The muscular system
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle, or myocardium
It is the involuntary, striated muscle tissue that forms the walls of the heart,
Responsible for its rhythmic contractions that pump blood throughout the body.
It is unique, found only in the heart,
What is a skeletal muscle type?
Skeletal muscle is voluntary
Striated (striped) tissue attached to bones via tendons enabling body movement, posture, and facial expressions through rapid, powerful contractions.
But it tires easily and works in antagonistic pairs (like biceps/triceps) for joint movement.
What is smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is involuntary.
Non-striated, spindle-shaped tissue with a single central nucleus, found lining hollow organs (intestines, bladder, blood vessels, airways).
It controls automatic functions like digestion, blood flow, and pupil size, contracting slowly and sustainedly.
Also, moving substances through internal passageways.
Functions of muscular type
Movement: Enables walking, lifting, and facial expressions through skeletal muscle contraction, and internal movement like blood flow (cardiac) and food passage (smooth).
Posture & Stability: Keeps the body upright and prevents collapse.
Heat Production: Muscle activity generates heat.
Circulation: The heart pumps blood; smooth muscles in blood vessels adjust vessel diameter.
Digestion & Waste: Smooth muscles move food through the digestive tract and help with urination and childbirth.
Protection: Muscles cushion and protect internal organs.
Memory Trick: “My Pretty Hot Chocolate Drinks Please”
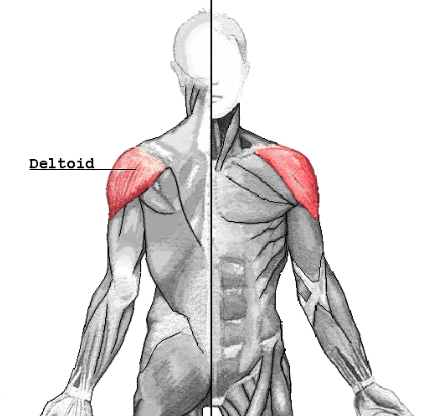
Deltoid muscle
Located in the shoulder, abduction which is lifting the arm away from the body.
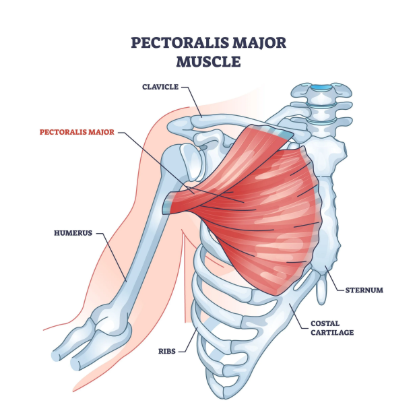
Pectoral (pectoralis major) muscle
Located in the chest, flexation and abduction which is bringing arm across the chest.
Rectus Abdominals muscle
Located at the core/truck, flexation of truck which is bending forward and twisting or rotation.
Gluteus maximus muscle
Buttocks, extension or external rotation of hip/leg (straightening the hip)
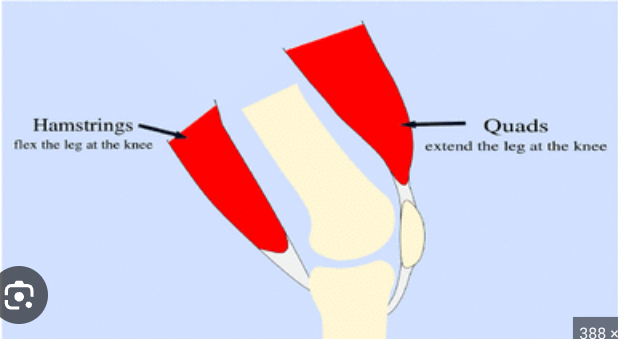
Quadriceps femoris muscle and Hamstrings muscle
Located at the front of the thigh, extension at the knee, which is straightening the leg.
Back of thigh, flexion at the knee which is bending the leg.

