C2: Vision
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:49 AM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
when light comes into the eye it hits the retina which synapse onto .....
photoreceptors --> ganglion cells --> optic nerve
2
New cards
Why is the optic nerve unmyelinated at the eye?
- because myelin would reflect light
- becomes myelinated it leaves the eye
- becomes myelinated it leaves the eye
3
New cards
the ganglion cells exit the eye to form the .....
optic nerve
4
New cards
axons from the retinal ganglion cells relay visual signals as _______ via the _____ and ____
action potentials
optic nerve
optic tract
optic nerve
optic tract
5
New cards
AP --> optic tract --> optic nerve --> where?
1. lateral geniculate nuclei
2. superior colliculi
3. pre-tectal area
2. superior colliculi
3. pre-tectal area
6
New cards
visual pathway projections to the LATERAL GENICULATE NUCLEUS
- main subcortical region that processes visual information for perception
- majority of retinal axons terminate here
- signals sent to the primary visual cortex (V1); fibers to the occipital cortex
- majority of retinal axons terminate here
- signals sent to the primary visual cortex (V1); fibers to the occipital cortex
7
New cards
visual pathway projections to the SUPERIOR COLLICULI
- saccadic or fast eye movements
- visual, somatic, and auditory information
- adjust head/eyes toward the stimulus
- visual, somatic, and auditory information
- adjust head/eyes toward the stimulus
8
New cards
draw the primary visual pathway
do it
9
New cards
visual pathway projections to the PRE-TECTAL AREA
- pupillary light reflexes
- light accommodation reflex
- light accommodation reflex
10
New cards
R visual field of L eye goes to what part of the retina
temporal retina
11
New cards
L visual field of L eye goes to what part of the retina
nasal retina
12
New cards
L visual field of R eye goes to what part of the retina
temporal retina
13
New cards
R visual field of R eye goes to what part of the retina
nasal retina
14
New cards
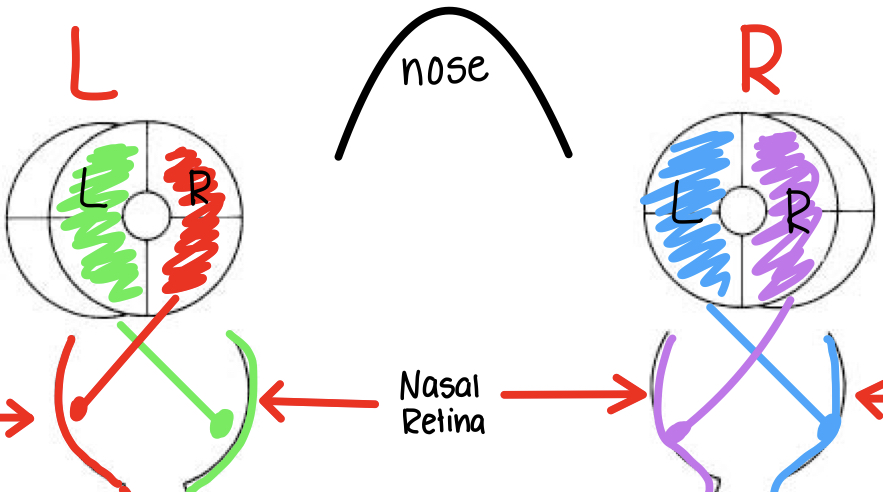
information from R visual field of R eye projects ....
