AP Biology Vocabulary
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Taxonomy
science of classification
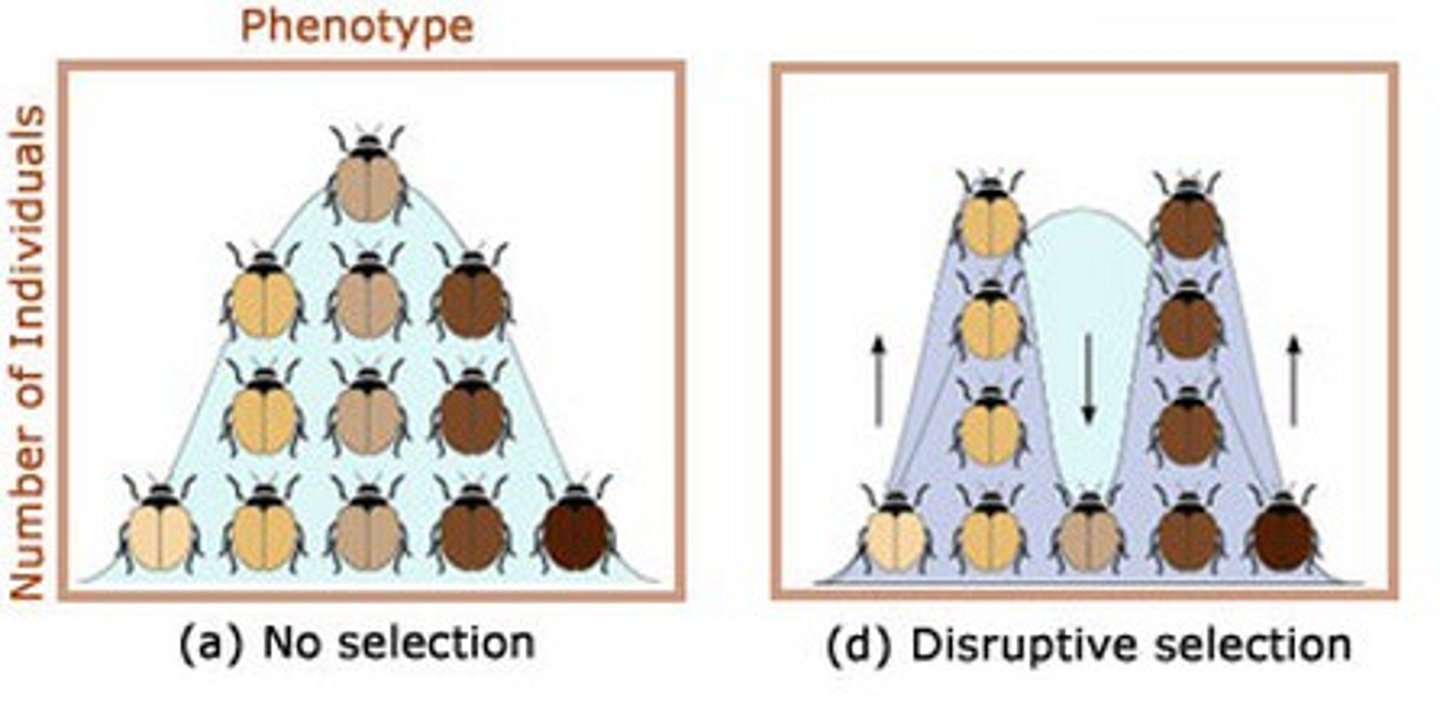
Disruptive selection
Favours extreme
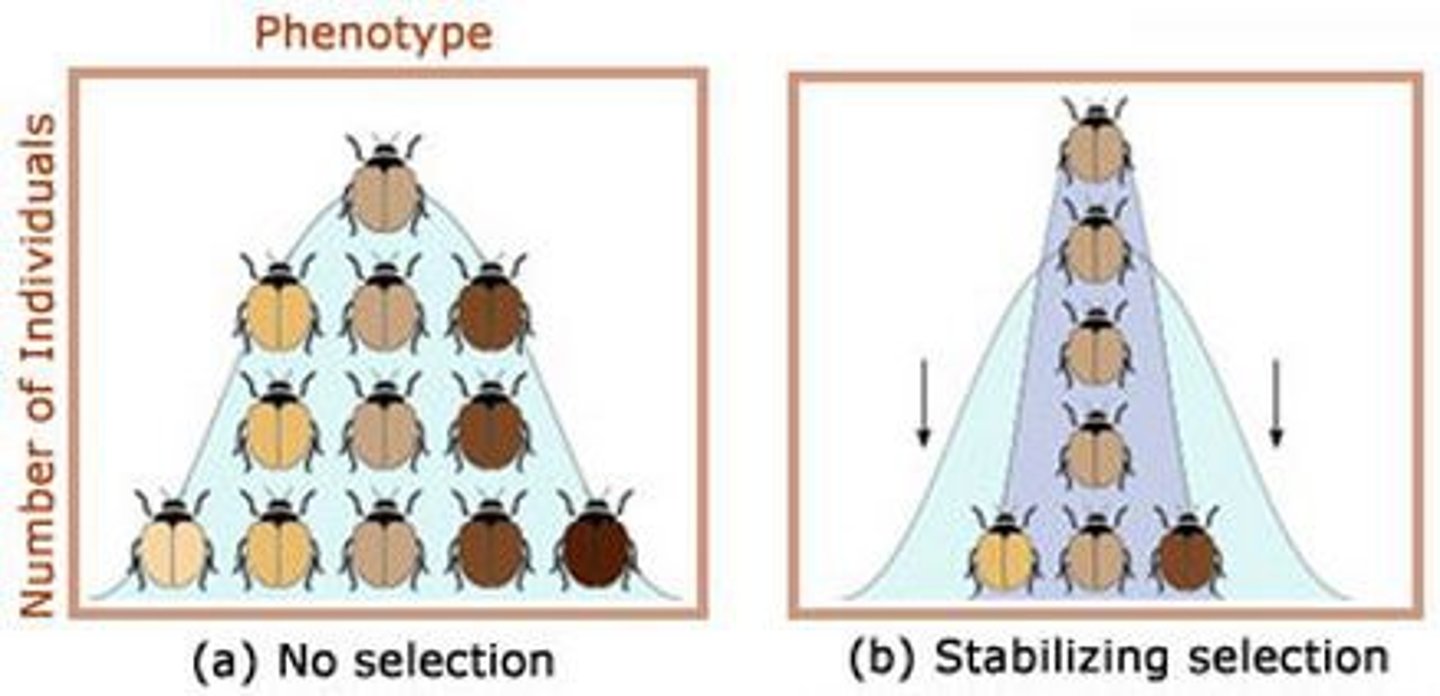
Stabilizing selection
Favours centre
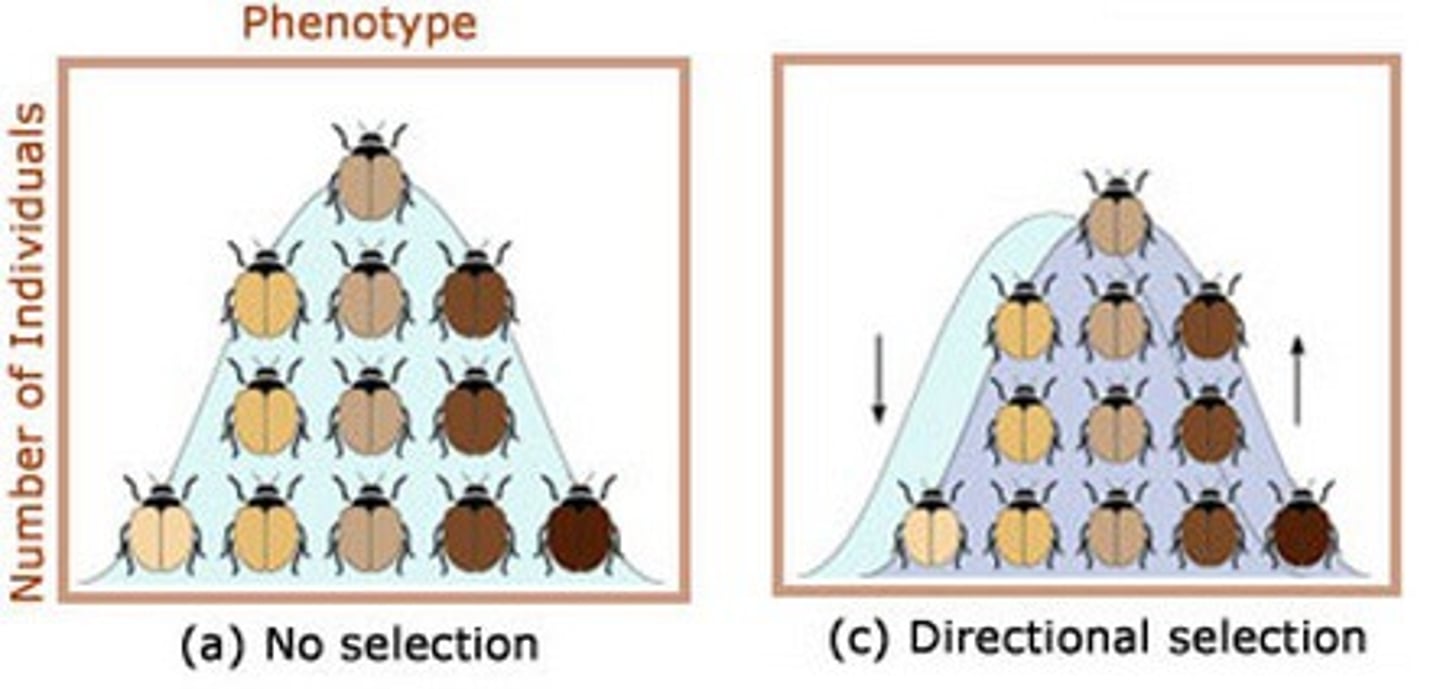
Directional selection
Favours 1 extreme
Behavioural isolation
Don't recognizing mating/courting behaviours
Mechanical isolation
Morphology doesn't line up
Temporal isolation
Breed at different times
Gametic isolation
Egg and sperm don't recognize eachother
Habitat isolation
Live in different habitats and do not meet
Gene flow
movement of alleles
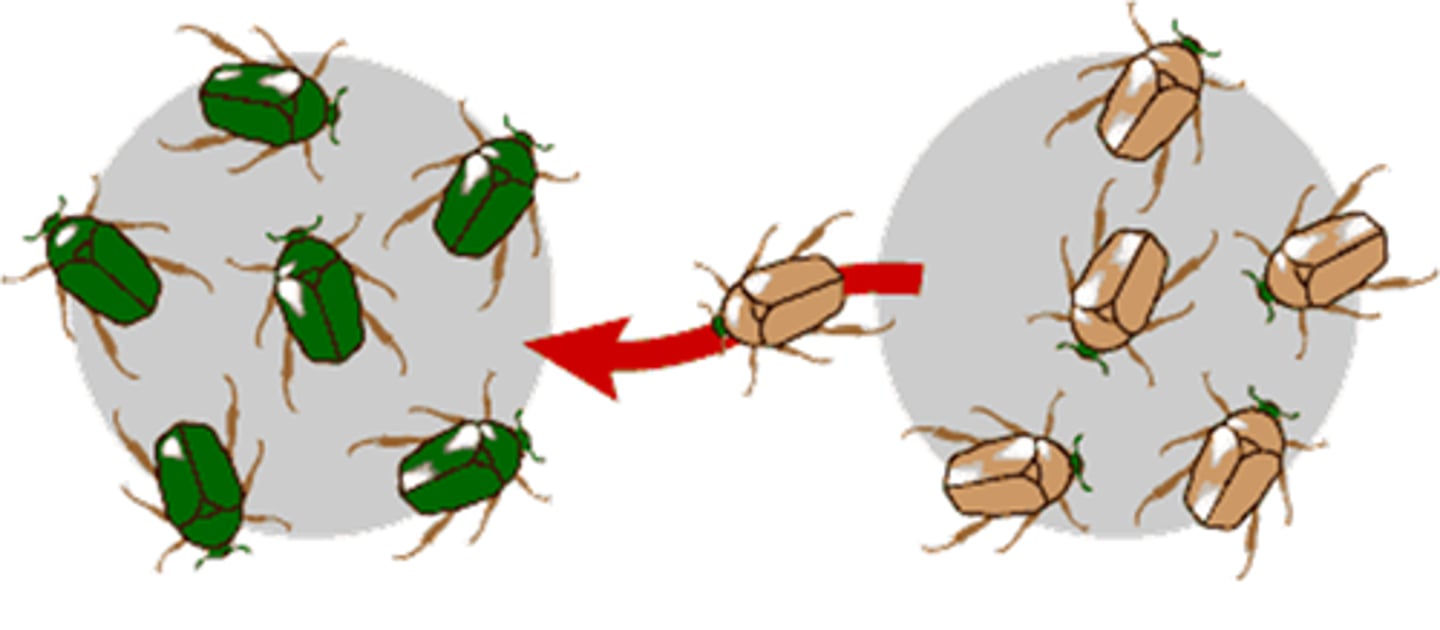
Reduced hybrid viability
Make but won't develop
Reduced hybrid fertility
Develop but can't reproduce
