DAT bio high yield
1/577
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
578 Terms
Biology Videos
Videos that cover the same info as notes and incorporate practice questions.
Bio Bites
Short practice questions to reinforce learning as you progress through biology.
Bio Question Bank
A resource to practice what you've learned in biology.
DAT Bootcamp practice tests 1-10
Recommended practice tests to finish and review before taking the DAT.
Carbohydrates
Used as fuel and structural support, containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO).
Monosaccharides
Carbohydrate monomers, examples include ribose, fructose, and glucose.
Ribose
A five carbon monosaccharide.
Fructose
A six carbon monosaccharide.
Glucose
A six carbon monosaccharide.
Disaccharides
Contain two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond, resulting from a dehydration reaction.
Examples of Disaccharides
Common examples include sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Polysaccharides
Contain multiple monosaccharides connected by glycosidic bonds to form long polymers.
Starch
Form of energy storage for plants.
Glycogen
Form of energy storage in animals.
Proteins
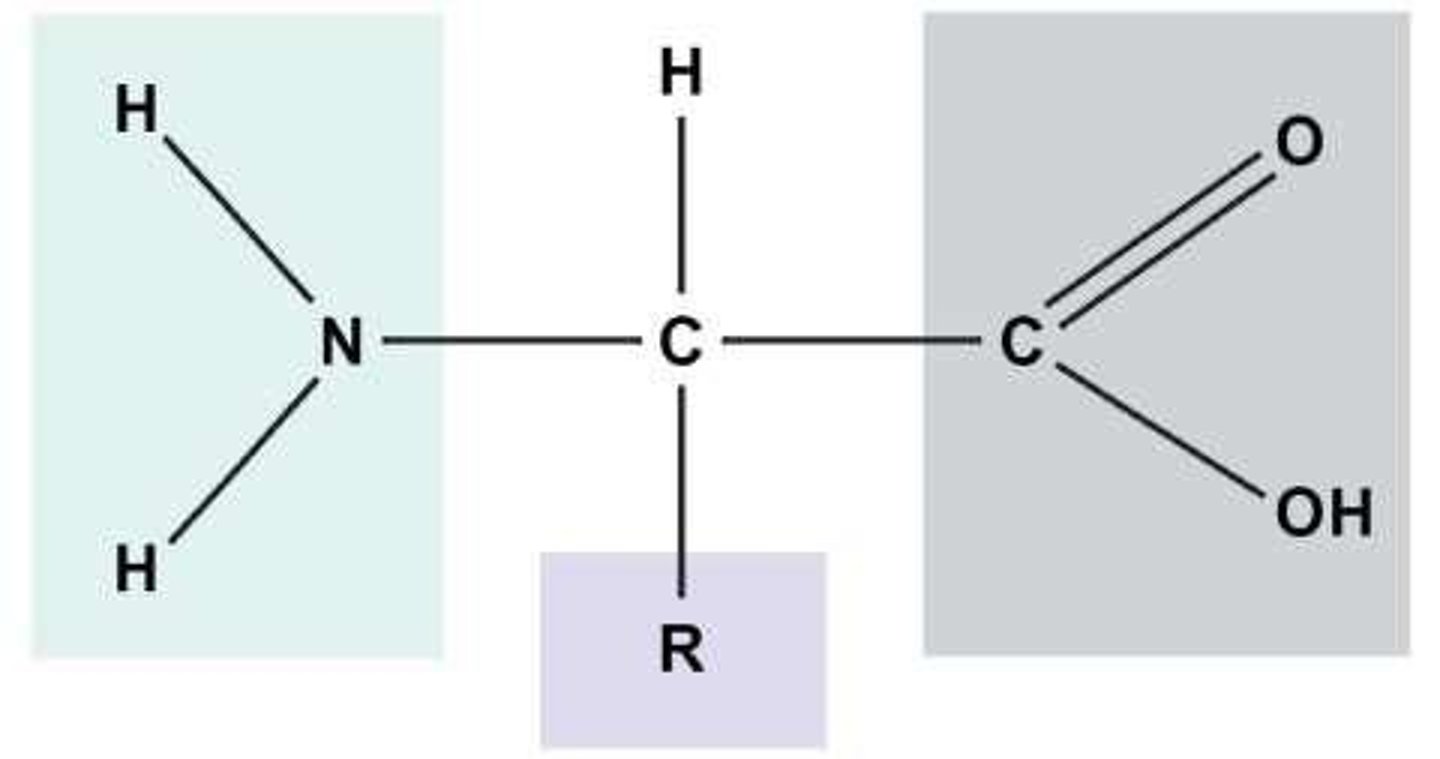
Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms (CHON) and are made of amino acids.
