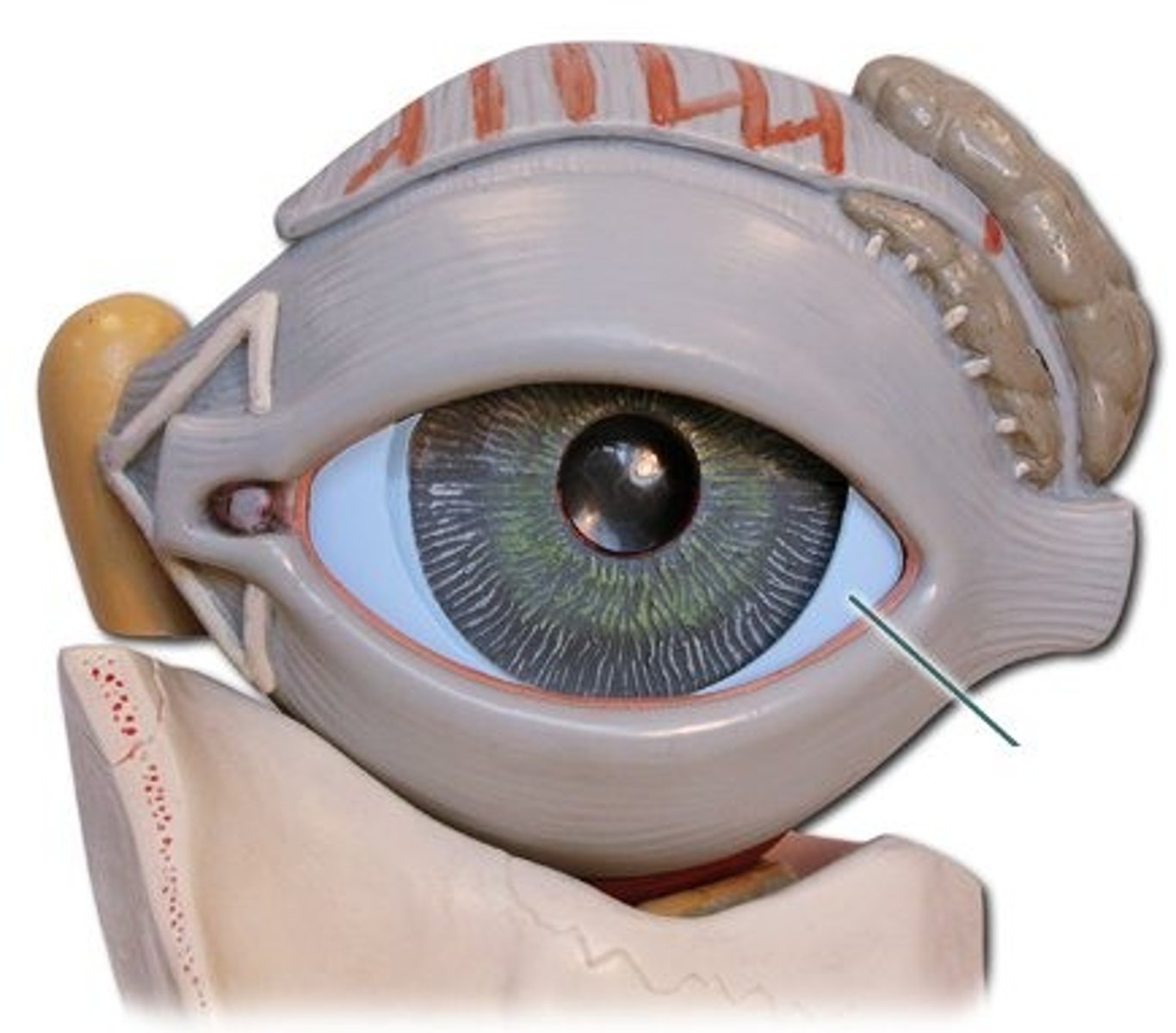
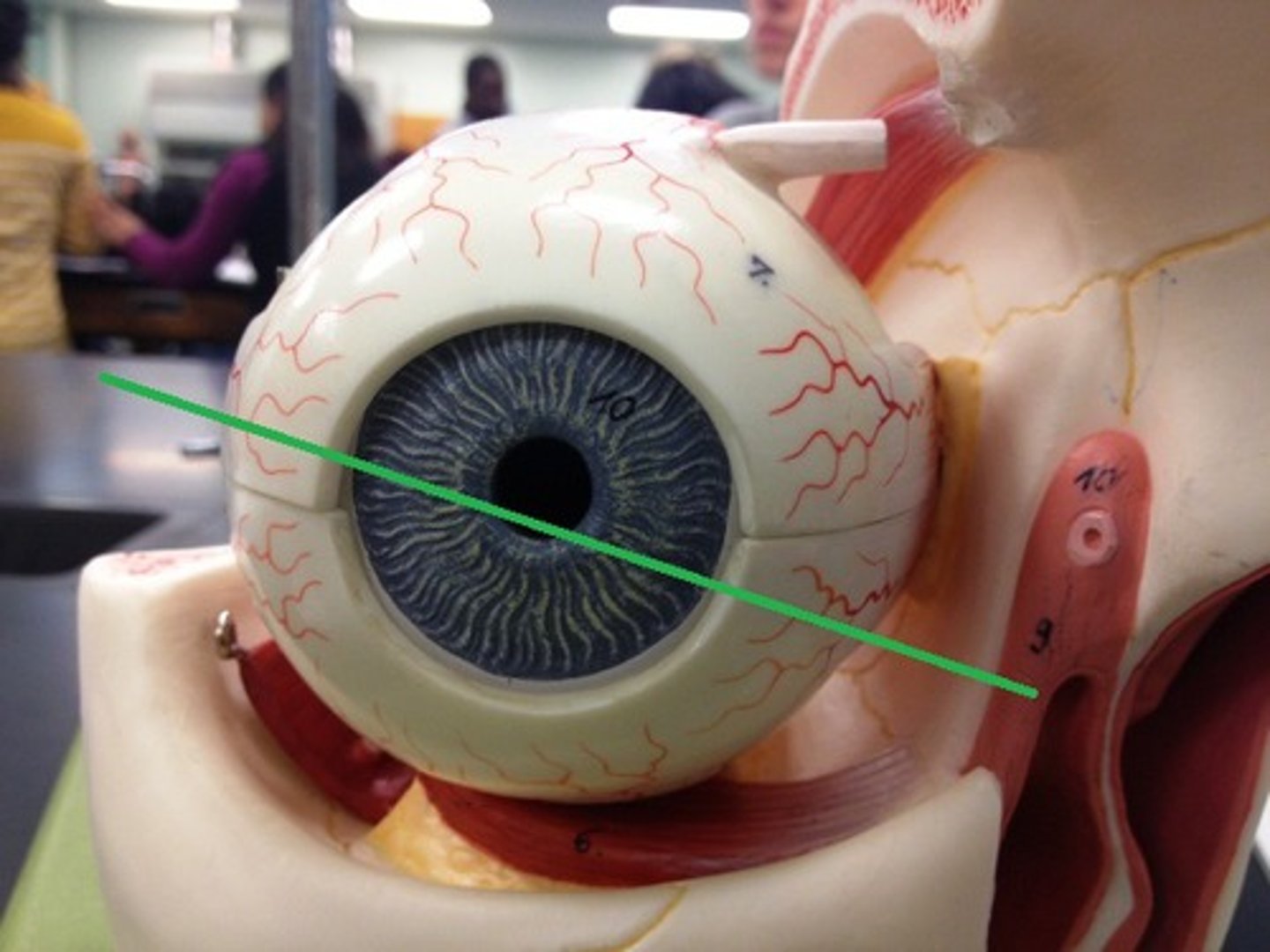
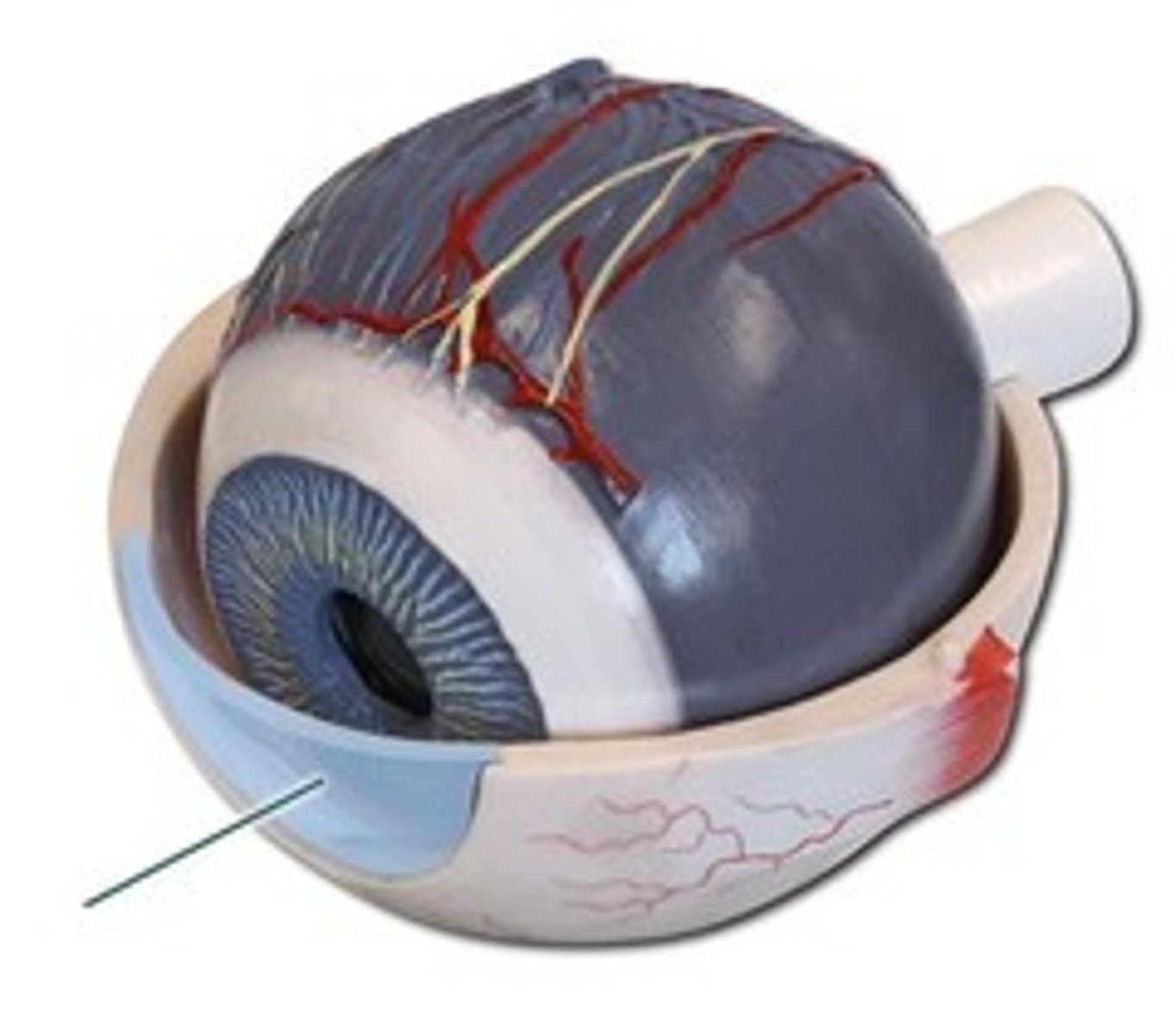
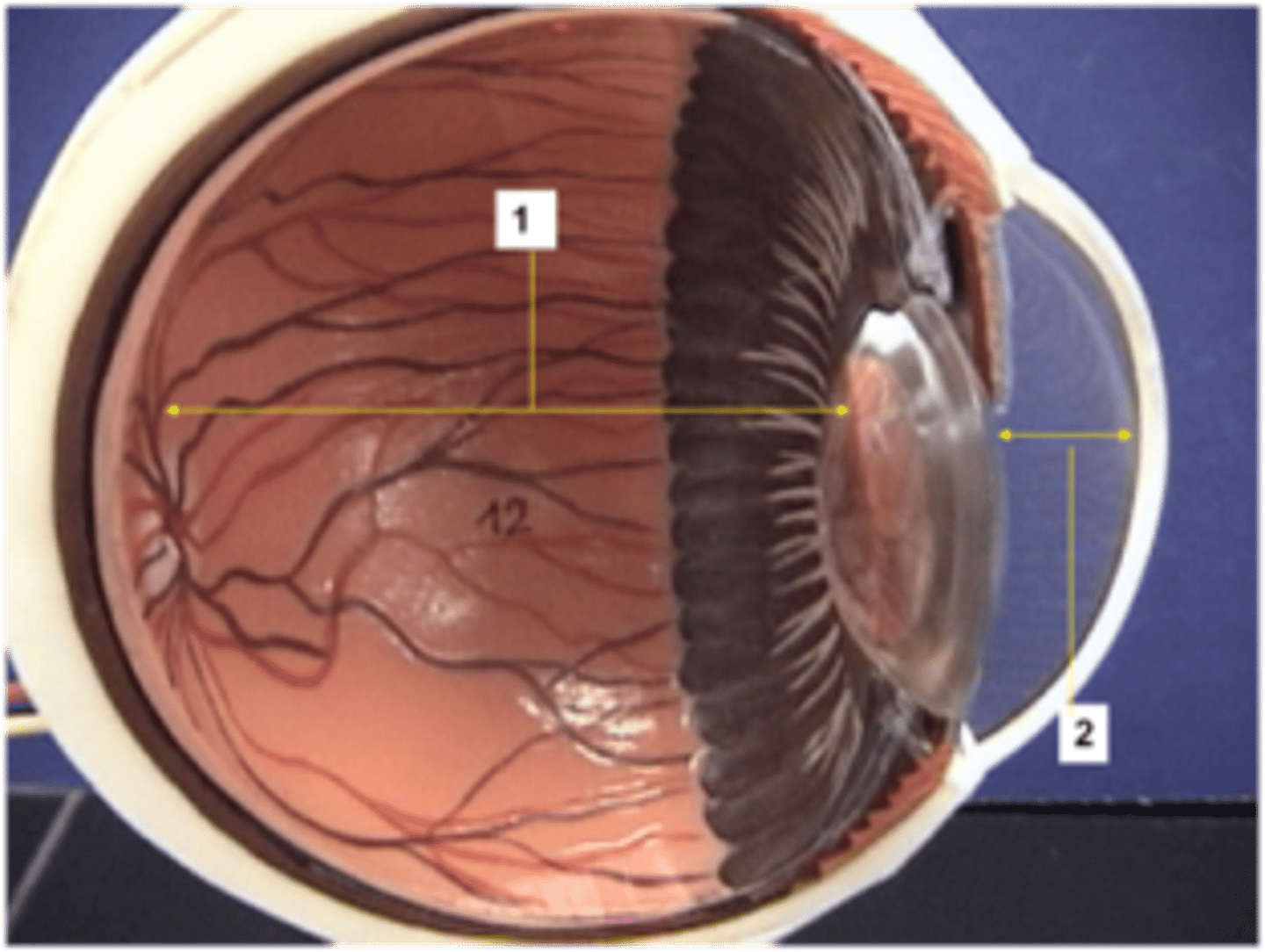
Cornea
Transparent anterior portion of sclera that refracts light
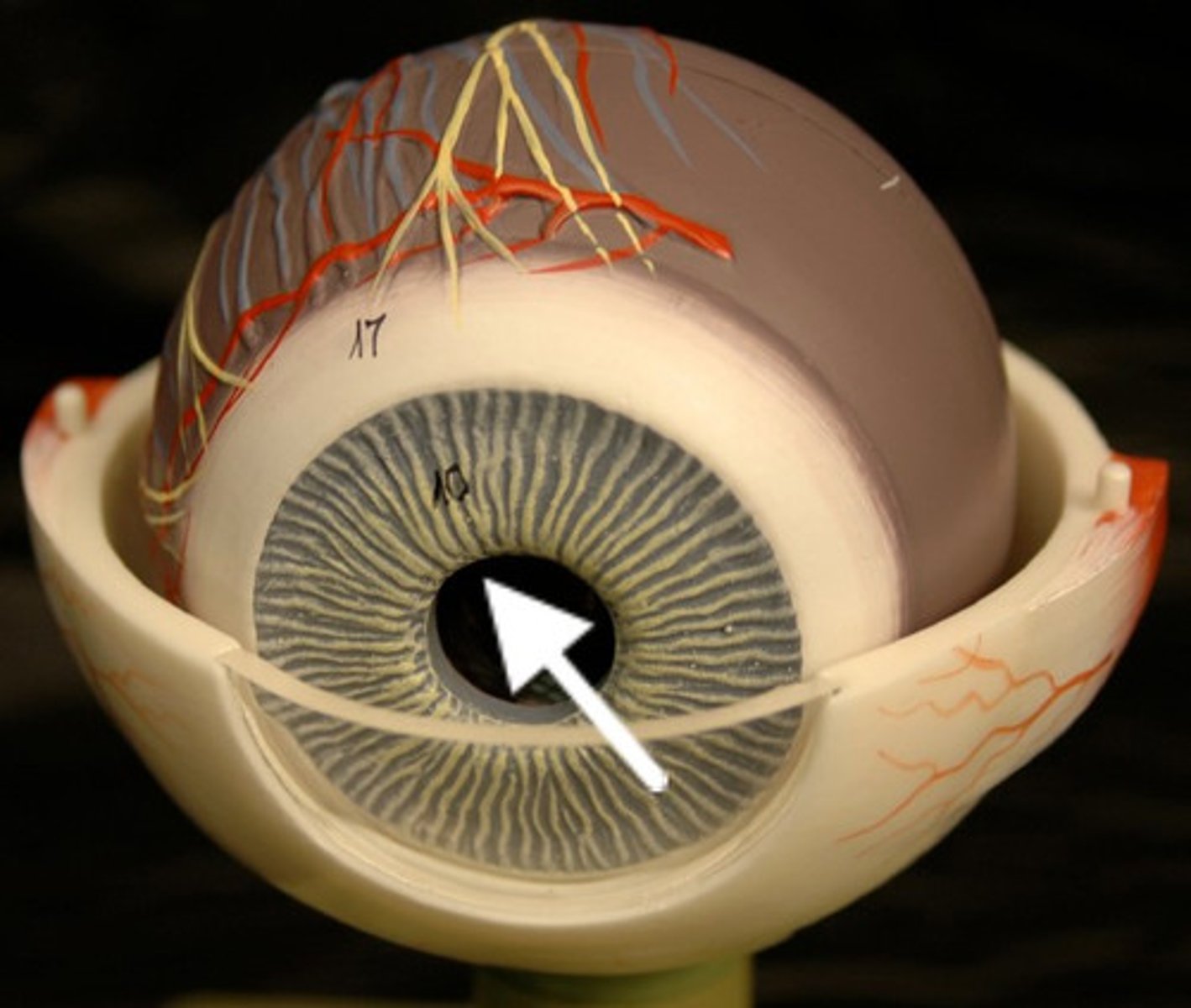
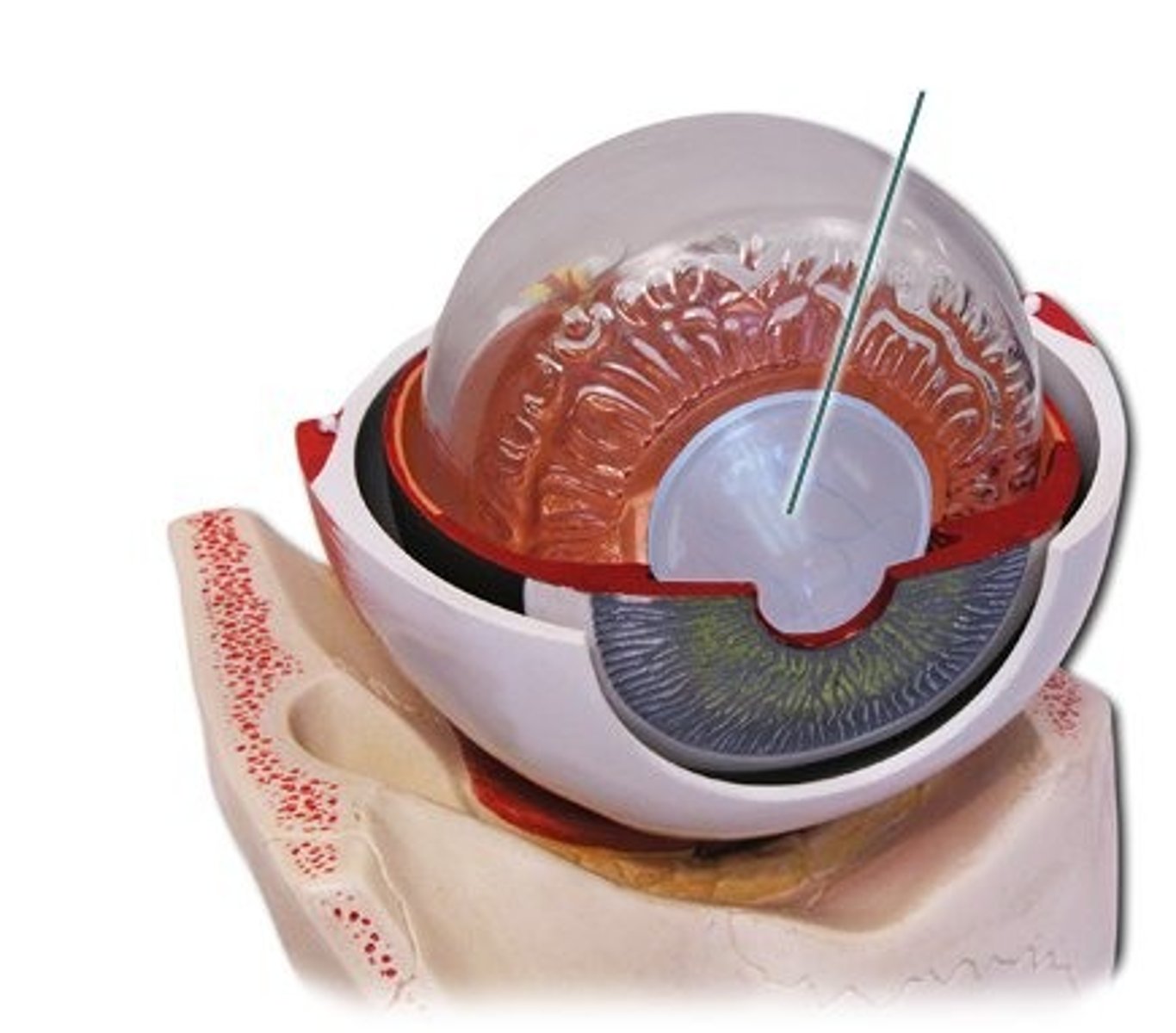
Pupil
Opening in the iris that controls light entry
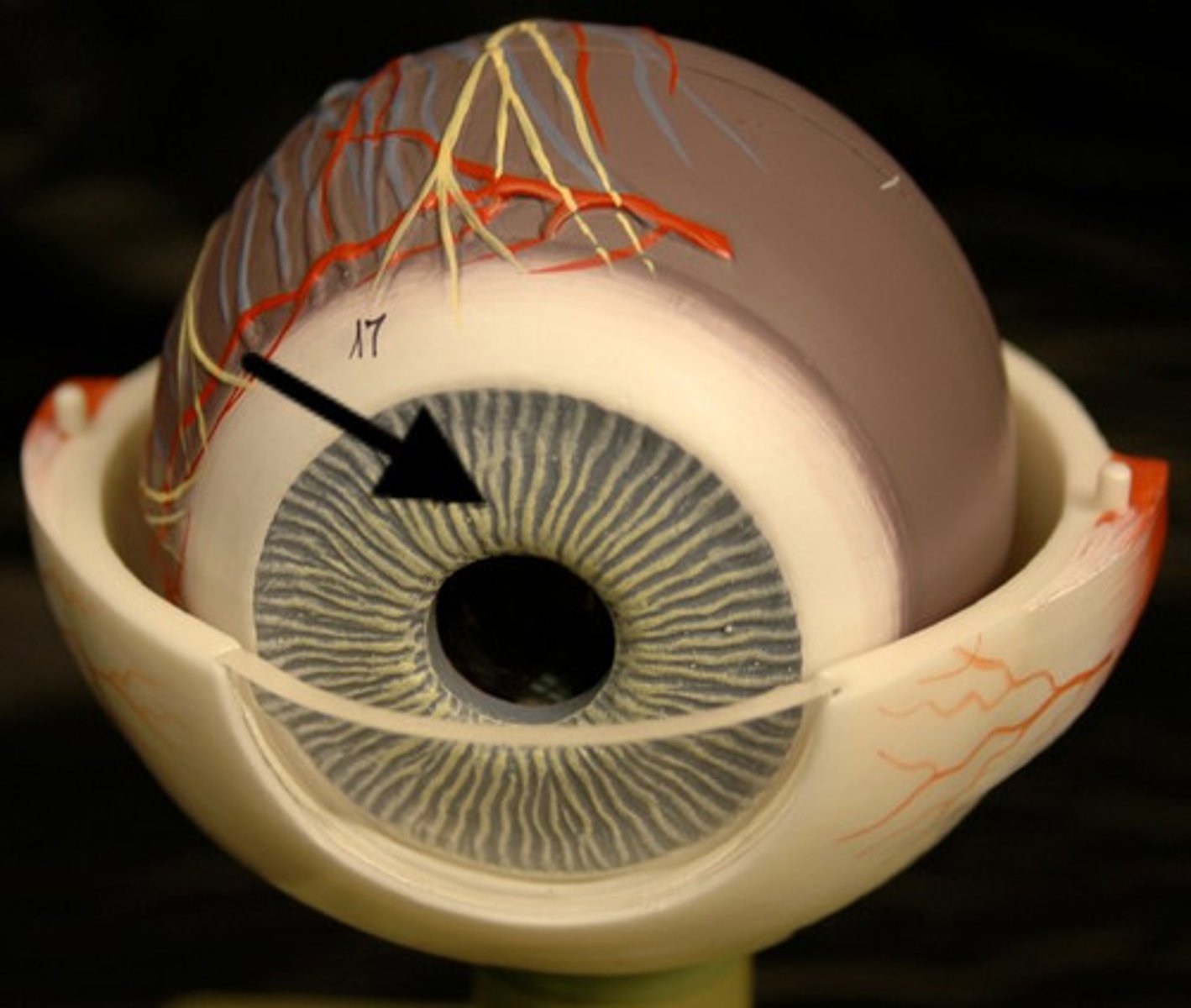
Iris
Colored part of the eye; regulates pupil size