Hybrid breakdown
Reproduce but offspring are weaker
Morphological species
defined by structure
Ecological species
defined by ecological niche
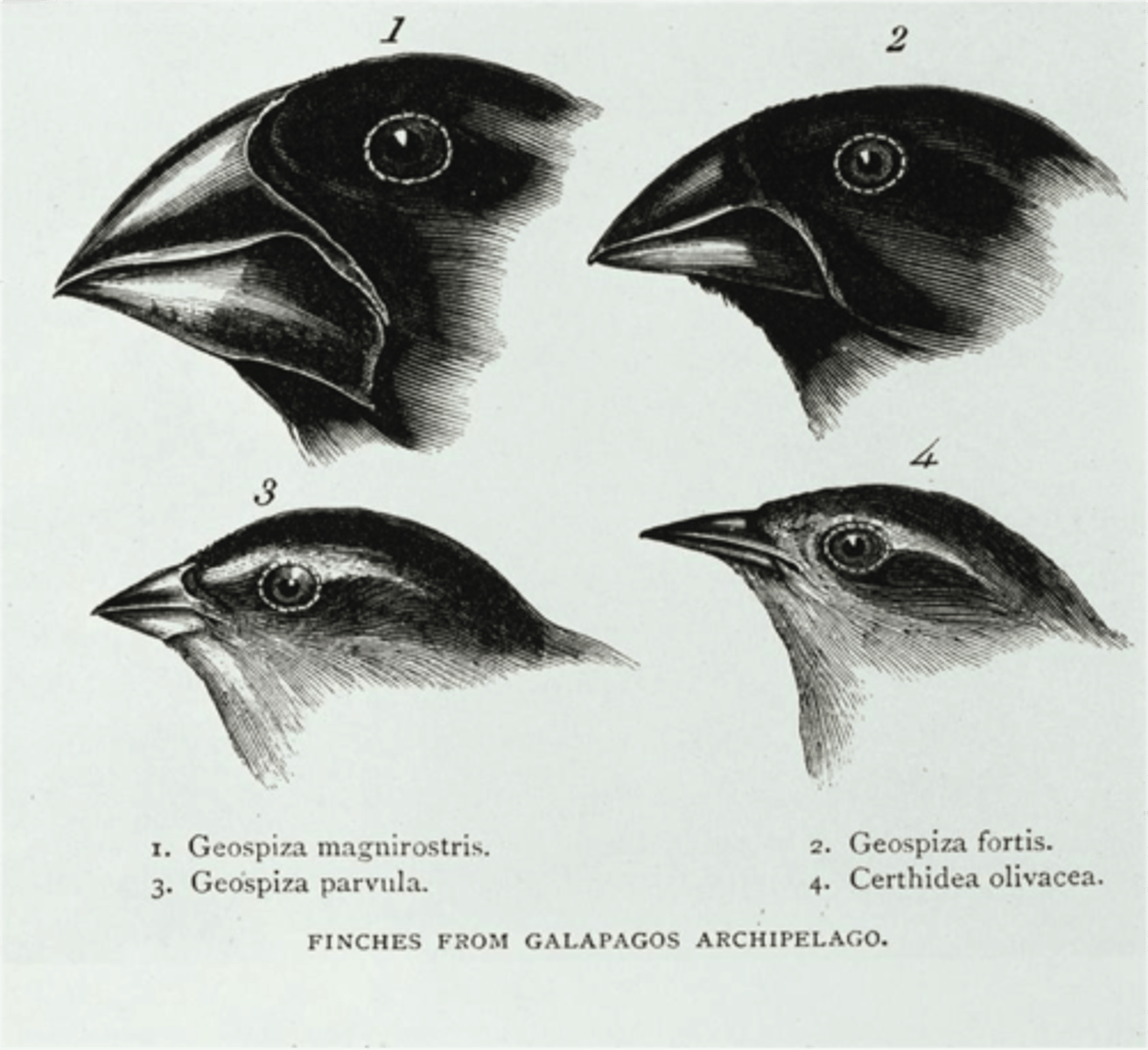
Phylogenetic species
smallest group of organisms that share a common ancestor
Evidence supporting evolution
Comparative anatomy, fossil record, DNA sequencing, documented observations of evolution
Homologies (related to comparative anatomy)
Shared characteristics because of common ancestry
Vestigial structures
A structure that is present but no longer serves its original purpose
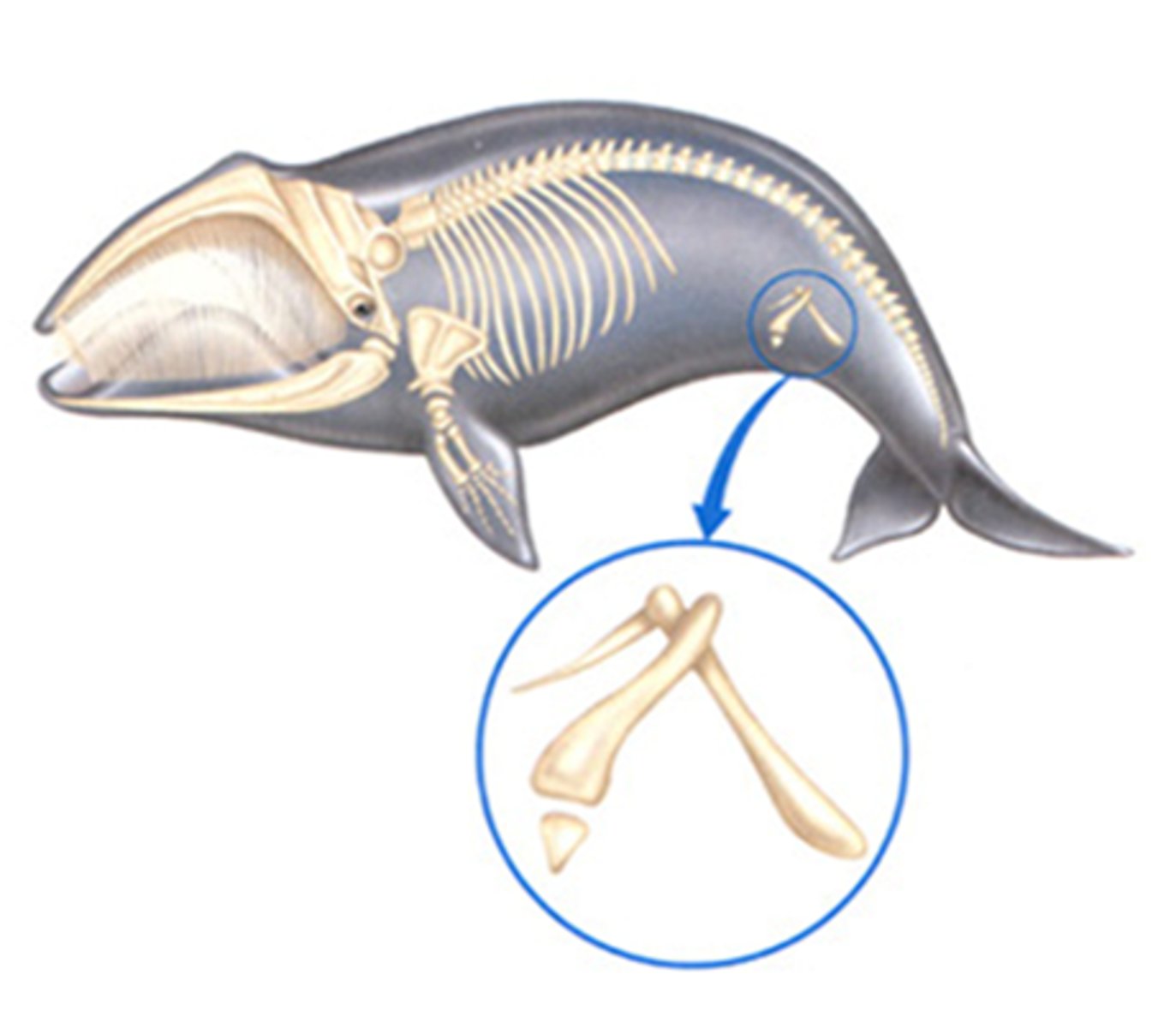
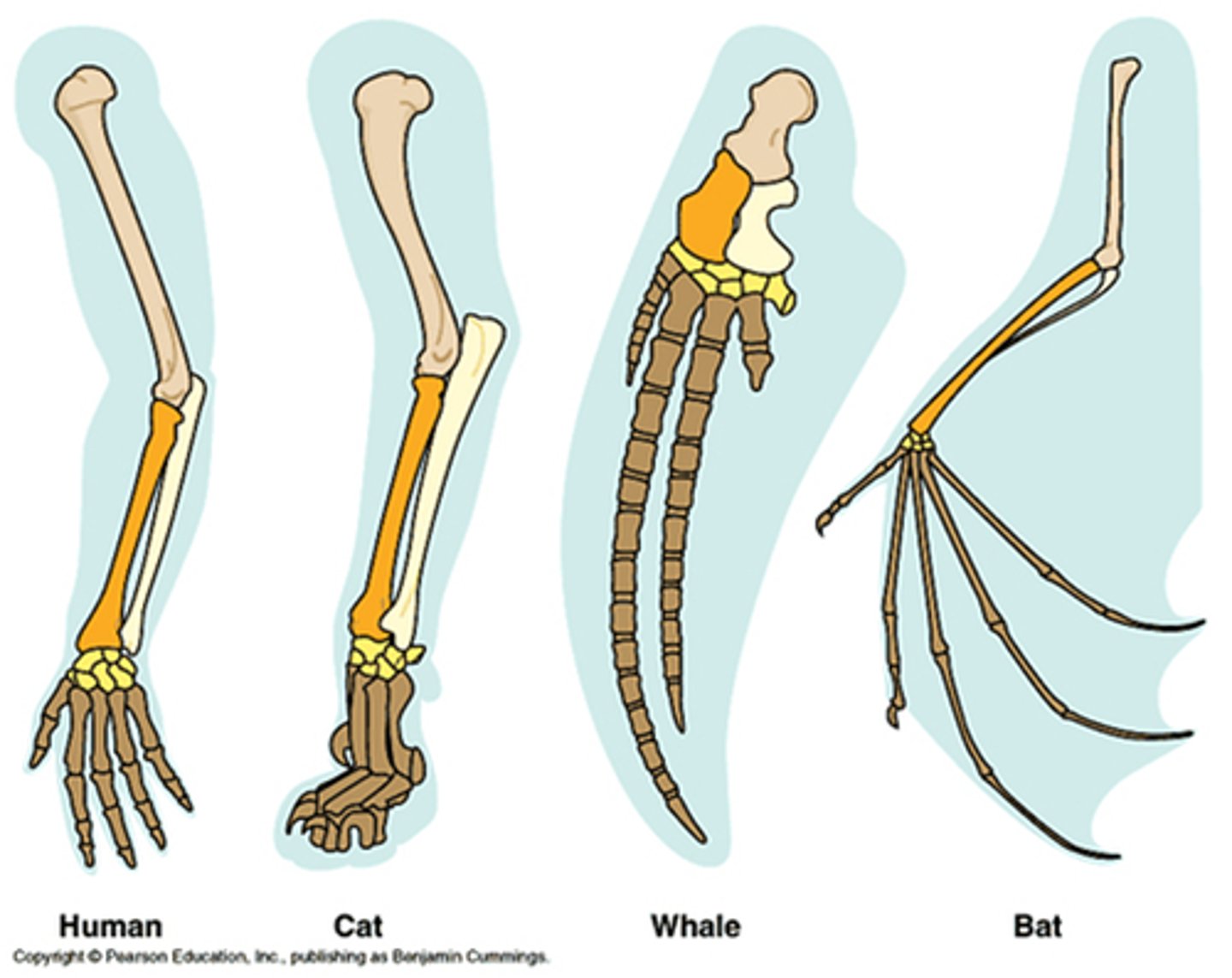
Homologous structures (divergent)
Same structure, different function
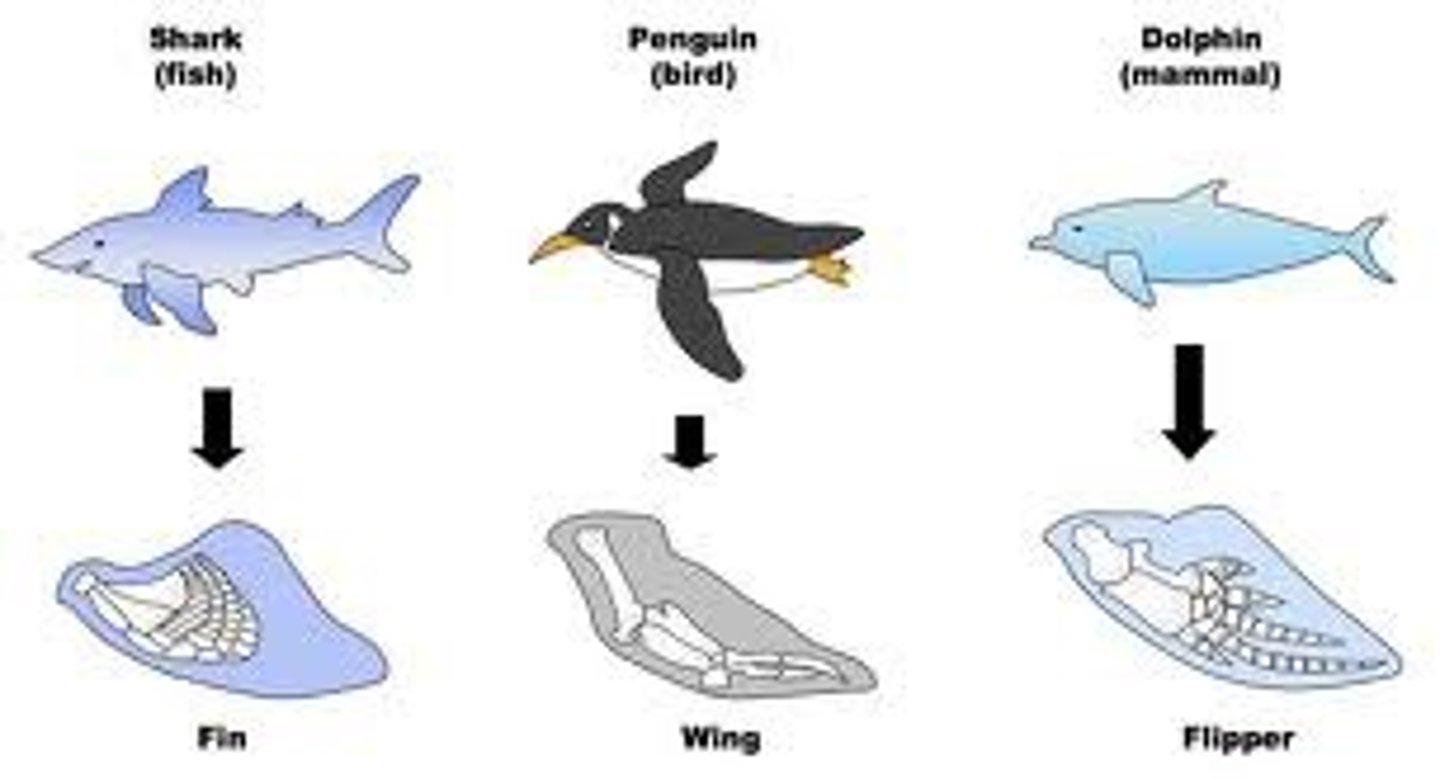
Analogous structures (convergent)
