Diagnostics Pulm Radiology
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
The average accumulated background of radiation dose to an individual for one year, exclusive of radon in US
1 mSv, by exposure to 1 mG of radiation
What is the mean radiation doe to adult from a chest radiograph (front vs side)
0.02 for PA and 0.08 for LL
Indications of a CXR
Diagnose conditions involving the chest wall- can include bony structures, lungs, heart, great vessels
screen for job related lung diseases
check position of medical equipment
initial screening tool for cancer or TB
When is a CXR emergent
chest pain, SOB, chest injury, hemoptysis, decreased breath sounds, determination for pneumothorax, pneumonia, rib fracture, cardiomegaly, effusion
When is a CXR urgent
symptoms lasting more than 3 weeks without obvious diagnostic cause; changes in cough or new cough, dyspnea, chest or shoulder pain
When is a CXR chronic
follow up, surveillance for COPD and lung cancer
Using a CXR for preventative screening
not generally recommended due to limited effectiveness for early lung cancer (low sensitivity) and false positives. It should be used for screening in specific situations like when individuals are exposed to occupational lung diseases or high risk populations where access to LDCT is limited
CXR CI
No absolute CI
consider in pregnancy, children, metal implants (more for MRI), immobility, medical necessity
What do you need to do before interpreting any CXR
verify name, MRN, correct date, correct study
What are CXR markers used for
put on images to determine side of body or landmark by writing date of procedure or name, or R and L
CXR during expiration
this increases the attenuation of the normal lung, increases the contrast between lung and pneumothorax or the demonstration of unilateral air trapping as lungs appear denser, widening of cardiac silhouette due to more horizontal position and increased basal opacity with obscures the pulmonary blood vessels, mimicking lung disease
heart appear larger, mediastinum shifts to normal side, scapulas tucked, sensitivity not increased over inspiratory CSR in detecting pneumothoraxes
CXR during inspiration
generally better quality, lungs more expanded, diaphragm below 9th rib, heart and mediastinum less enlarged, lung bases less hazy, scapulas winged
What is considered a well penetrated CXR
Penetration is the degree to which Xray's have passed through the body. A well penetrated is one where the vertebrae are just visible behind the heart, and the left hemidiaphragm should be visible to the edge of the spine
In what cases would there be a loss of hemidiaphragm contour or of the paravertebral tissue lines in CXR?
lung or mediastinal pathology
What does overpenetration look like on a CXR?
overexposed, too dark, lungs look black, too many x rays reaching x ray plate
What does under penetration look like on CXR?
underexposed, lung and heart too white, cannot see spine behind heart, too few x rays reaching Xray plate
Problems with rotating CXR
interpretation is difficult: difficult to know if trachea is deviated, lung density changes due to asymmetry of overlying soft tissue, difficult to comment accurately on heart size, thickness of soft tissue in chest is altered, spinous processes lie nearer one clavicle than the other
What to give attention to with describing abnormalities in CXR
location, size, shape, density of abnormality
Density on CXR
an area on the x ray that is brighter than expected
Opacity on CXR
an area of increased density on the xray
Lucency on CXR
the opposite of density, where more x-rays pass through less dense regions; abnormal lucency can occur when there is too much of it or when it's an atypical location
Consolidation of CXR
a pattern of abnormal pulmonary opacification
Atelectasis on CXR
a pattern of abnormal pulmonary opacification that indicates collapse
Interstitial opacification on CXR
a pattern of abnormal pulmonary opacification that appears as lines
Nodular opacification on CXR
a pattern of abnormal pulm opacification that appears at dots
Pleural thickening on CXR
may be a sign of lung cancer, idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, or mycobacterial infection
Air trapping on CXR
the retention of air in lung parenchyma distal to an obstruction of one or more airways
What are alveolar infiltrates on the chest X ray?