Ciliary muscle
Changes shape of the lens for focusing
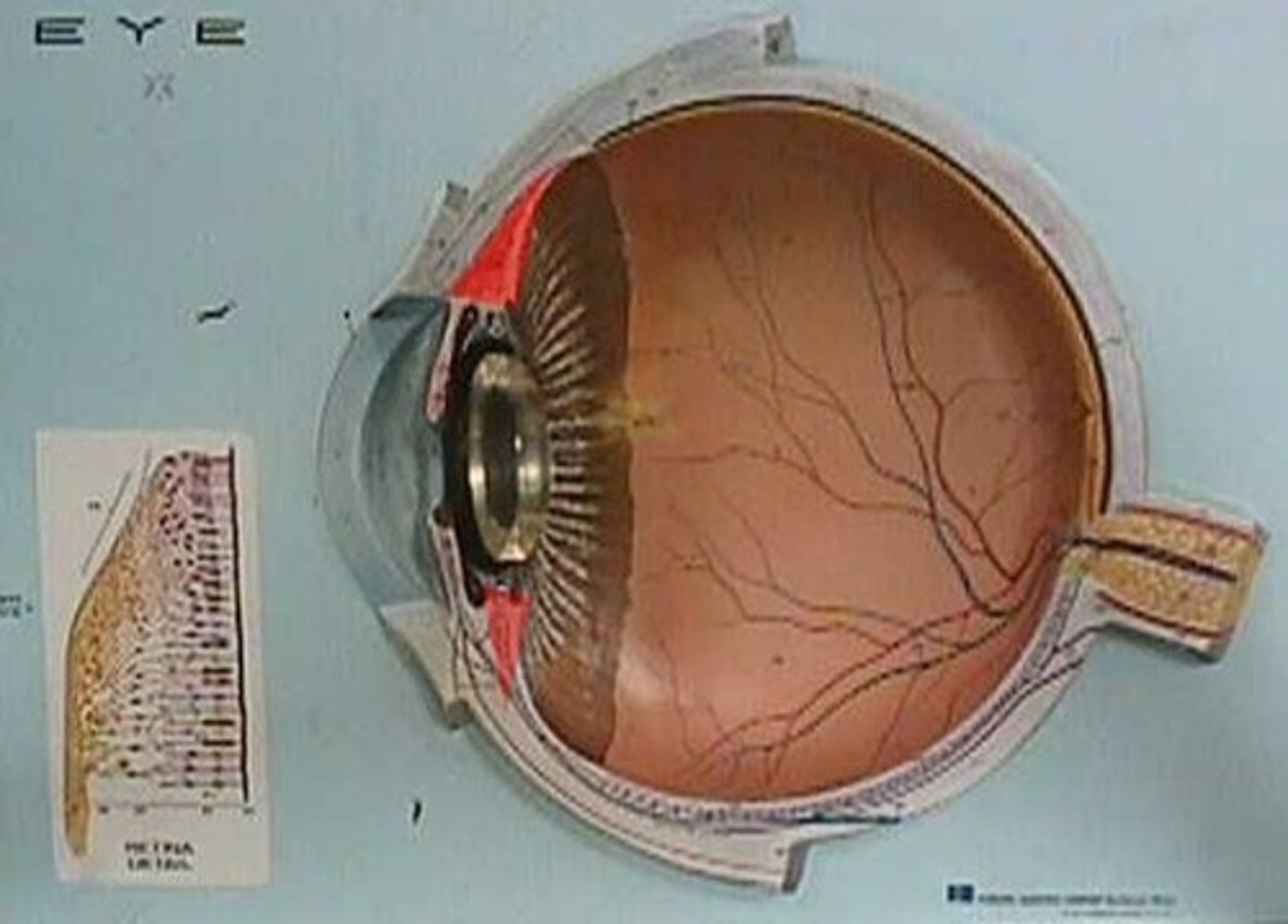
Lens
Transparent structure that focuses light on retina
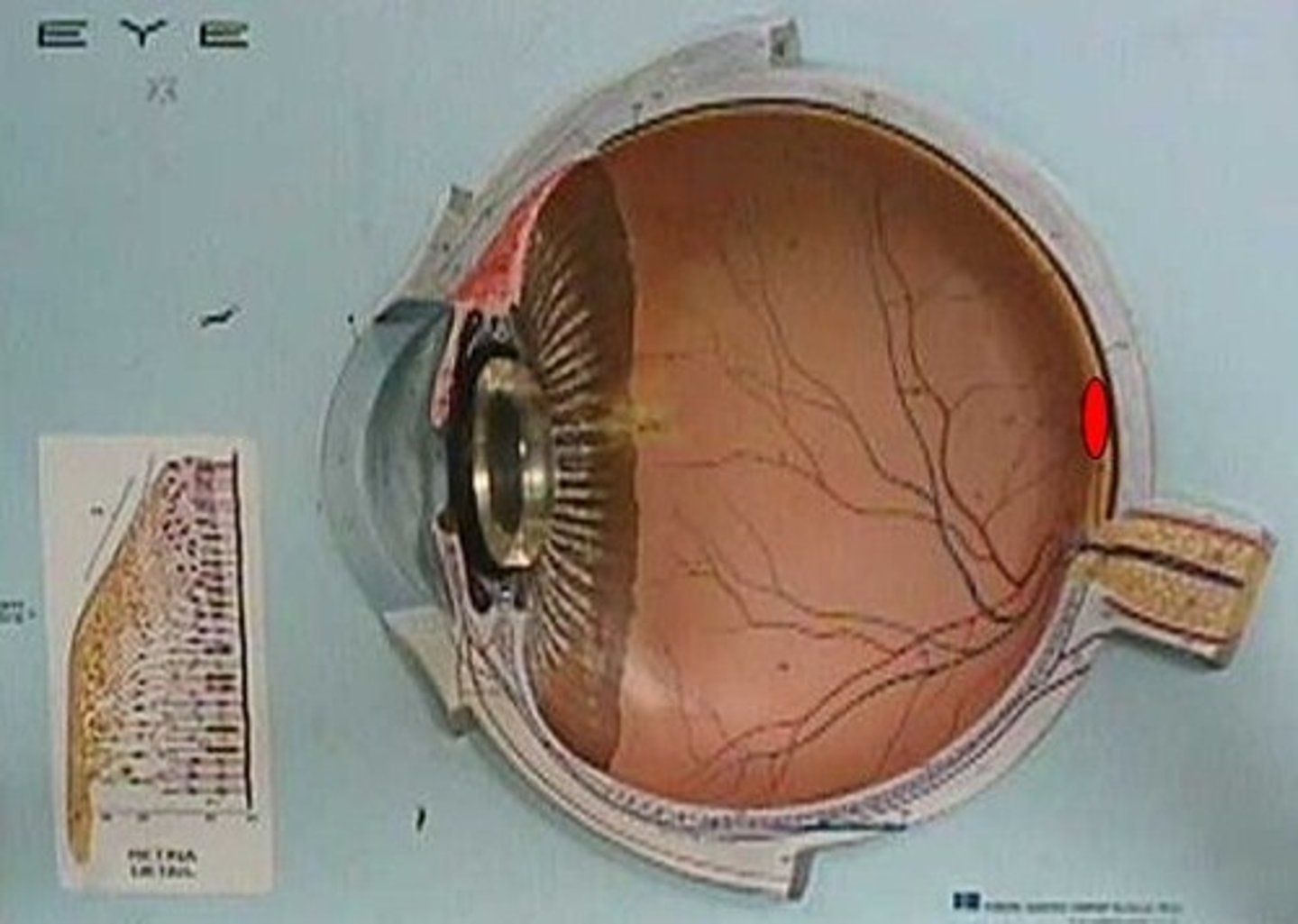
Macula
Area of retina for detailed central vision
Fovea centralis
Small depression in macula with highest visual acuity
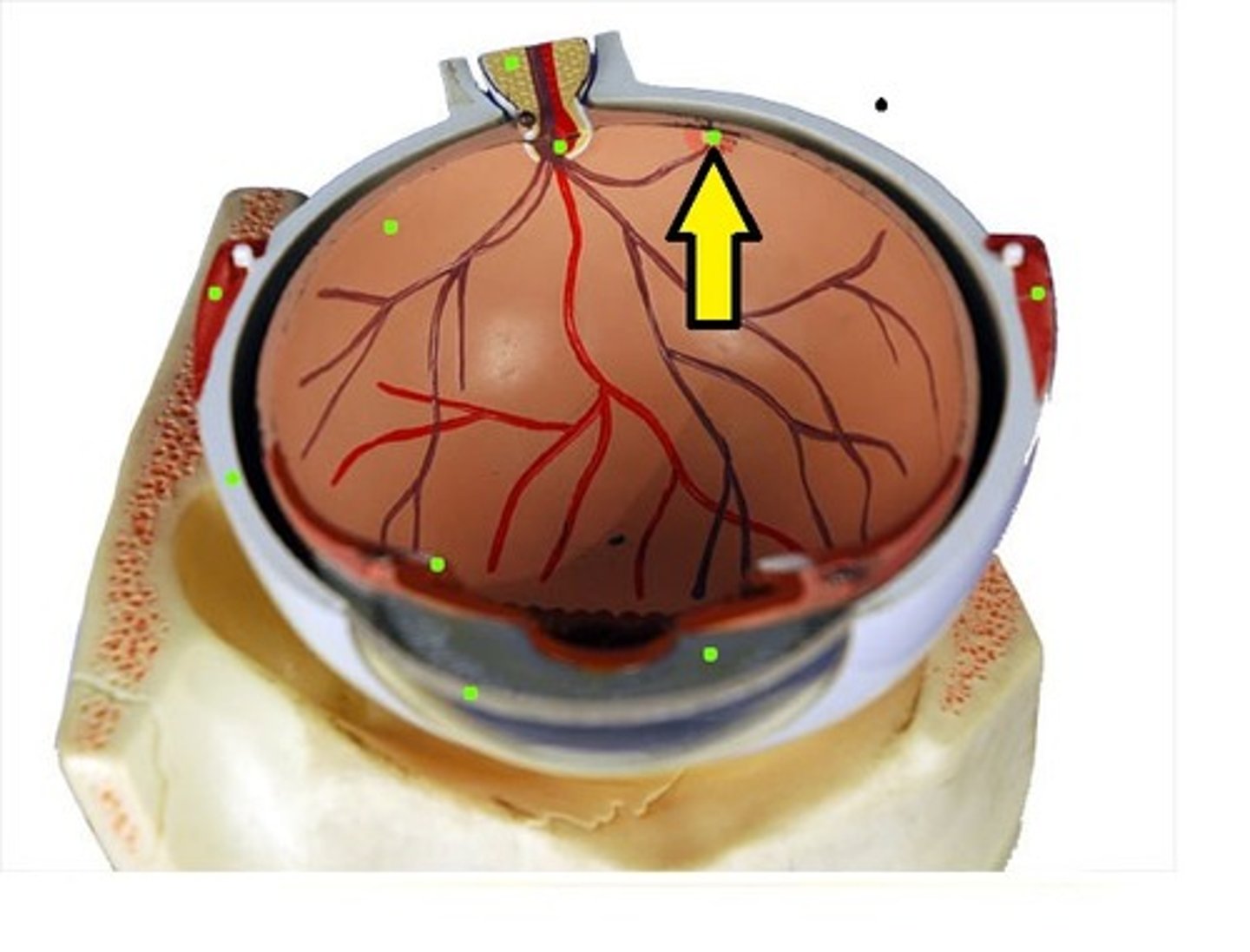
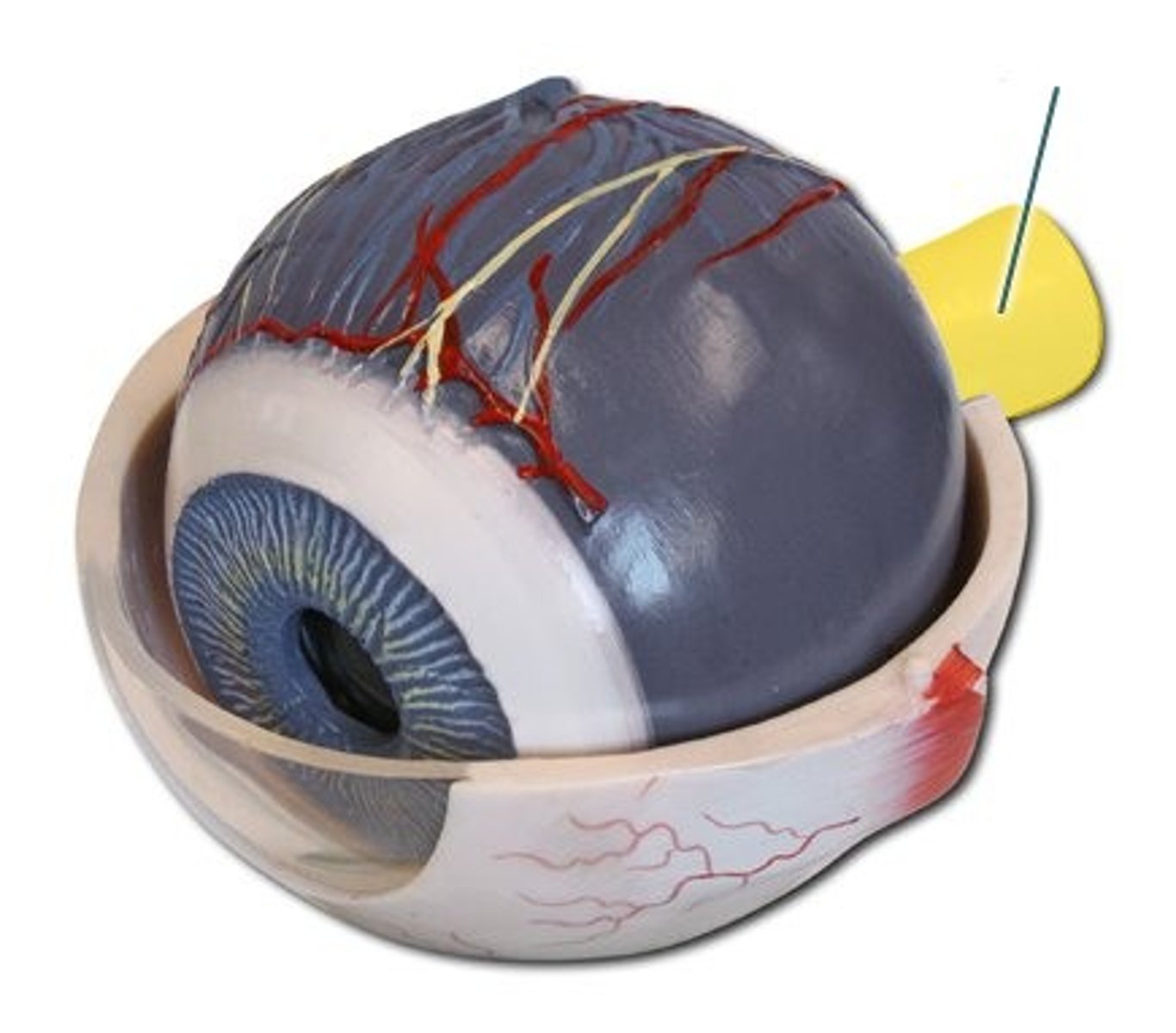
Optic disc
Blind spot; where optic nerve exits the eye
