Academic Decathlon - Chemistry 2022-2023
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/178
Last updated 1:13 PM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific Revolution
a term often used to describe the emergence of modern science during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries; much current scholarship questions the concept of a Scientific Revolution.
2
New cards
practice that was particularly popular during the Middle Ages that focused on trying to change other metals into gold or silver.
Alchemy
3
New cards
the process of relying on experiments and observations in the natural sciences
Empiricism
4
New cards
the simplest type of substance with unique physical and chemical properties
Elements
5
New cards
a charged particle formed when an atom either gives up one or more electrons or gains one or more electrons
Ion
6
New cards
the average mass of an atom of an element; it is the weighted average of the isotopes based on the proportion of each isotope in a given element sample.
Atomic mass
7
New cards
an instrument used to measure the relative masses of ions
mass spectrometers
8
New cards
the idea that matter is made up of fundamental particles called atoms
Atomic theory of matter
9
New cards
state of matter characterized by molecules being spread out from each other and therefore highly compressible; takes the shape of any container it is in, creating uniform pressure in all directions
gas
10
New cards
English chemist and physicist who formulated atomic theory and the law of partial pressures
John Dalton
11
New cards
first to propose that matter was composed of small, indestructible particles or atoms
Leucippus and Democritus
12
New cards
measure of how hot or cold a substance is relative to another substance; a measure of the thermal (motion) energy content of a system
temperature
13
New cards
a law stating that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the pressures of the individual gases in the mixture
law of partial pressures
14
New cards
the starting substances in a chemical reaction
reactants
15
New cards
the substances that are formed in a chemical reaction
products
16
New cards
of the same proportion of each element.
Proust's law of definite proportions
17
New cards
mass law that states if two elements react to form more than one compound, the masses of one element will combine with the other element in a whole number ratio
Law of Multiple Proportions
18
New cards
Published in 1808 by John Dalton; included Dalton's basic atomic principles
A New System of Chemical Philosophy
19
New cards
the very dense positively charged center part of the atom that contains the protons and neutrons and, consequently, most of the mass of the atom
nucleus
20
New cards
fundamental particle of matter that has a negative charge; discovered by J. J. Thompson in 1896
electrons
21
New cards
a discrete unit or quantum of electromagnetic radiation; forms include microwaves, light waves, X rays, and gamma rays; photons are emitted when electrons move from one energy state to another in an atom, for example, when an excited electron drops from the sixth energy level to the second energy level; the energy released to make the change is the energy of the emitted photon.
proton
22
New cards
a fundamental particle of matter found in the nucleus that has a mass of 1.009 amu but no electric charge; first identified by Sir James Chadwick in 1932
neutrons
23
New cards
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom; this identifies the type of atom; for example, all atoms with seven protons are nitrogen.
atomic number
24
New cards
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
mass number
25
New cards
an alternate form of the same element that has a different mass number due to its having a different number of neutrons
isotope
26
New cards
a nuclear species of an atom characterized by mass (protons + neutrons), charge (protons), and energy content
nuclide
27
New cards
an atom whose nucleus will break up to form a more stable arrangement of the nuclear particles; natural or artificial transmutation was first discovered by Antoine Henri Becquerel in 1896; radioactivity is not affected by the chemical state of the atom, and thus processes like burning do not destroy an atom's radioactivity.
radioactive atoms
28
New cards
Abbreviated amu and also called a Dalton, it is the mass equal to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
atomic mass units
29
New cards
An isotope of hydrogen with one proton and one neutron in the nucleus having an atomic weight of 2.014
Deuterium
30
New cards
radioactive carbon
C-14
31
New cards
a metal alloy made with primarily iron and carbon whose composition varies; other components can include nickel, chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, or zirconium.
Steel
32
New cards
the smallest possible unit of energy; this unit can apply to any form of energy.
quantum
33
New cards
a discrete unit or quantum of electromagnetic radiation; forms include microwaves, light waves, X rays, and gamma rays; photons are emitted when electrons move from one energy state to another in an atom, for example, when an excited electron drops from the sixth energy level to the second energy level; the energy released to make the change is the energy of the emitted photon.
photon
34
New cards
the spectrum produced when atoms absorb specific wavelengths of incoming light and become excited from lower to higher energy levels; this pattern of absorption can be used in identifying an element.
absorption spectrum
35
New cards
the line spectrum produced when excited atoms return to lower energy levels and emit photons characteristic of the element; the pattern of emission can be used in identifying an element.
emission spectrum
36
New cards
a model of the atom where electrons orbit the nucleus like planets around the sun, but at predetermined distances; electrons can transition from one orbit to a different empty one.
Bohr model of the atom
37
New cards
a model of the atom that explains the presence of electrons as "stationary" waves in orbitals
quantum mechanical model
38
New cards
the emission of an electron from a metal's surface as a result of the absorption of a photon (electromagnetic radiation); this phenomenon was first explained by Albert Einstein; the amount of energy varies depending on the metal and the wavelength of the photon.
photoelectric effect
39
New cards
an experiment showing that electrons are scattered off crystals of nickel and interfere with each other - also know as "electron diffraction"
Davisson-Germer Experiment
40
New cards
Danish physicist whose model of the atom and how it absorbs and emits energy contributed to quantum theory and is also widely used in the teaching of elementary chemistry today.
