Imaging Exam 2 - Images from Slides
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
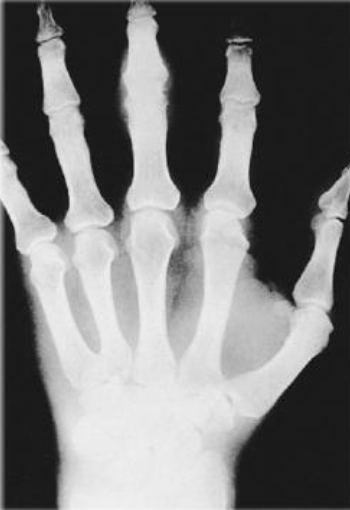
Inflammatory or Pre-Erosive Stage of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
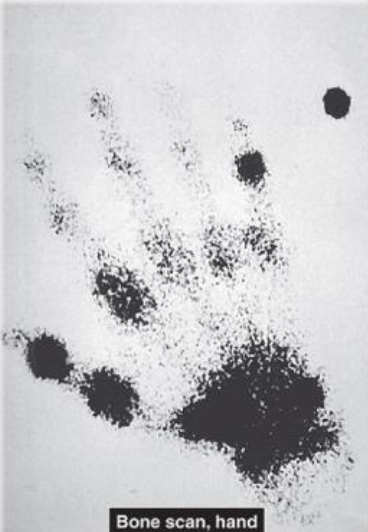
Early Stage of RA on a Bone Scan
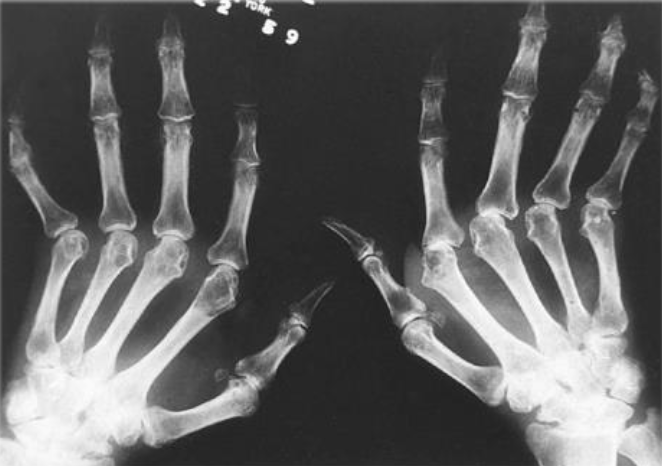
Advanced Stage of RA on a Radiograph
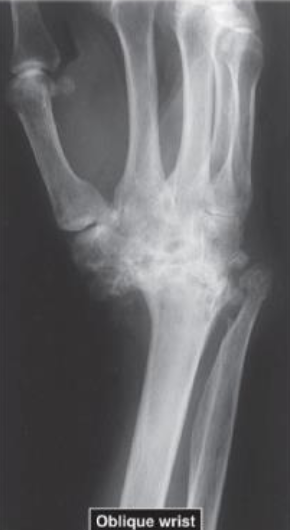
Oblique Radiograph of Ankylosis of Wrist
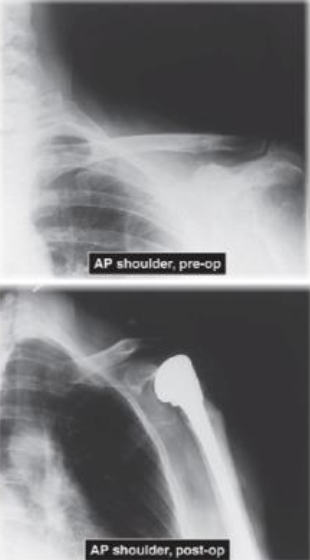
AP View of Humeral Head Prosthetic Replacement
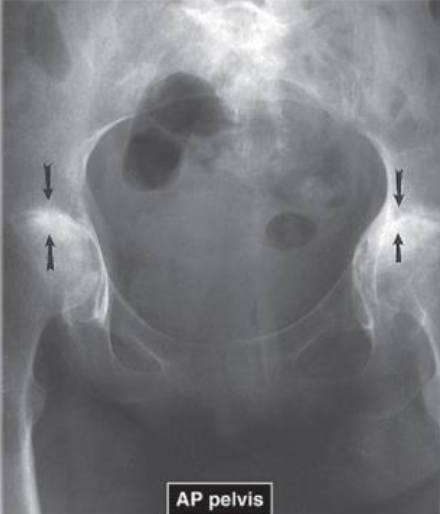
AP of Pelvis showing RA in Bilateral Hips
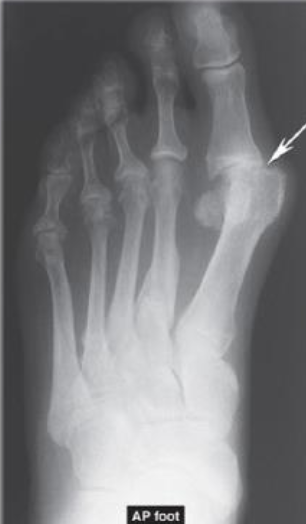
AP of Foot showing Erosion of 1st MTP Joint
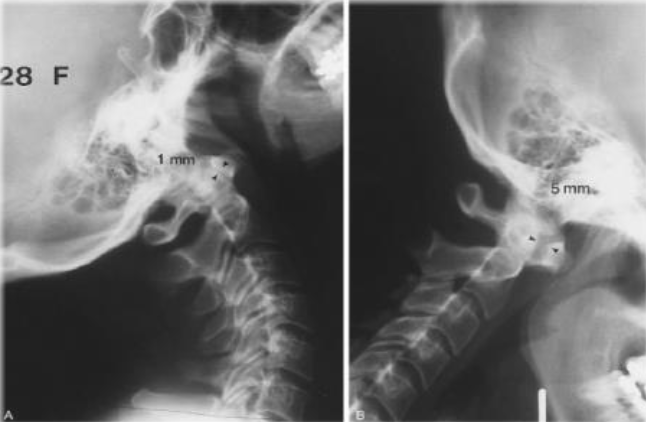
RA in Cervical Spine causing C1-C2 Subluxation
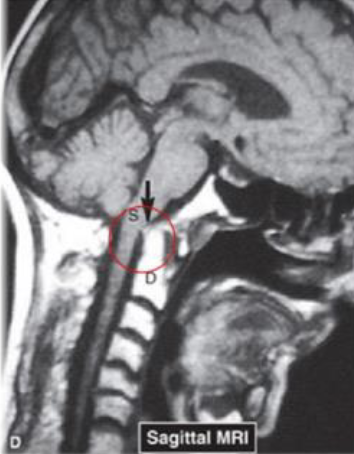