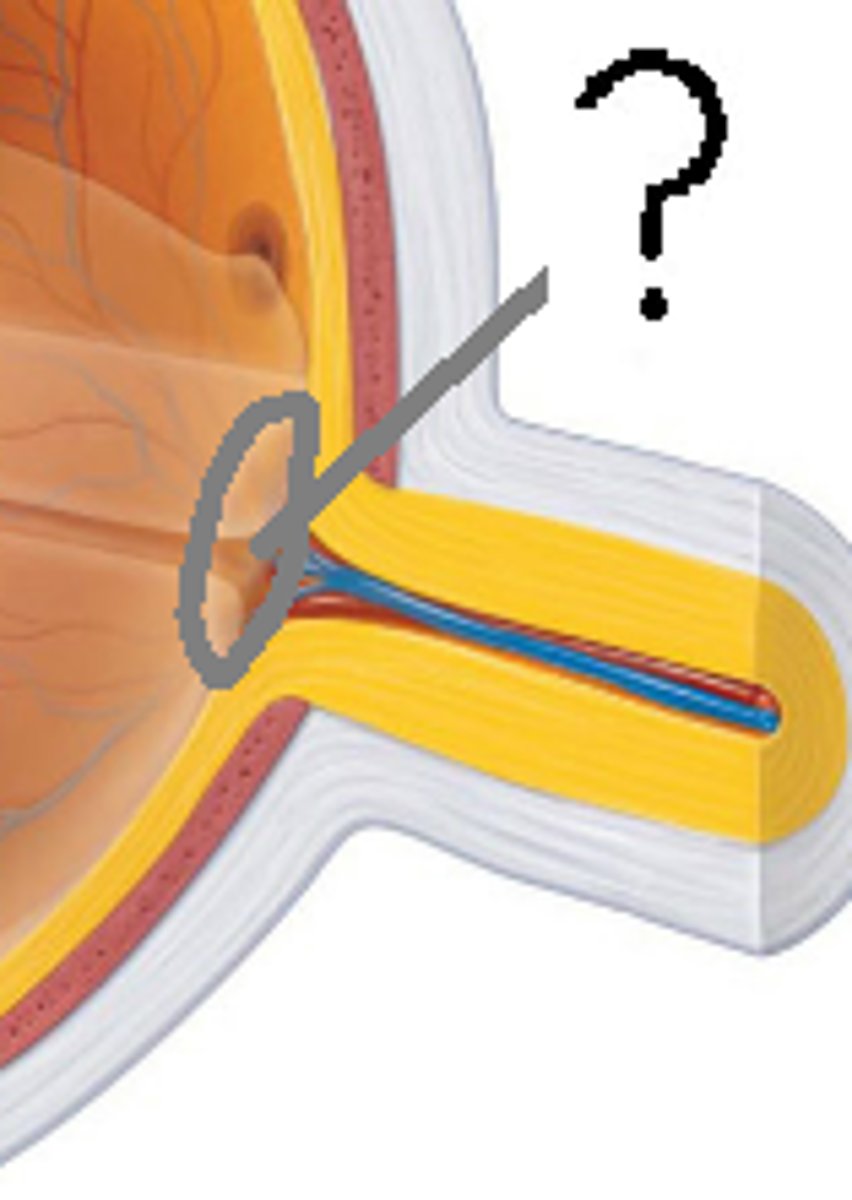
Optic nerve
Transmits visual signals from retina to brain
Anterior segment (aqueous humor)
Fluid-filled space between cornea and lens
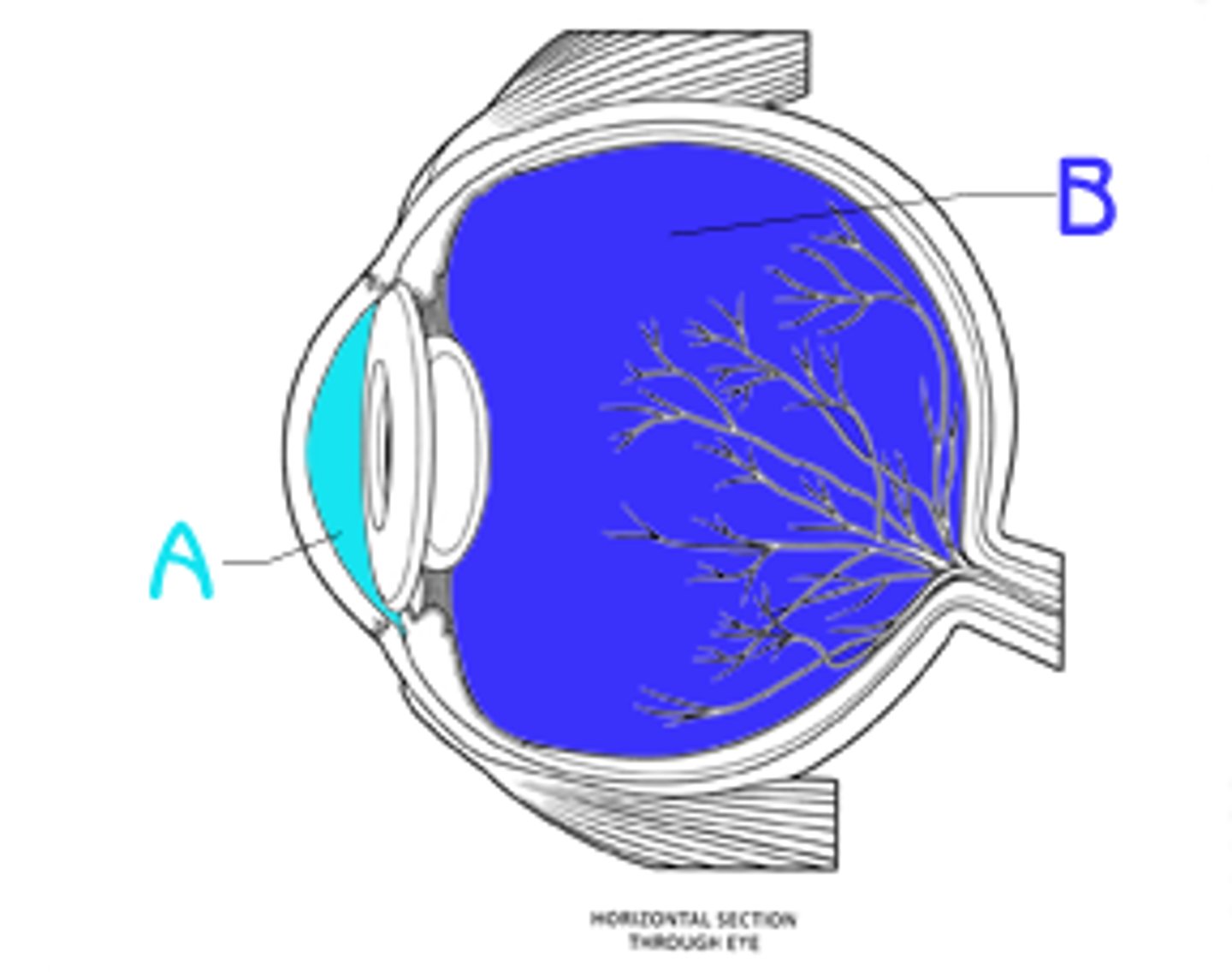
Posterior segment (vitreous humor)
Gel-filled space between lens and retina
Rods
Photoreceptors for dim light and peripheral vision
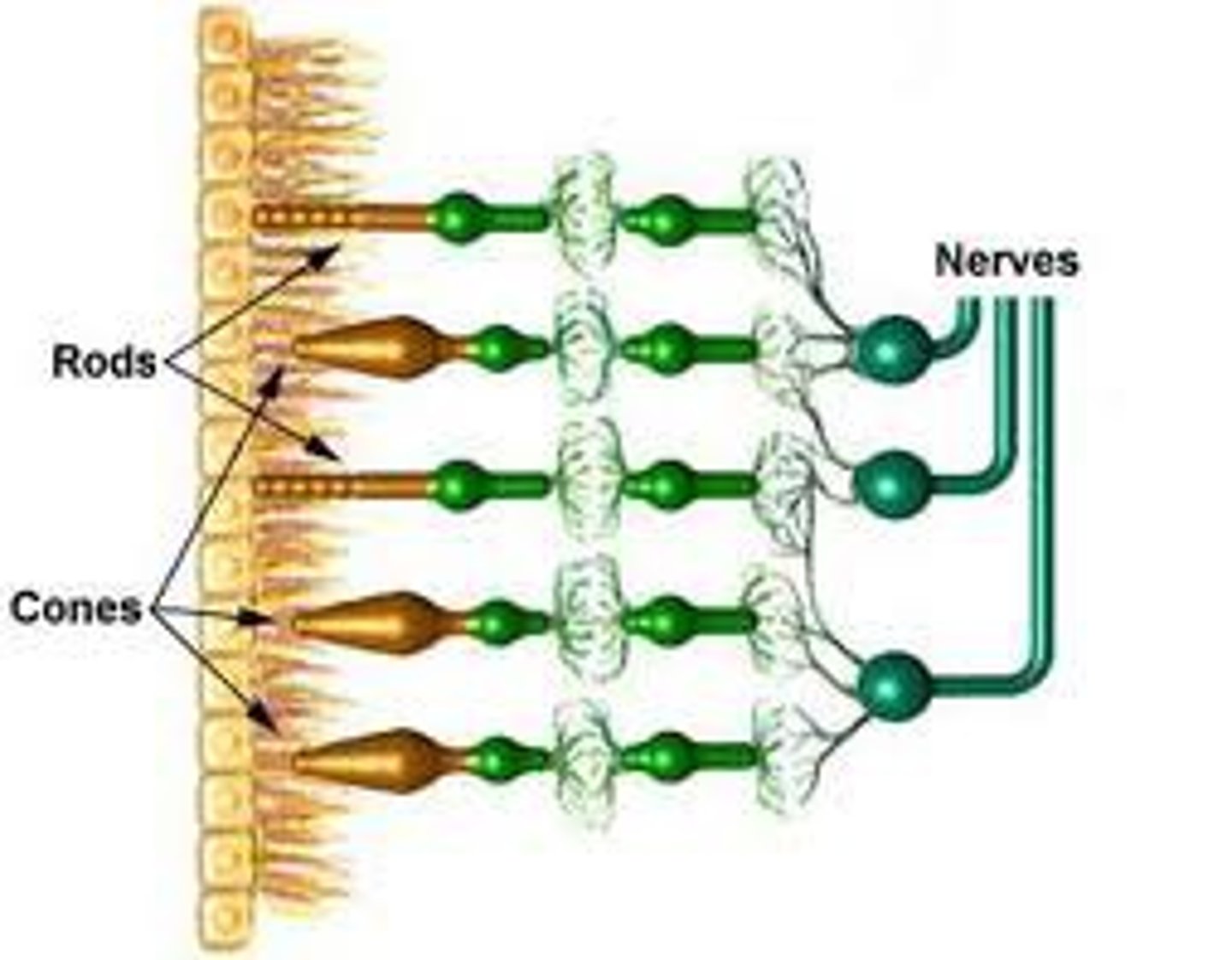
Cones
Photoreceptors for color vision and sharp detail
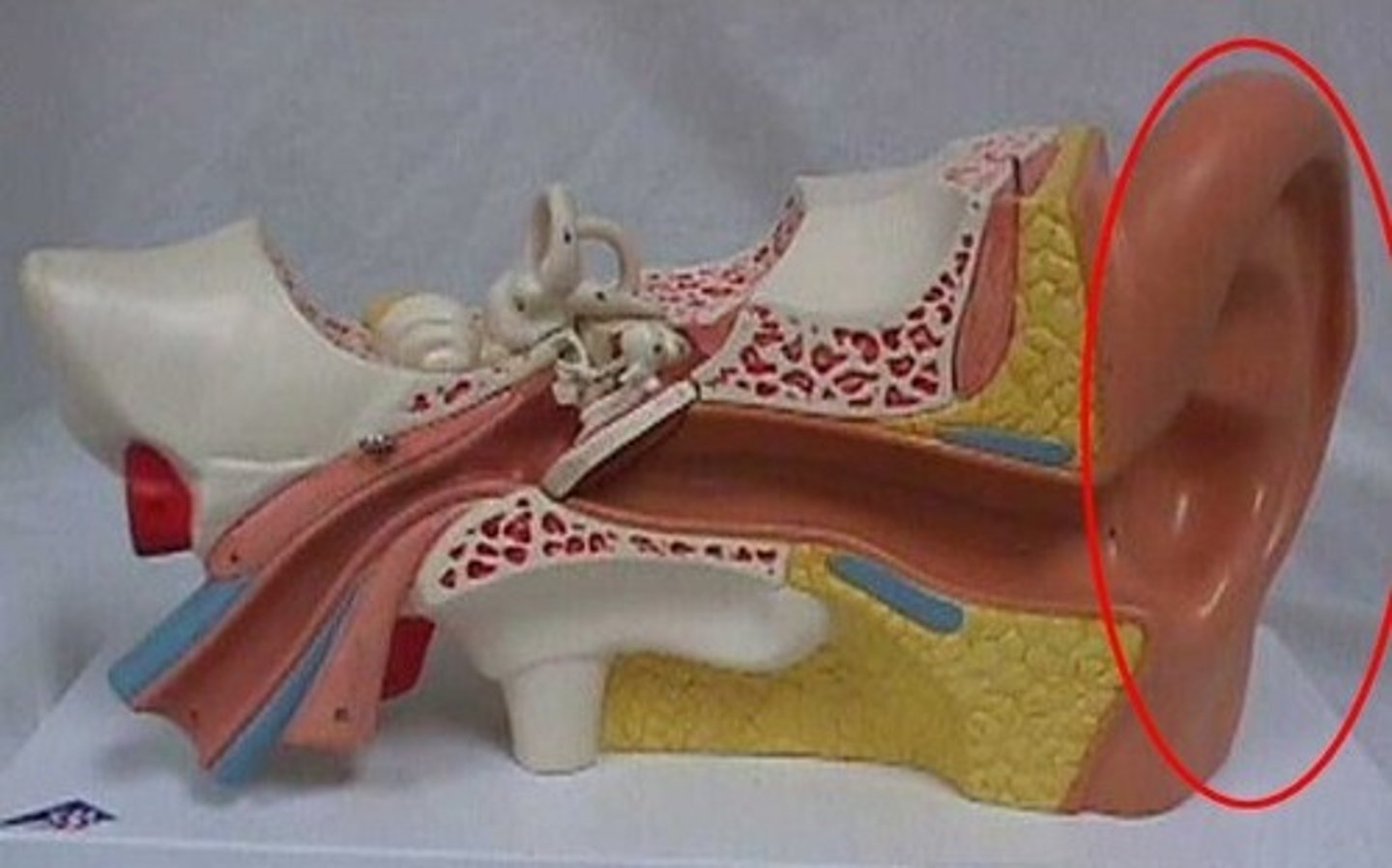