Niels Bohr (1885-1962)
41
New cards
the representation of the areas occupied by electrons in the atom; the types of electron clouds include ones with different shapes called "orbitals."
electron "cloud
42
New cards
in an atom, the area in space around the nucleus where an electron is found; each orbital holds only one or two electrons.
orbital
43
New cards
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
periodic table
44
New cards
column on the periodic table; for example, alkali metals (group 1) or noble gases (group 18)
groups
45
New cards
half the distance between two adjacent atoms in an element's crystal
Atomic radius
46
New cards
the amount of energy needed to remove a mole of electrons from a mole of atoms (one electron per atom) in the gaseous state; measured in kilojoules per mole
ionization energy
47
New cards
the energy change, in kJ, when one mole of atoms of an element adds a mole of electrons (one per atom)
Electron affinity
48
New cards
the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in relative units
Electronegativity
49
New cards
bonds that occur between two oppositely charged ions
ionic bond
50
New cards
a molecule that contains at least two different elements that are chemically combined in a fixed ratio
compound
51
New cards
an attractive force that exists between two atoms such that the combination of atoms behaves as a unit that requires force (energy) to break apart
chemical bond
52
New cards
the sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms in a chemical bond
covalent bonds
53
New cards
a compound consisting of two or more atoms held together by a chemical bond
molecule
54
New cards
force created by the attraction of oppositely charged ions or charged particles
electrostatic force
55
New cards
the force in a bond that holds the atoms within a molecule together
intramolecular
56
New cards
a type of bond that forms between metal atoms in a solid metal, where the atoms act as if positive ions form and electrons are mobile in a "sea" and so can conduct an electric charge
metallic bonds
57
New cards
written expression using symbols and subscripts to indicate the number and type of each atom in a chemical unit
chemical formula
58
New cards
the type of force that attracts one molecule to another molecule
intermolecular forces
59
New cards
a solid or liquid mixture of two or more metals; some common alloys include steel, brass, and bronze.
alloy
60
New cards
an alloy of primarily copper and zinc with varying proportions of each metal
Brass
61
New cards
weak forces of attraction between atoms or molecules that result from permanent or temporary electrostatic forces
van der Waals forces
62
New cards
a molecule with an unequal overall distribution of permanent positive and negative charge; such a molecule has a net dipole moment that is not equal to zero.
polar molecules
63
New cards
weak attraction that results from a polar molecule inducing a dipole in an atom or in a nonpolar molecule by disturbing electron arrangement of the nonpolar species
induced dipoles
64
New cards
a momentary induced dipole created when a polar molecule distorts the electron cloud of a nonpolar molecule
temporary dipoles
65
New cards
a molecule without a net permanent dipole
nonpolar molecules
66
New cards
a type of dipole-dipole force between molecules involving the attraction of a hydrogen, which is bound to one strongly electronegative atom, either a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom in another molecule; for example, the bond that occurs when the hydrogen in a water molecule is attracted to the nitrogen atom in an ammonia molecule.
Hydrogen bonds
67
New cards
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
DNA
68
New cards
discovered the structure of DNA
James Watson and Francis Crick
69
New cards
British chemist and physicist who established that water is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen and who calculated the density of the earth (1731-1810)
Henry Cavendish
70
New cards
repeating pattern of positive and negative ions forming an ionic compound
Ionic lattice
71
New cards
an extended lattice formed of covalent bonds, such as in SiO2 or diamond
covalent network
72
New cards
Compounds with ionic bonds exist as lattice networks extending in three dimensions. Sodium chloride consists of a lattice of alternating Na+ and Cl- ions.
Sodium Chloride Lattice Structure
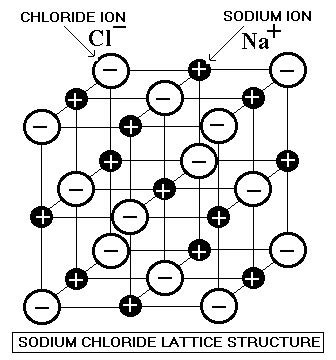
73
New cards
The structure of part of a DNA double helix.
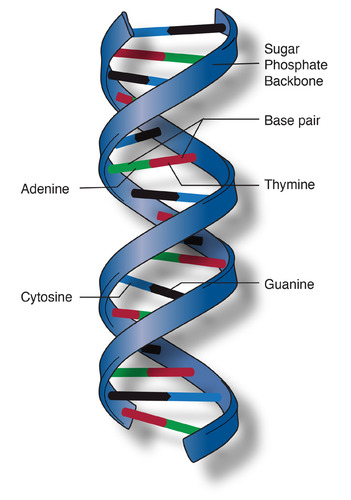
74
New cards
A summary of intermolecular forces
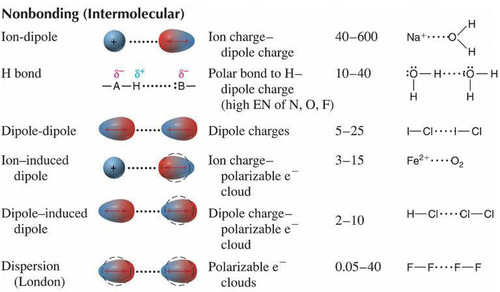
75
New cards
A summary of intramolecular forces.