Dens Impinging on Spinal Cord from RA (Sagittal MRI)
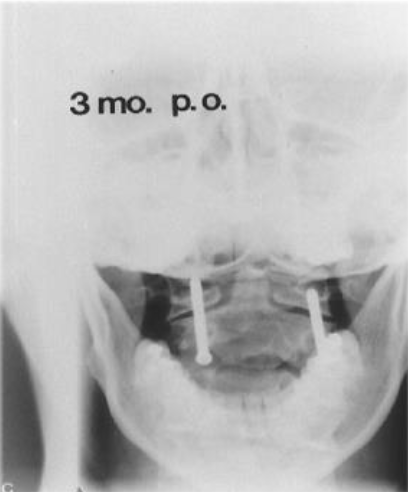
C1-C2 Surgical Fixation due to RA
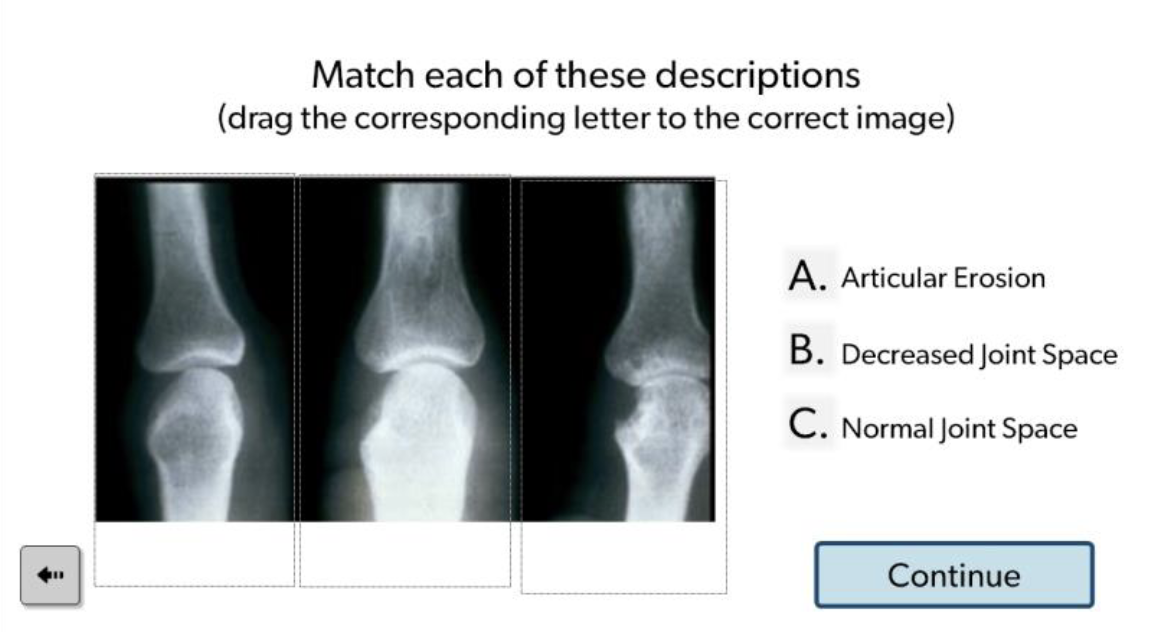
C, B, A
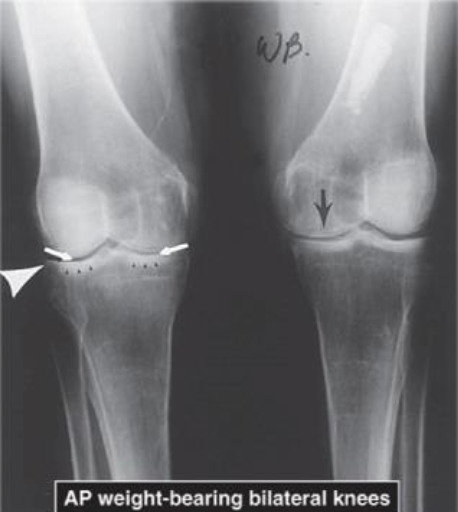
AP WB Bilateral OA Knees
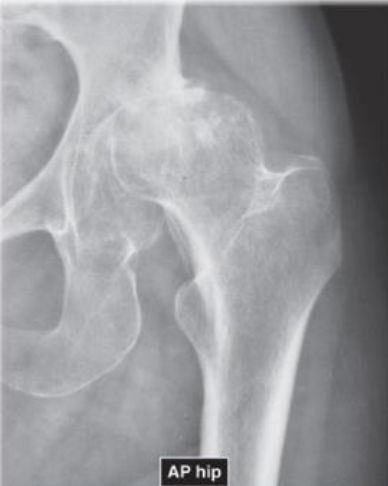
AP of Hip OA with Pseudocysts
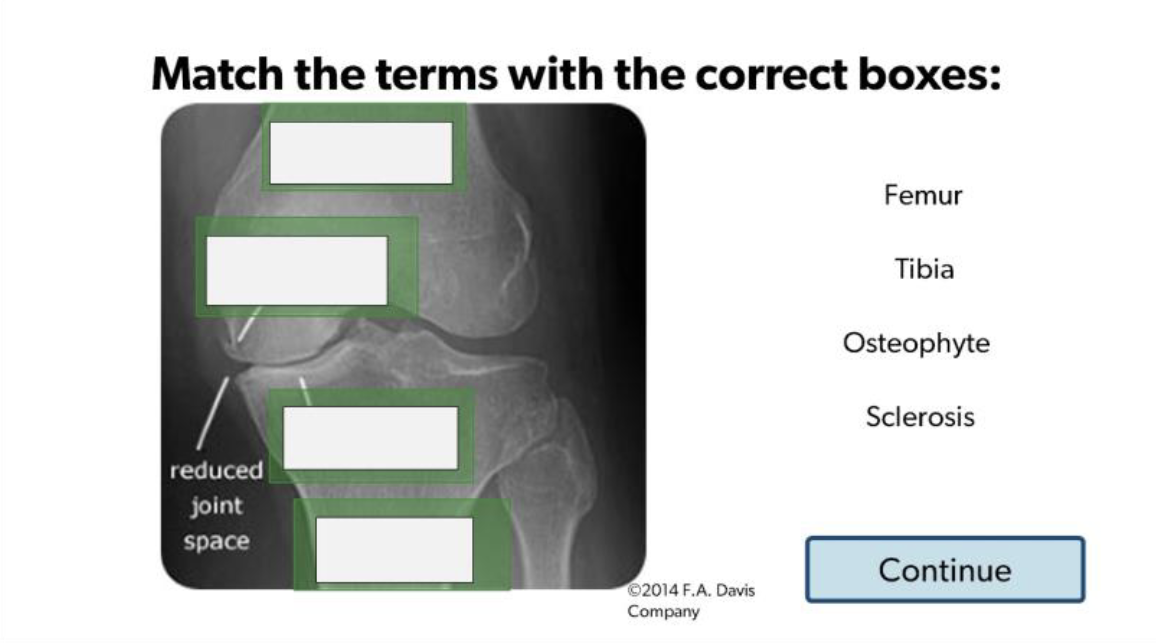
(Top Down) Femur, Osteophyte, Sclerosis, Tibia
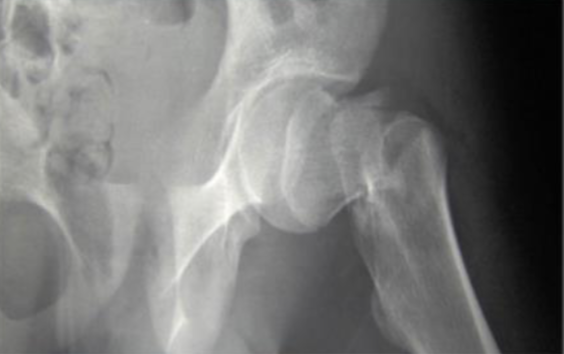
Osteoporosis in LE
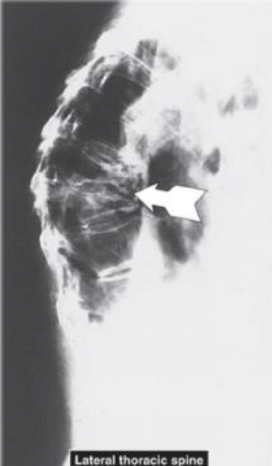
Lateral View Thoracic Spine - Vertebral Compression Fractures (#1 Common Fracture from Osteoporosis)
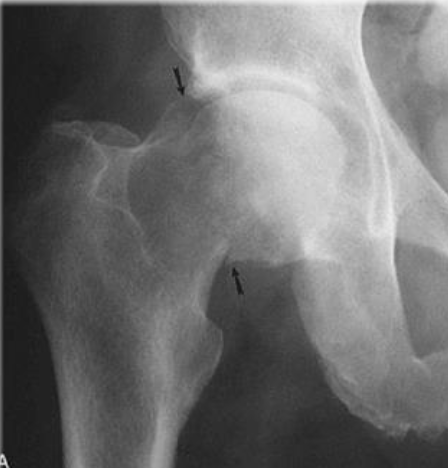
Femoral Neck Fracture (#2 Common Fracture from Osteoporosis)
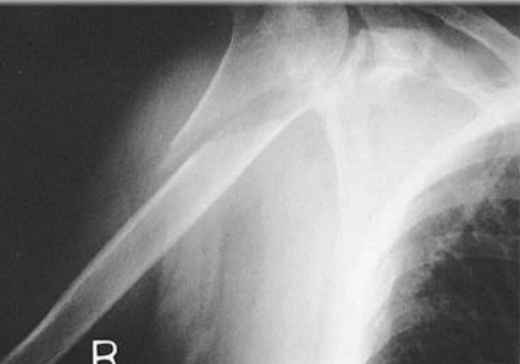
R Proximal Humerus Fracture (#3 Common Fracture from Osteoporosis)
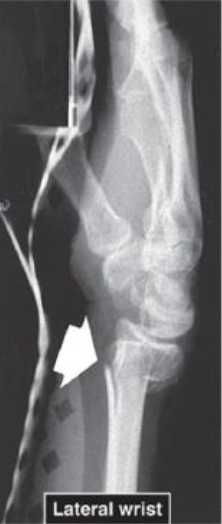