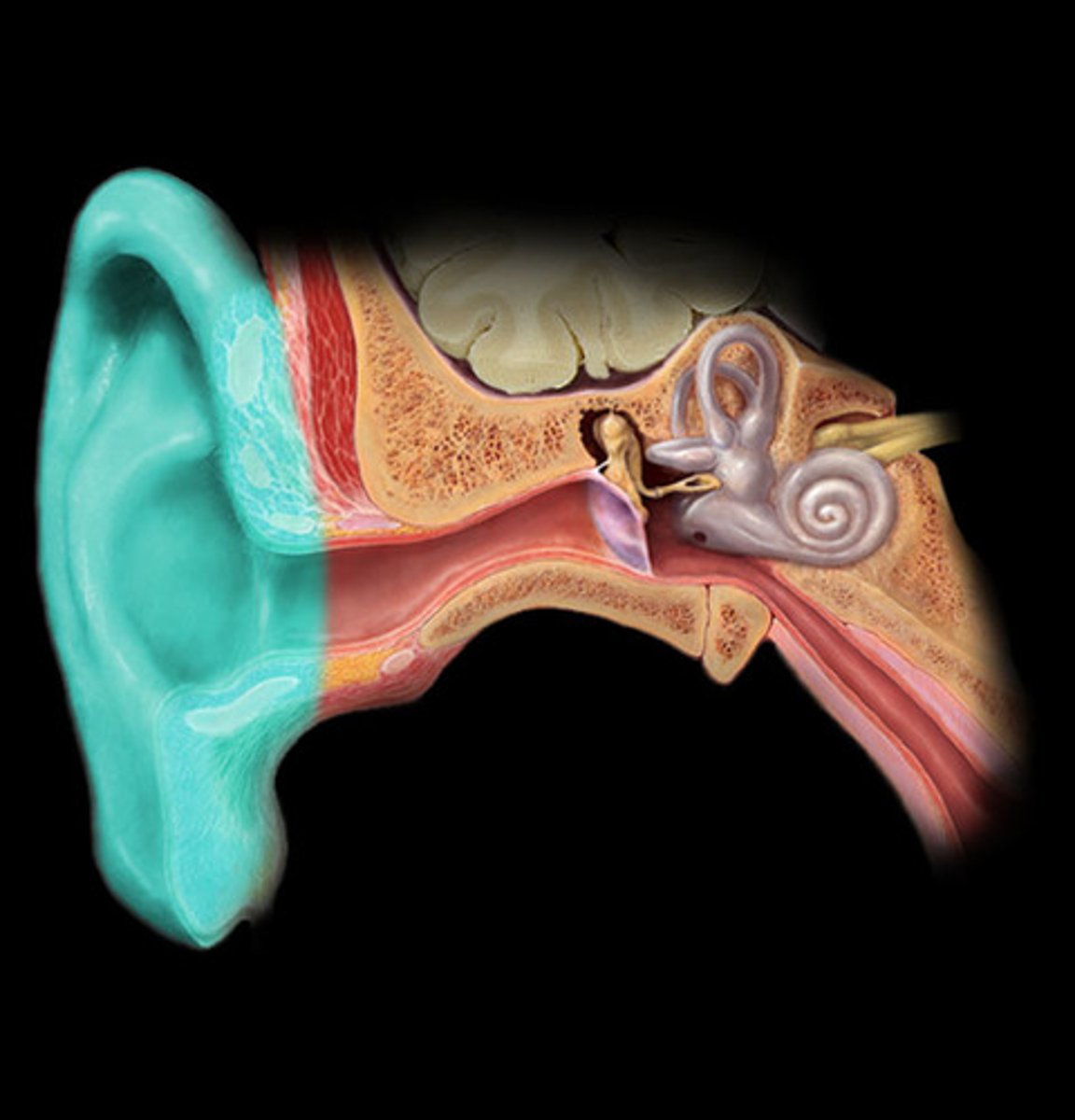
External ear
Collects and funnels sound waves to tympanic membrane
Middle ear
Air-filled space with ossicles that amplify sound
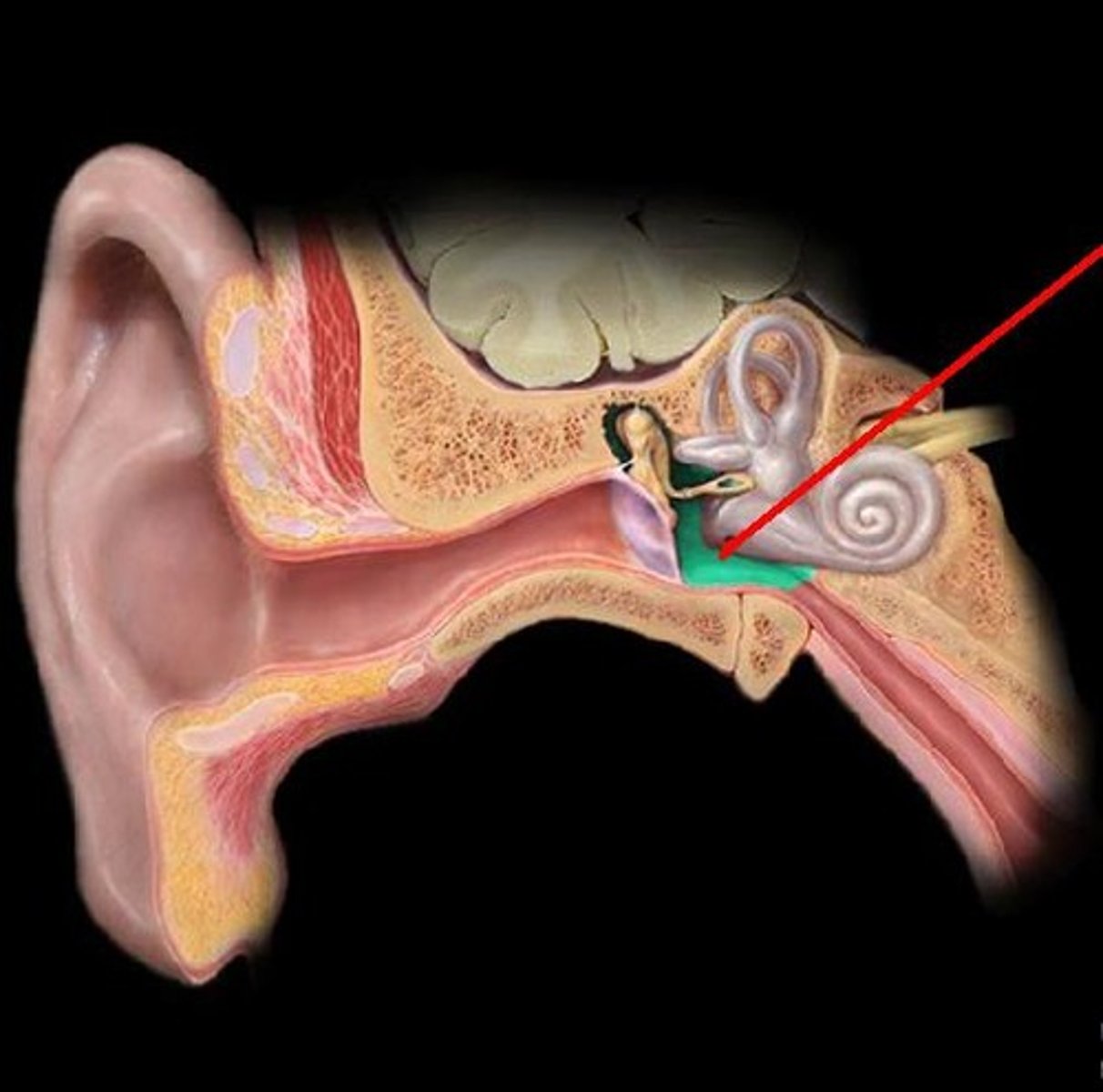
Inner ear
Contains sensory organs for hearing and balance
Auricle
External ear structure that funnels sound into auditory canal
External acoustic meatus
Ear canal; conducts sound to tympanic membrane
Tympanic membrane
Eardrum; vibrates with sound waves