ACROSS (contralateral) to LEFT LGN and LEFT V-1
15
New cards
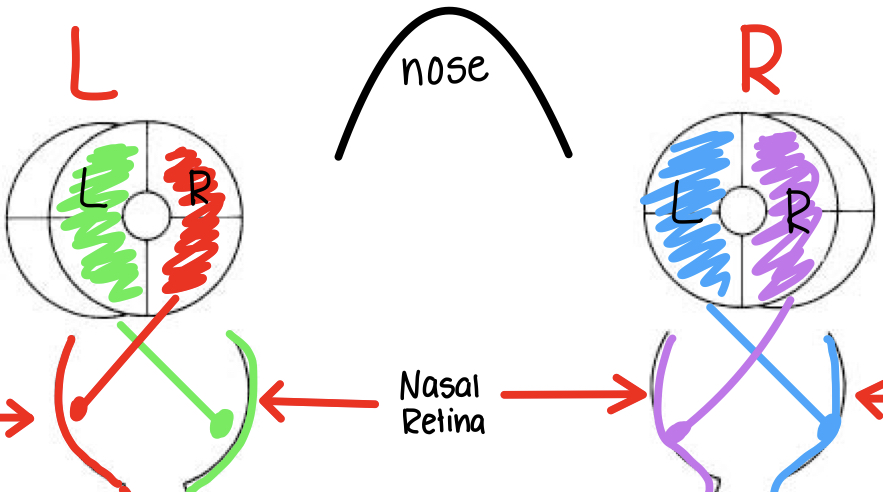
information from L visual field of R eye projects ....
contralateral to right LGN RIGHT V-1
16
New cards
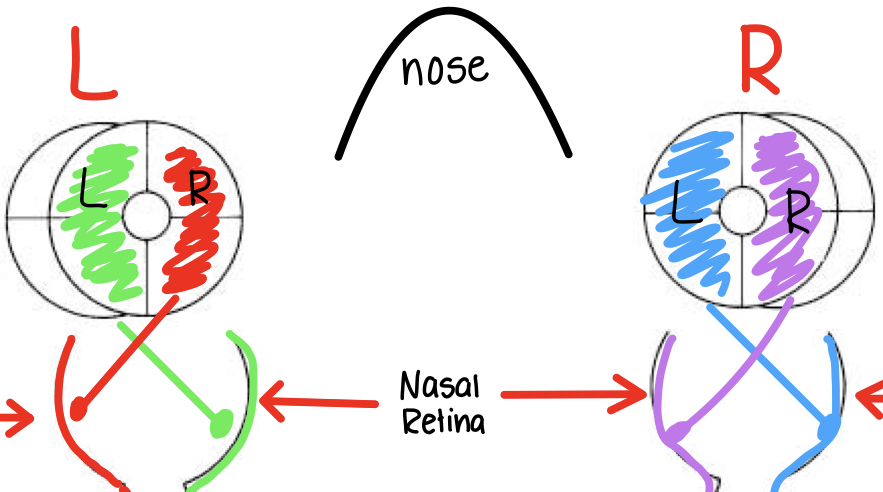
information from L visual field of L eye projects ....
ACROSS (contralateral) to RIGHT LGN and RIGHT V-1
17
New cards
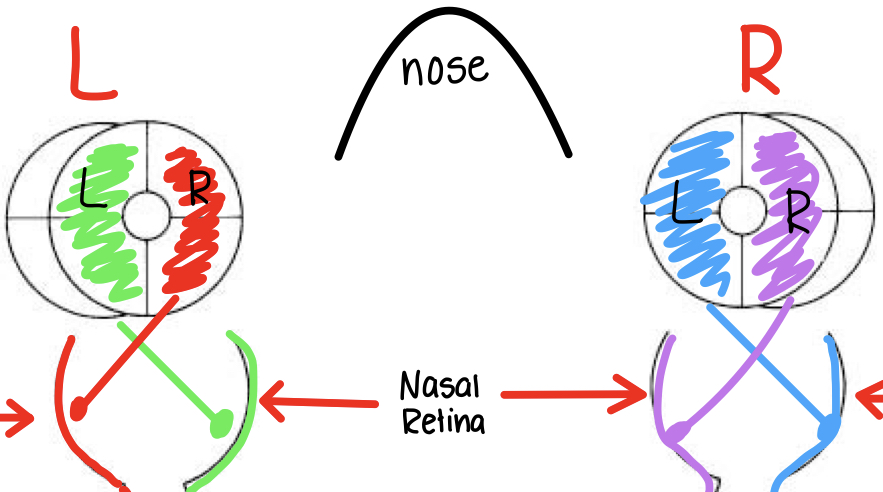
information from R visual field of L eye projects ....