Different structure, same function
What do fossil records show
change, origins, extinctions
Evolution
gradual change to improve fitness
Niche
organisms "job" in the ecosystem
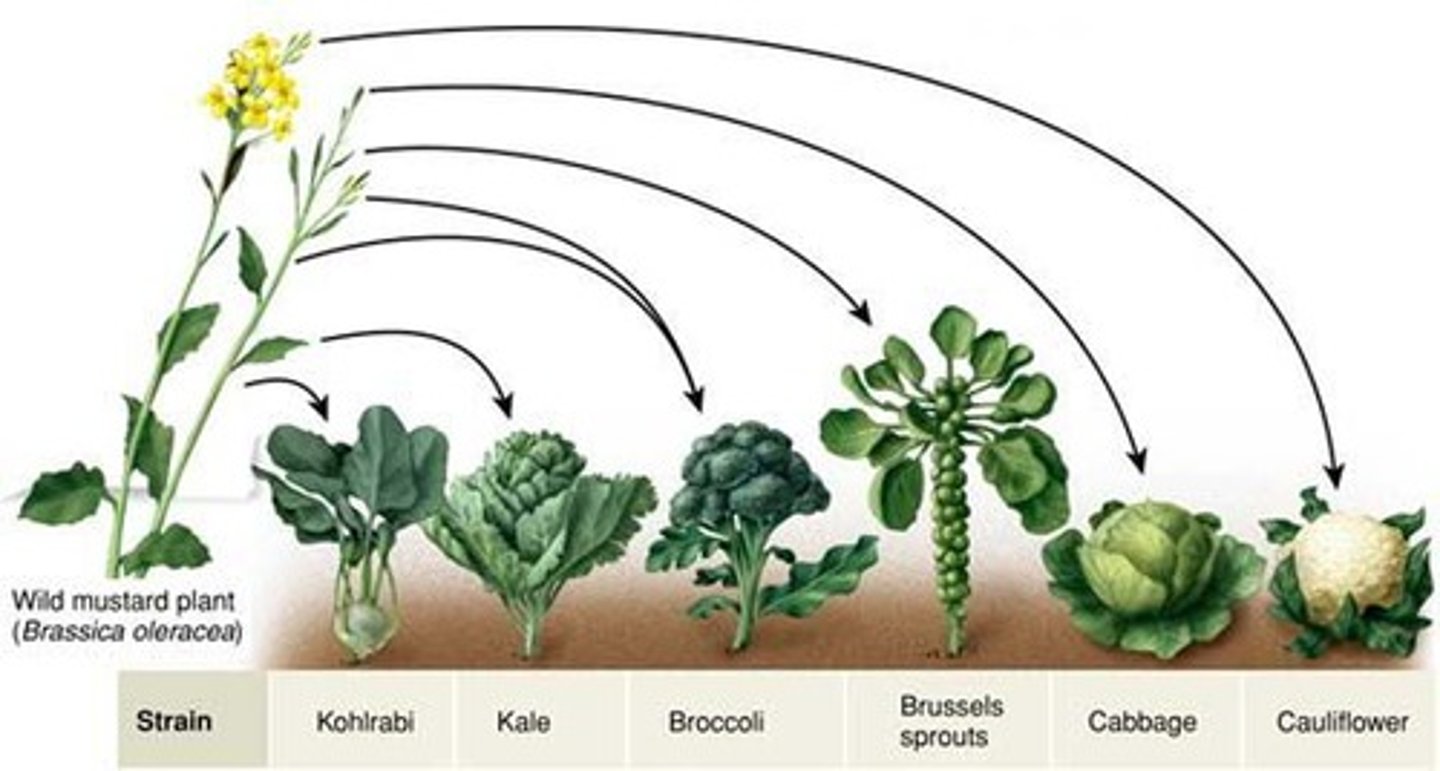
Artificial selection
Selective breeding to have desirable traits in offspring (humans)
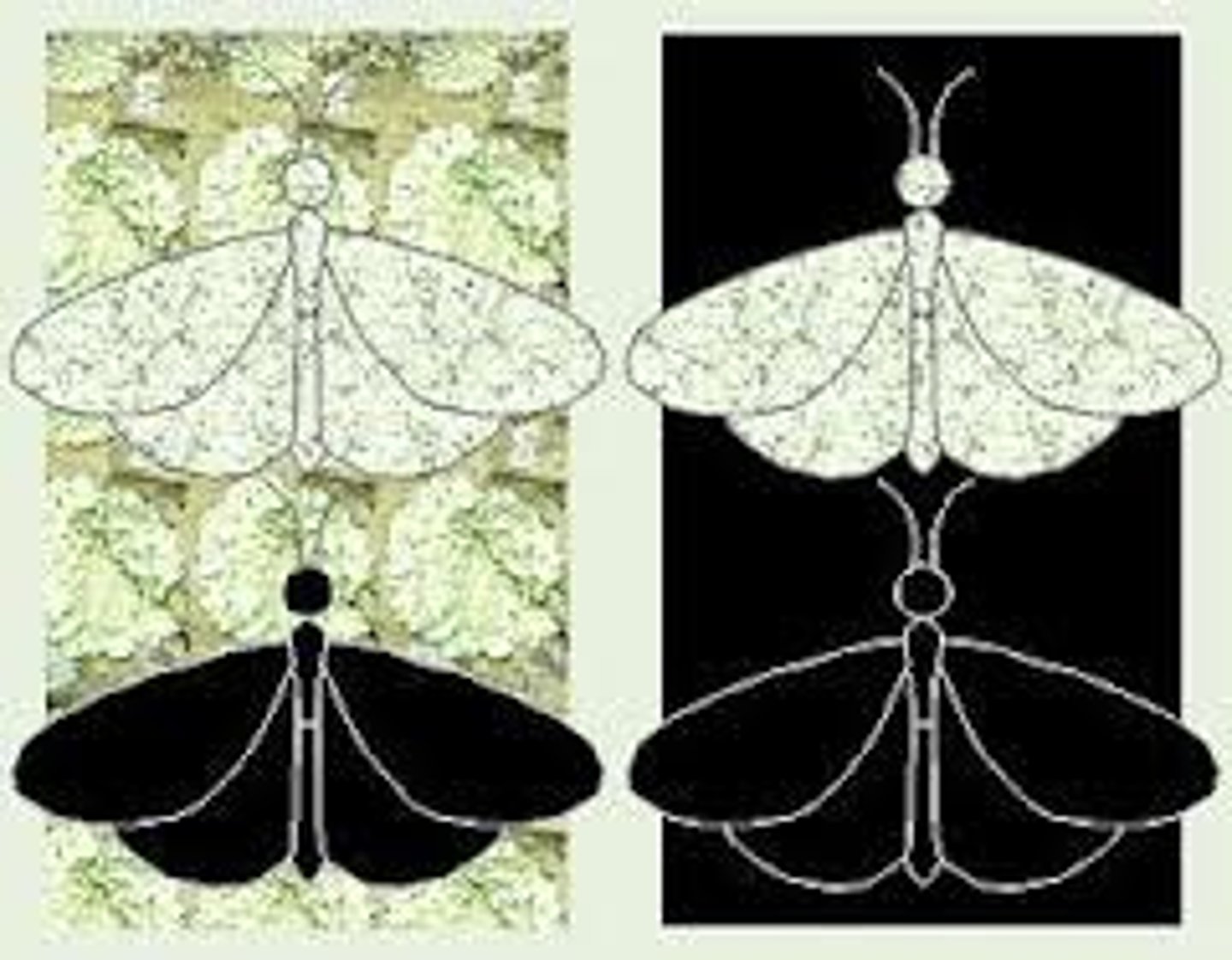
Natural selection
Environment chooses the favourable traits
Adaptations
changes in structure, function, or behaviour that improve fitness
Genetic variation
Different types of genes in a species or population
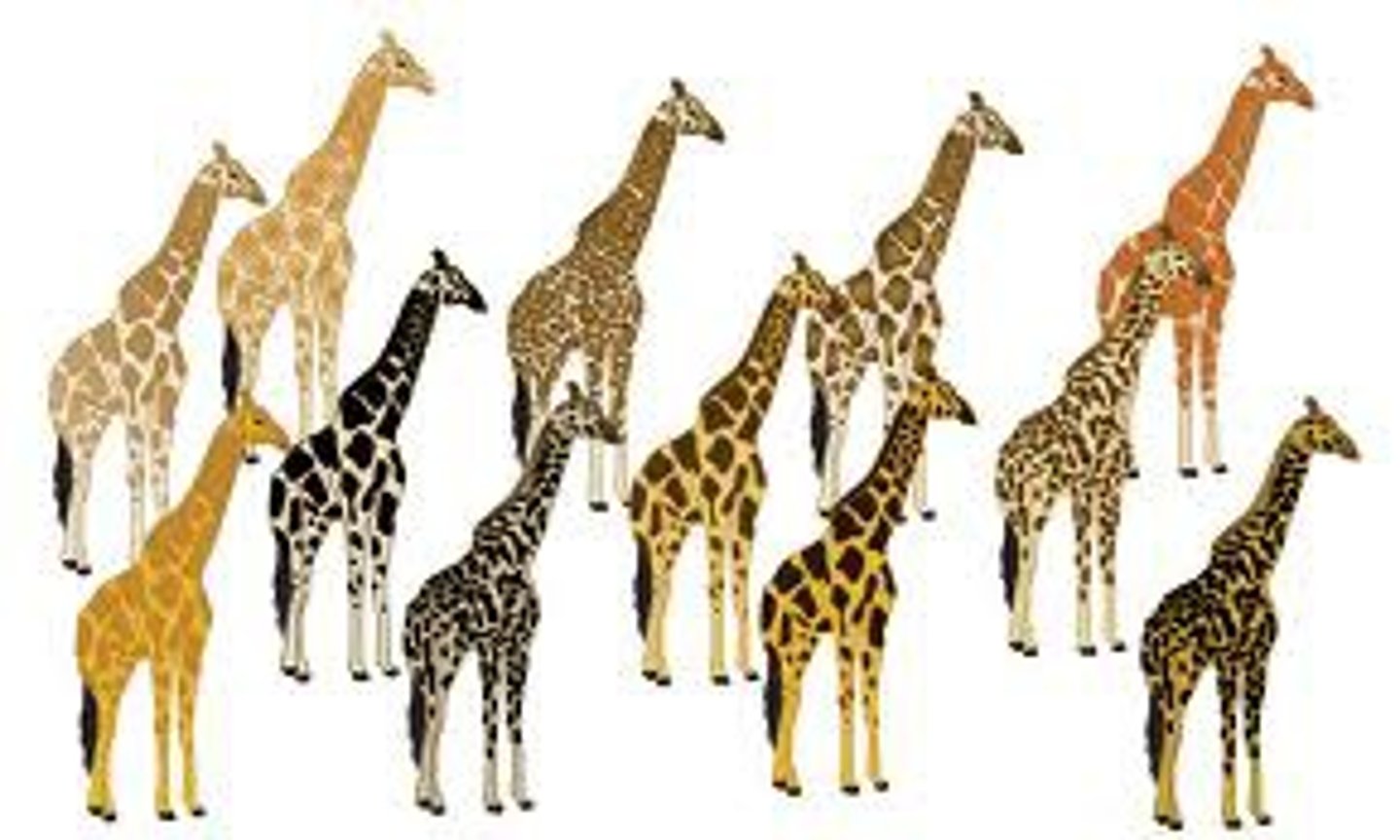

Reproductive success
Likelihood of an individual contributing fertile offspring to the next generation
Heritability
Ability of a trait to be passed on
extant
Exists
extinct