Amino acids
Monomers of proteins that link together to build polypeptides.
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass.
Element
A pure substance with specific physical/chemical properties that cannot be broken down.
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical properties of the element.
Molecule
Two or more atoms joined together.
Intramolecular forces
Attractive forces that act on atoms within a molecule.
Intermolecular forces
Forces that exist between molecules and affect physical properties of the substance.
Monomers
Single molecules that can polymerize, or bond with one another.
Polymers
Substances made up of many monomers joined together in chains.
Dehydration (condensation) reaction
Creates a covalent bond between monomers and releases water.
Hydrolysis
A reaction that breaks a covalent bond using water.
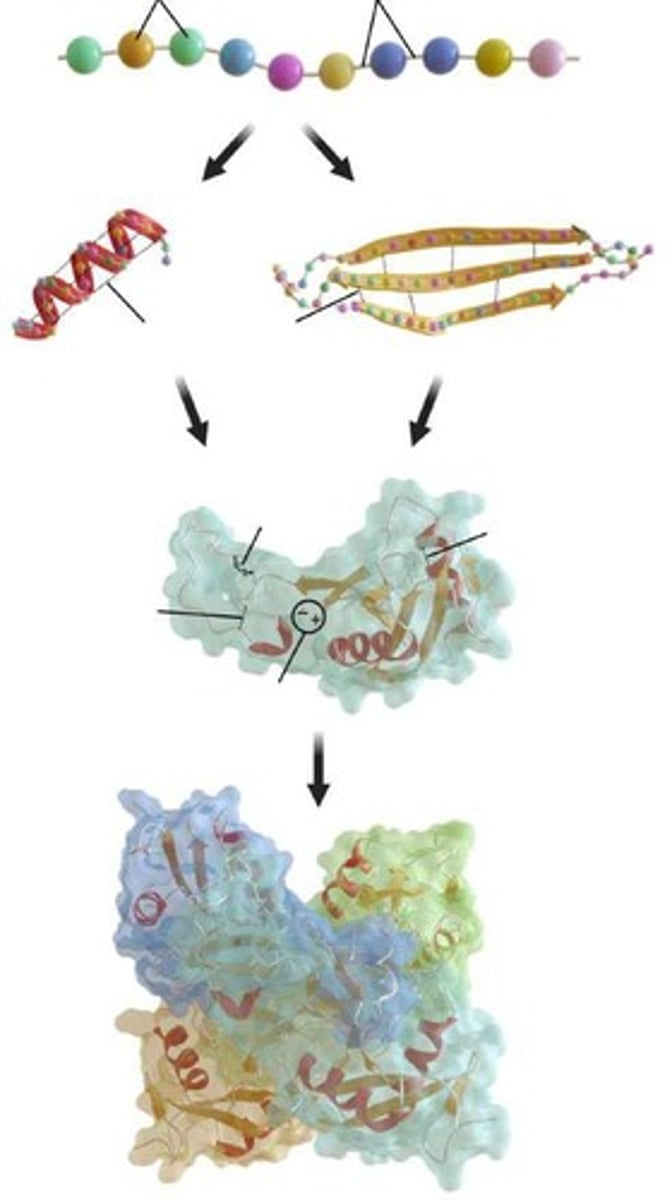
Primary structure
Sequence of amino acids connected through peptide bonds.
Secondary structure
Intermolecular forces between the polypeptide backbone (not R-groups) due to hydrogen bonding. Forms α-helices or β-pleated sheets.
Tertiary structure
Three-dimensional structure due to interactions between R-groups. Can create hydrophobic interactions based on the R-groups.
Quaternary structure
Multiple polypeptide chains come together to form one protein.
Protein denaturation
Describes the loss of protein function and higher order structures. Only the primary structure is unaffected.
Storage (Protein Function)
Reserve of amino acids.
Hormones (Protein Function)
Signaling molecules that regulate physiological processes.
Receptors (Protein Function)
Proteins in cell membranes which bind to signal molecules.
Structure (Protein Function)
Provide strength and support to tissues (hair, spider silk).