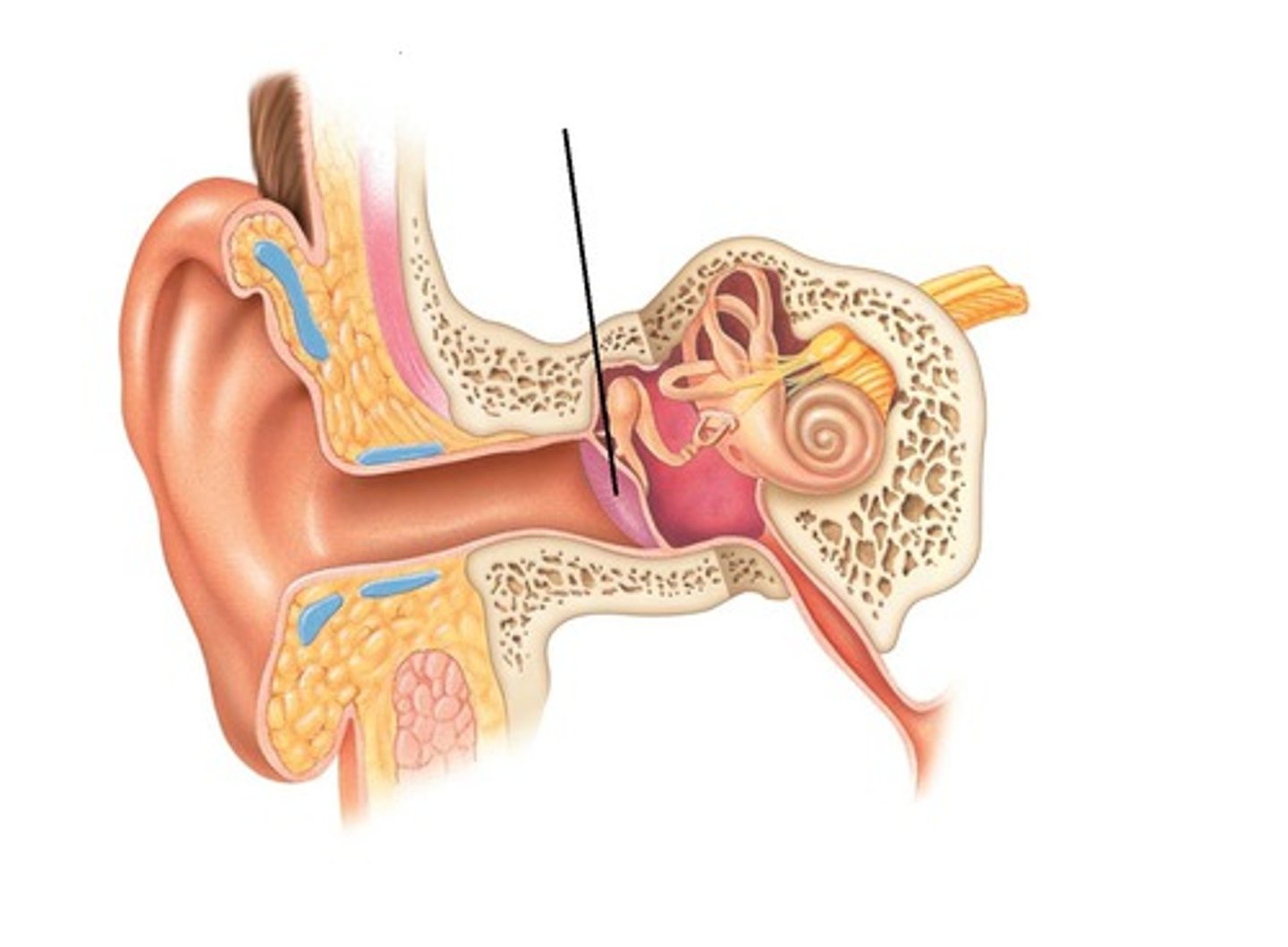
Malleus
First ossicle; transmits vibrations from tympanic membrane to incus
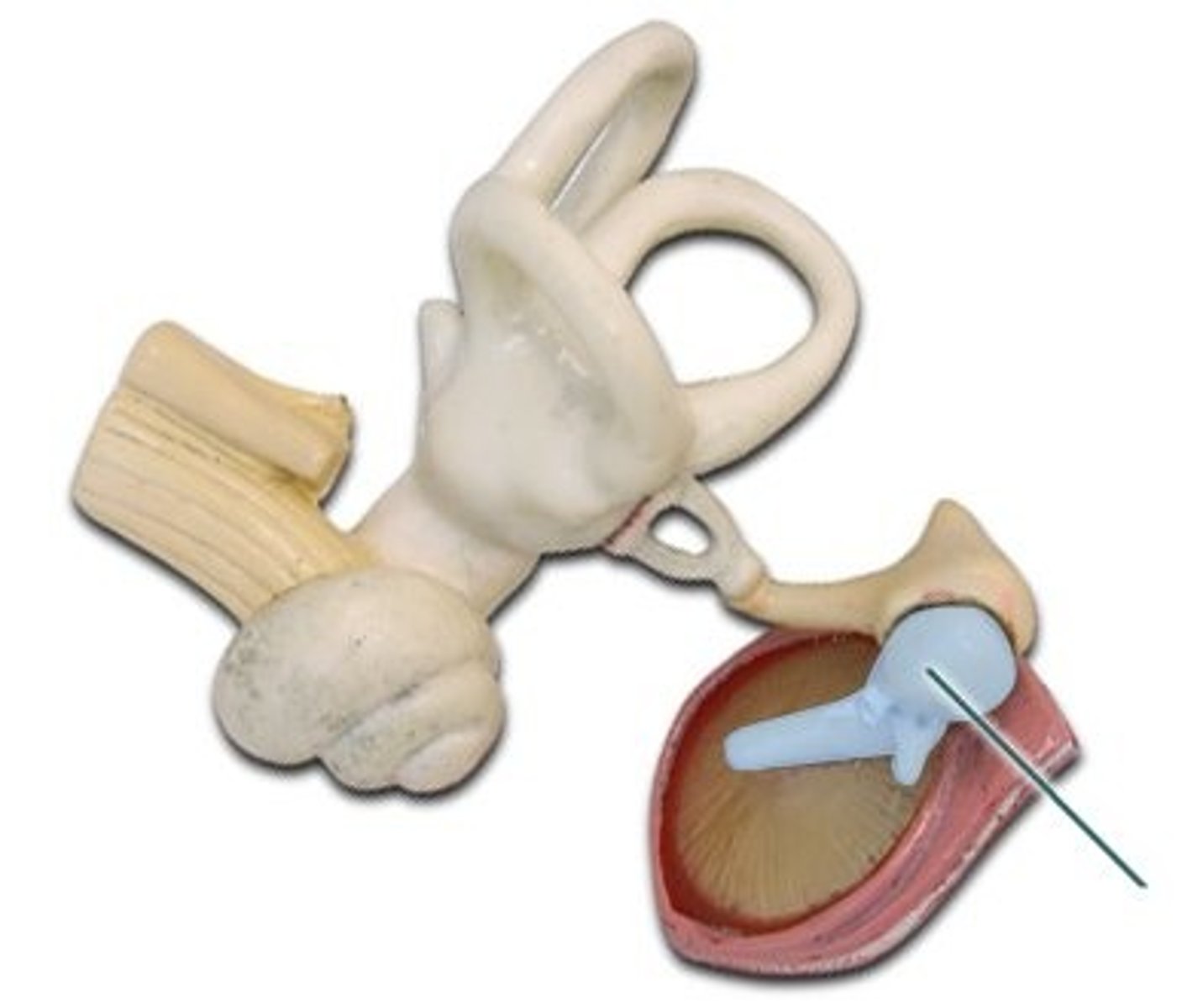
Incus
Middle ossicle; transmits vibrations from malleus to stapes
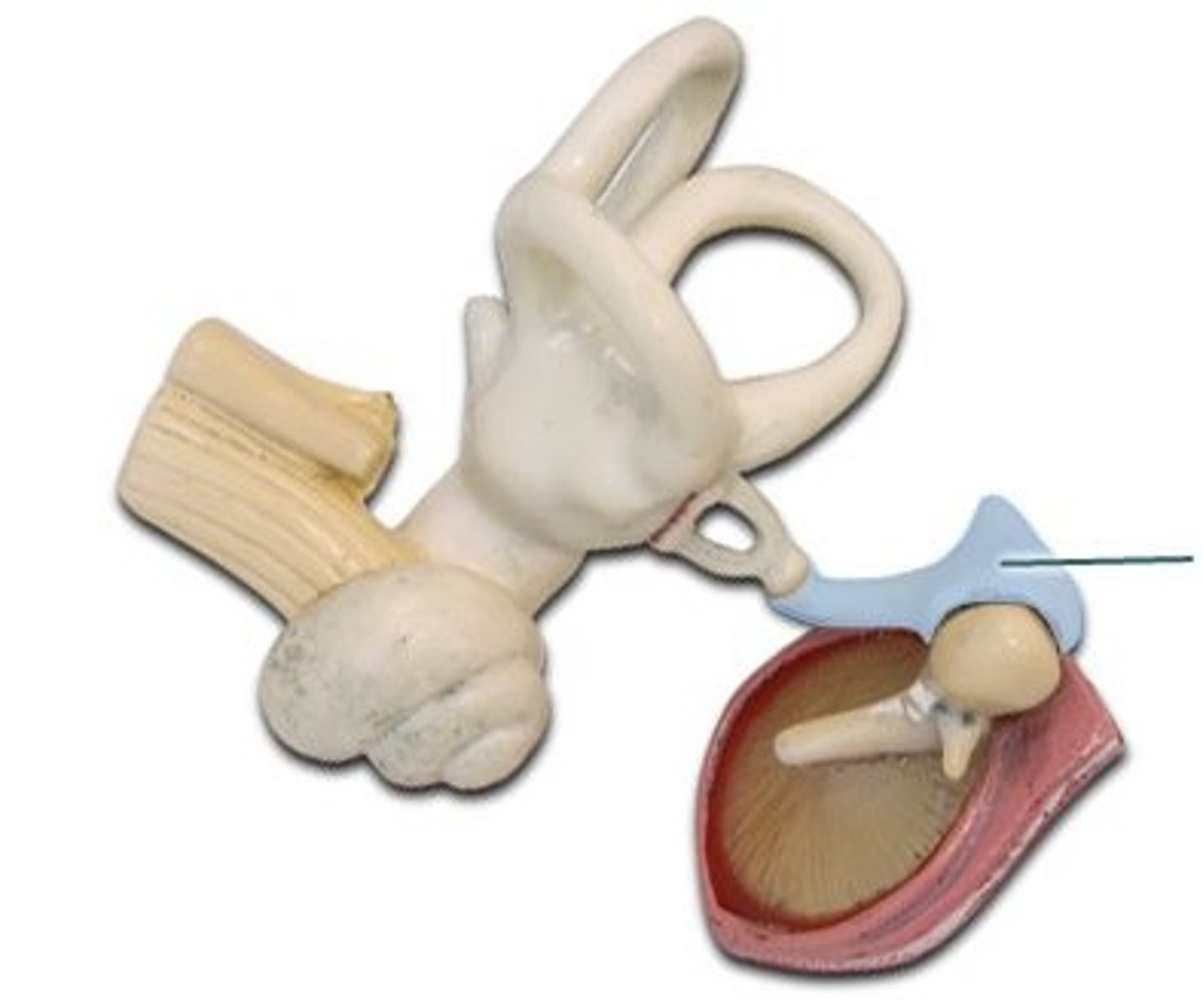
Stapes
Last ossicle; transmits vibrations to oval window
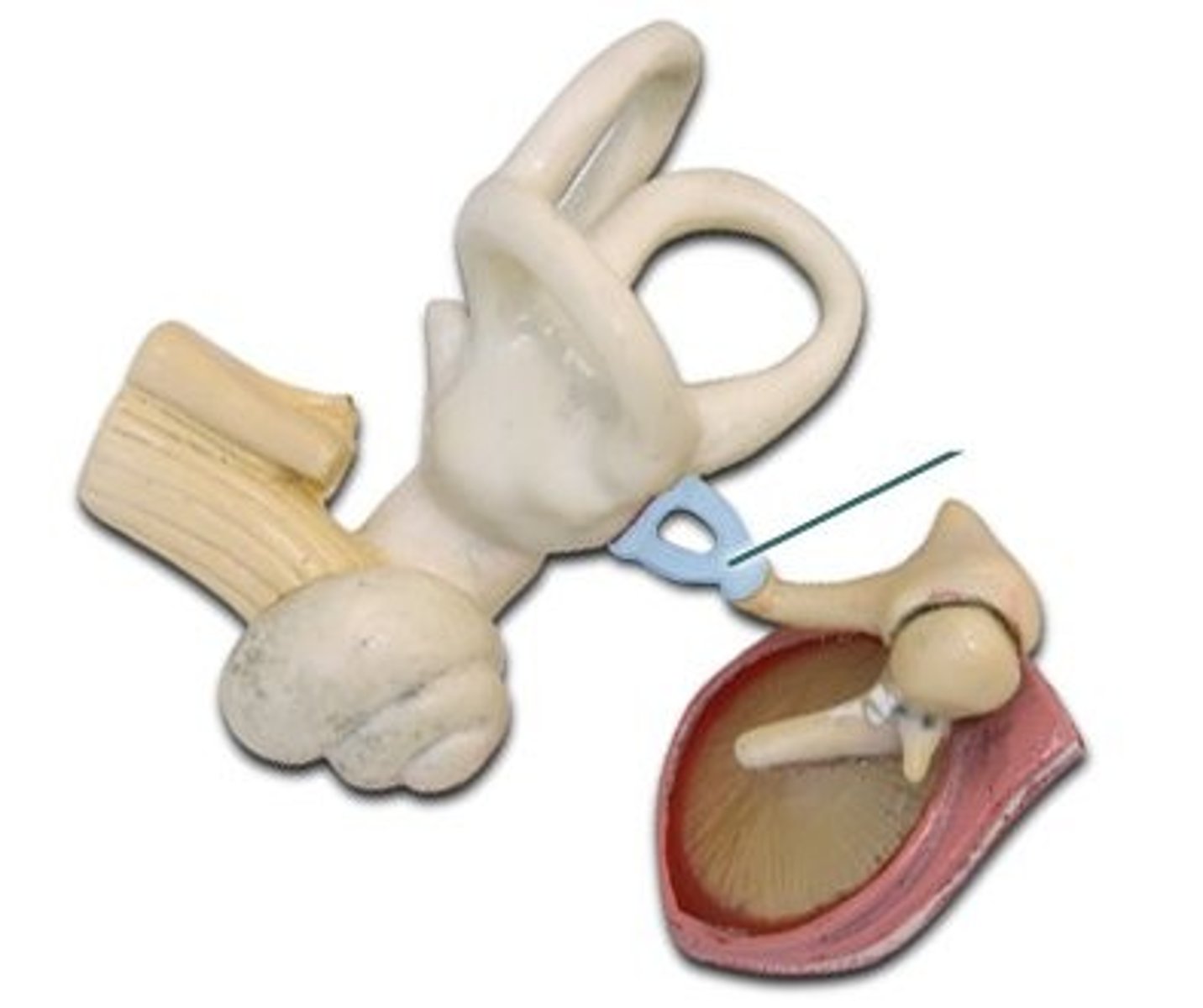
Auditory tube
Equalizes air pressure between middle ear and throat
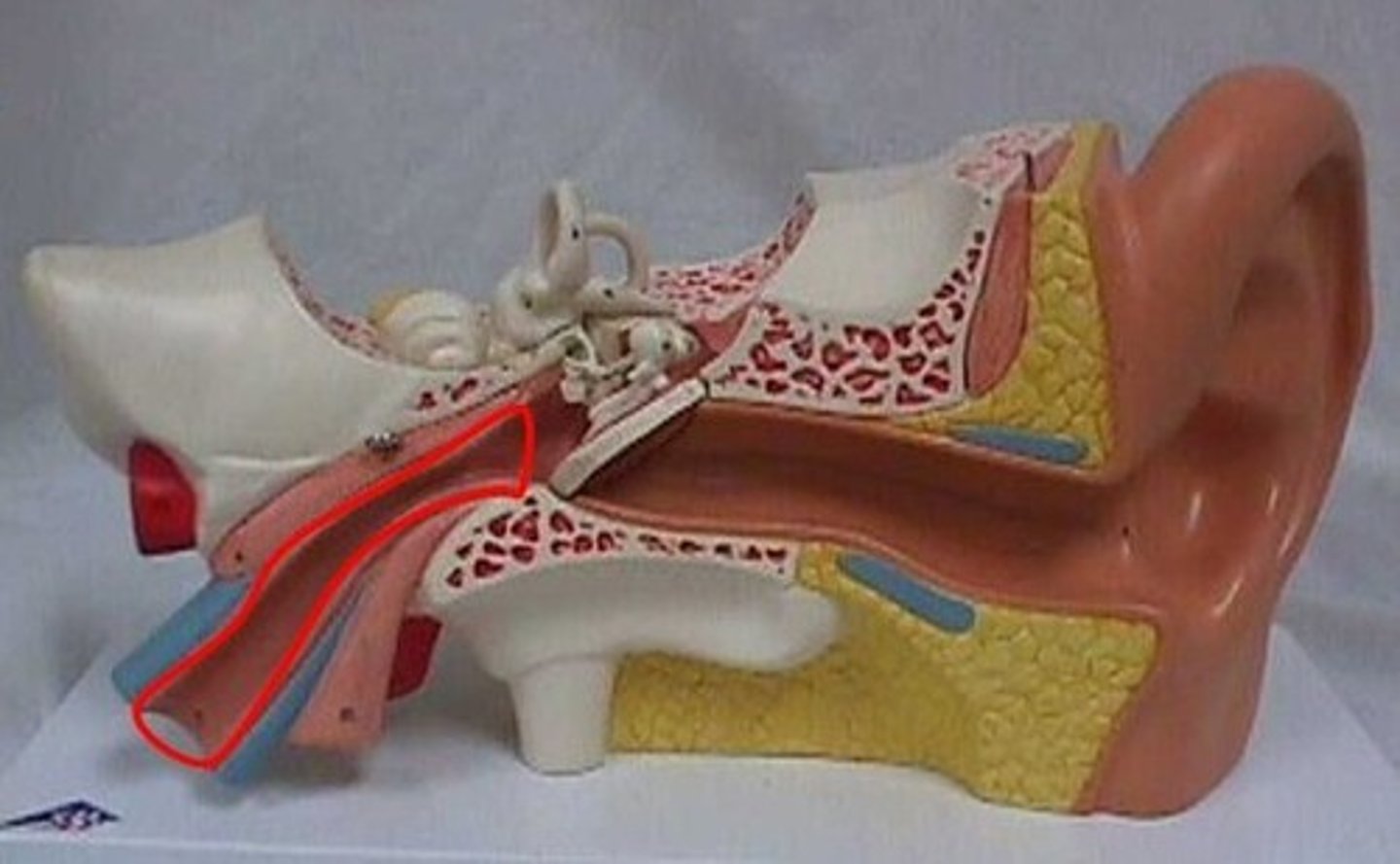