No longer exists
species
A group of organisms that are closely related and can successfully mate
Eukaryotes common ancestry evidence
membrane-bound organelles, linear chromosomes, genes that contain introns
Reasons for evolution
genomic changes, fossil record changes, resistance to things, pathogens
Genomic
study of genomes (genes and their functions)
pathogens
organisms that cause disease
Mutations
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change
Sexual reproduction and genetic variation
mutations (meiosis), crossing over and fertilization (biggest sources)
Microevolution
changes in allele frequencies
Genetic drift
random change with allele frequencies
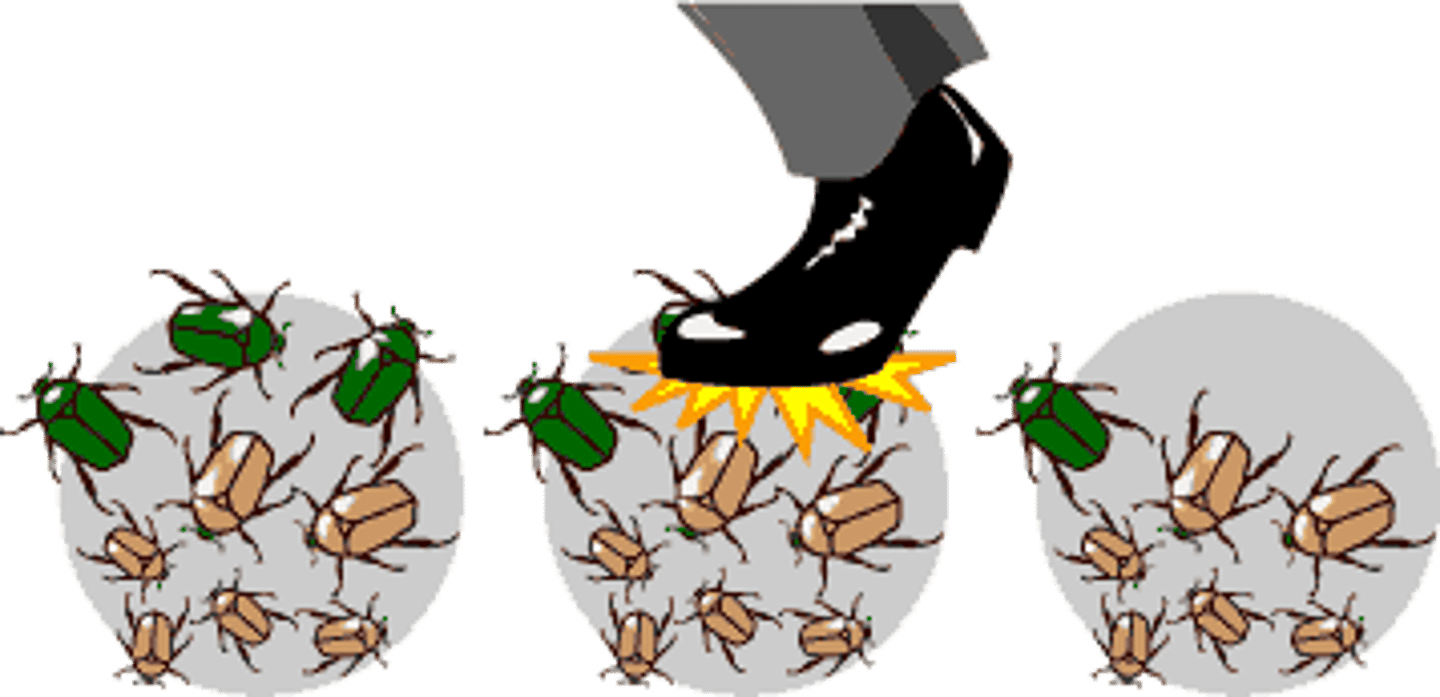

Conditions of Hardy-Weinberg
No mutation, random mating, large pop. size, no gene flow, no natural selection