Bicep branchii and Tricep branchii
The bicep is located in front of the upper arm, flexion at the elbow which is bending arms.
Tricep is located back of upper arms, extension at the elbow which is straightening the arm.
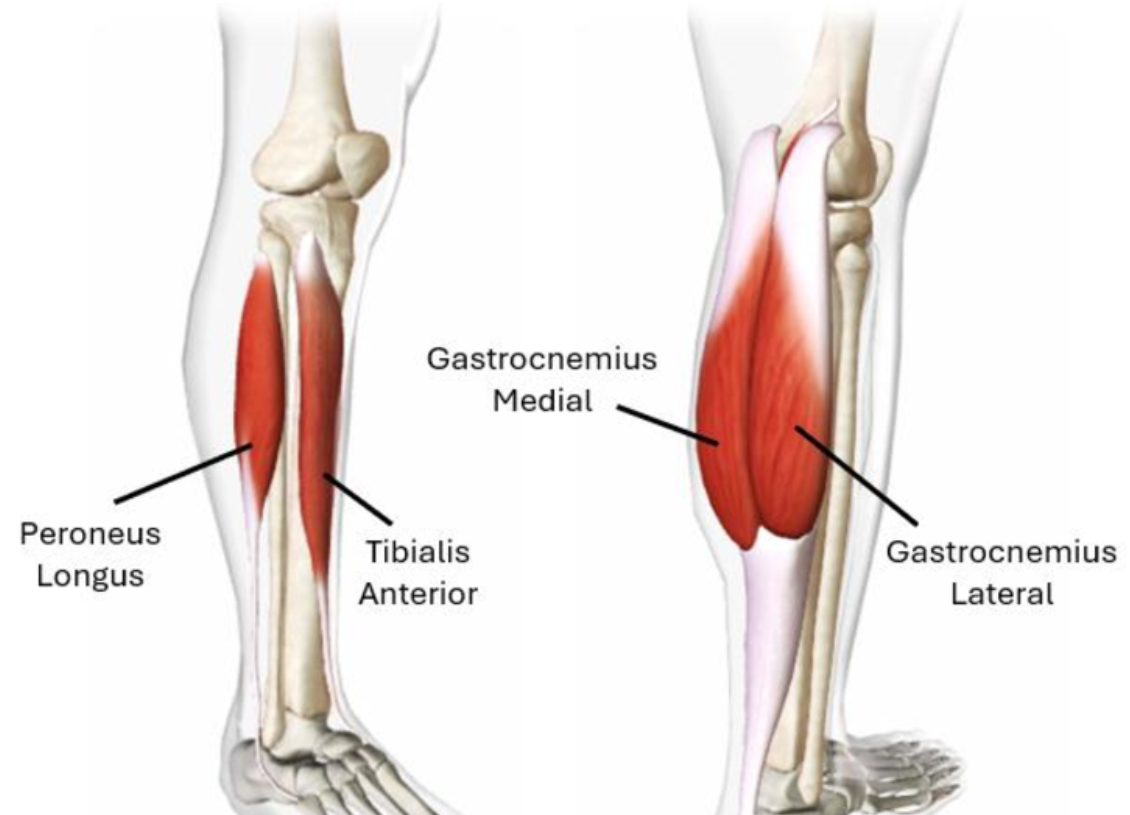
Gastrocnemius muscle and tibialis anterior muscle
Located at the calf (back of lower leg), plantor flexion which is pointing toes and foot downwards at the ankle.
Located in front of the lower leg, dorsi flexion which is lifting toe and foot upwards.
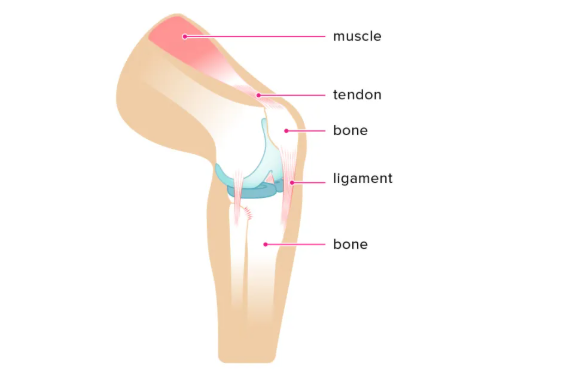
What are tendons?