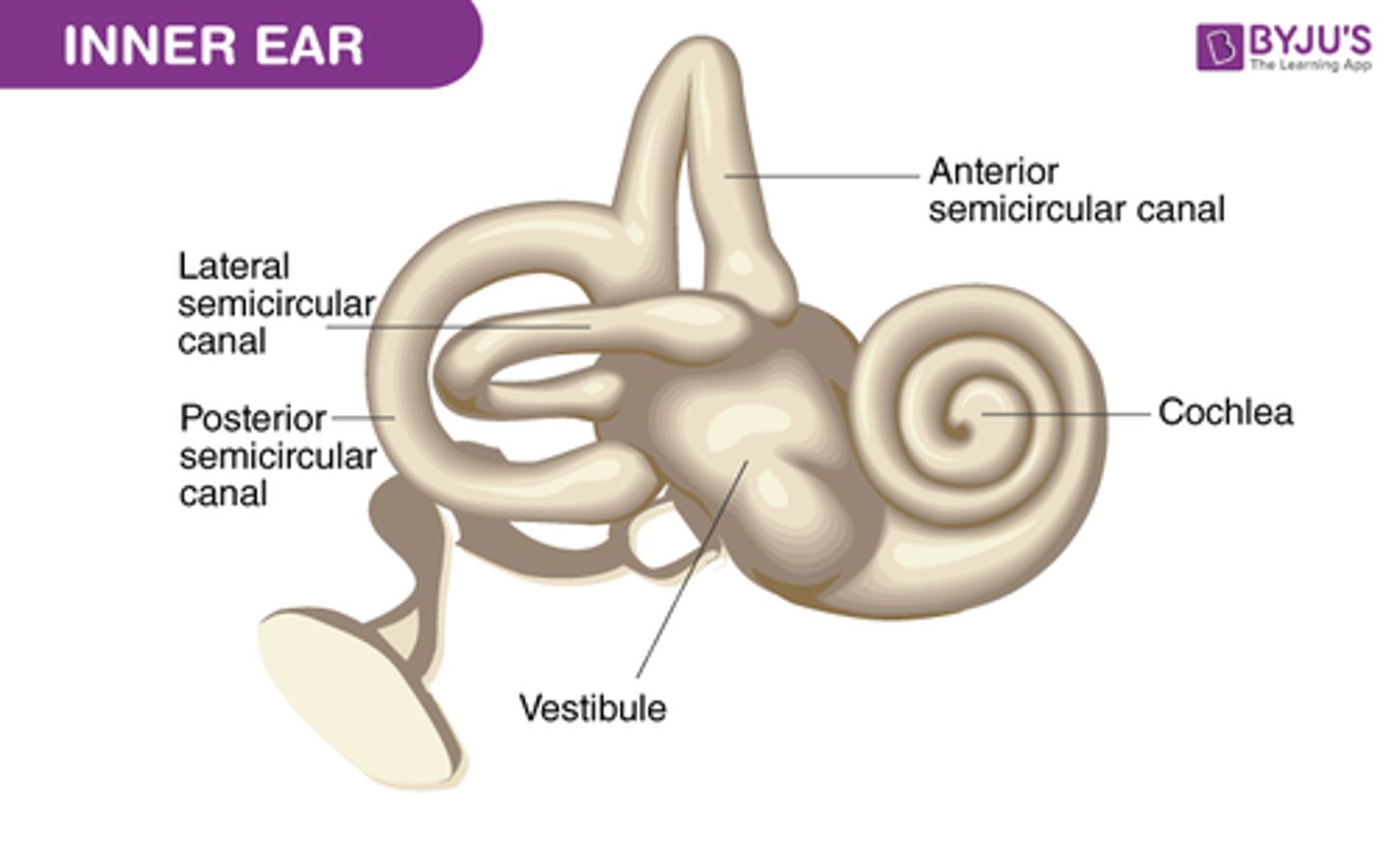
Semicircular canals
Detect rotational equilibrium (dynamic balance)
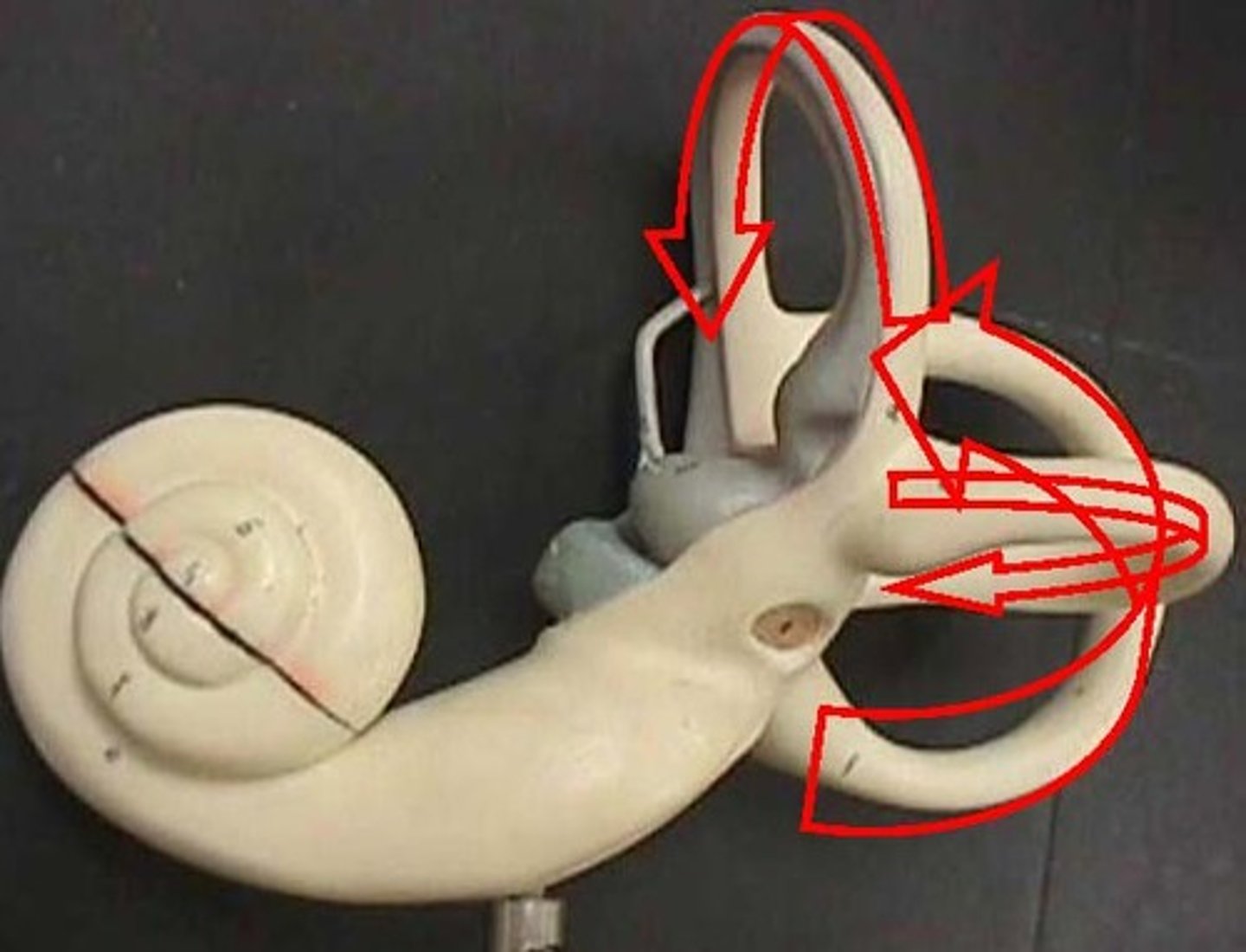
Vestibule
Detects static equilibrium and linear acceleration
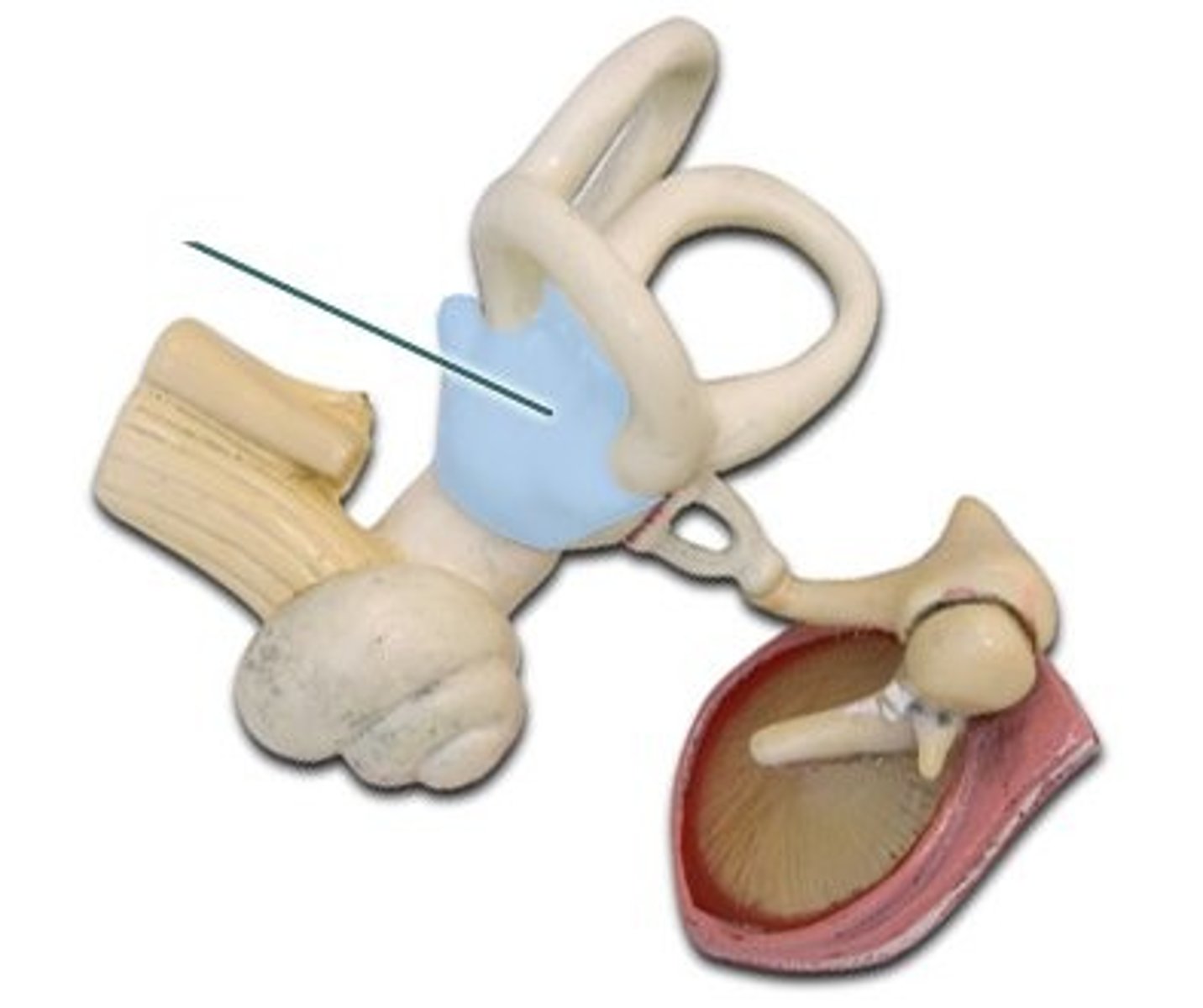
Cochlea
Contains organ of Corti; responsible for hearing
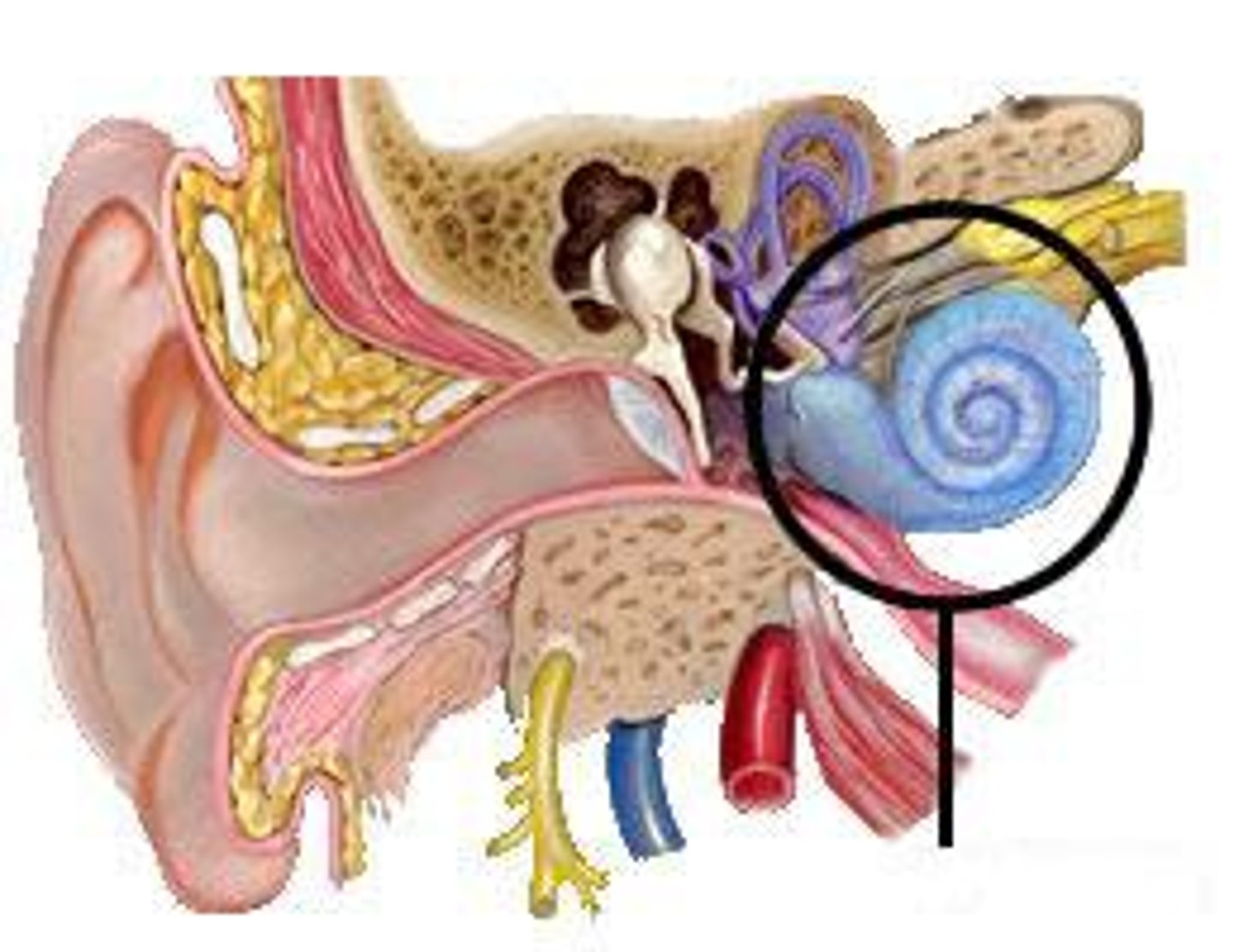
Vestibulocochlear nerve
Carries hearing and balance signals to brain
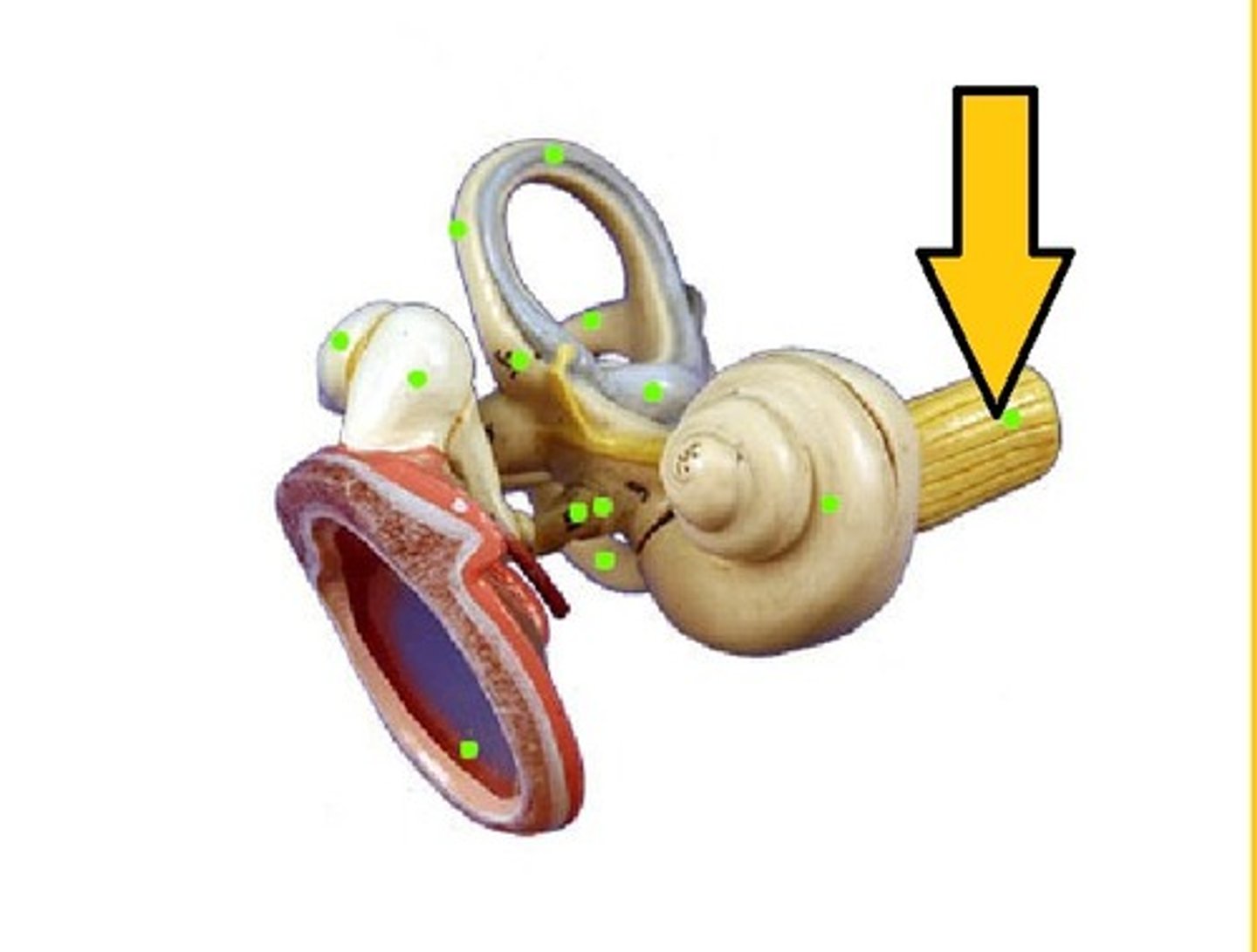