Phylogenetic
evolutionary relatedness
speciation
Formation of new species
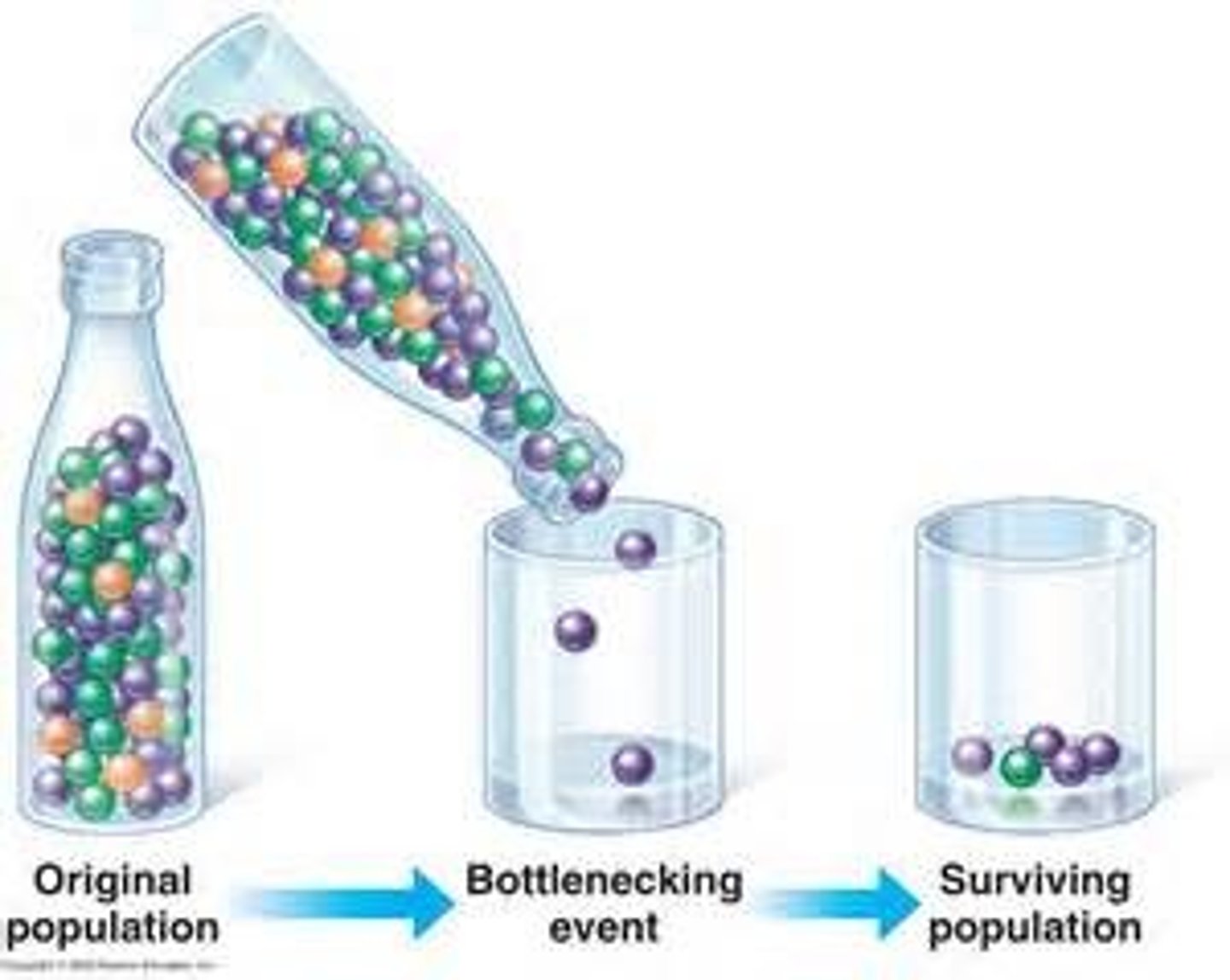
bottleneck effect (genetic drift)
sudden environmental change causes pop. reduction
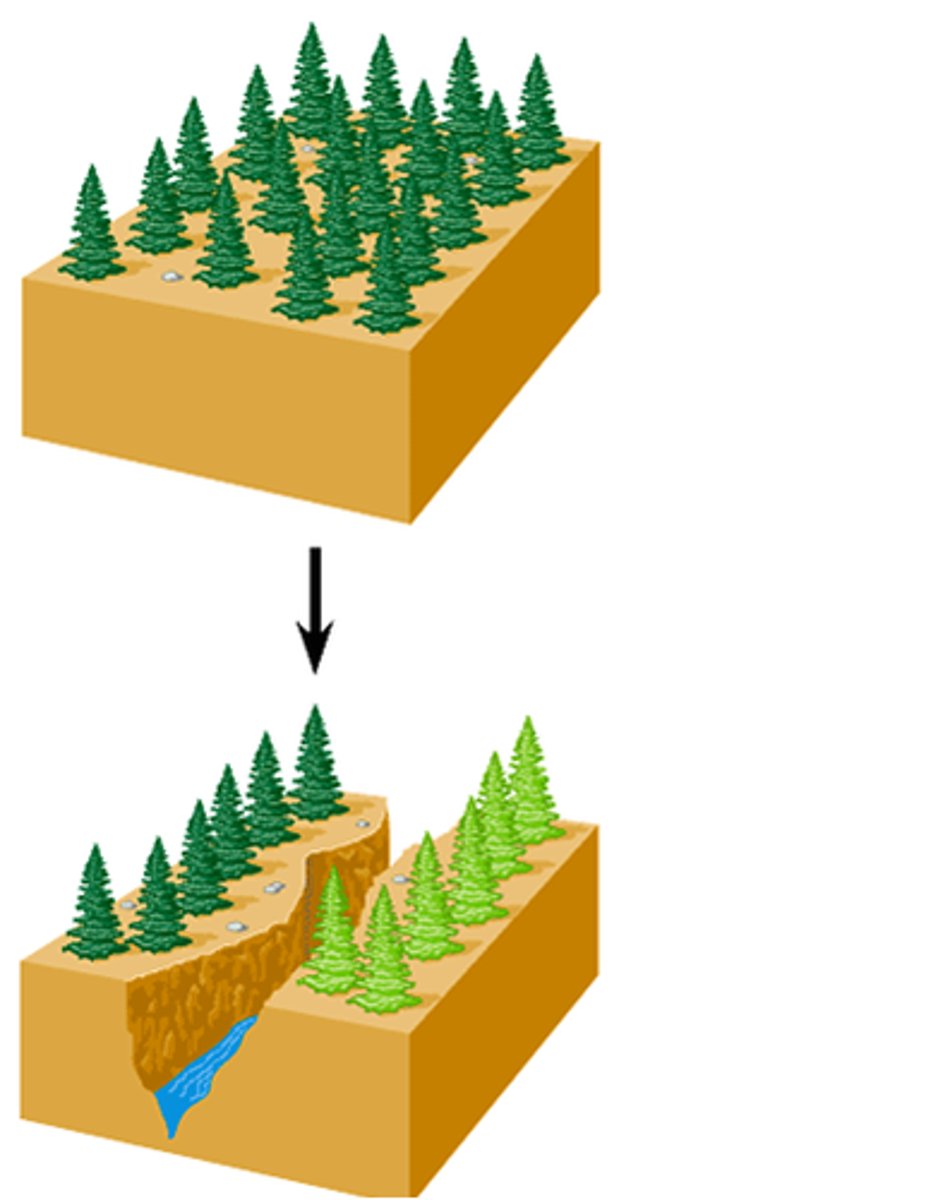
founder effect (genetic drift)
few individuals become isolated
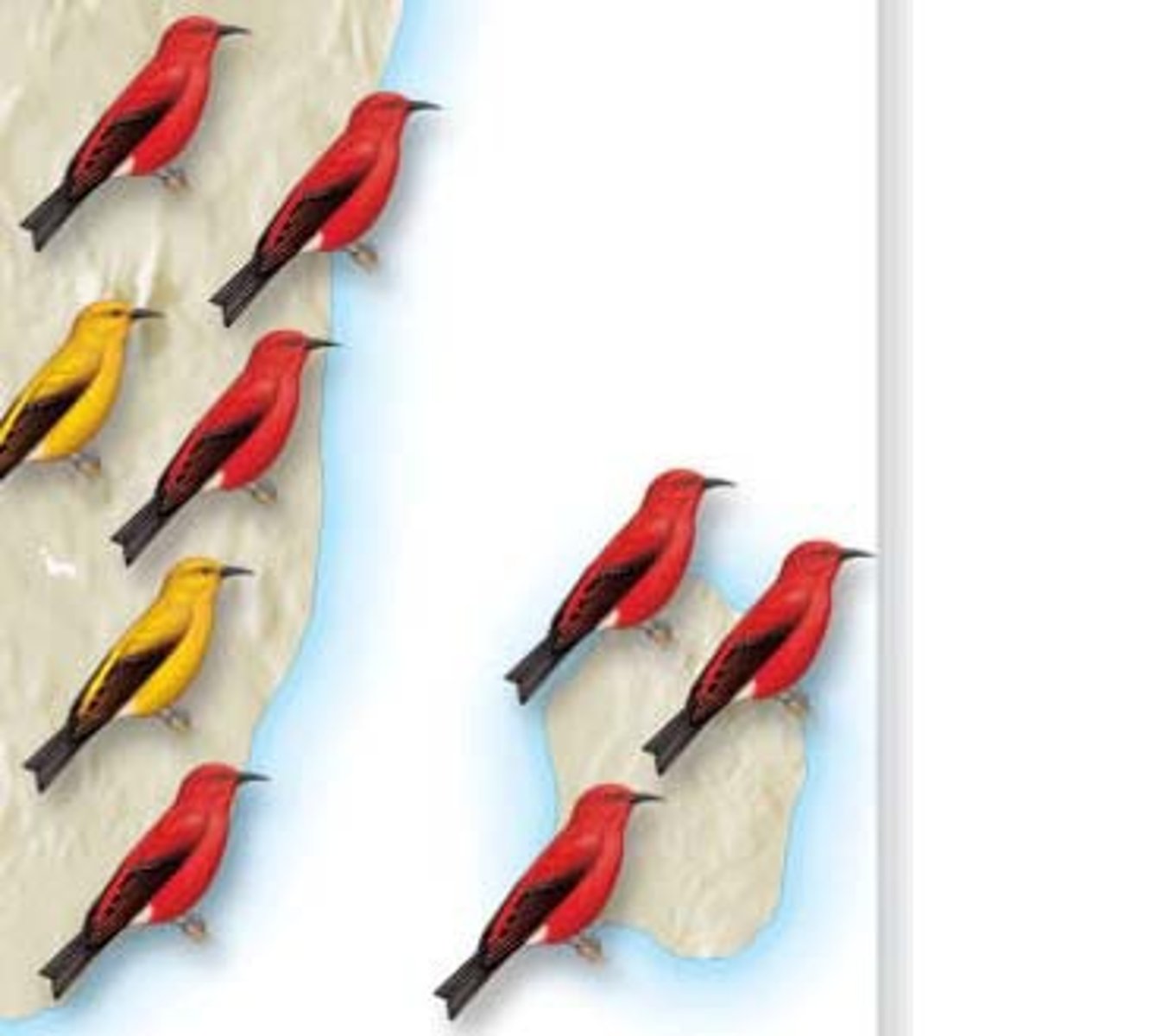

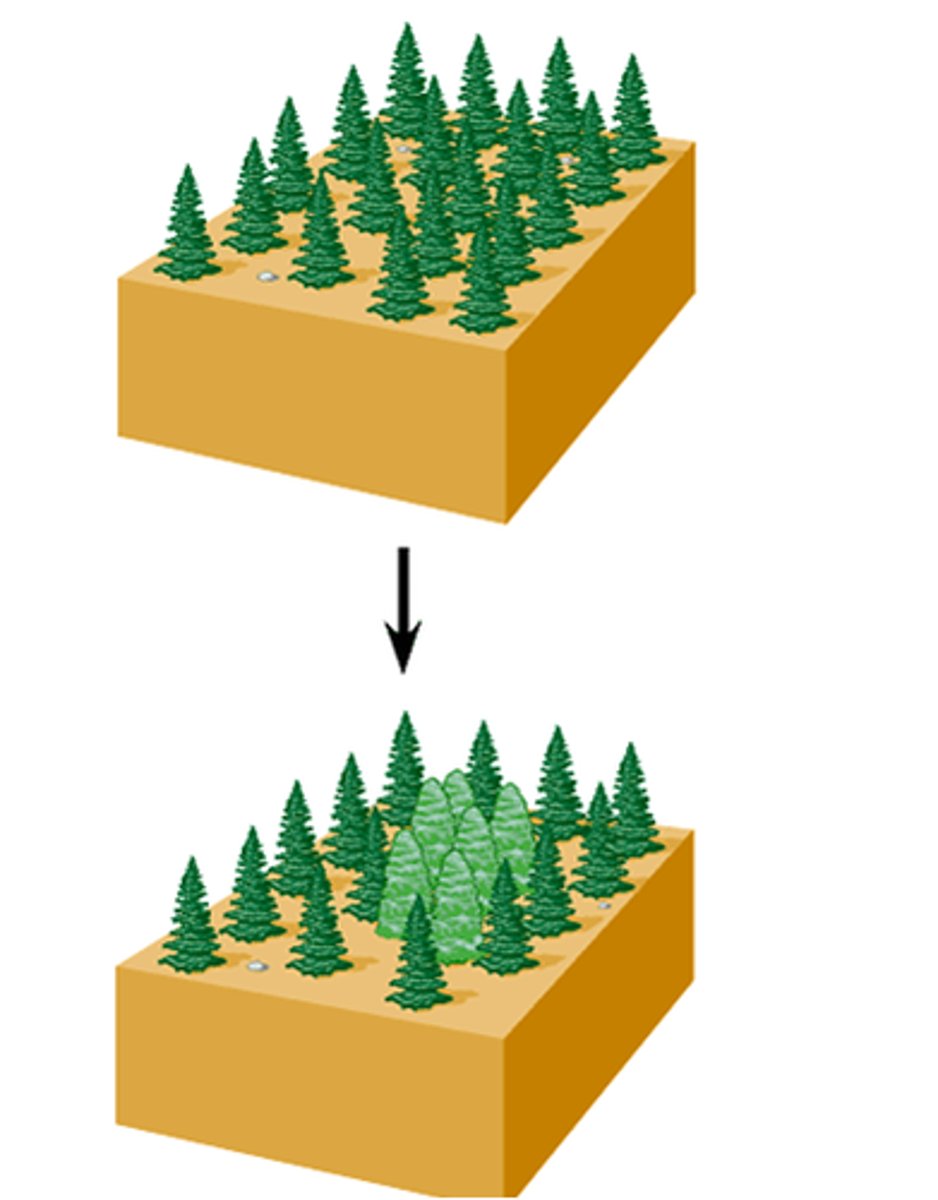
Allopatric speciation
speciation that occurs with geographic isolation
Sympatric speciation
Speciation without a divided population (factors are sexual selection, new niches because of habitat differentiation, polyploidy)
Polyploidy
organism has extra sets of chromosomes (can be fertile and create new species)
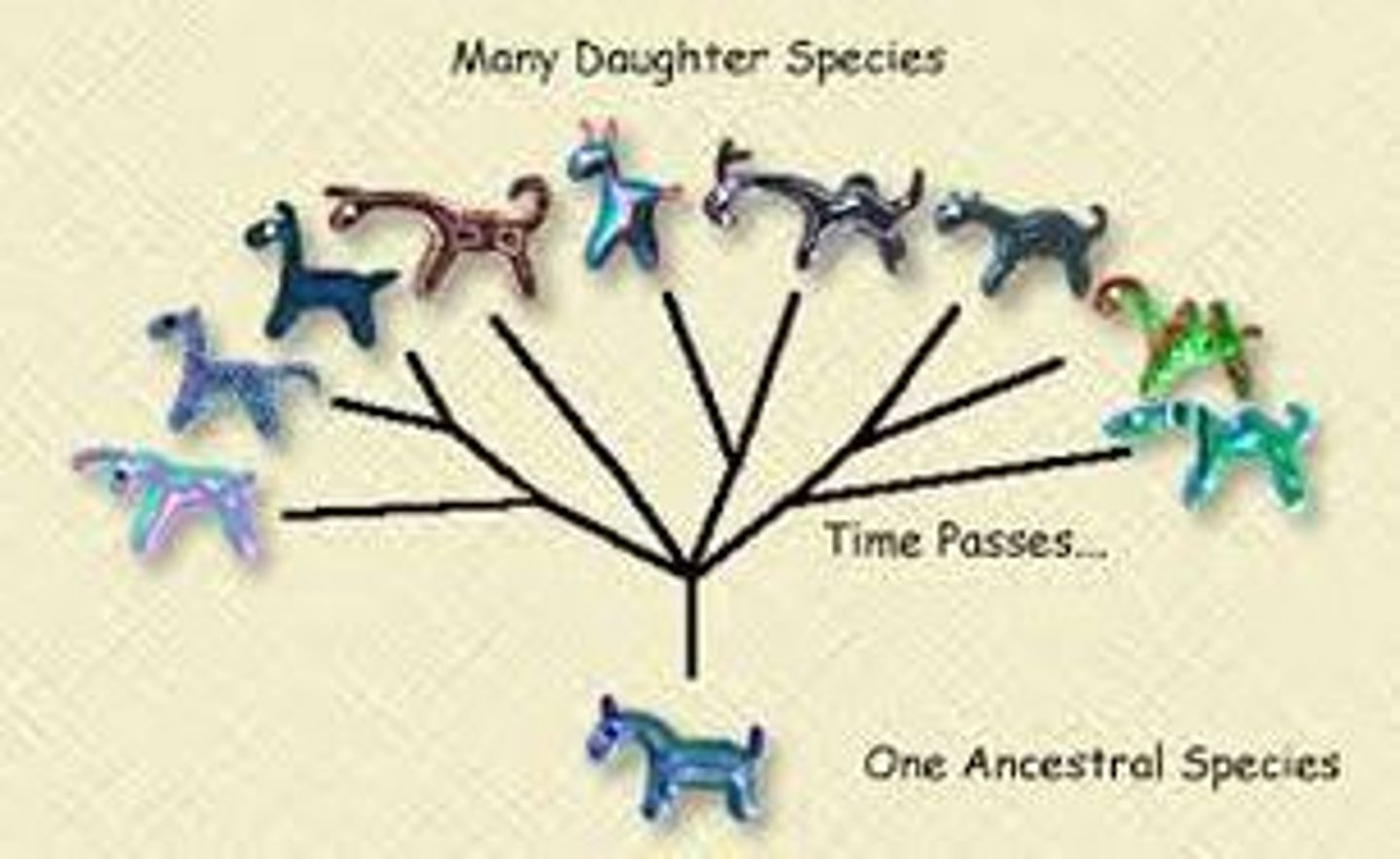
Adaptive radiation