Lateral Wrist view of Distal Radius Fracture (#4 Common Fracture from Osteoporosis)
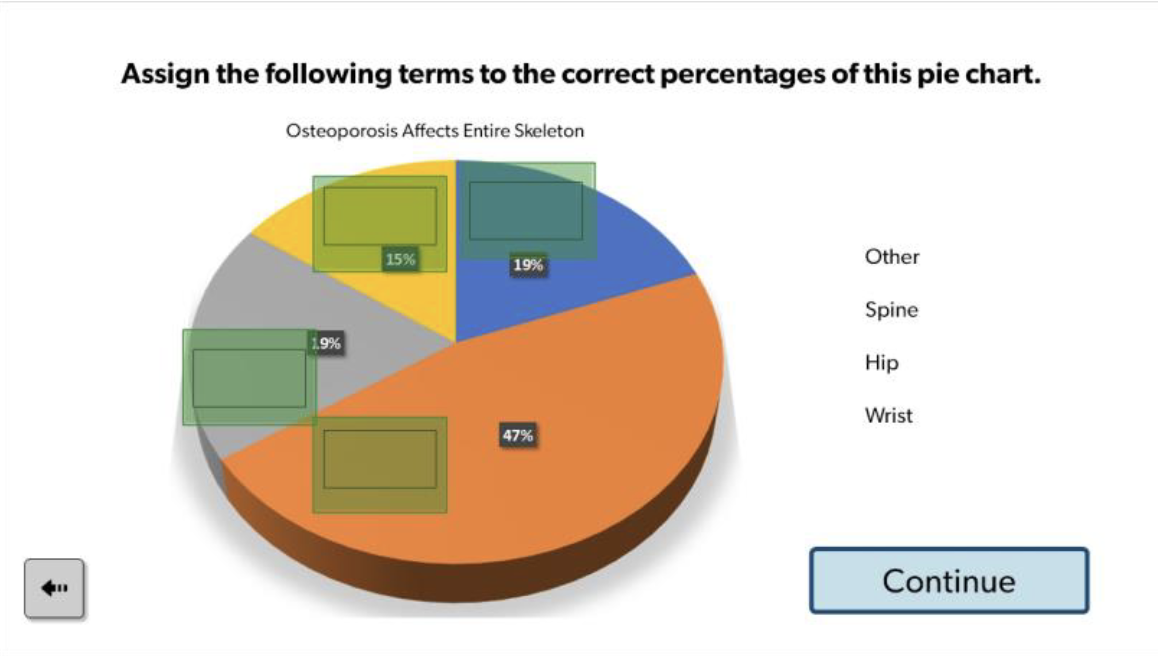
Spine - 47% (largest, orange)
Wrist - 19% (blue)
Hip - (yellow)
Other - 19% (gray)
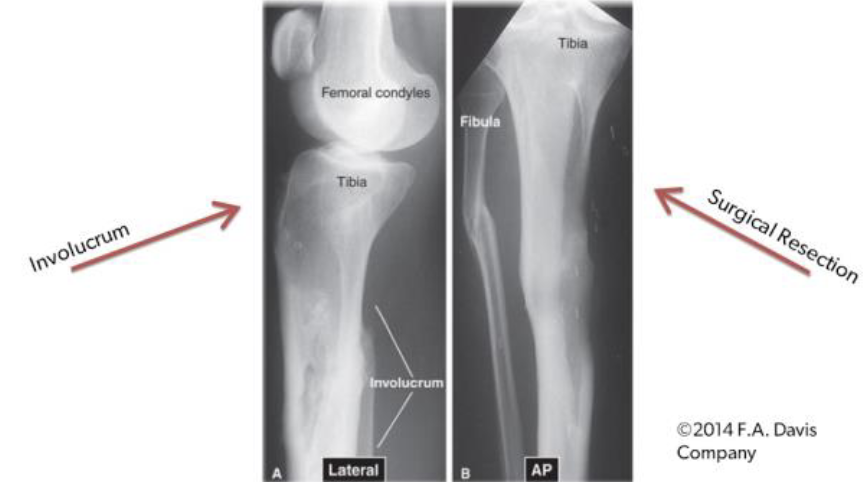
Lateral and AP view of Femur/Tibia with Chronic Osteomyelitis
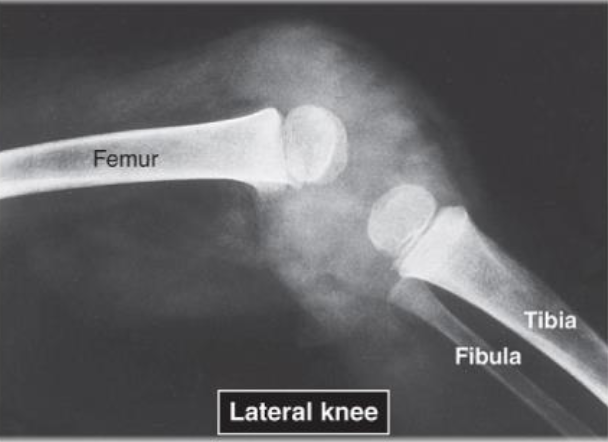
Lateral view of Knee with Infectious Arthritis
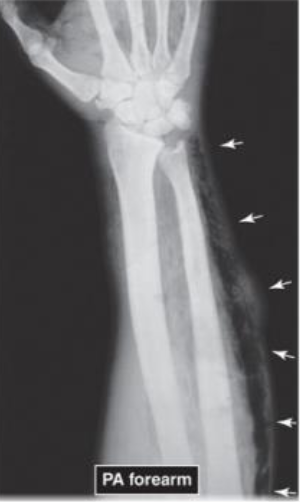
PA of Forearm with Gas Gangrene
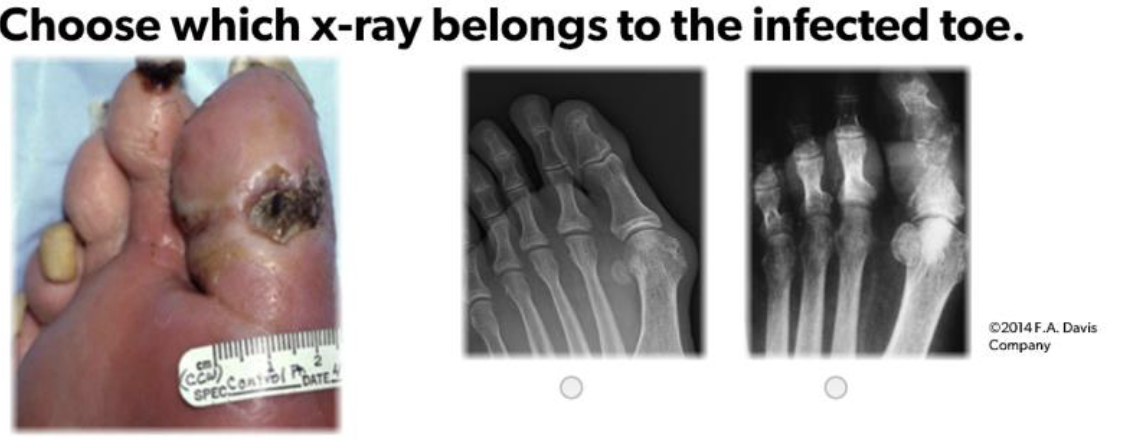
Image on Right
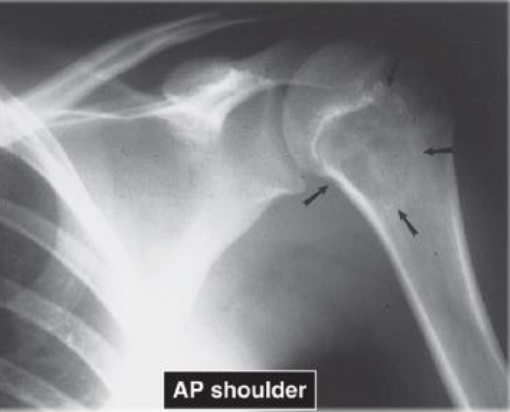
AP of Shoulder showing example of Benign Tumor Characteristics - Chondroblastoma
Narrow zone of transition
Well-defined margins
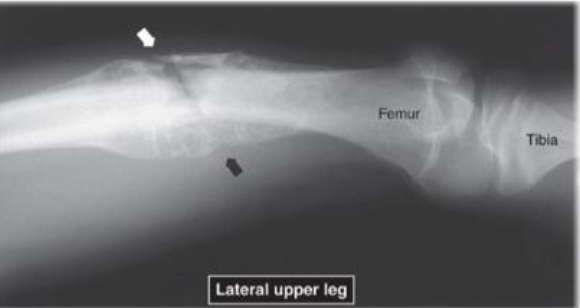
Lateral Upper Leg view with example of Malignant Tumor Characteristics - Ewing’s Sarcoma:
Poorly defined margins
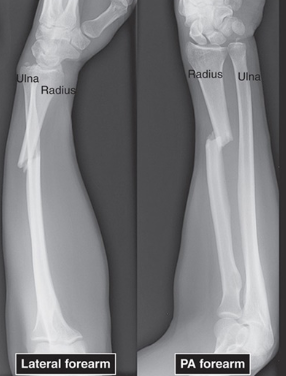
Radiographic Positioning for Trauma Example - Lateral Forearm and PA Forearm
Adapt from normal positioning to accommodate injury
At least 2 views at right angles to each other
Extremity fractures should include adjacent proximal and distal joint examinations
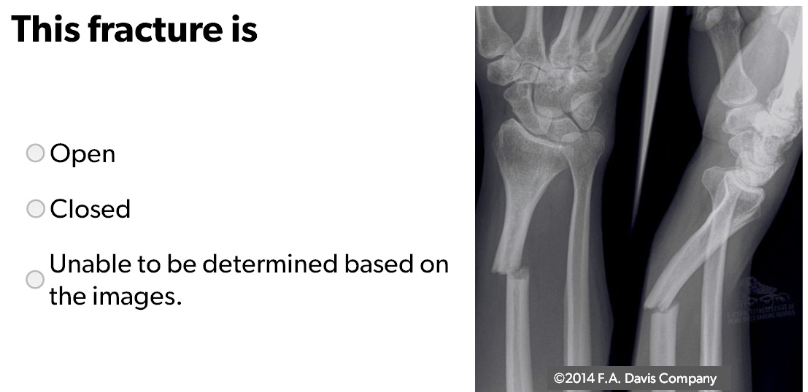
Closed Fracture of Distal Radius (bone did not break through skin)
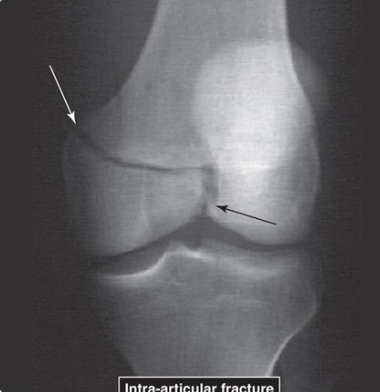
Intra-Articular Fracture of Femur
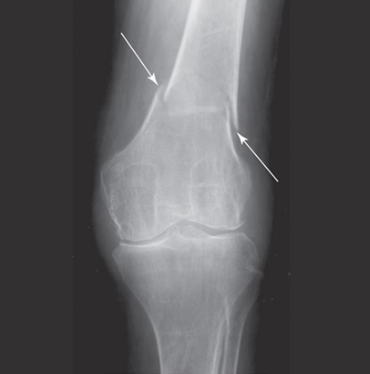
Extra-Articular Fracture of Femur
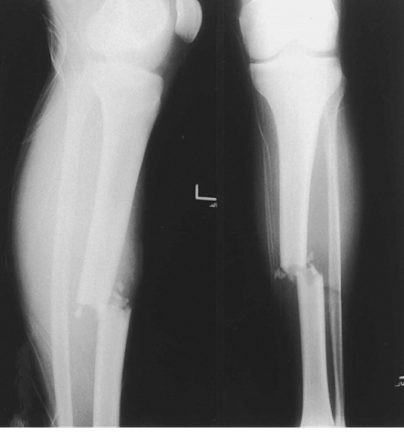
Lateral View (left) and AP View (right) of L Tibia Mid-Shaft
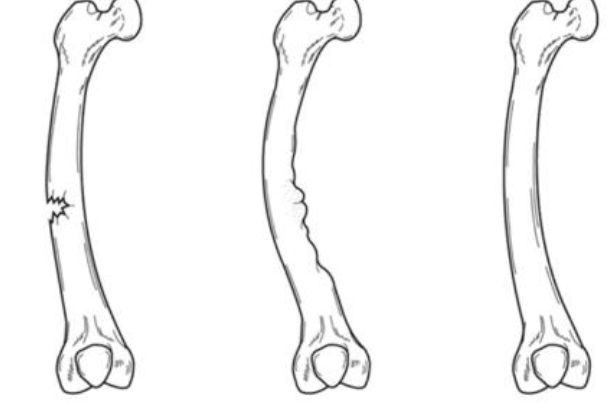
Complete Fracture
Distal fragment displaced lateral and anterior to proximal fragment
Transverse fracture line with comminution