these are areas of increased density or opacity on a chest xray or CT scan that indicate fluid, inflammation, or other abnormalities in the alveoli
Appearance of alveolar infiltrates on the CXR
patchy or diffuse areas of increased density; air bronchograms (black lines representing airways surrounded by infiltrates); may have puffy of ground glass appearance
Causes of alveolar infiltrates
pneumonia, pulmonary edema, ARDS, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, lung cancer, pulmonary embolism
What are interstitial infiltrates on CXR
buildup of cells or noncellular material in the tissue surrounding the air sacs in the lungs- they are abnormalities seen on imaging tests such as CXR or CT that indicate inflammation or fluid accumulation in the interstitial space of the lungs
What are the causes of interstitial infiltrates
infection such as pneumonia, TB, sarcoidosis, AI such as RA, lupus, scleroderma, environmental exposure like asbestos, silica, coal dust, medications like chemo or ABX, and idiopathic
Alveolar vs Interstitial Opacities
alveolar = air sacs
They are radiolucent and can contain blood, mucous, tumor, or edema
Interstitial = vessels, lymphatics, bronchi, and CT
Radio dense, interstitial disease with prominent lung markings with aerated lungs
ABCDE of CXR interpretation
airway, bones, cardiac, diaphragm, everything else
Airway of CXR
trachea, mediastinal width, aortic knob
DO NOT MISS deviate trachea
B of CXR
lung field outlines, symmetry, pleural
DO NOT MISS pneumothrorax
C of CXR
heart size on PA film, heart borers, heart shape
D of CXR
hemidiaphragm levels, diaphragm shape or contour, costophrenic angles
DO NOT MISS subdiaphragmatic free air (pneumo-peritoneum)
E of CXR
NG tube, pacemaker, ECG electrodes, PICC line, foreign body, ET tube
RIPE pneumonic for CXR image quality
Rotation: medial aspect of each clavicle should be equidistant from the spinous processes
Inspiration: the 5-6 anterior ribs, lung apices, both costophrenic angles and the lateral rib edges should be visible
Projection: not if AP or PA view
Exposure: the left hemidiaphragm should be visible to the spine and the vertebrae should be visible behind the heart
PA view of CXR
PA CXR is a standard front chest XR that uses XR beam to image the chest from back to front, and is the best general xray for examining heart, lungs, and other structures of the chest
PA technique of CXR
the patient stands facing a flat surface with their chest against the xray film--> the patient holds their arms up or to their sides and rolls their shoulders forward--> the xray beam passes through the patient from back to front --> the patient inhales deeply to fill their lungs
when do we perform an AP CXR?
In ICU, OR, Pt room; when patient is too sick to stand up or leave their bed
AP technique of CXR
patient lies on their back or is partly upright --> x ray tube is placed in front of patient's chest--> x ray film or detect panel is placed behind chest
Difference between AP and PA views of CXR
PA: scapula is seen in periphery of thorax, clavicles project over lung fields, posterior ribs are distinct, position of markers
AP: scapulae are over lung fields, clavicles are above the apex of lung fields, position of markers, anterior ribs are distinct
What are limitations of the AP CXR?
Heart side- heart appears larger and mediastinum appears more prominent
Lung bases- position limits depth of respiration which can limit evaluation of lung bases
Rotation: patients may be slightly rotated which can affect interpretation of the mediastinum
CXR lateral technique
Patient is standing, left side of thoraxx is adjacent to the image receptor, both arms raised above the head, preventing superimposition over the chest, chin raised out of image field, midsagittal plane must be perpendicular to divergent beam
Lateral CXR is most commonly ordered with what?
PA image
Advantages and disadvantages of decubitus CXR
A: allows for better visualization of fluid or air in the lungs, useful to determine the extent of loculation of fluid or air, can detect smaller amounts than upright CXR
D: uncomfortable for patient, may be difficult to interpret if patient is malpositioned
Technique of decubitus CXR
patient is lying on their side, for pneumothorax the side of interest should be up, for pleural effusions the side of interest should be down
Applications of CT
CT enables direct imaging and differentiation of soft tissue structures like liver, lung tissue, and fat. Therefore, it is a valuable tool in searching for large space occupying lesions, tumors, metastasis. They can not only reveal the presence but also the size, location, and extent of a tumor
CT Indications
To evaluate abnormalities shown on CXR. To demonstrate or exclude a suspected CXR abnormality. To demonstrate an abnormality in a patient with a normal CXR
CT contraindications
pregnancy, excessive, radiation exposure, contrast contraindication (iodine sensitivity, shellfish allergy, kidney disease)
Pathology of Pneumothorax
spontaneous, traumatic, iatrogenic, tension, extension of mediastinal air, air leak followign resection, bronchopleural fistula
History of pneumothorax
Most often presents with sudden onset of dyspnea and pleuritic chest pain, usually felt unilateral but in rare cases central or bilateral. Symptoms usually develop wen the patient is at rest, but sometimes can develop during exercise, air travel, invasive procedure or trauma to the chest, neck, gut, abdomen. Typical age is early 20s for a spontaneous pneumo
Pneumothorax PE
If small, findings may not evident.