An evolutionary pattern: many species evolve from a single species
Why are speciation rates often rapid in situations where adaptive radiation occurs or during times of ecological stress?
ecological opportunities or environmental pressures drive rapid adaptation to new niches or survival strategies
- increase is also caused by genetic variation, isolation of populations, and strong selection pressures
Connection between speciation and change in gene frequency, change in the environment, natural selection, and genetic drift
no gene flow, adaptations to new conditions, reproductive isolation (diverging traits), random allele changes (genetic drift)
3 domains of life
archea, bacteria, and eukarya
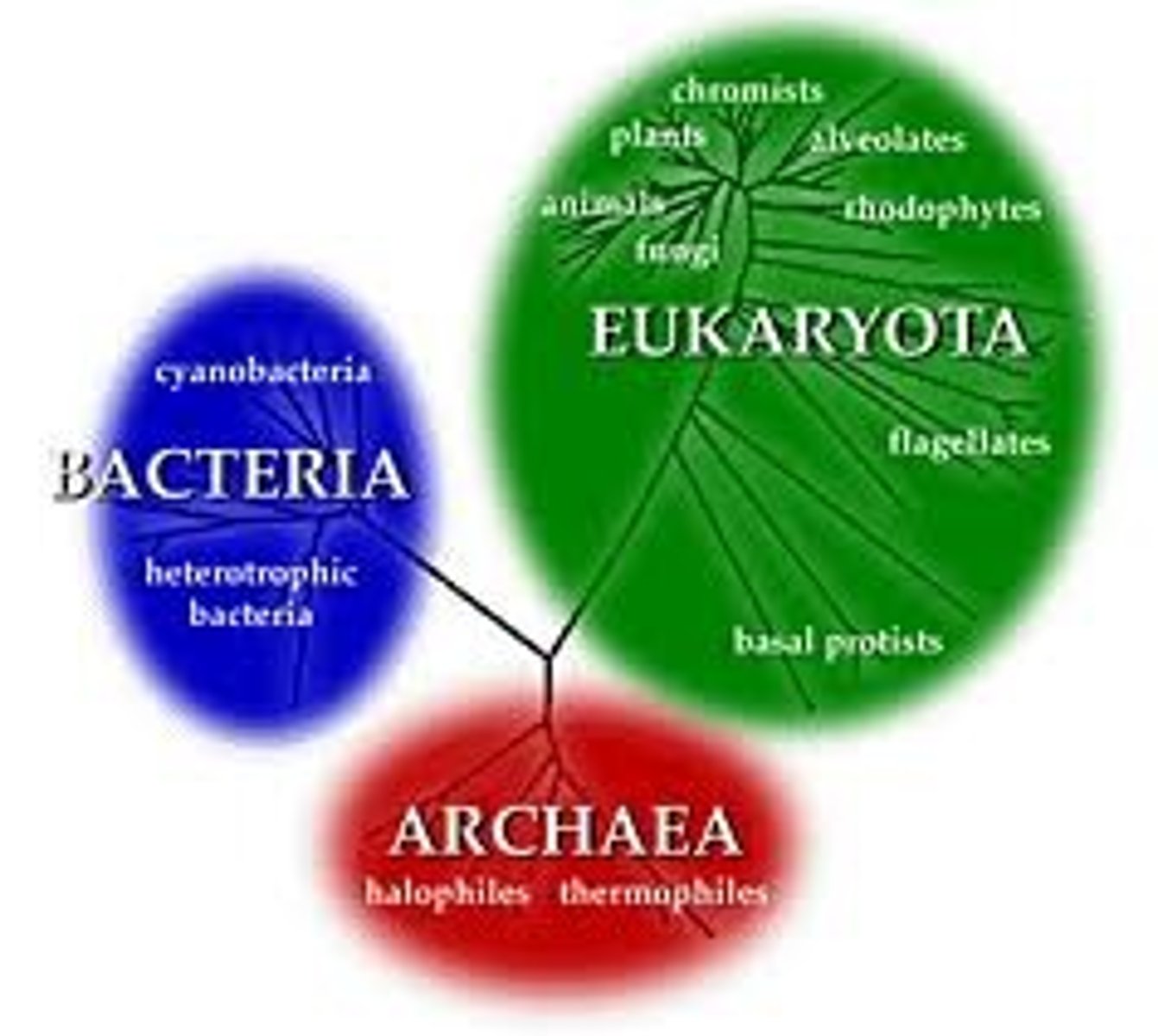
Process the the 3 domains share