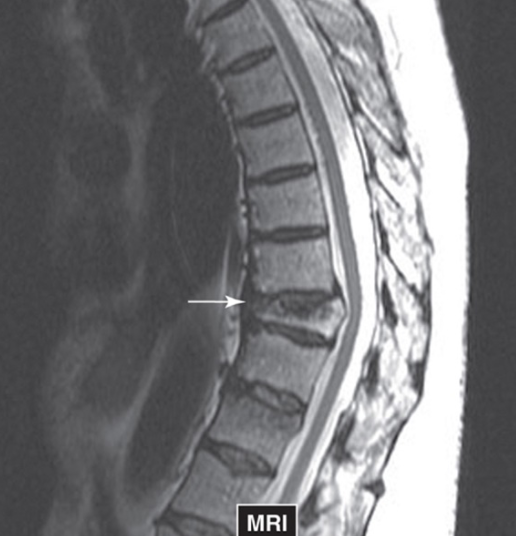
Example of Vertebral Compression on MRI
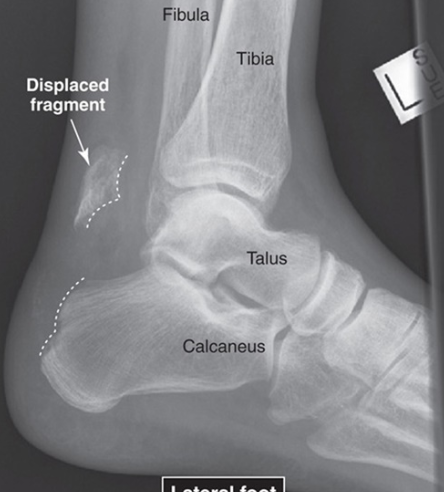
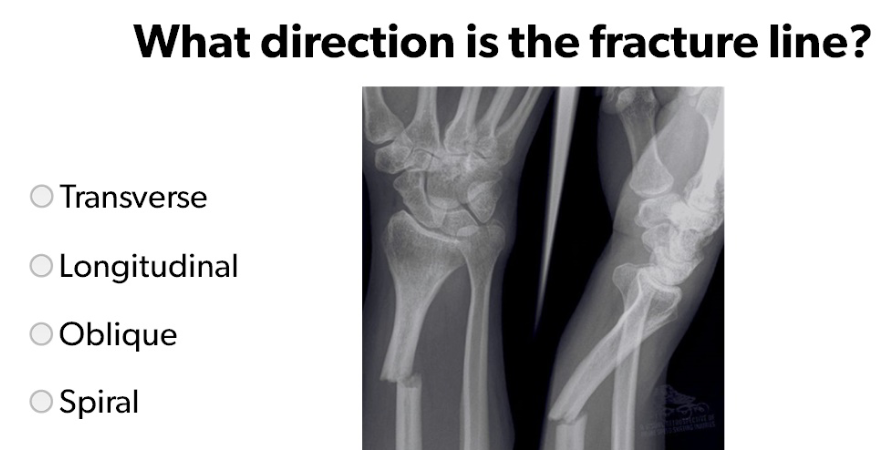
Example of Avulsion Fracture of Lateral Foot
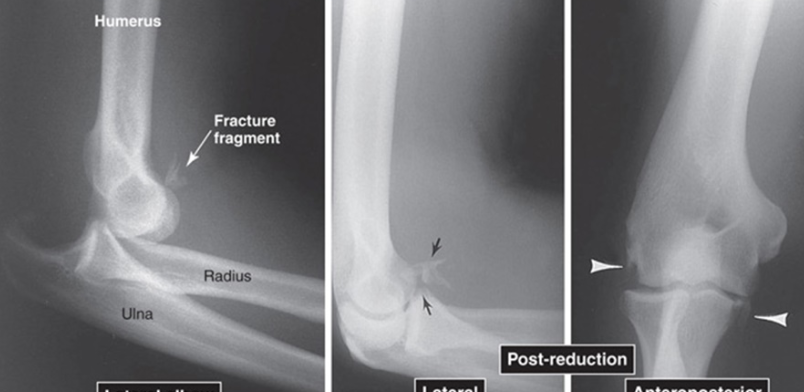
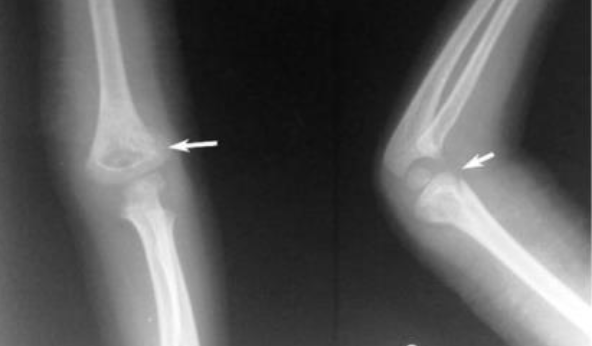
Example of Elbow Dislocation in Lateral, and Anteroposterior (AP) Views
The two images on the right being post-reduction
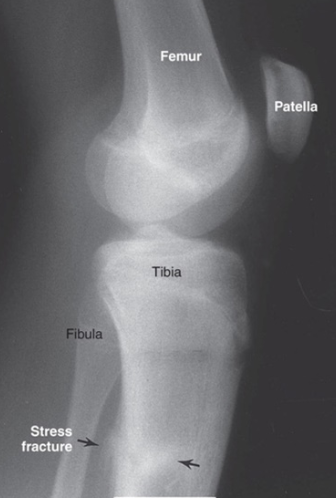
Lateral View of Knee showing Stress Fracture on Tibia as result of Abnormal Stress Overload
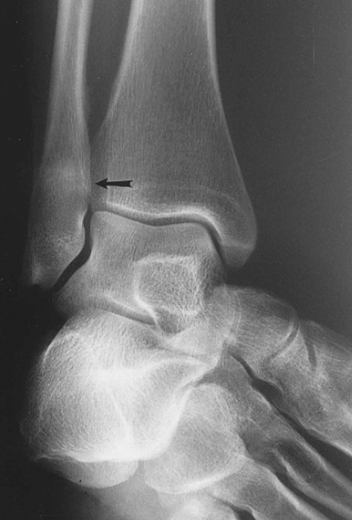
Stress Fracture of Distal Fibula
Transverse
Example of Difficulties assessing Fractures in Children due to:
Growth plates
Dense growth lines
Secondary centers of ossification
Large nutrient foramina
Cartilage model not evident on radiograph