If large, characteristic findings include decreased chest excursion on the affected side, enlarged hemothorax on the affected side, diminished breath sounds, absent tactile or vocal fremitus, hyper resonant percussion, as well as subq emphysema
labored breathing or accessory muscle use suggests sizable pneumothorax
tracheal deviation late sign of tension pneumo
hemodynamic compromise is ominous sign of tension pneumothorax or impending cardiopulmonary collapse
Tension PTX pathophysiology
A tension pneumothorax arises when air in the pleural space builds up enough pressure to interfere with venous return, leading to hypotension, tachycardia and severe dyspnea
Traditional teaching suggested that contralateral shift of the trachea and mediastinum, splaying of the ribs, and flattening of the ipsilateral diaphragm represent radiographic tension. However, these findings may result from atmospheric intrapleural pressure on the side of the pneumothorax while the pleural pressure on the contralateral side remains negative. Clinical evidence of tachycardia, hypotension, and severe dyspnea is more indicative of tension
Signs of a pneumothorax
deep sulcus
Needle decompression for a tension pneumothorax (traditional vs modern)
traditional: 2nd intercostal space in the midclavicular line. Difficulty finding the correct anatomical site, often times going too medially. 14g angiocath will fail to reach the chest cavity in more than 50% of cases
Modern: 4th or 5th intercostal space in the anterior axillary line. Chest wall is thinner making it easier to reach chest cavity. Less vital structures that could be injured. Easier to identify correct anatomical landmarks
Diagnostic imaging for pneumothorax
CT, CXR, US
US findings for pneumothorax
Lung sliding, comet tails (vertical artifact)
One CT scan is the same number of ____ CXR
