Topic 14/15 - Particle Model
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Define: Density
Mass per unit volume.
State the equation linking density, mass and volume.
Mass = Density x Volume.
State the symbols for density, mass and volume.
Density = p
Mass = m
Volume = V
State the units for density, mass and volume.
Density = kg/m3
Mass = kg or g.
Volume = m3 or cm3
Describe the arrangement of particles in a solid.
Closely packed in a definite shape and volume. Arranged in a regular pattern.
Describe the movement of particles in a solid.
Vibrate in fixed positions.
Describe the arrangement of particles in a liquid.
Closely packed. Definitive volume but no definitive shape. Arranged in a random, irregular pattern.
Describe the movement of particles in a liquid.
Flow around one another.
Describe the arrangement of particles in a gas.
Far apart. No definitive shape and volume. Arranged in a random, irregular pattern.
Describe the movement of particles in a liquid.
Randomly in all directions at high speeds.
Order the states of matter from least to most amount of kinetic energy.
Solid, liquid and gas.
Which states of matter have a definitive shape?
Solid.
Which states of matter have a definitive volume?
Solids and liquids.
Which states of matter can be compressed?
Gases.
Why are gases easily compressed?
There are large gaps between particles so it’s easier to push them closer together.
Order the states of matter from least to most dense.
Gas, liquid and solid.
Which state of matter is the most dense?
Solid.
Which state of matter is the least dense?
Gases.
What is always conserved when a substance undergoes a change of state?
Mass.
What is the difference between physical and chemical changes?
Physical changes can be reversed whereas chemical changes cannot be easily reversed.
Why is a change of state describes as a physical rather than chemical change?
The material can be reserved to its previous properties.
Is a change of state a chemical or physical change?
Physical.
Which two states of matter have similar densities?
Liquids and solids.
Describe the change of state that occurs when a solid turns into a liquid.
Melting.
Describe the change of state that occurs when a liquid turns into a solid.
Freezing.
Describe the change of state that occurs when a gas turns into a liquid.
Condensation.
Describe the change of state that occurs when a liquid turns into a gas.
Evaporation.
Describe the change of state that occurs when a solid turns into a gas.
Sublimation.
Describe the change of state that occurs when a gas turns into a solid.
Deposition.
Which change of state occurs during melting?
Solid to liquid.
Which change of state occurs during freezing?
Liquid to solid.
Which change of state occurs during evaporation?
Liquid to gas.
Which change of state occurs during condensation?
Gas to liquid.
Which change of state occurs during sublimation?
Solid to gas.
Which change of state occurs during deposition?
Gas to solid.
What is the internal enrgy of a substance?
The energy stored by the particles.
Which two things can heating a substance do?
Raise its temperature or change the state.
If temperature of a system increases, what does this temperature increase depend on?
Mass of substance heated, type of material and energy input into the system.
How does heating cause a substance to change state?
Heating matter gives particles more energy, breaking the bonds of attraction between particles.
Which equation links change in thermal energy, change in temperature, specific heat capacity and mass?
Change in thermal energy = change in temperature, specific heat capacity and mass.
State the units for change in thermal energy, change in temperature, specific heat capacity and mass.
Change in thermal energy = J.
Mass = Kg.
Specific heat capacity = J/kg °C.
Change in temperature = °C.
State the symbols for change in thermal energy, change in temperature, specific heat capacity and mass.
ΔQ = Change in thermal energy.
m = Mass.
c = Specific heat capacity.
Δθ = Change in temperature.
Define: Specific heat capacity.
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C.
What is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the substance by 1 °C?
Specific heat capacity.
A substances heats up and cools down quickly. Does this substance have a low or high specific heat capacity?
Low.
A substances heats up and cools down slowly. Does this substance have a low or high specific heat capacity?
High.
A substance has a low specific heat capacity. Does it heat up and cool down quickly or slowly?
Quickly.
A substance has a high specific heat capacity. Does it heat up and cool down quickly or slowly?
Quickly.
Why do substances that warm up and cool down quickly have higher specific heat capacity?
It takes more energy to change its temperature.
Why do substances that warm up and cool down quickly have lower specific heat capacity?
It takes much less energy to change its temperature.
Does water have a high or low specific heat capacity?
High.
Why is water ideal for heating homes?
It has a high specific heat capacity so the water remains hot in a radiator for a long time.
Do good electrical conductors of heat have high or low specific heat capacity?
Low.
Define: Specific latent heat.
Amount of thermal energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance with no change in temperature.
What is the amount of thermal energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance with no change in temperature called?
Specific latent heat.
State the symbol and units for specific latent heat.
Symbol = L. Units = J/kg.
What is specific latent heat of fusion?
The thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of solid to liquid with no change in temperature.
What is the thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of solid to liquid with no change in temperature called?
Specific latent heat of fusion.