Immunity (Protein Function)
Antibodies that protect against foreign substances.
Enzymes (Protein Function)
Regulate rate of chemical reactions.
Catalysts
Increase reaction rates by lowering the activation energy of a reaction.
Transition state
The unstable conformation between the reactants and the products.
Phosphatase
Cleaves a phosphate group off of a substrate molecule.
Phosphorylase
Directly adds a phosphate group to a substrate molecule by breaking bonds within a substrate molecule.
Kinase
Indirectly adds a phosphate group to a substrate molecule by transferring a phosphate group from an ATP molecule.
Feedback regulation of enzymes
Occurs when the end product of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction inhibits the enzyme's activity by binding to an allosteric site.
Competitive inhibition
Occurs when a competitive inhibitor competes directly with the substrate for active site binding.
Induced fit theory
Describes how the active site molds itself and changes shape to fit the substrate when it binds.
Ribozyme
An RNA molecule that can act as an enzyme (a non-protein enzyme).
Cofactor
A non-protein molecule that helps enzymes perform reactions.
Coenzyme
An organic cofactor (i.e., vitamins).
Inorganic cofactors
Usually metal ions.
Denaturation
The process by which protein enzymes lose their functional shape.
Optimal temperatures and pH
Conditions required for protein enzymes to function effectively.
Noncompetitive inhibition
Occurs when the noncompetitive inhibitor binds to an allosteric site that modifies the active site.
Allosteric site
A location on an enzyme that is different from the active site.
Competitive inhibition
A type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site.
Enzyme kinetics plot
A graph used to visualize how inhibitors affect enzymes.
Lipids
Organic molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms (CHO), characterized by long hydrocarbon tails that make them hydrophobic.
Triacylglycerol (triglyceride)
A lipid molecule with a glycerol backbone and three fatty acids connected by ester linkages.
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids with no double bonds that pack tightly and are solid at room temperature.
Vmax
The maximum reaction velocity of an enzyme.
Michaelis Constant (KM)
The substrate concentration at which the velocity is 50% of the maximum reaction velocity.
Saturation
Occurs when all active sites are occupied, causing the rate of reaction to plateau despite increasing substrate concentration.
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids that contain double bonds, preventing tight packing and increasing membrane fluidity.
Phospholipids
Lipid molecules with a glycerol backbone, one phosphate group, and two fatty acid tails, making them amphipathic.
Cholesterol
An amphipathic lipid molecule that is a component of cell membranes and a precursor to steroid hormones.
Lipoproteins
Molecules that allow the transport of lipid molecules in the bloodstream due to an outer coat of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins.
Waxes
Simple lipids with long fatty acid chains connected to alcohols.
Carotenoids
Lipid derivatives containing long carbon chains with double bonds that function mainly as pigments.
Sphingolipids
Lipids with a backbone of aliphatic amino alcohols, important for structural support, signal transduction, and cell recognition.
Glycolipids
Lipids found in the cell membrane with a carbohydrate group attached instead of a phosphate group.
Nucleic acid polymerization
The process that occurs as nucleoside triphosphates are added to the 3' end of the sugar-phosphate backbone.
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids contain nucleotide monomers that build into DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymers.
DNA
DNA is an antiparallel double helix, in which two complementary strands with opposite directionalities (positioning of 5' ends and 3' ends) twist around each other.
Antiparallel Strands
DNA strands run parallel to each other, but in opposite directions.
Nucleosides
Nucleosides contain a five-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base.
Nucleotides
Nucleotides contain a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group.
mRNA
mRNA is single-stranded after being copied from DNA during transcription.
Deoxyribose sugars
Deoxyribose sugars (in DNA) have a hydrogen at the 2' carbon while ribose five-carbon sugars (in RNA) have a hydroxyl group at the 2' carbon.
miRNA
Small RNA molecules that can silence gene expression by base pairing to complementary sequences in mRNA.
Phosphodiester bonds
Phosphodiester bonds are formed through a condensation reaction where the phosphate group of one nucleotide (at the 5' carbon) connects to the hydroxyl group of another nucleotide (at the 3' carbon) and releases a water molecule as a by-product.
rRNA
rRNA (ribosomal RNA): It is formed in the nucleolus of the cell and helps ribosomes translate mRNA.
dsRNA
Some viruses carry their code as double stranded RNA.
Central Dogma of Genetics
The central dogma of genetics states that information is passed from DNA → RNA → proteins.