200
US sensitivity and specificity
US sensitivity is 86-90% and specificity is 97-100%
What is the lung point in a pneumothorax US
the interface of where the healthy lung starts and where the pneumothorax ends
What is M mode in pneumothorax US?
seashore appearance in normal lung but barcode appearance in pneumothorax due to absence of lung movement
What is pleural thickening on CXR
Pleural thickening is a buildup of scar tissue in the lining around the heard, caused by inflammation, infection, lung disease, or malignancy. It is more common in men, smokers, and tall pts with low body weight. Appears on a chest X-ray as an irregular density or stripe at the lung's apex or deformed areas at top of lung
What are pleural plaques and when do we see this?
Pleural plaques are caused by asbestos fibers where they become trapped in the pleura, leading to inflammation and scarring
What is a Pancoast tumor?
This is a soft tissue opacity or mass in the apex of the lung. You may also find asymmetry of the lung apices, thickening of the pleura, local rib destruction, tracheal deviation, mediastinal enlargement. Symptoms include severe shoulder and arm pain, horners syndrome, atrophy of the intrinsic hand muscles. Additional testing is needed: CT, MRI, PET
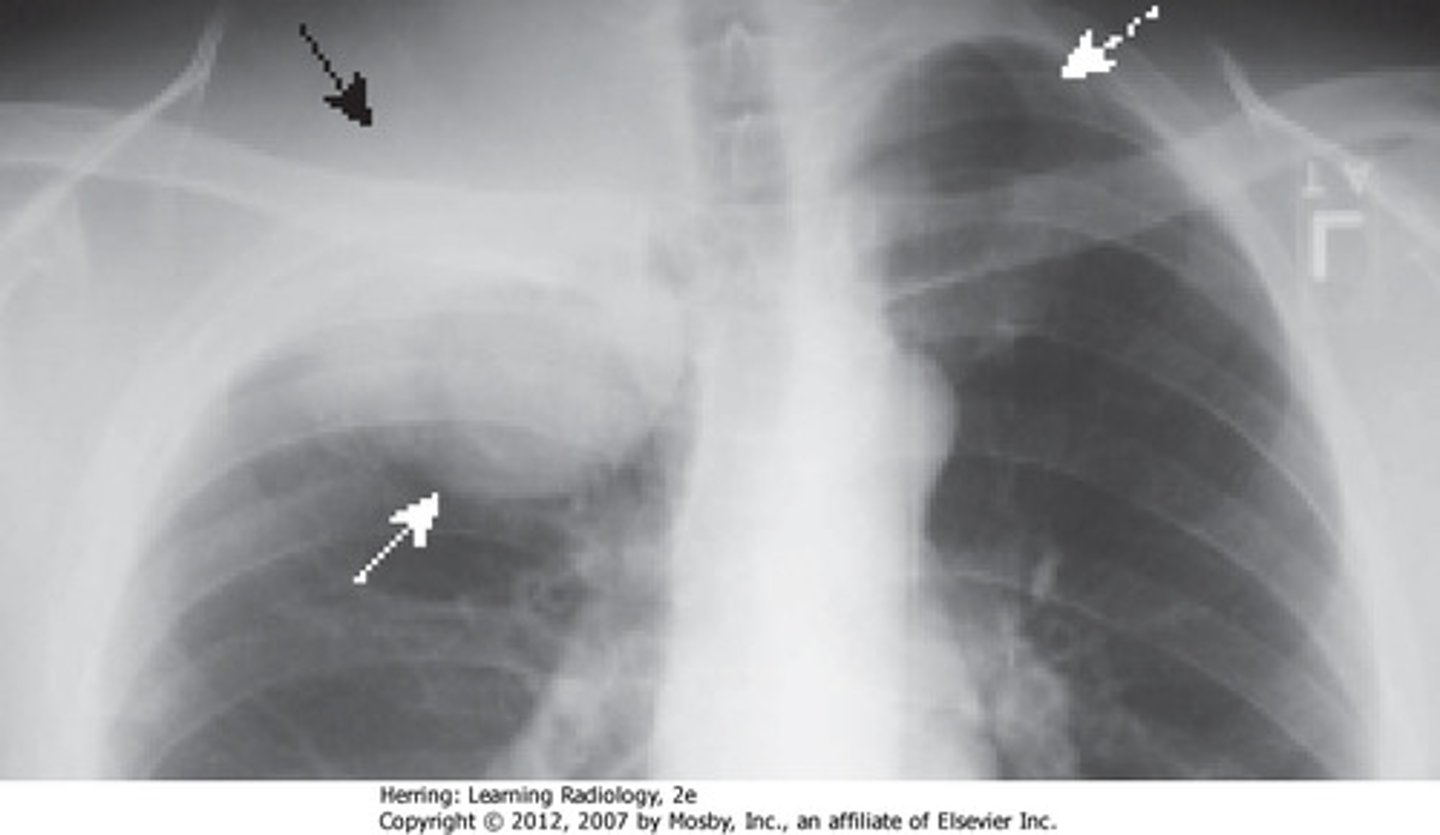
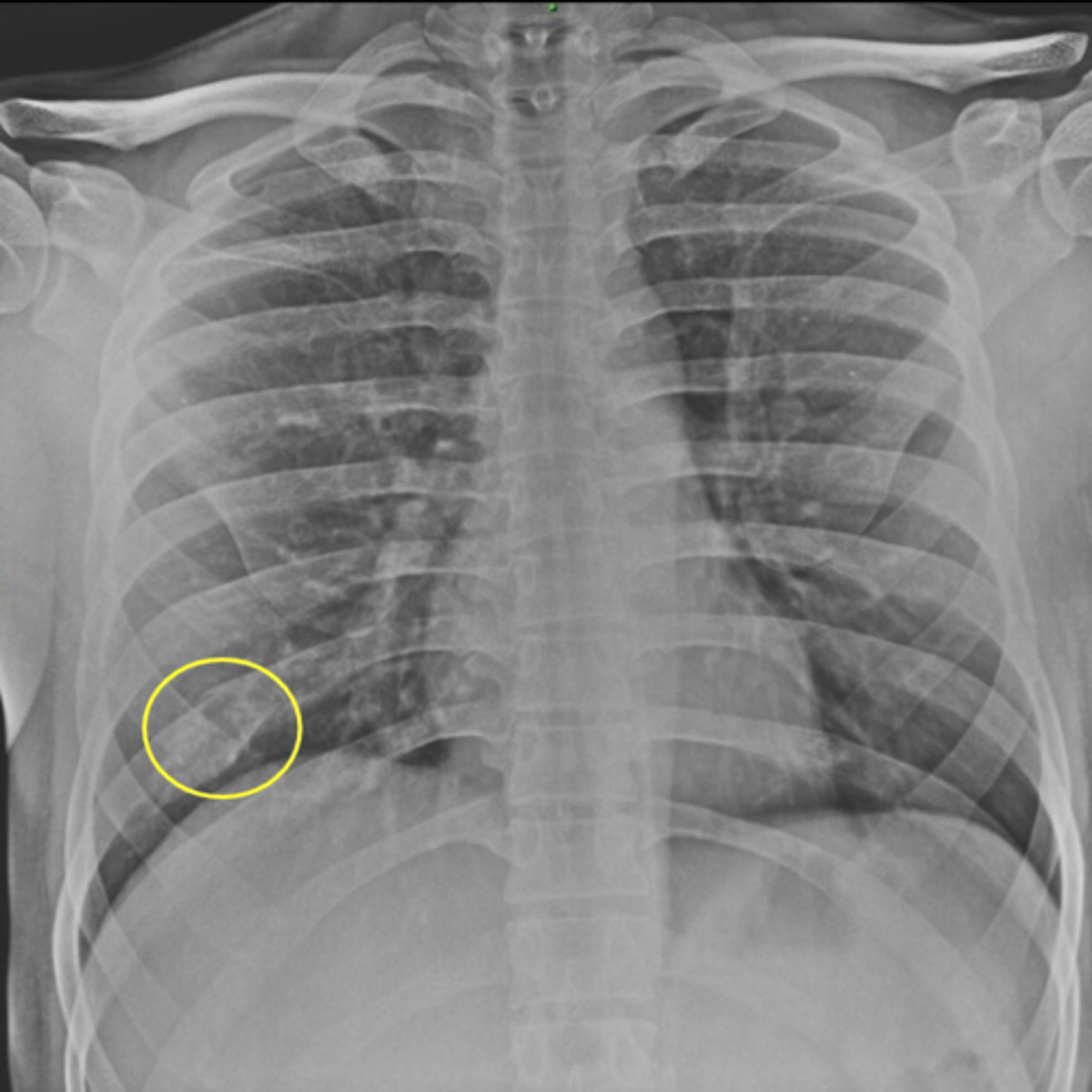
rib fracture on CXR
Subcutaneous emphysema patho
injury to the parietal pleura that allows for the passage of air into the pleural and subq tissues. The air from the alveolus spreads into the endovascular sheath and lung hilum into the endothoracic fascia. The air in the mediastinum spreads into the cervical viscera and other connected tissue planes. The air originates from external sources. Gas generation locally by infections, usually necrotizing infections