LEFT V-1
18
New cards
a lesion of the LEFT optic nerve would cause what?
left eye blindness
19
New cards
a lesion of the RIGHT optic nerve would cause what?
right eye blindness
20
New cards
lesion of optic chiasm
- bitemporal heteronymous hemianopsia
- loss of L visual field of L eye
- loss of R visual field of R eye
- loss of L visual field of L eye
- loss of R visual field of R eye
21
New cards
lesion of LEFT optic tract
- right homonymous hemianopsia
- loss of both RIGHT visual fields
- loss of both RIGHT visual fields
22
New cards
lesion of RIGHT optic tract
- LEFT homonymous hemianopsia
- loss of both LEFT visual fields
- loss of both LEFT visual fields
23
New cards
lesion of LEFT optic radiations
- LEFT homonymous hemianopsia
- loss of both RIGHT visual fields
- loss of both RIGHT visual fields
24
New cards
lesion of RIGHT optic radiations
- LEFT homonymous hemianopsia
- loss of both LEFT visual fields
- loss of both LEFT visual fields
25
New cards
lesion of LEFT V-1
RIGHT homonymous hemianopsia with macular sparing
26
New cards
lesion of RIGHT V-1
LEFT homonymous hemianopsia with macular sparing
27
New cards
macular sparing is characteristic of what type of lesion?
V-1
primary visual cortex
primary visual cortex
28
New cards
anopsia
loss of vision
29
New cards
hemianopsia
blindness in half the visual field
30
New cards
quadrantanopsia
blindness of one quadrant of the visual field
31
New cards
heteronymous lesion
visual field losses are NOT THE SAME in both eyes
32
New cards
homonymous lesion
affecting the SAME SIDE of the visual field of both eyes
33
New cards
draw the pupillary light reflex
do it
34
New cards
direct light reflex
constriction of pupil that light is shining in
35
New cards
consensual light reflex
shining a light into one eye causes the pupil of the other eye to contract
36
New cards
what can be used to distinguish an optic tract lesion from a lesion more distal in the visual pathway?
light reflex
37
New cards
with lesions distal to optic tract, a small beam of light into only the blind half of each retina results in?
pupillary constriction because the visual pathway is interrupted beyond the optic tract and pretectum
38
New cards
optic nerve lesion interrupts the _____ limb of the pupillary light reflex
it abolishes what light reflexes?
are light reflexes in the good eye still active?
Would both pupils react when increased light is shown in the good eye?
it abolishes what light reflexes?
are light reflexes in the good eye still active?
Would both pupils react when increased light is shown in the good eye?
afferent
direct and consensual from the blind eye (both eyes would not dilate)
yes
yes
direct and consensual from the blind eye (both eyes would not dilate)
yes
yes
39
New cards
oculomotor nerve lesion interrupts the ____ limb of the pupillary light reflex
resulting in ...
resulting in ...
efferent
mydriasis (dilation); loss of direct and consensual responses in the ipsilateral eye
mydriasis (dilation); loss of direct and consensual responses in the ipsilateral eye
40
New cards
result of an incomplete LEFT optic radiation lesion
right homonymous quadrinopsia
41
New cards
result of an incomplete RIGHT optic radiation lesion
LEFT homonymous quadrinopsia
42
New cards
acromegaly
rare disease cause by pituitary gland tumor
elevated GH (pituitary) levels stimulate excess amounts of IGF-1 (liver)
PRESSURE on surrounding brain tissue
elevated GH (pituitary) levels stimulate excess amounts of IGF-1 (liver)
PRESSURE on surrounding brain tissue
43
New cards
extra IGF-1 in acromegaly is responsible for .....
slow but progressive GROWTH and swelling of various tissues, bones, and organs
44
New cards
what is the occurrence of acromegaly?