RNA world hypothesis
The RNA world hypothesis is the theory that early life forms relied on self-replicating RNA both to store genetic information and to catalyze chemical reactions before the evolution of DNA and proteins.
Endosymbiotic theory
The endosymbiotic theory states that eukaryotes developed when aerobic bacteria were internalized as mitochondria while the photosynthetic bacteria became chloroplasts.
Modern cell theory
Modern cell theory states that all lifeforms have one or more cells, the cell is the basic structural, functional, and organizational unit of life, all cells come from other cells (cell division), and genetic information is stored and passed down through DNA.
Phosphate group
A phosphate group is part of nucleotides and is involved in forming phosphodiester bonds.
tRNA
tRNA (transfer RNA): Small RNA molecule that participates in protein synthesis.
5' end
The 5' end of a nucleic acid strand has a free phosphate group.
3' end
The 3' end of a nucleic acid strand has a free hydroxyl group.
Five-carbon sugar
A five-carbon sugar is a component of nucleotides and nucleosides.
Nitrogenous base
A nitrogenous base is a component of nucleotides and nucleosides.
Protein
Proteins largely replaced RNA in catalyzing reactions (ribozymes being a notable exception).
Metabolism
The set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms.
Biochemistry
The study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that possess a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes.
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Ribosomes
Molecular machines that synthesize proteins by translating messenger RNA.
Double Membrane
A structure consisting of two lipid bilayers that surrounds certain organelles.
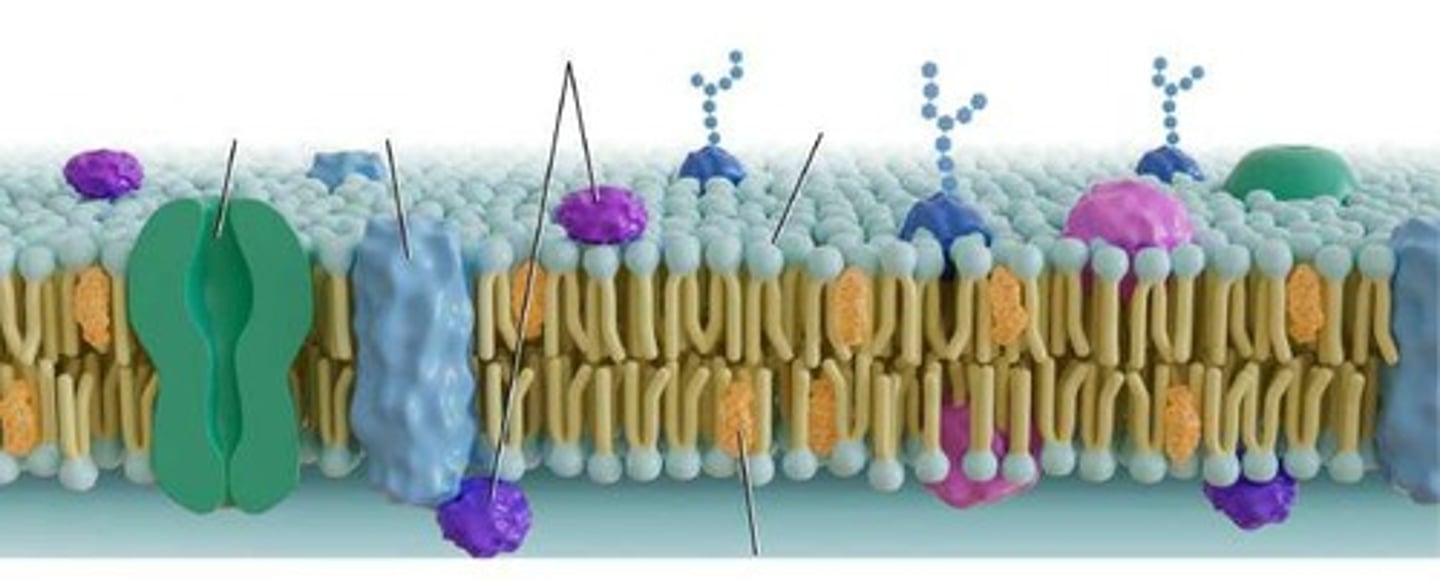
Integral Proteins
Proteins that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer and can function as receptors or channels.
Transmembrane Proteins
A type of integral protein that spans the entire phospholipid bilayer.