Normal volume of pleural fluid
0.1-0.2 ml/kg
Pleural effusion causes
sterile, infection, inflammatory, malignant, chylothorax, diaphragmatic injury, biliary fistula, Boerhaave syndrome
Sx of Pt with pleural effusion
dyspnea, cough, chest pain, weakness, fever, weight loss, hemoptysis, recent trauma, cardiac surgery, cancer dx
PE of someone with pleural effusion
Signs are closely related to the size of a pleural effusion. Labored breathing or accessory muscles used in LARGE effusions. Decreased or absent tactile fremitus, dullness to percuss, diminished breath sounds over site of effusion. bronchial breath sounds are frequently present immediately above the effusion
Buzzword for pleural effusion on CXR
formation of a meniscus
In the average person, the diaphragm should be intersected by the __ and __ anterior ribs at the midclavicular line
5th and 7th
How many ribs are viewable on the PA inspiratory film
10
In what condition will you see an increase in number of viewable ribs
COPD or foreign body aspiration (hyperinflation)
In what condition will you see a decrease in number of viewable ribs
RLD, pleural effusions, atelectasis (under expansion)
Parenchymal crowding can mimic the appearance of what on a CXR
ILD
In a hiatal hernia what may you see
retrocardiac air fluid level within a paraoesophageal hernia or intrathoracic stomach
Ruptures diaphragm
sensitivty of reuptured diaphragm
pneumonia
bacterial pneumonia on CXR
viral pneumonia on CXR
aspiration pneumonia on CXR
Atelectasis
Signs of atelectasis
lobar atelectasis
segmental atelectasis
subsegmental atelectasis
Right lung collapse in a PA view
Cavitation on CXR
Causes of cavitation
Features of cavitations
What can cavitations be from?
Cavitations are an incidation for _____
CT scan
How does pleural effusion look on CXR
Hemothroax is indistinguishable from