Round window
Relieves pressure in cochlea after sound waves pass through
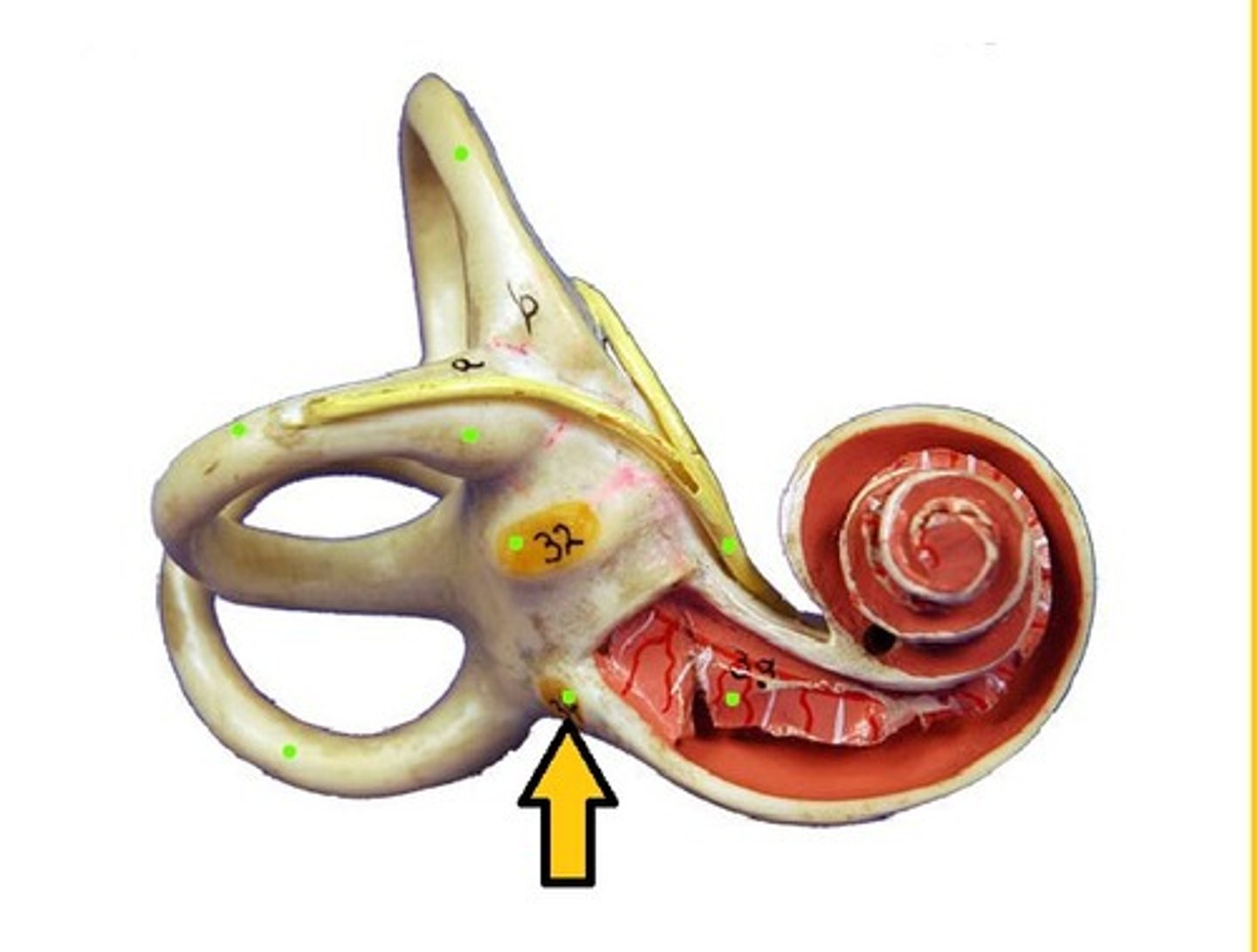
Oval window
Receives vibrations from stapes into cochlea
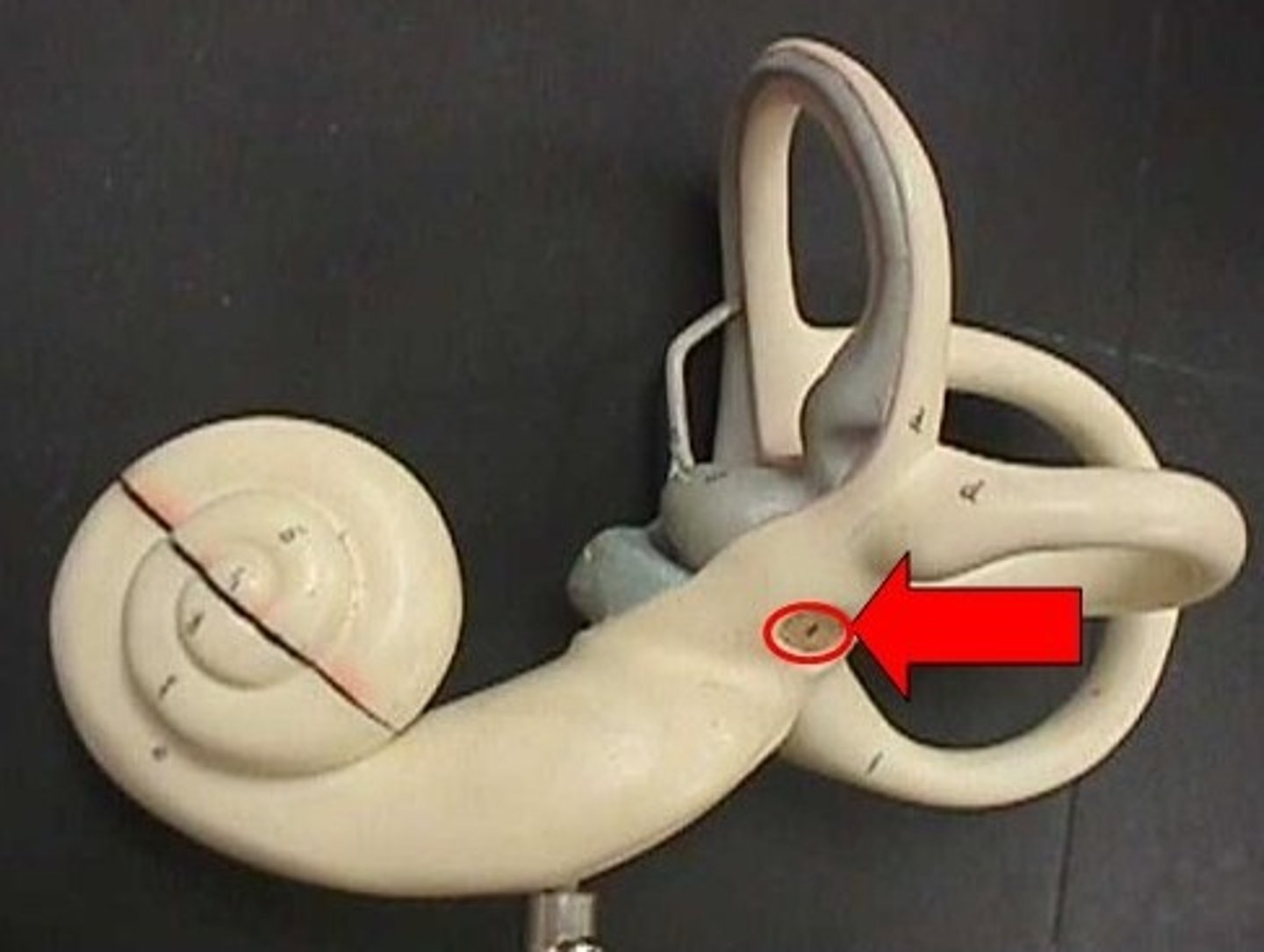
Scala vestibuli
Upper chamber of cochlea; filled with perilymph
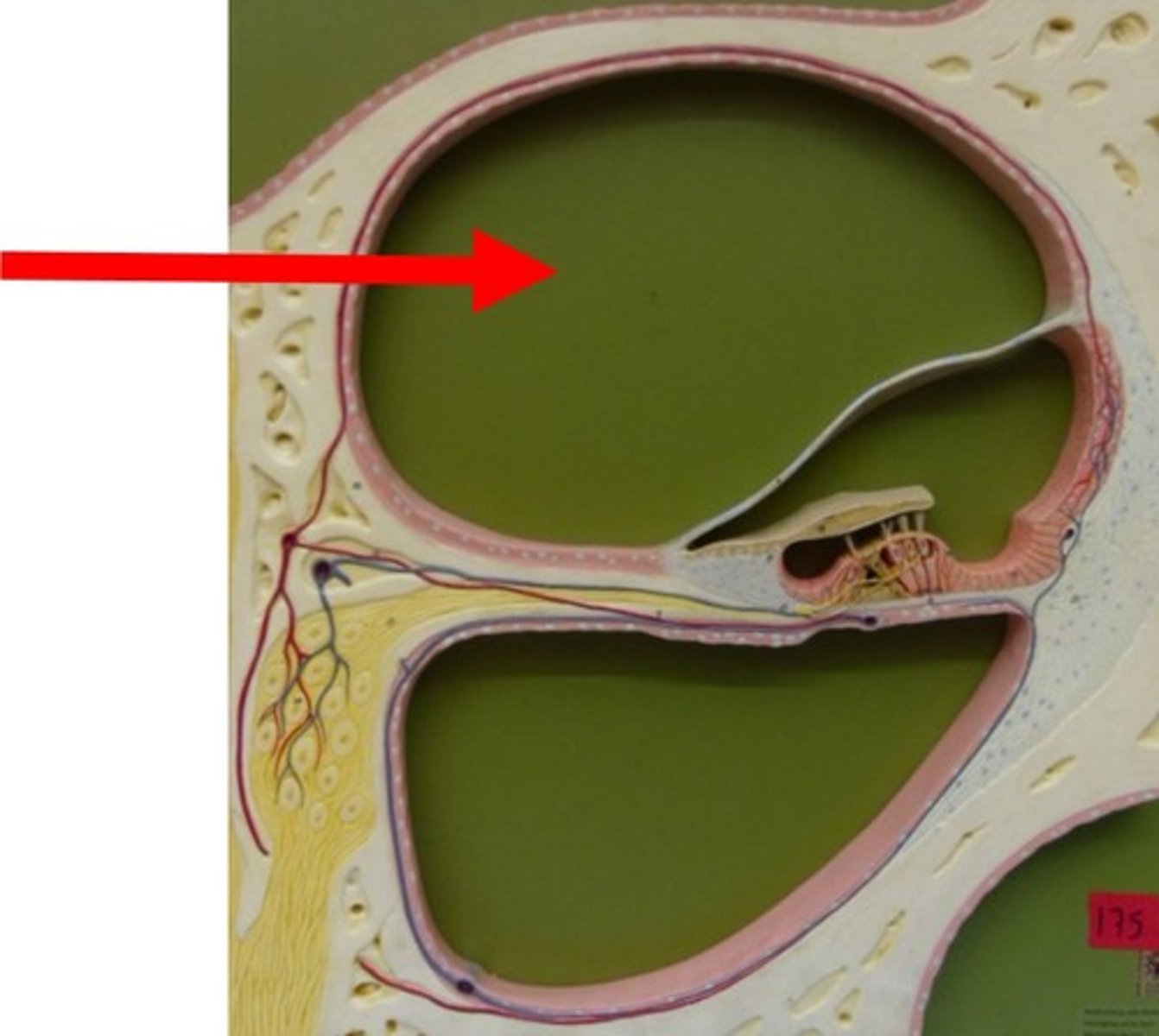
Cochlear duct
Middle chamber; contains endolymph and organ of Corti
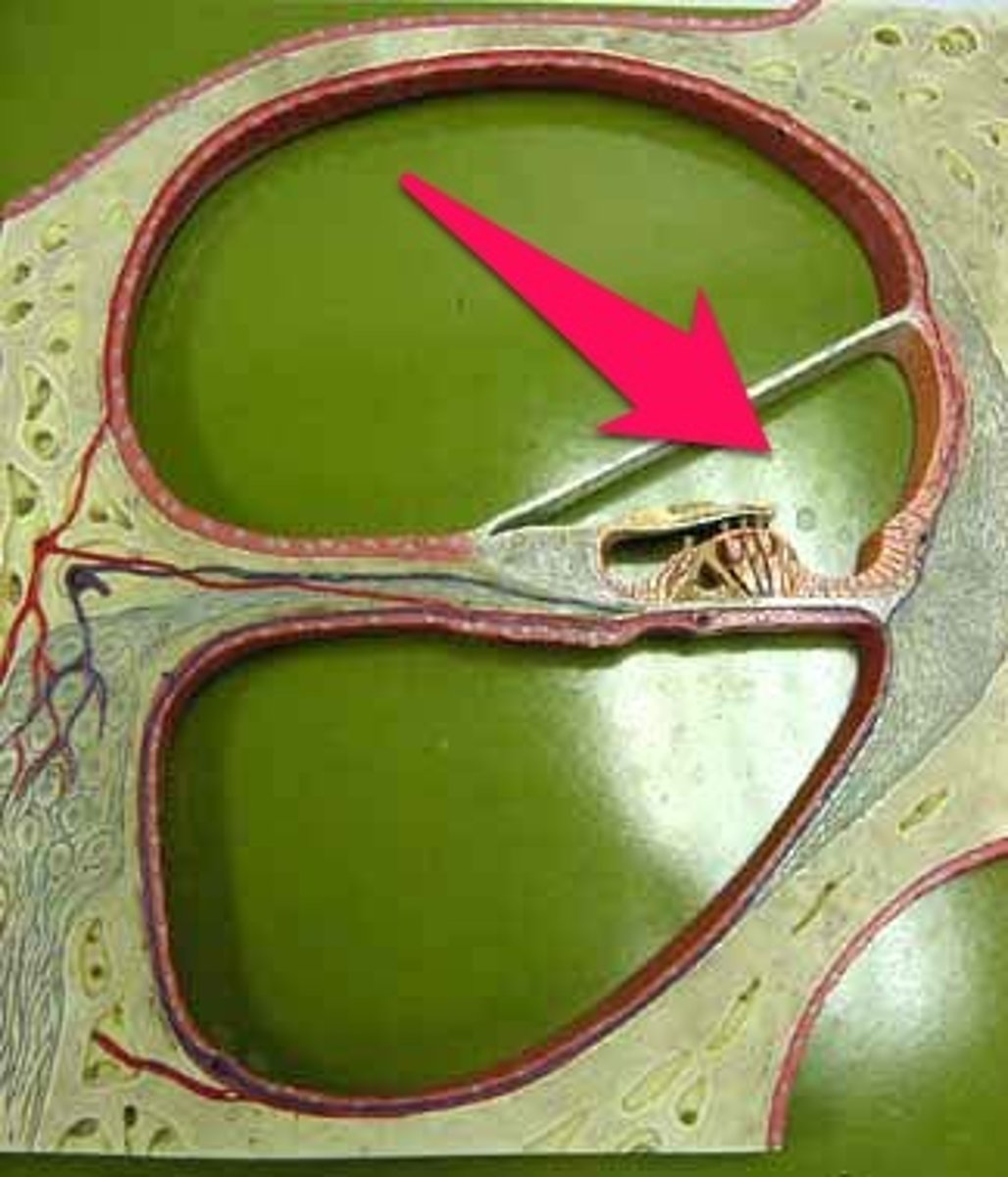
Scala tympani