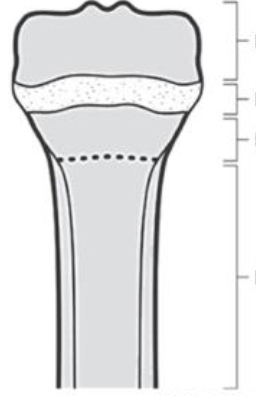
(Top Down) Epiphysis, Physis (epiphyseal growth plate), Metaphysis, Diaphysis
Examples of Incomplete Fractures in Children - Left to Right:
Greenstick, Torus, Plastic Bowing
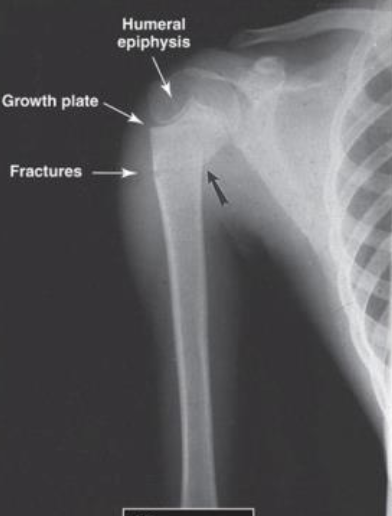
AP of Pediatric Upper Arm - Example of Incomplete or Greenstick) Fracture of Proximal Humeral Metaphysis
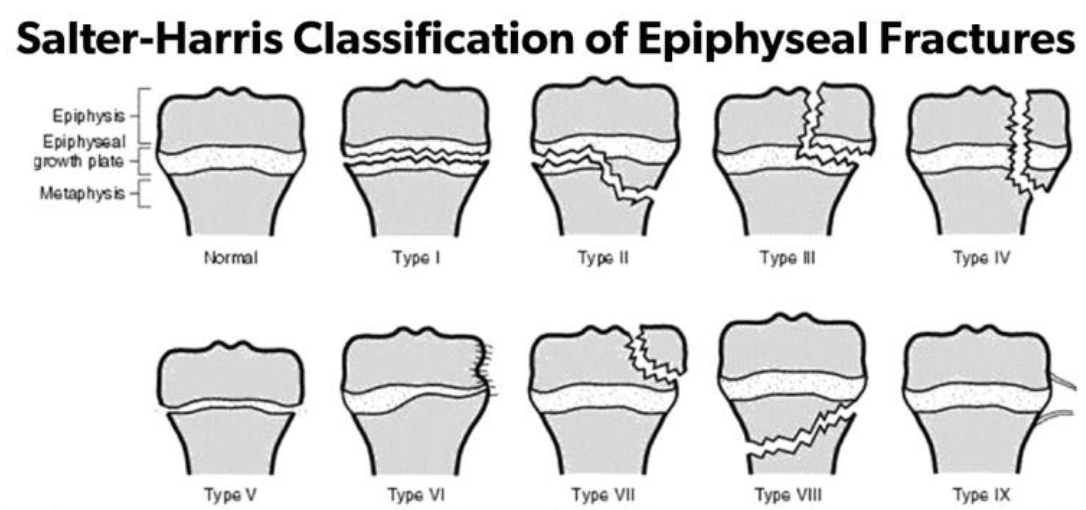
Salter-Harris Classification System for Epiphyseal Fractures
Type II MOST COMMON
15-20% of all fractures in children involve the growth plate
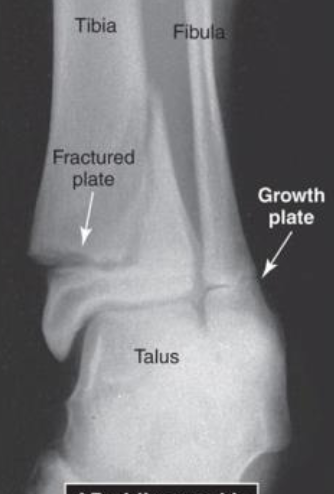
AP Oblique Ankle View of a Type II Salter Harris Epiphyseal Fracture at Distal Tibia
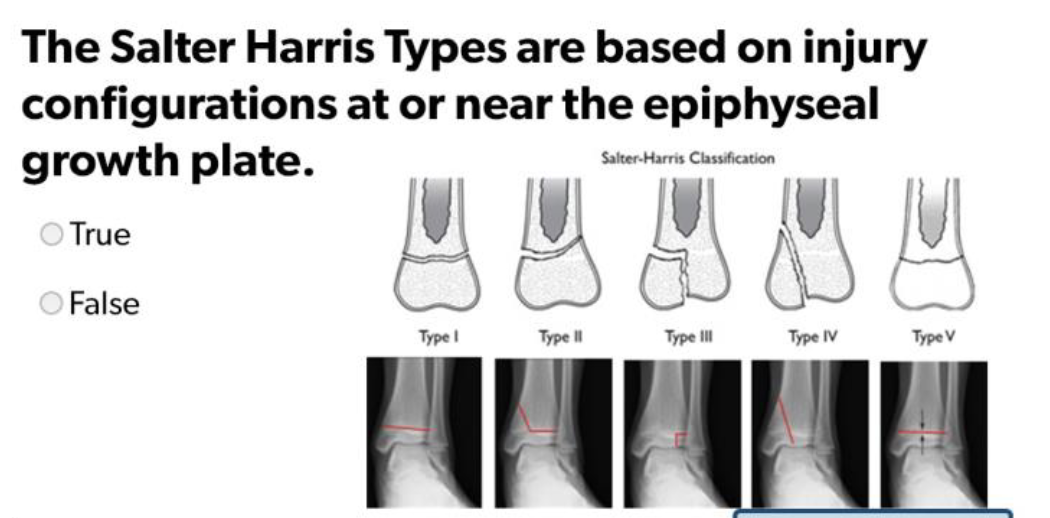
True
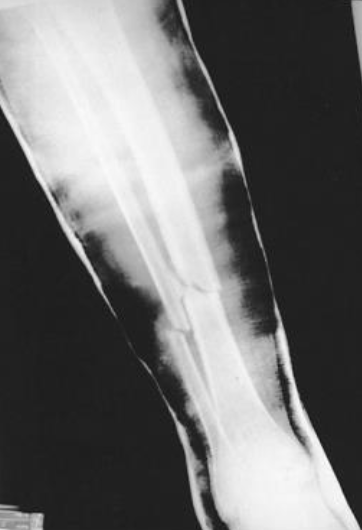
Tibia and Fibula Fractures, Casted
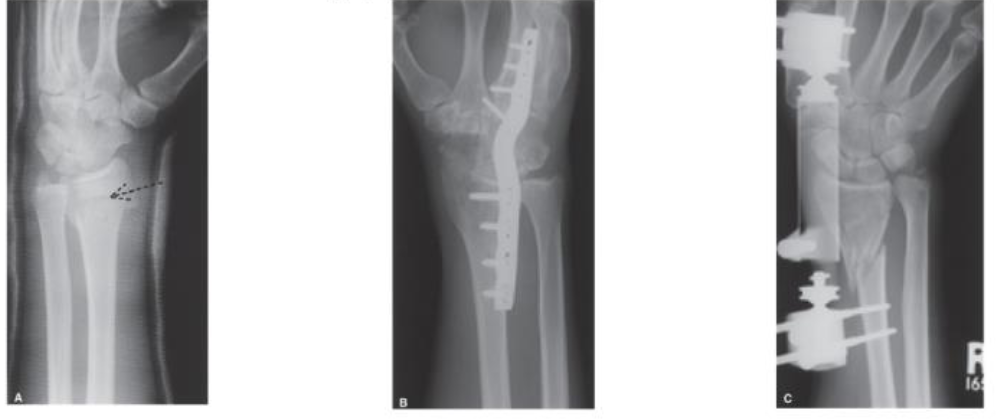
Types of Fixation - Left to Right:
External Fixation, Internal Fixation, Combination
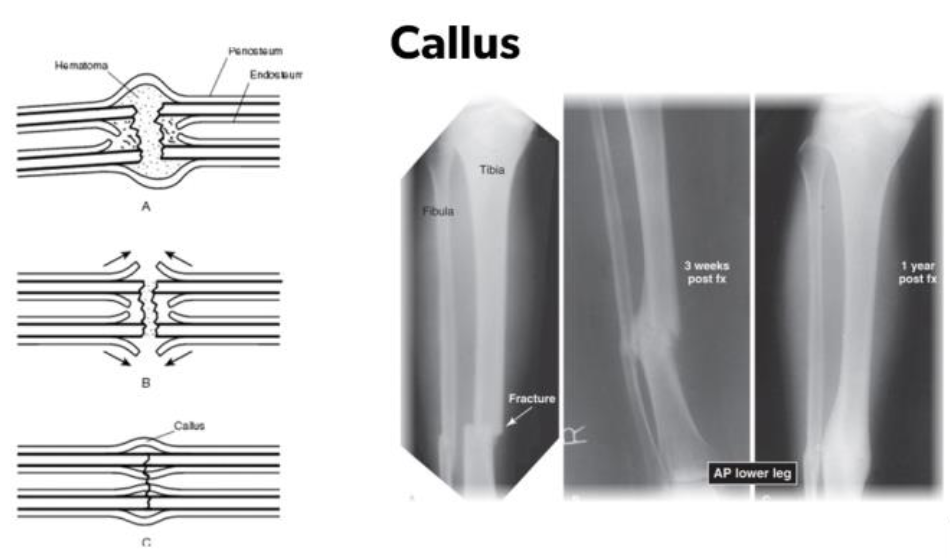
Callus Formation in Leg after Fracture Heals
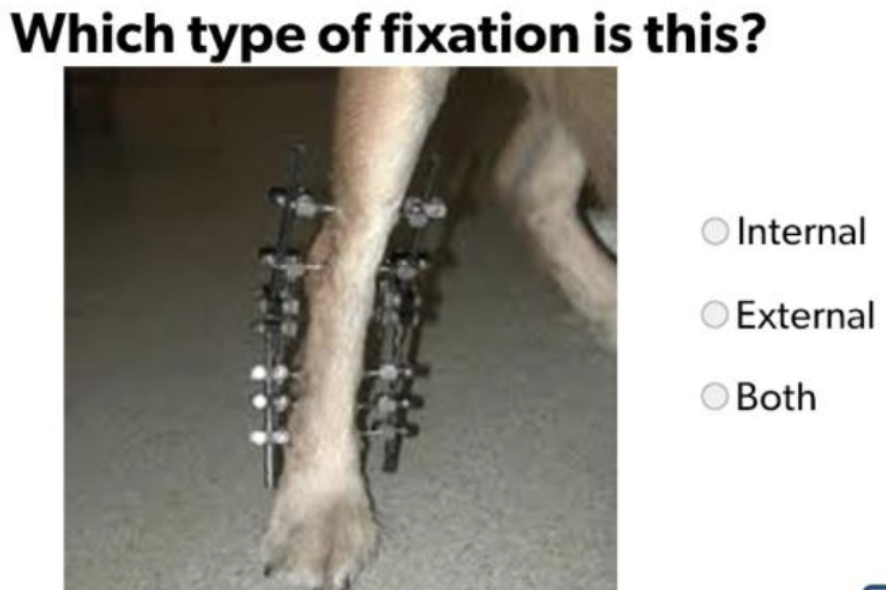
External Fixation
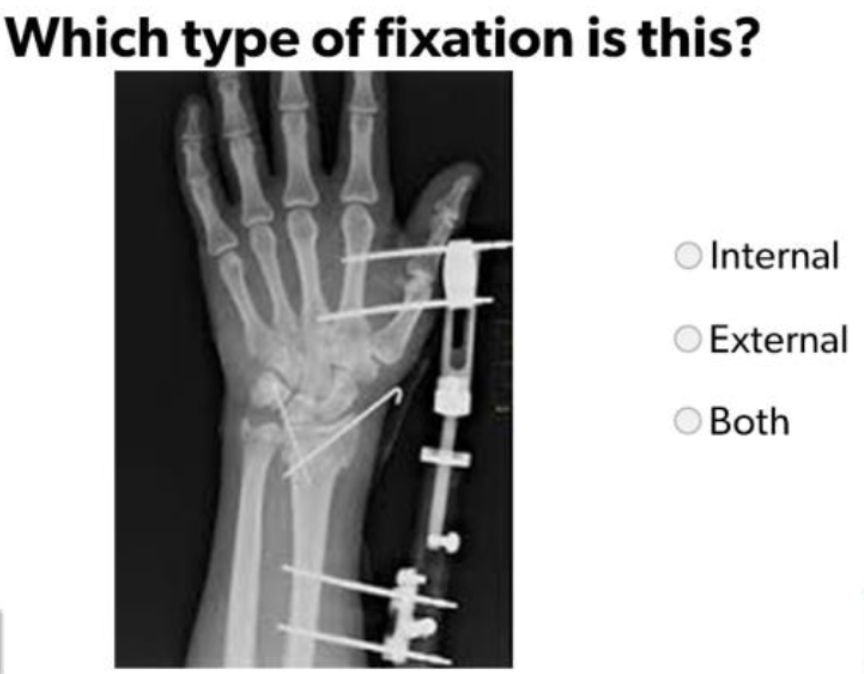
Both
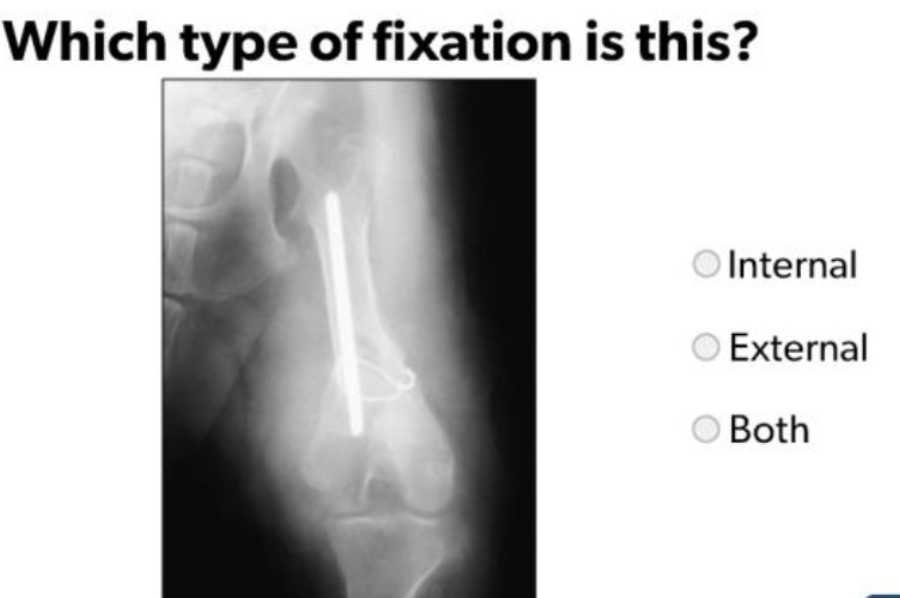
Internal Fixation
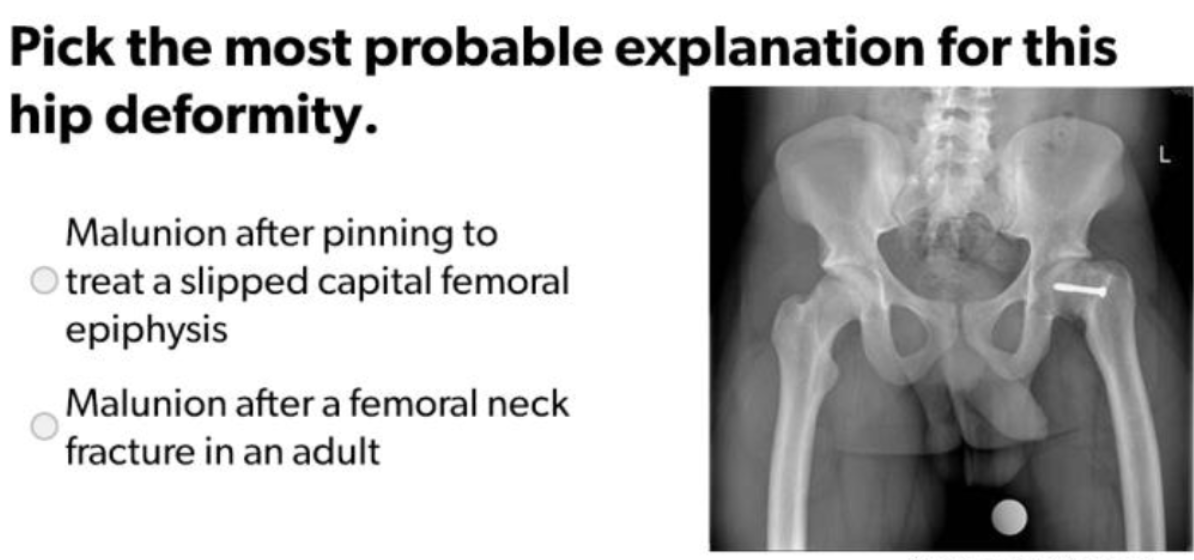
Malunion after pinning to treat a slipped capital femoral neck fracture in an adult
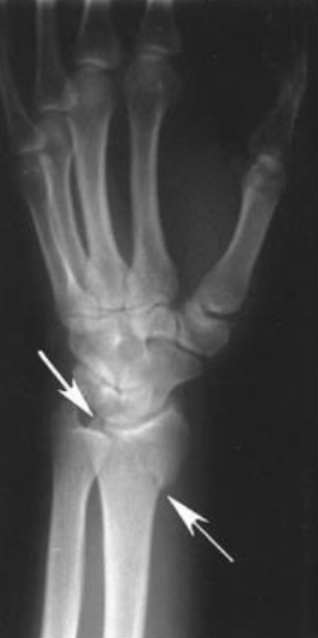
Accelerated DJD or Post-Traumatic Arthritis - Distal Radius Fracture, Intra-Articular Extension

AP Bilateral Shoulders - Pseudoarthrosis
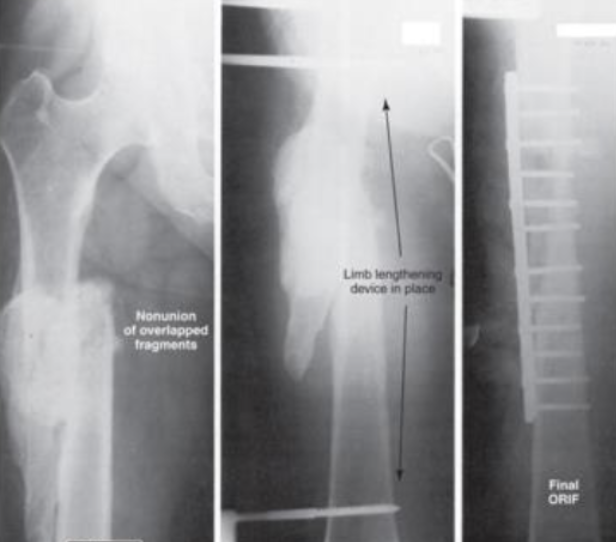
AP of Femur showing Bone Length Discrepancy
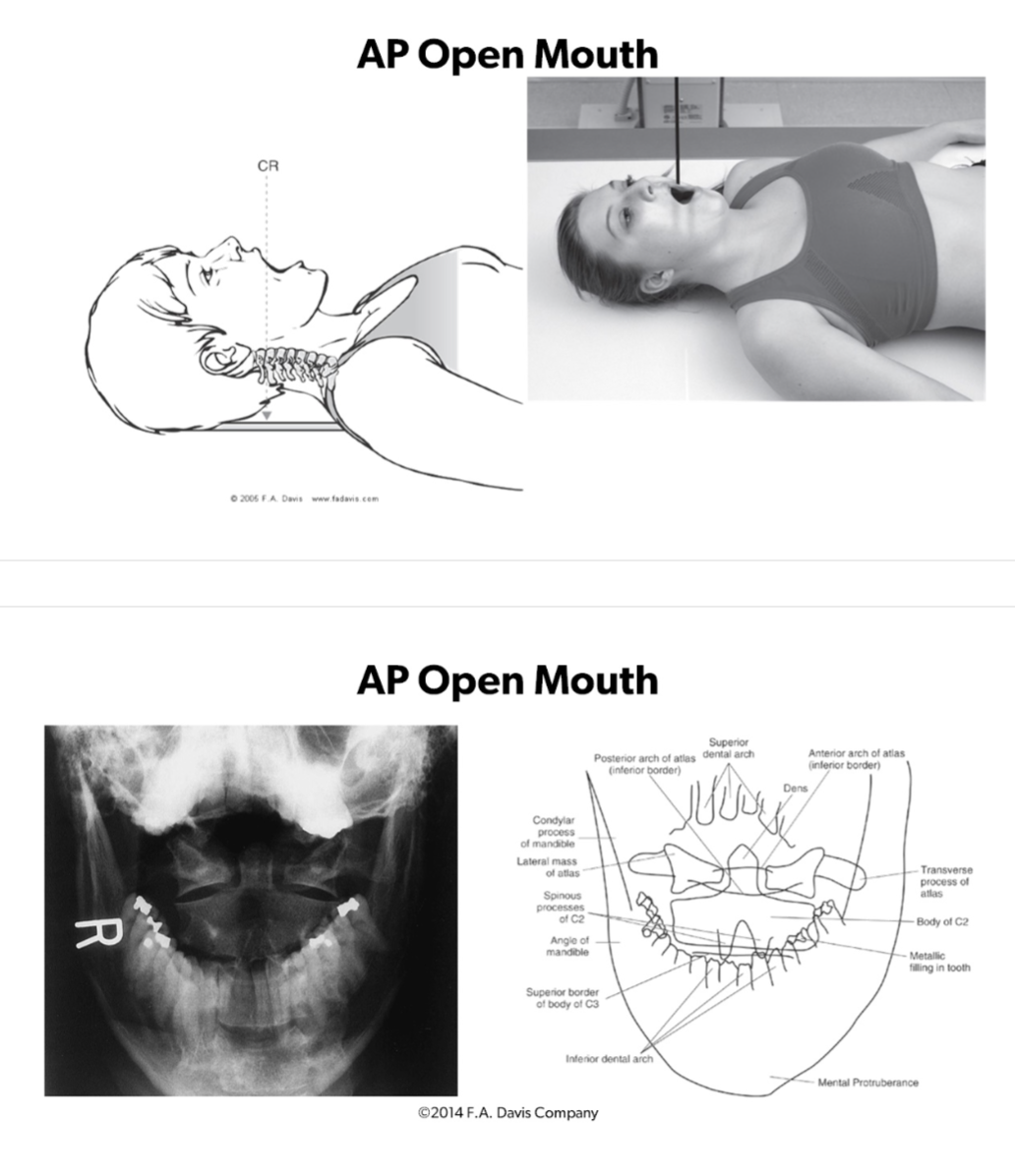
AP Open Mouth to assess:
ABCs
C1-C2 Joint Symmetry
Dens Midline b/w the Lateral Masses of C1
C2 Spinous Process Midline
