APHUG Unit 5 NG
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Agriculture
Cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for food or economic gain.
Climate Regions
are the areas that share similar temperatures and precipitation throughout the year
Mediterranean Agriculture
specialized farming that occurs only in areas where the dry-summer climate prevails, olives and tomatoes
Subsistence Agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
Bid-rent Theory
a geographical economic theory to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the CBD increases
CBD
Central Business District (downtown)
Intensive Agriculture
any agricultural system involving the application of large amounts of capital and/or labor per unit of cultivated land; may be part of either subsistence or commercial economy
Clustered Settlement
houses are grouped together in tiny clusters or hamlets
Dispersed Settlement
A rural settlement pattern characterized by isolated farms rather than clustered villages.
Linear Settlement
a pattern of settlements in which homes and other buildings follow the lines taken by the road
Monocropping
An agricultural method that utilizes large plantings of a single species or variety
Monoculture
farming strategy in which large fields are planted with a single crop, year after year
Crop Rotation
the system of growing a different crop in a field each year to preserve the fertility of the land
Plantation Agriculture
Production system based on a large estate owned by an individual, family, or corporation and organized to produce a cash crop. Almost all plantations were established within the tropics; in recent decades, many have been divided into smaller holdings or reorganized as cooperatives
Market Gardening
the relatively small-scale production of fruits, vegetables and flowers as cash crops, frequently sold directly to consumers and restaurants
Mixed Crop and Livestock
both animal and crops are farmed in the same area, it's helpful because farmers could distribute the workload more evenly through the year. Crops are used to feed animals and animals fertilize the field.
Extensive Agriculture
An agricultural system characterized by low inputs of labor per unit land area.
Shifting Cultivation
clearing forests to plant fields for a few years and then abandoning them
Slash and Burn Agriculture
Another name for shifting cultivation, so named because fields are cleared by slashing the vegetation and burning the debris.
Nomadic Herding (pastoral Nomadism)
migratory but controlled movement of livestock, A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals.
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
Domestication
the process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans
Foraging
searching for food that is already available as opposed to growing your own
Agricultural Hearth
an area where different groups began to domesticate plants and animals
Fertile Crescent
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
First Agricultural Revolution
Dating back 10,000 years, the First Agricultural Revolution achieved plant domestication and animal domestication
Second Agricultural Revolution
improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of farm produce through industrialization. Freed up labor from farms for other purposes in society.
Enclosure System
a system in which communal lands were replaced by farms owned by individuals, and use of the land was restricted to the owner or tenants who rented the land from the owner
Third/Green Agricultural Revolution
When selective breeding and genetically modified organisms were introduced to agriculture. Began in the 1960s and continuing today.
Genetically Modified Organism
an organism produced by copying genes from a species with a desirable trait and inserting them into another species. Crops and livestock have been genetically modified over time.
Dual Agriculture (Dual agricultural Economy)
An economy having two agricultural sectors that have different levels of technology and different patterns of demand
Agribusiness
Commercial agriculture characterized by integration of different steps in the food-processing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations.
Hybrid Crops
type of gmo; crossbreed organisms to create new organisms
Farm Subsidies
Government funding or support for farmers to help them survive financially. Crop insurance, direct cash or loans and disaster assistance.
Crop Insurance
Insurance coverage designed to protect a farmer's financial investment in his or her crops. Covers losses to a crop's profitability.
Organic Agriculture
production of crops without the use of synthetic pesticides or fertilizers
Family Farm
A farming operation wholly owned by a family or family corporation that sells its products to some defined market, either directly or through a cooperative
Corporate Farm
a large farm that is run by a corporation, or an agricultural company
Vertical Integration
Practice where a single entity controls the entire process of a product, from the raw materials to distribution
Commodity Chain
A chain of activities from the manufacturing to the distribution of a product.