Lower chamber of cochlea; filled with perilymph
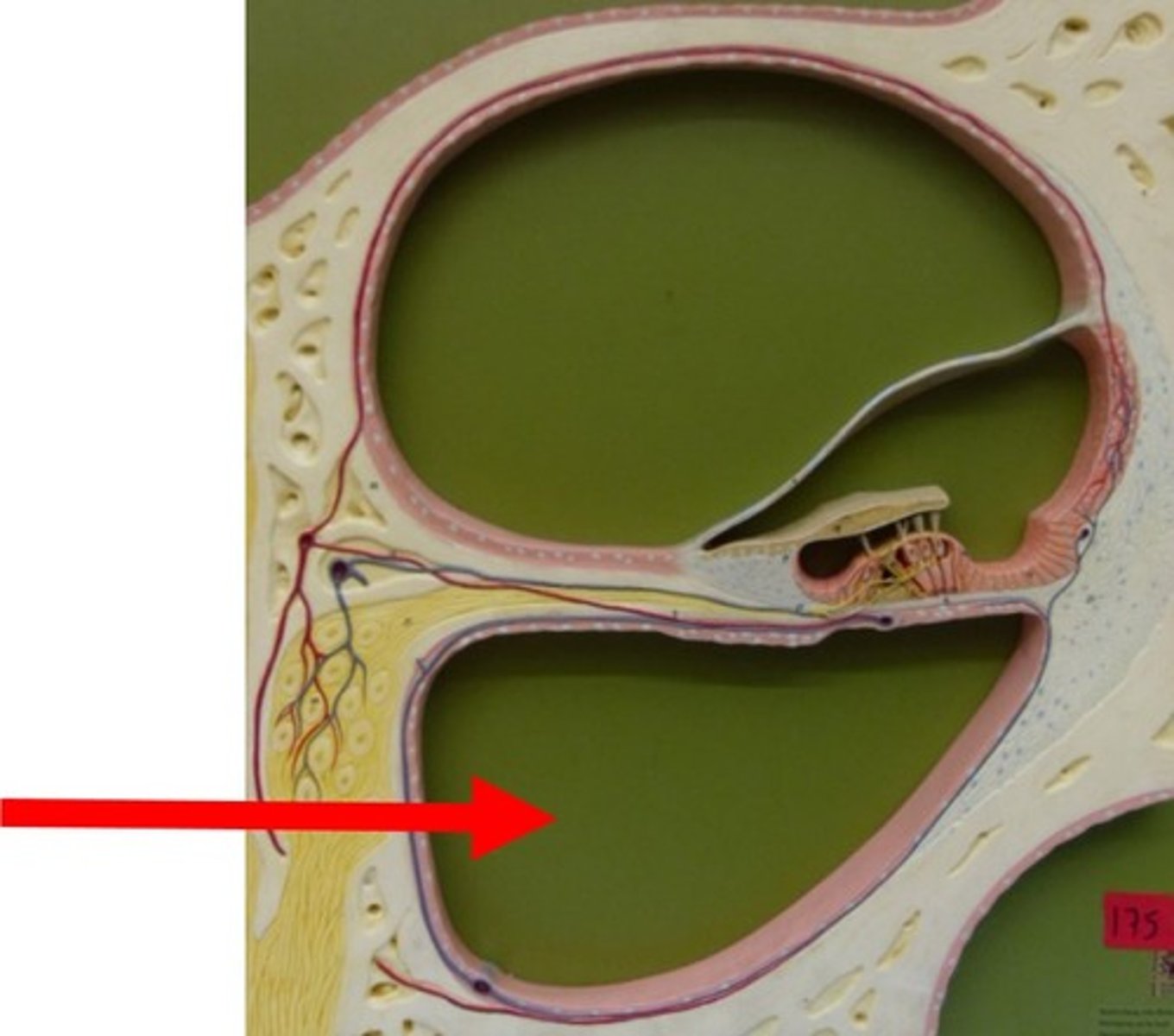
Vestibular membrane
Separates scala vestibuli from cochlear duct
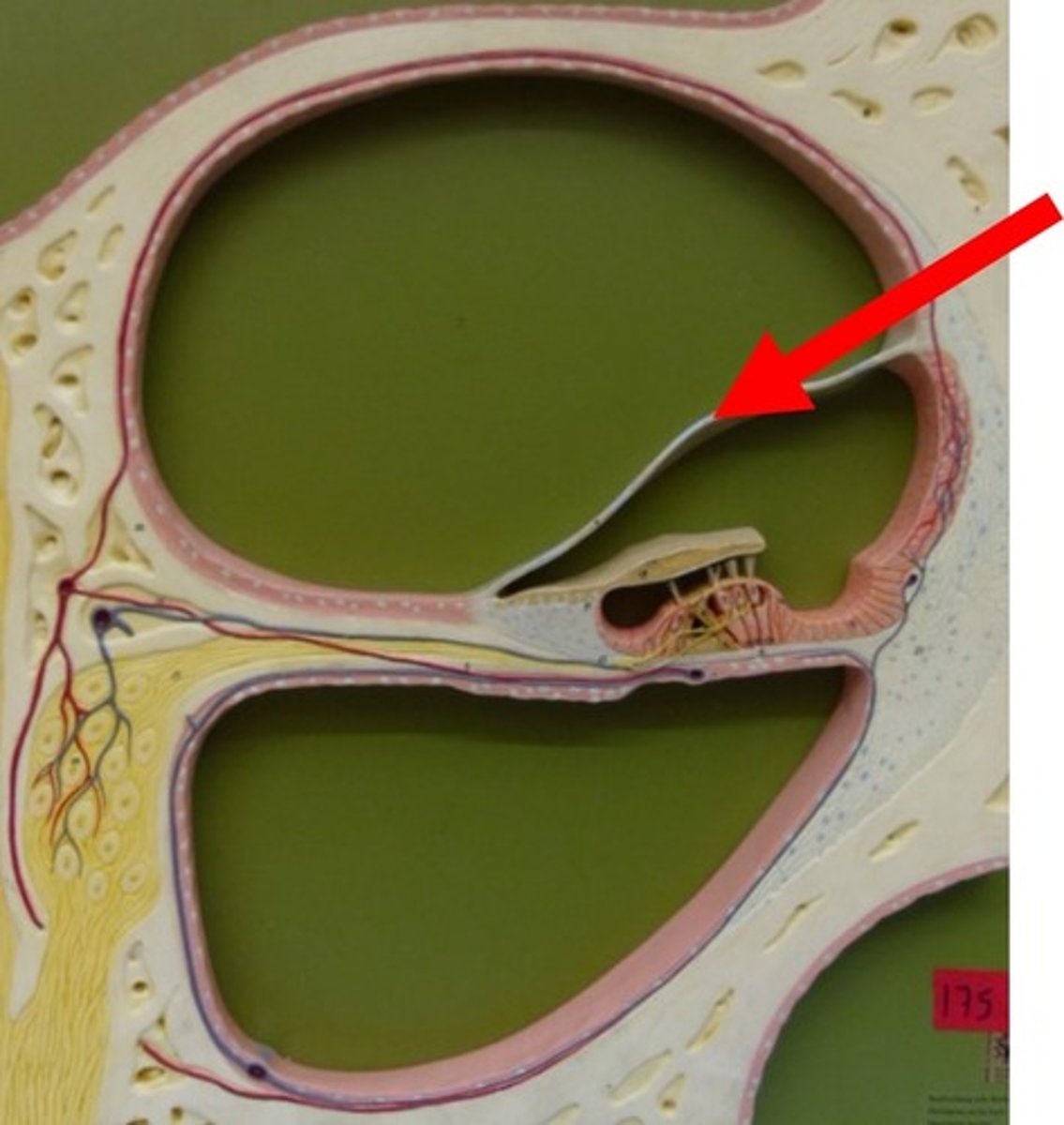
Tectorial membrane
Gel-like membrane above hair cells in organ of Corti
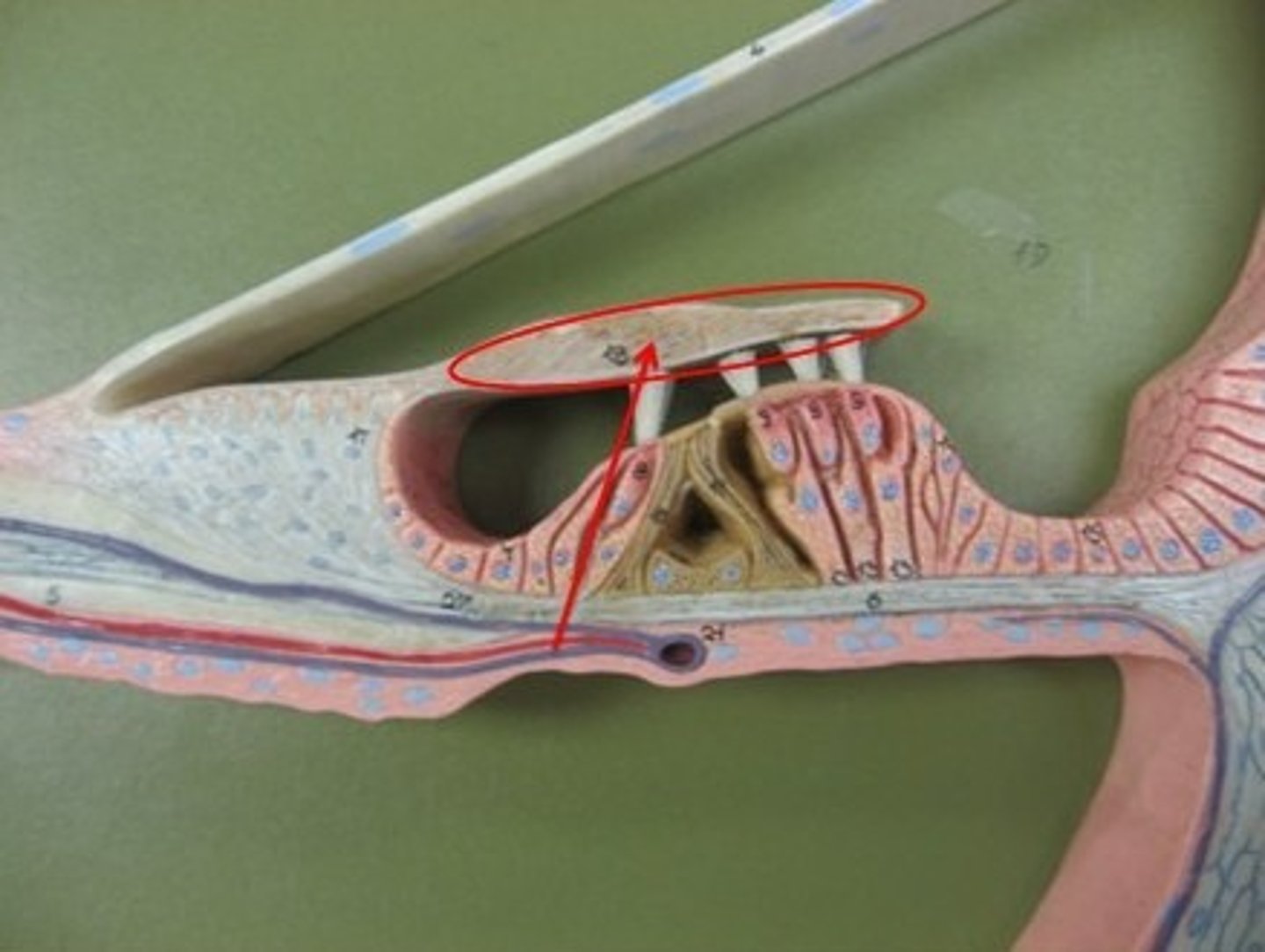
Basilar membrane
Membrane that supports hair cells in organ of Corti
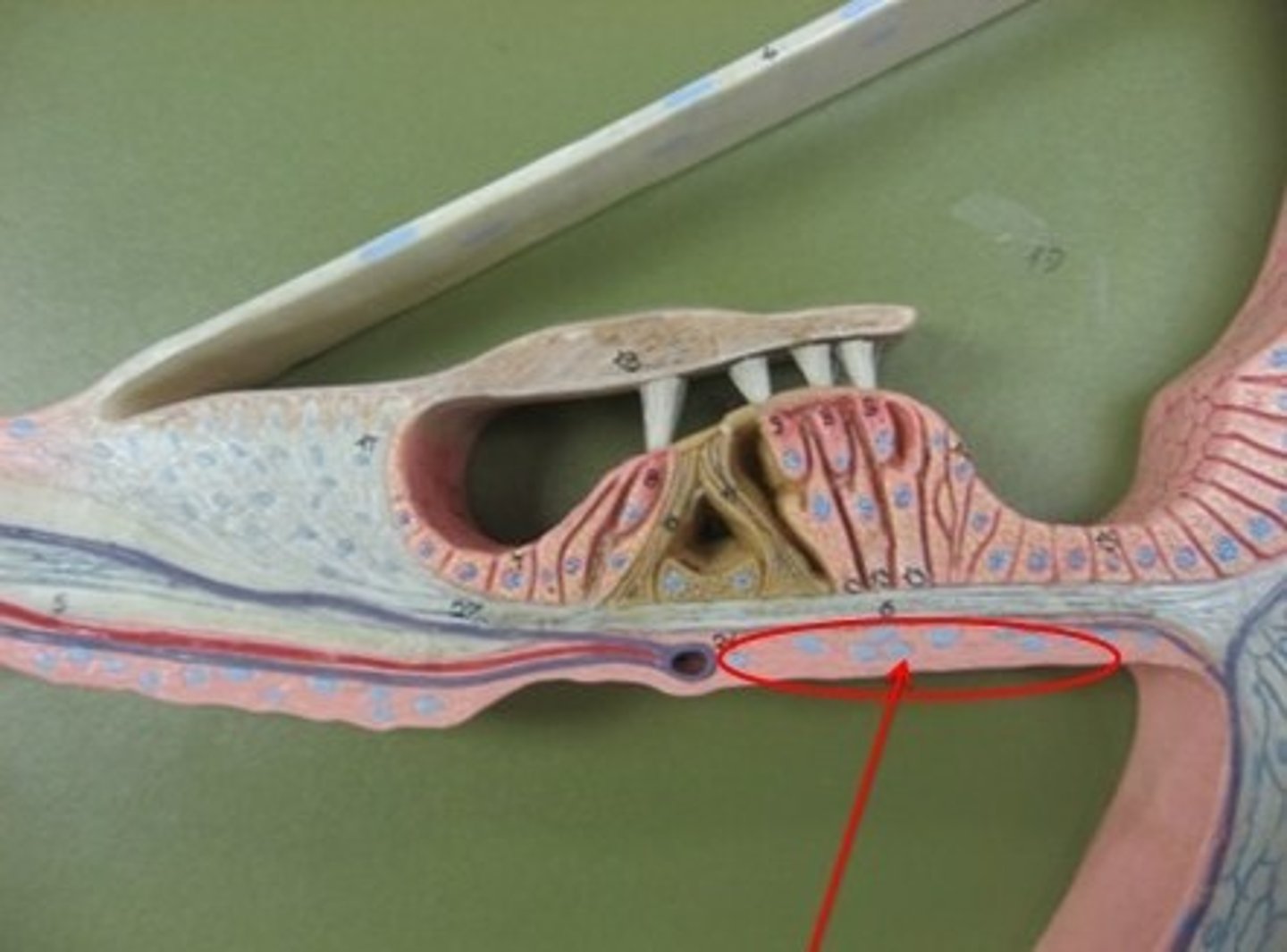
Organ of Corti
Hearing receptor organ containing hair cells