DNA replication and cellular respiration
Scientific hypothesis about the origin of life on earth
abiotic synthesis of small molecules, joining into macromolecules, packaging of molecules into protocells (droplets with consistent internal chemistry), and origin of self-replicating molecules
Age of Earth (when did proka and eukar emerge)
Earth is 4.6by, prokaryotes is 3.5by, and eukaryotes is 1.8by
maximum parsimony
simplest phylogenetic tree
Characteristics of early planet
lack of oxygen, lots of gases (nitrogen and methane), volcanic eruptions
How Miller and Urey tested the Oparin-Haldane hypothesis and what they learned
mixed basic compounds with electric voltage to show that creating organic molecules is possible
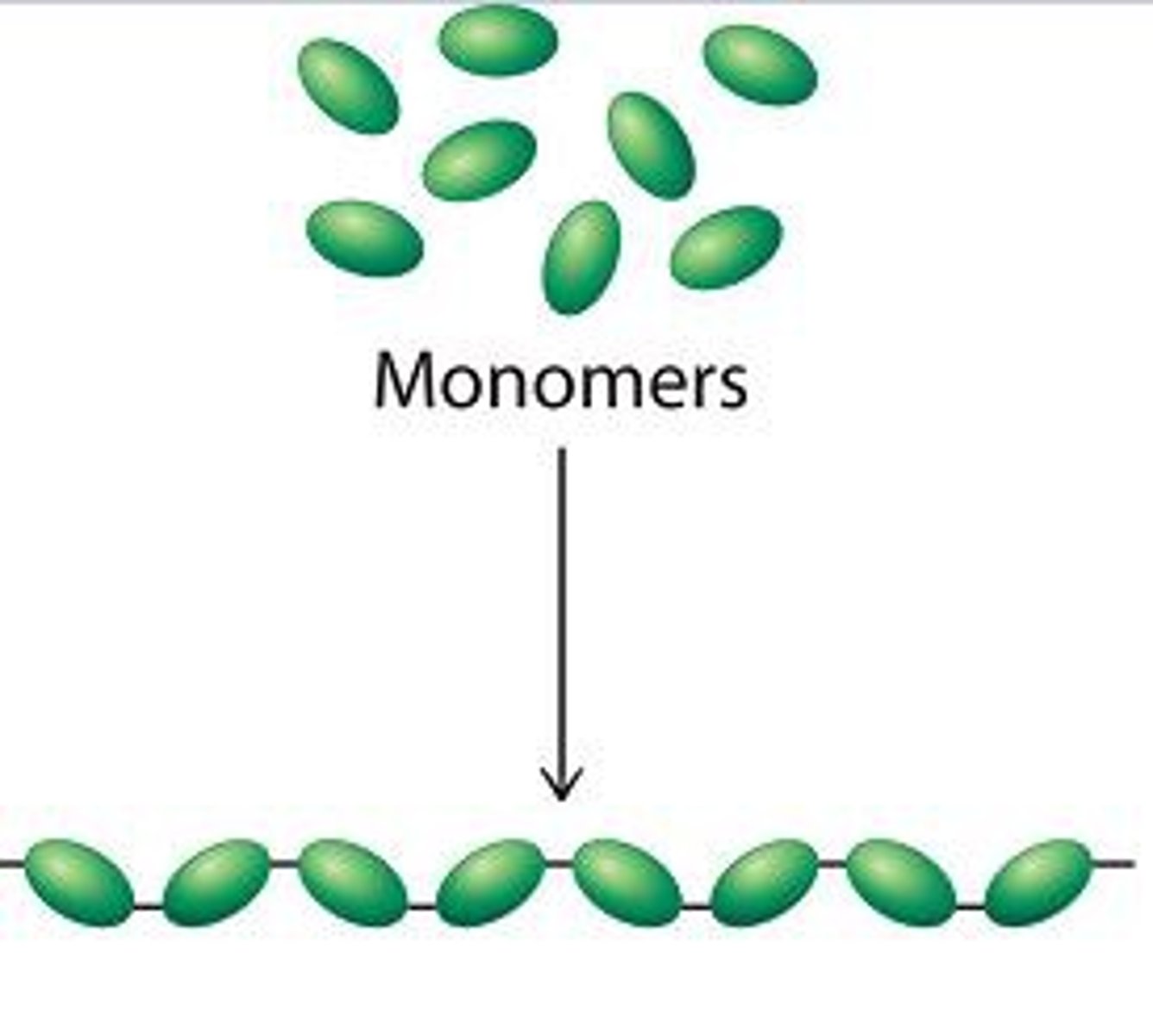
Polymerization