It is tough, fibrous connective tissues that connect muscle to bones.
What is an antagonist pair?
Muscles are in a pair of antagonist pairs across the joints, which means as one contracts another relaxes.
Agonist- contracts to cause movement.
Antagonist- relaxes and lengthens to move.
E.G. when flexing the elbow the bicep contracts and triceps relaxes.
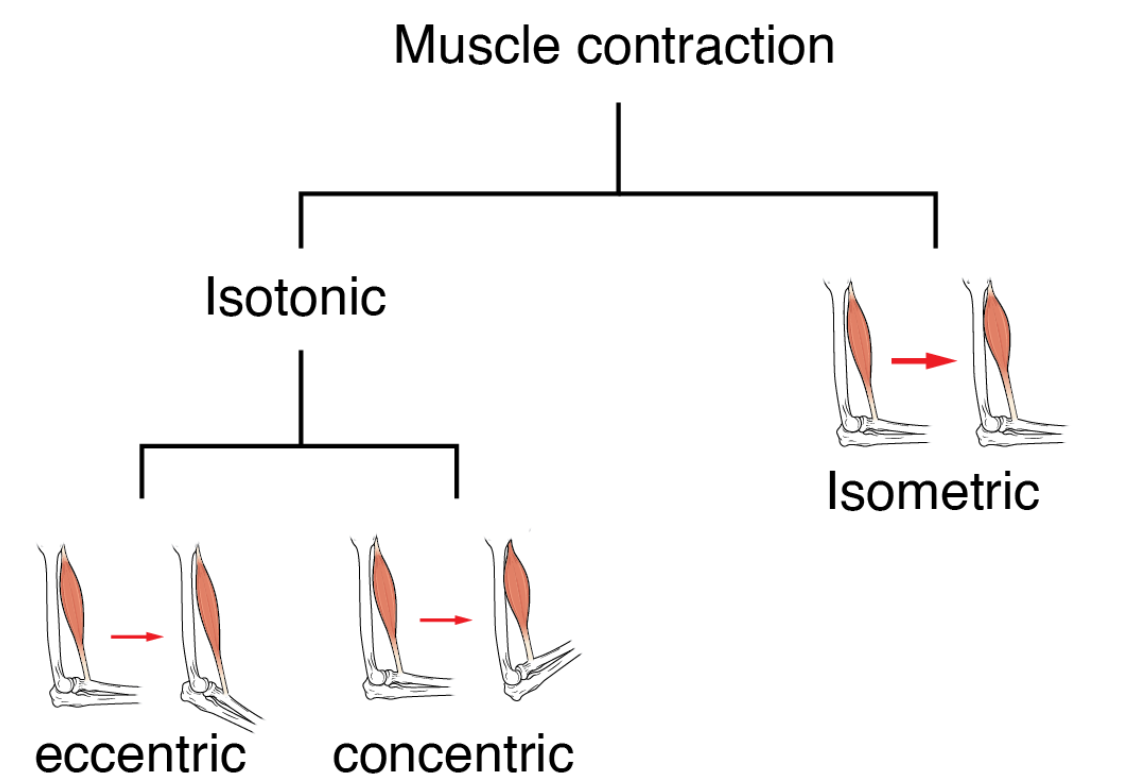
Types of contraction?
Isotonic- muscle shortens and lengthens to produce movement e.g lifting or walking.
Isomentric- contracts but doesn’t change also increases tension e.g holding plank or pushing against immovable object.
Concentric- muscle shortens while producing force e.g lifting weight slowly in bicep curl.
Eccenntric- lengthens by producing force like brake e.g lower weight slowly in bicep curl.