6 per 100,000 people
2-3 new cases each year per 1,000,000 people
2-3 new cases each year per 1,000,000 people
45
New cards
T/F acromegaly effects men and women at different rates
FALSE
46
New cards
what age group is most commonly diagnosed with acromegaly?
middle aged adults
47
New cards
complications of acromegaly
high blood pressure
cardiomyopathy
osteoarthritis
diabetes
sleep apnea
spinal cord compression
headaches
vision loss***
cardiomyopathy
osteoarthritis
diabetes
sleep apnea
spinal cord compression
headaches
vision loss***
48
New cards
is there a cure for acromegaly?
what about treatments?
what about treatments?
no
drug therapy, radiation therapy, surgery
drug therapy, radiation therapy, surgery
49
New cards
what happens when you leave acromegaly untreated?
death
50
New cards
growth of the pituitary tumor common in acromegaly often leads to pressure on the ...
leading to ...
leading to ...
optic chiasm
loss of peripheral vision (tunnel vision)
loss of peripheral vision (tunnel vision)
51
New cards
LEFT optic NERVE lesion ...
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct = no, blockage of afferent signal
consensual = yes, uninterrupted
right eye:
direct = yes, uninterrupted
consensual = no, blockage of afferent signal
direct = no, blockage of afferent signal
consensual = yes, uninterrupted
right eye:
direct = yes, uninterrupted
consensual = no, blockage of afferent signal
52
New cards
RIGHT optic NERVE lesion ...
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct = yes, uninterrupted
consensual = no, blockage of afferent signal
right eye:
direct = no
consensual = yes
direct = yes, uninterrupted
consensual = no, blockage of afferent signal
right eye:
direct = no
consensual = yes
53
New cards
RIGHT optic TRACT lesion ...
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left:
direct = yes, still innervation of edinger-westphal
consensual = yes, loss of only one pathway
right:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
direct = yes, still innervation of edinger-westphal
consensual = yes, loss of only one pathway
right:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
54
New cards
OPTIC CHIASM lesion ...
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left:
direct = yes, still innervation of edinger-westphal
consensual = yes, loss of only one pathway
right:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
direct = yes, still innervation of edinger-westphal
consensual = yes, loss of only one pathway
right:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
55
New cards
LEFT oculomotor nerve lesion:
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left:
direct = no, loss of innervation of sphincter muscle
consensual = no, loss of efferent nerve
right:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
direct = no, loss of innervation of sphincter muscle
consensual = no, loss of efferent nerve
right:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
56
New cards
RIGHT oculomotor nerve lesion:
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left eye:
direct =
consensual = light in R eye
right eye:
direct =
consensual = light in L eye
left:
direct = yes
consensual = yes
right:
direct = no, loss of innervation of sphincter muscle
consensual = no, loss of efferent nerve
direct = yes
consensual = yes
right:
direct = no, loss of innervation of sphincter muscle
consensual = no, loss of efferent nerve
57
New cards
what would happen in a LEFT or RIGHT optic radiation lesion?
none of the afferent or efferent nerves would be affected so everything would still work
58
New cards
projection from the pretectal nucleus are
bilateral
59
New cards
what performs the first stage of visual processing?
retina
60
New cards
in the retina, stimulation of light activates?
photoreceptors with the production of electrical signals (AP)
61
New cards
what are the two classes of photoreceptors?
rods = absent in fovea
cones = concentrated in fovea
cones = concentrated in fovea
62
New cards
cones and rods:
high vs low threshold
high vs low threshold
cones = high threshold
rods = low threshold
rods = low threshold
63
New cards
rods function under conditions of _____ illumination
scotopic (low)
64
New cards
cones function under conditions of ___ illumination
photopic (daylight)
65
New cards
how many cones are in the eye?