In farming -
1) Farmer/field
2) Processors (mills/silos)
3) Distributors (trucks, trading, cargo shipts)
4) Retailers/Grocery Stores (restaurants)
Tariffs
Taxes on imported goods, including crops
Used to make foreign goods more expensive and domestic ones more preferable
NAFTA/USMCA
North American Free Trade Agreement; allows open trade with US, Mexico, and Canada, including crops
Von Thunen Model
model developed by vonThunen, German economist and landowner, to explain the forces that control the prices of agricultural commodities and how those variable prices affect patterns of agricultural land utilization
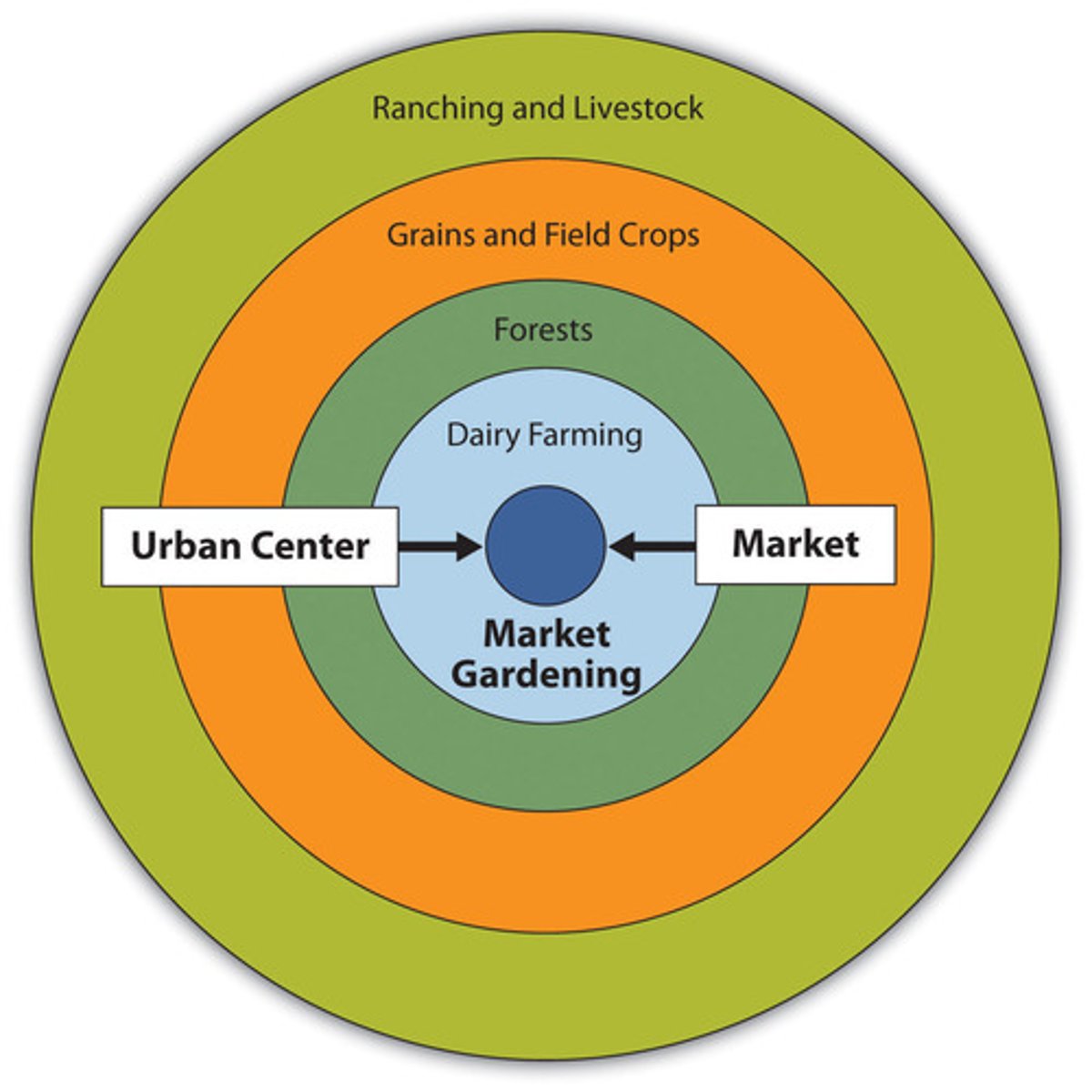
Ranching/Livestock Farming
commercial grazing of livestock, requires lots of land
Global Supply Chain
Worldwide trade of goods and services
For food, some crops are grown in some countries, then transported to other countries where they're processed, and then moved again to be sold in another country
Cash Crops
crops, such as tobacco, sugar, and cotton, raised in large quantities in order to be sold for profit
Fair Trade
trade in which fair prices are paid to producers in developing countries.
Agricultural Landscapes
a landscape resulting from the interactions between farming activities and a location's natural environment
Agroecosystem
An ecosystem created by agriculture. Typically it has low genetic, species, and habitat diversity.
Deforestation
Destruction of forests.
Lots of deforestation is due to increasing need/want for farmland
Terrace Farming (terracing)
a farming system that is in the form of steps going up a mountain
Reservoirs
a large natural or artificial lake used as a source of water supply.
Irrigation
A way of supplying water to an area of land
Aquifer
A body of rock or sediment that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater.
Wetlands
a lowland area, such as a marsh or swamp, that is saturated with moisture, especially when regarded as the natural habitat of wildlife.
Desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semi-dry areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.
Biodiversity (in Agriculture)
Due to monocropping and subsidies, diversity of organic life (plants and animals) is decreasing
Less diversity due to modern agriculture
Salinization of soil
in arid regions, water evaporates leaving salts behind
debt-for-nature swap
When agencies such as the World Bank make a deal with third world countries that they will cancel their debt if the country will set aside a certain amount of their natural resources.
Conservation
Protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
Precision Agriculture
use of computer technology and geographic information systems to automatically vary the chemicals applied to a crop at different places within a field
Local Food Movement
Food is Produced within a fairly limited distance from where it is consumed to reduce use of fossil fuels and commercial farming
Organic Farming
the use of natural substances rather than chemical fertilizers and pesticides to enrich the soil and grow crops
Food Security
Physical, social, and economic access at all times to safe and nutritious food sufficient to meet dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
Food Insecurity
a condition in which people do not have adequate access to food
Suburbanization
The process of population movement from within towns and cities to the rural-urban fringe.
Hunger
the natural physical drive to eat, prompted by the body's need for food
Food Deserts
Areas where it is difficult to find affordable, healthy food options. More common in highly populated low-income urban neighborhoods where there are fewer grocery stores
Economies of Scale
Cost reduction as you produce more
Large corporate farms have economies of scale advantage over small family farms, which means they can offer lower prices