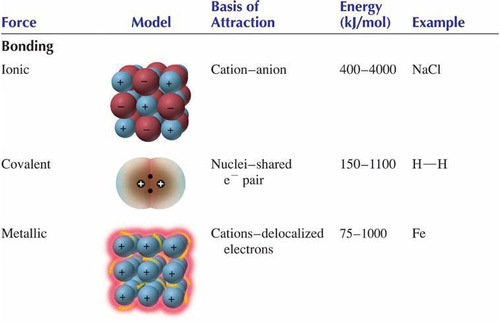
76
New cards
The Bohr model of the atom.
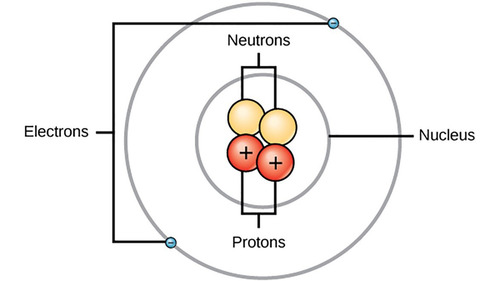
77
New cards
In the quantum mechanical model, the electrons are not at exact distances or fixed locations and do not rotate in orbits
The quantum mechanical model of the atom.
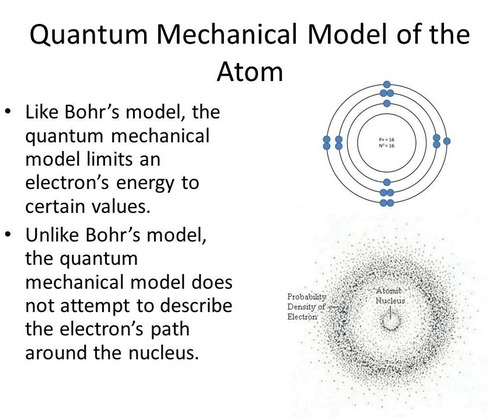
78
New cards
a gas law that states that equal
volumes of an ideal gas contain equal numbers of
particles at constant temperature and pressure and
thus the volume of a gas is directly proportional to
the number of moles of the gas
volumes of an ideal gas contain equal numbers of
particles at constant temperature and pressure and
thus the volume of a gas is directly proportional to
the number of moles of the gas
Avogadro's law
79
New cards
a solid held together by weak intermolecular forces between the molecules; typical molecular solids have relatively low melting points and boiling points.
molecular solids
80
New cards
one of several possible forms of an element; for instance, carbon can be graphite, diamond, or buckminsterfullerene (commonly called "buckyballs").
allotropes
81
New cards
any substance with a low thermal conductivity and/or low electrical conductivity
insulator
82
New cards
a unit cell of a crystal where there is a particle at each corner of a cube and one in the center
body-centered cubic
83
New cards
describes a crystal structure that has atoms at each corner of the cube and six atoms at each face of the cube
face-centered cubic
84
New cards
a crystal structure based on a hexagonal unit cell layering
close-packed hexagonal
85
New cards
refers to the appearance of a substance's surface in reflected light; metals have luster.
lustrous
86
New cards
producing sound
sonorous
87
New cards
a state of matter such as a solid, liquid, or gas
phase
88
New cards
describes the property of a substance indicating it can easily be flattened into thin sheets
malleable
89
New cards
the property of a metal that describes how easily the metal can be pulled into a wire without breaking
ductile
90
New cards
the condition of a chemical reaction when the forward rate and the reverse rate are equal, so there is no apparent change
Equilibrium
91
New cards
the endpoint of the liquid-gas curve on a phase diagram; it is the point at which a vapor and liquid become indistinguishable.
critical point
92
New cards
the one temperature and pressure at which all three phases of a substance (solid, liquid, and gas) exist at the same time in equilibrium with each other
triple point
93
New cards
the temperature at which a substance transitions from a solid to a liquid; usually measured at 1 atmosphere of pressure
melting point
94
New cards
the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid substance equals the atmospheric pressure; normal boiling points are defined at 1 atmosphere of pressure.
boiling point
95
New cards
- invented analytic balance
- discovery of fixed air ( CARBON DIOXIDE) by pouring acid on chalk and capturing the bubbles (heavier than air)
- discovery of fixed air ( CARBON DIOXIDE) by pouring acid on chalk and capturing the bubbles (heavier than air)
Joseph Black (1728-1799)
96
New cards
the process of being surrounded by water solvent molecules; this process can also form solid crystals called hydrates.
hydration
97
New cards
capable of being dissolved
soluble
98
New cards
incapable of being dissolved
Insoluble
99
New cards
a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout
homogenous mixture (solution)
100
New cards
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solvent