10 million
66
New cards
how many rods are in the eye?
100 million
67
New cards
are rods present in the fovea?
no bitch
68
New cards
are cones present in the fovea?
f*ck yeah
69
New cards
rods contain what photo-pigment?
rhodopsin
70
New cards
are rods or cones poor in detail?
rods
71
New cards
do you use rods or cones in night vision?
rods
72
New cards
Are the cones or rods responsible for color vision?
cones
73
New cards
Are the cones or rods responsible for visual acuity?
cones
74
New cards
what photopigment do cones contain?
opsin
3 types - red, blue, green
3 types - red, blue, green
75
New cards
at night, there is not enough _____ to stimulate opsin in cones
light energy to generate an electrical signal (NO AP)
76
New cards
is rhodopsin in rods or opsin in cones lower threshold?
rhodopsin in rods
77
New cards
is there enough light energy at night to stimulate rhodopsin in rods?
yes
78
New cards
during the day, rhodopsin in rods is ...
fully saturated so they are unable to generate an AP
79
New cards
what happens to rods when you walk into a dark room after being outside on a sunny day?
rhodopsin takes a bit to desaturate from lack of white light
80
New cards
action potentials generated by cones and rods are relayed to ...
V-1
81
New cards
within the retina, rods and cones synapse onto ...
which then synapse onto ...
which then exit the eye to form ...
which then synapse onto ...
which then exit the eye to form ...
bipolar cells
ganglion cells
optic nerve
ganglion cells
optic nerve
82
New cards
axons from the retinal ganglion cells relay visual signals principally to the .....
lateral geniculate nuclei
83
New cards
color processing involves a series of _____ steps that begin in the ___ with ____ which then go through the ____ to ___
heirarchial
retina
three classes of cones
LGN
V-1
retina
three classes of cones
LGN
V-1
84
New cards
in V-1, color cells are clustered and project to ____ which in turn to project to _____ and the final stage takes place in the _____
V-2
posterior inferior temporal (PIT) cortex
inferior temporal cortex (V4)
posterior inferior temporal (PIT) cortex
inferior temporal cortex (V4)
85
New cards
stages in hierarchal processing of color>
retina (cones)
LGN
V-1
V-2
posterior inferior temporal (PIT) cortex
inferior temporal cortex (V4)
LGN
V-1
V-2
posterior inferior temporal (PIT) cortex
inferior temporal cortex (V4)
86
New cards
what is the function of the inferior temporal cortex (V4)?
final stage of color processing takes place here
help shape decision making
help shape decision making
87
New cards
what are the functions of V1-V3a?
processing information, shapes, and textures
88
New cards
what is the function of V4?
color recognition
89
New cards
most common cause of color blindness
genetic fault in development of one or more of the three sets of cones
90
New cards
is there a cure for color blindness?
no
91
New cards
other causes of color blindness
brain or retinal damage
accidents or trauma (occipital lobe)
damage to retina from UV light
degenerative diseases of the eye
deficiency of vitamin K
accidents or trauma (occipital lobe)
damage to retina from UV light
degenerative diseases of the eye
deficiency of vitamin K
92
New cards
about _____% of males and _____% of females are color blind
8%
.5%
.5%
93
New cards
it total or partial color blindness more common?
partial
94
New cards
more than 95% of all variations in human color vision involve what receptors in male eyes?
red and green
95
New cards
color blindness is _____ linked
X chromosome
96
New cards
because color blindness is X linked, ______% of women have a ____ th color cone and can be considered ______
2-3
4
tetrachromats
4
tetrachromats
97
New cards
Ishihara color test
most common test used to diagnose color deficiencies
98
New cards
prosopagnosia
face blindness, inability to recognize faces
99
New cards
prosopagnosia affects ____% of the US population
2.5%
100
New cards
are there any treatments for prosopagnosia
no