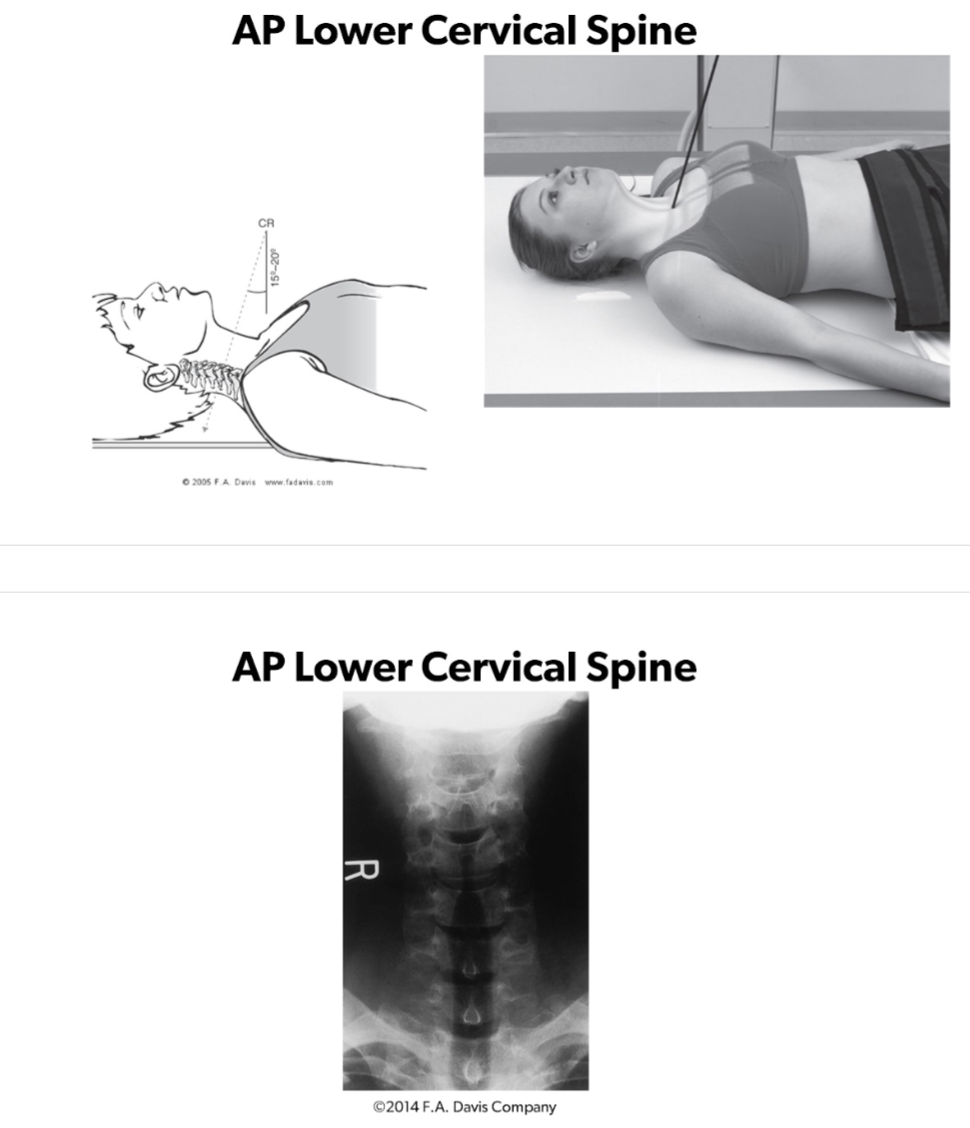
AP Lower Cervical Spine to Assess:
ABCs
C3-C7
C2-C3 IV Disc Space
T1 Ribs
Spinous Processes Midline
Pedicles Equidistant
Uncinate Processes
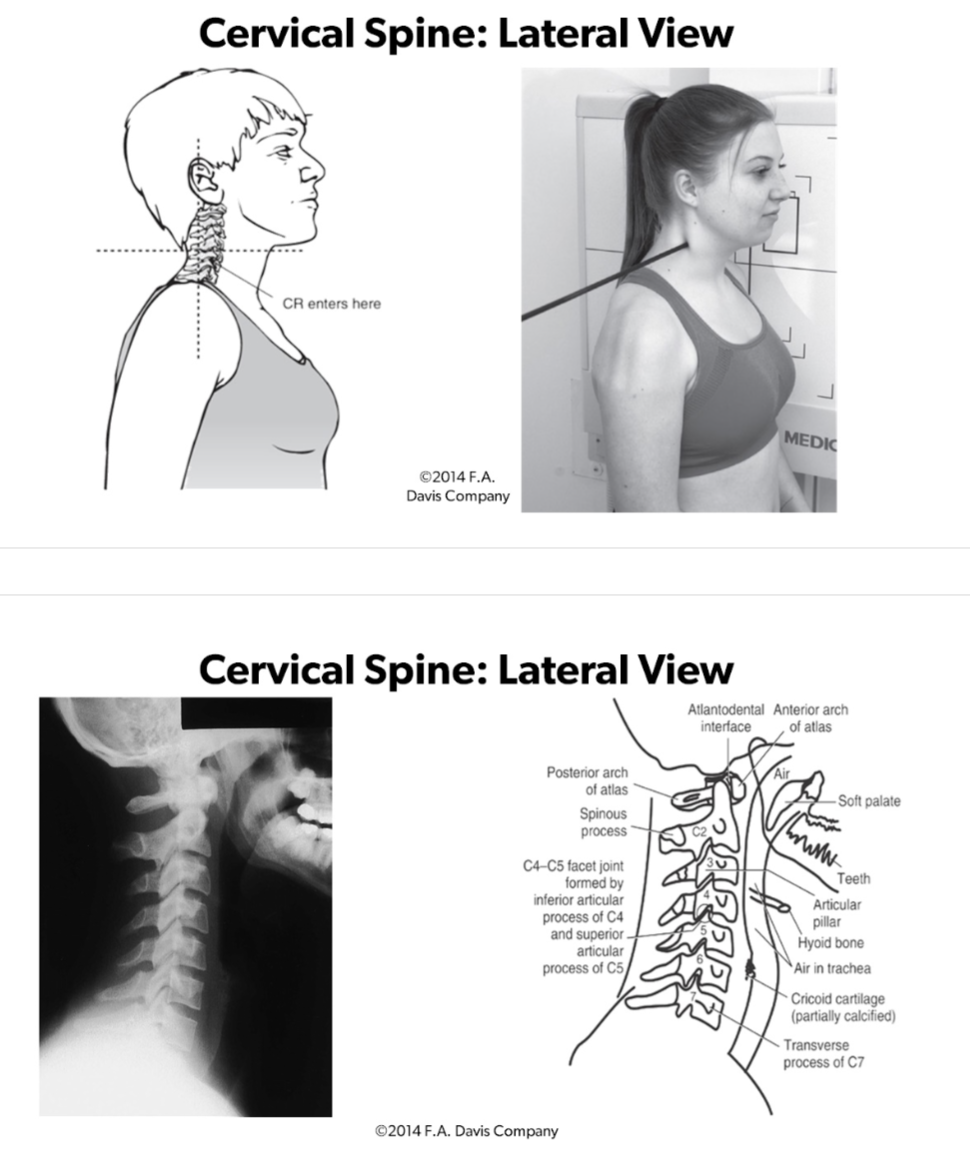
Lateral View Cervical Spine to Assess:
3 parallel lines
IV Disc Spaces
Atlantodental interspace
Retropharyngeal space <7mm
Retrotracheal space 14mm kids, 22mm adults
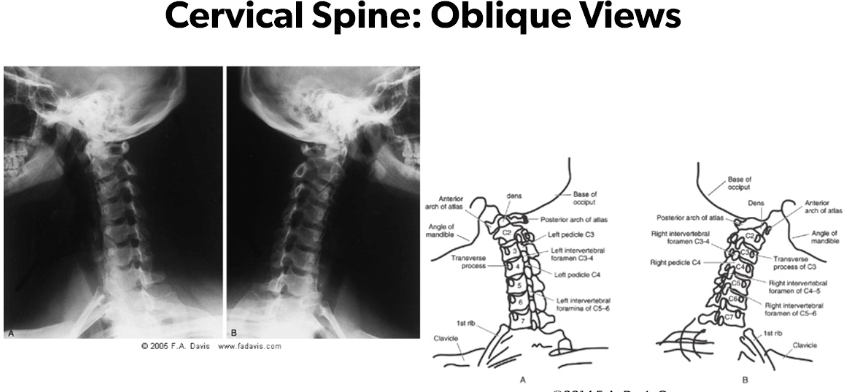
Oblique Views of Cervical Spine to assess:
ABCs
Intervertebral foramina are seen individually
Both R and L side oblique views are made
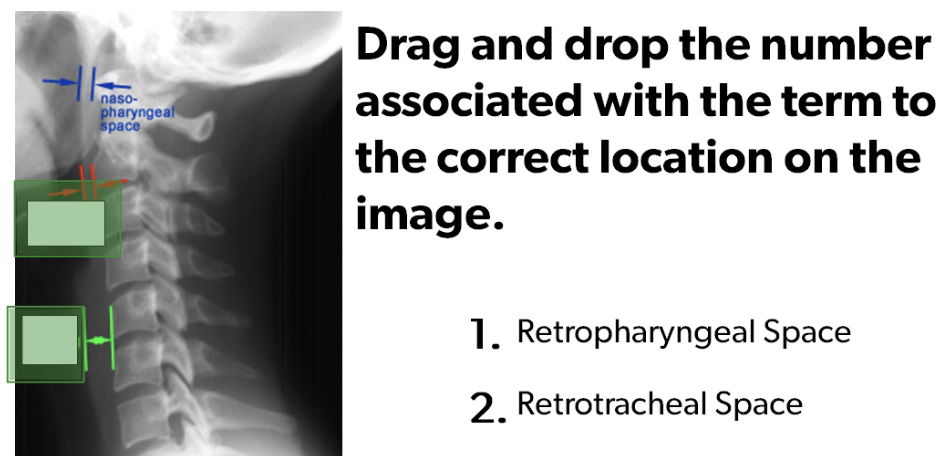
Top = 1, Bottom = 2
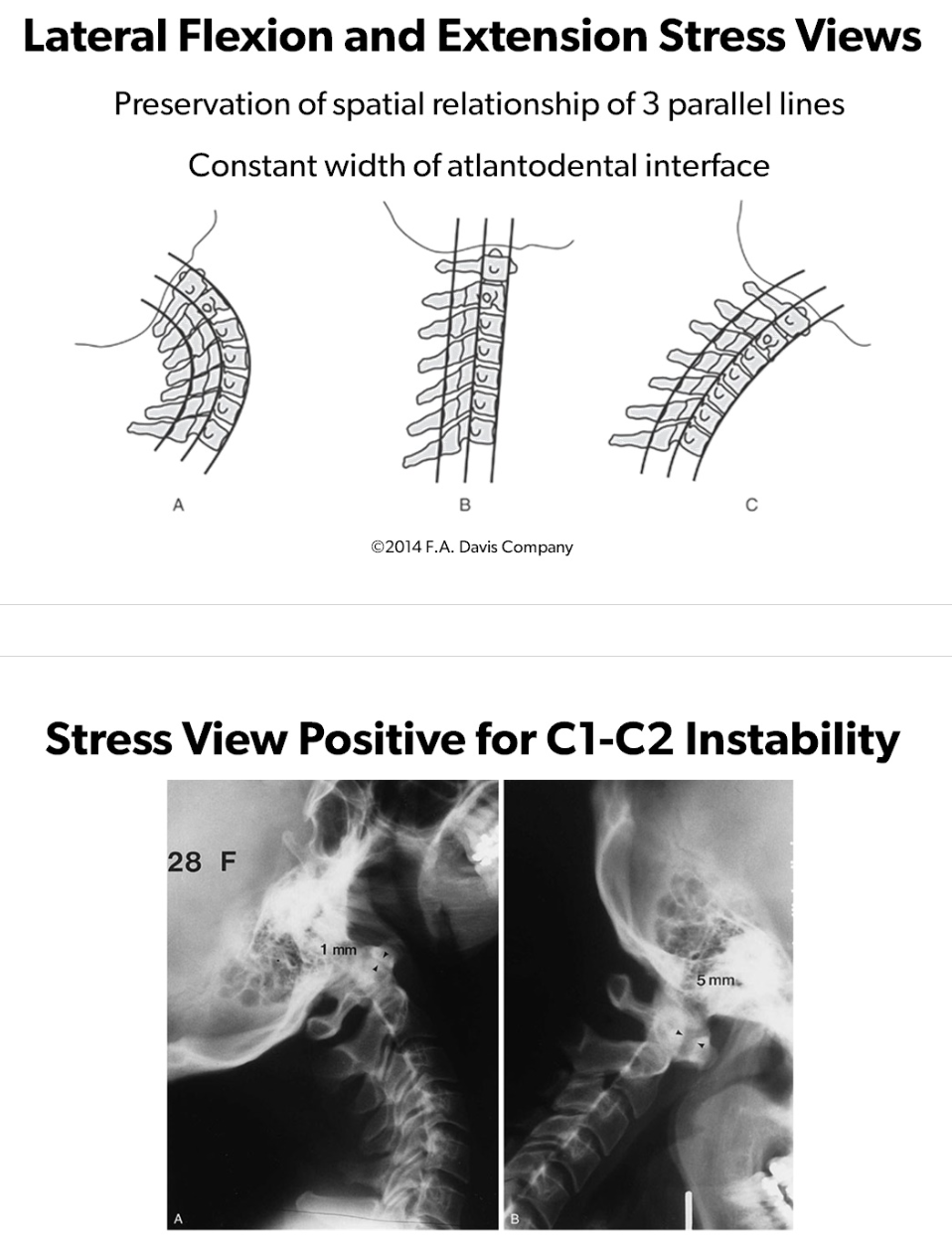
Lateral Flexion and Extension Stress Views to identify C1-C2 Instability
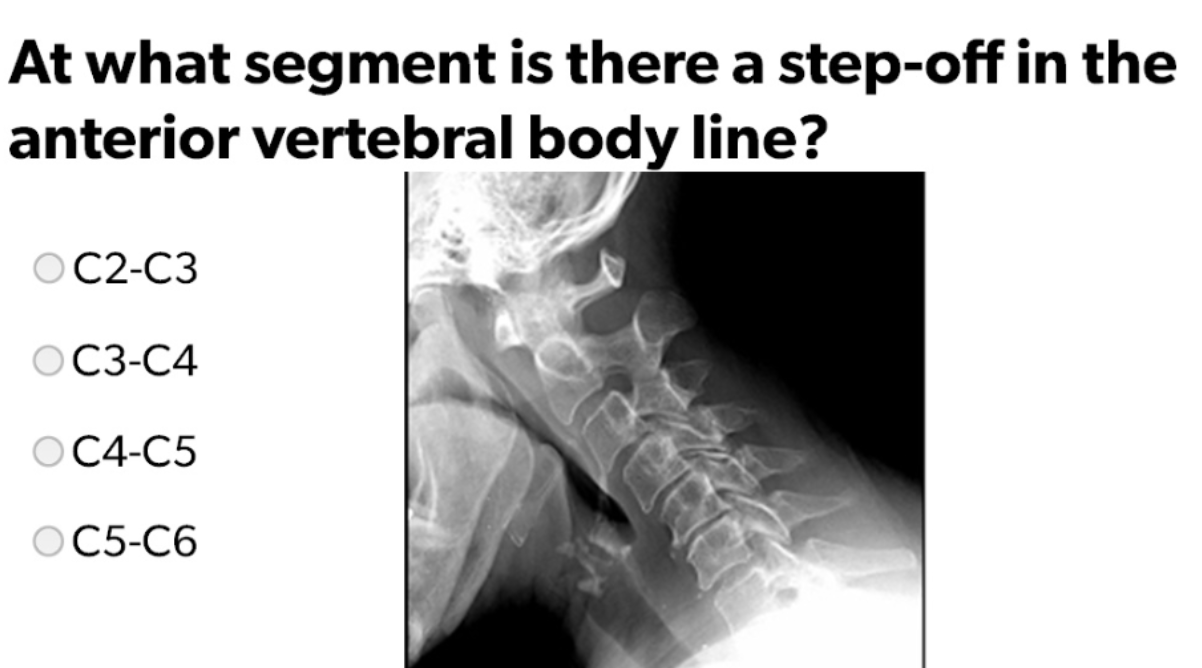
C3-C4
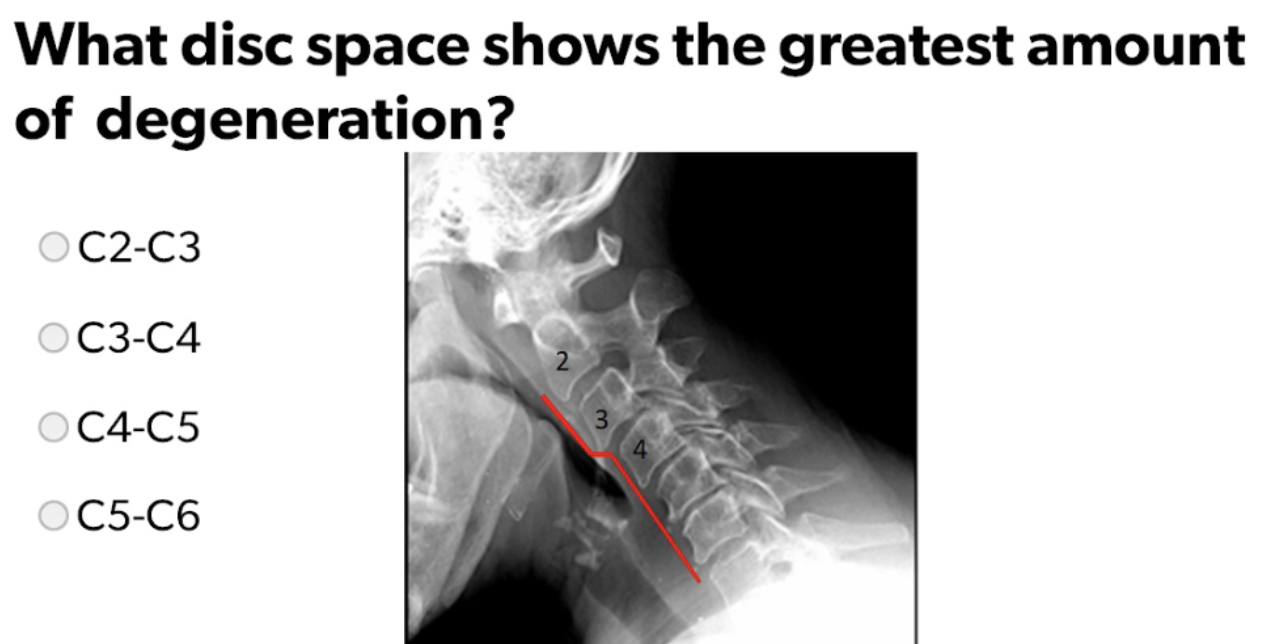
C4-C5