large molecules of repeating monomers (small molecules) e.g. proteins (amino acids are the monomers)
Continental drift can explain distribution of species
continents were once connected so species could spread before they became geographically isolated --> species evolved separately leading to the distinct flora and fauna
How extinction events open habitat that may result in adaptive radiation
fewer competitors, more ecological niches vacant --> surviving species can rapidly diversify to fill new niches, leading to evolution
RNA
probably the first genetic material (RNA --> protein is the origin of life)
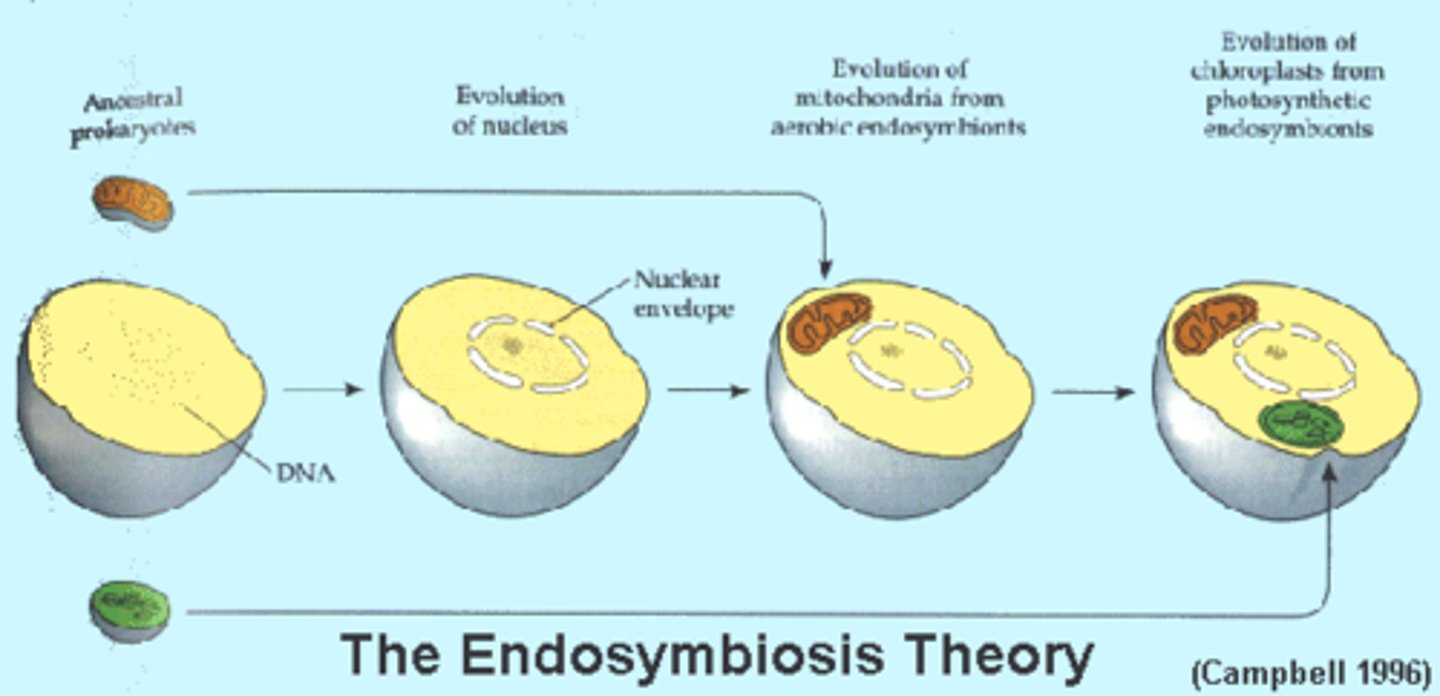
Endosymbiotic theory
certain kinds of prokaryotes began living inside larger cells and evolved into the organelles of modern-day eukaryotes