What is specific latent heat of vaporisation?
The thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of liquid to gas with no change in temperature.
What is the thermal energy required to convert 1 kg of liquid to gas with no change in temperature?
Specific latent heat of vaporisation.
What is the difference between specific heat capacity and specific latent heat?
Specific heat capacity is used for a change in temperature in the same state.
Specific latent heat is used for a change in state but no change in temperature.
State the equation linking mass, specific latent heat and thermal energy.
Thermal energy = Mass x Specific latent heat.
State the symbols for mass, specific latent heat and thermal energy.
Q = Thermal energy.
m = Mass.
L = Specific latent heat.
State the units for mass, specific latent heat and thermal energy.
Thermal energy = J.
Mass = kg.
Specific latent heat = J/kg.
State the equation linking pressure, area and force.
Force = Pressure x Area.
What is the unit for pressure?
Pascals.
State the symbols for pressure, area and force.
Pressure = P.
Force = F.
Area = A.
State the units for pressure, area and force.
Pressure = Pa.
Force = N.
Area = m cubed.
At what angle does pressure produce a net force to any surface?
Right angle.
Explain the pressure of a gas in terms of the motion of particles.
The particles move in random directions. When they collide with the walls of a container they exert a force which acts at a right angle to the container. This causes pressure.
Which factor affects the average kinetic energy of gas molecules?
Temperature.
Describe how an increase in temperature affects particles and pressure in a gas.
Increased temperature means more energy given to particles as thermal energy is transferred to kinetic energy.
Particles move at faster speeds, causing frequent collisions with walls more often and with a greater impact/force.
This causes an increase temperature.
How does the temperature affect kinetic energy of particles?
Increased temperature means more thermal energy is transferred to kinetic energy.
The hotter the gas, higher the kinetic energy.
The cooler the gas, the lower the kinetic energy.
If gas A is at a low pressure, and gas B is at a high pressure, what can be said about the rate of collisions in each gas?
There are more collisions per second in gas A than in gas B.
When a gas is compressed, what happens to the volume?
Decreases.
When a gas is compressed, what happens to the pressure?
Increases.
When a gas is expanded, what happens to the volume?
Increased.
When a gas is expanded, what happens to the pressure?
Decrease.
How does reducing volume affect pressure? Why?
Pressure increases because molecules become more less out so rate of collision increases. Rate of change of momentum increases, and so force exerted on container increases, resulting in a lower pressure.
How does increasing volume affect pressure? Why?
Pressure decreases because molecules become more spread out so rate of collision decreases. Rate of change of momentum decreases, and so force exerted on container decreases, resulting in a lower pressure.
Is pressure directly or inversely proportional to volume?
Inversely.
What is Boyle’s law calculation?
P1V1 = P2V2.
What is absolute 0 in Kelvin and degrees Celsius?
0K or -273°C.
Explain what absolute 0 is.
The temperature at which particles are no longer moving, therefore have no kinetic energy and cannot collide with the container.
At which temperature do particles have no kinetic energy?
0K or -273°C.
What is 0K or -273°C known as?
Absolute 0.
How do you convert between degrees Celsius and Kelvin?
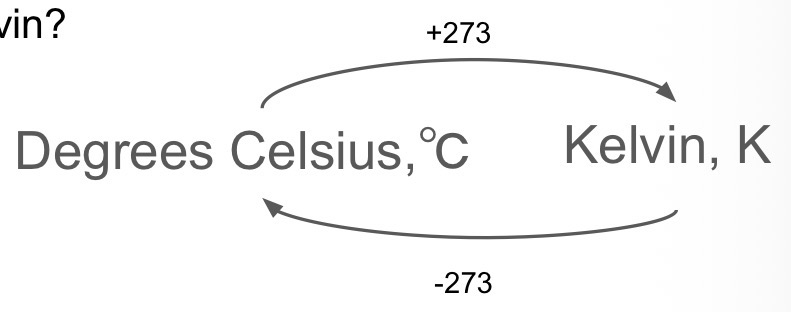
A change in temperature of 1K is equal to change in temperature of how many °C?
1.
What is the freezing point of water in Kelvin and °C?
273K and 0°C.
What is the boiling point of water in Kelvin and °C?
373K and 100°C.
What is work?
Transfer of energy by a force.
What increases when doing work on a gas?
Internal energy and therefore temperature.
Explain how work is involved when using a bicycle pump.
If a thumb is placed on the end of a bicycle pump and it is quickly compressed several times, it will be able to feel the pump getting very warm.
This is because work is done on the gas, kinetic energy increases and therefore a force is exerted, causing its temperature to rise.
What are insulating materials?
Poor conductors of heat.
Do insulating materials tend to have low or high densities?
Low.
Give an example of a good conductor.
Rubber or glass.
What do insulators usually contain?
Trapped air.