Exploring Roles of Occupational Therapy Managers: Differentiating Leadership and Management
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Managerial Roles
Interpersonal (e.g. figure head, leader, liaison)
Informational (e.g. monitor, disseminator, spokesperson)
Decisional (e.g. entrepreneur, disturbance handler, negotiator)
Managerial Skills
Conceptual skills to analyze and diagnose complex situations
Interpersonal skills (e.g. work with, problem solve, motivate)
Technical skills (e.g. job specific knowledge and techniques)
Political skills (e.g. build a power base, establish connections)
How should managers act?
By directing actions of the employees/subordinates
By managing the people who take actions
By managing information that propels people to take action
Roles of an Occupational Therapy Manager
Overseeing and coordinating the operations of a facility
Ensuring effective service delivery, coordination, and success
Providing leadership to the occupational therapy team
Fostering a positive work environment
Conducting team meetings to promote communication
Develop and implement strategic plans to achieve goals
Inform strategic decision-making (e.g. patient needs)
Meet operational needs (e.g. manage budget and resources)
Monitor financial performance (e.g. cost savings and profit)
Ensure compliance with regulations and requirements
Enforce quality assurance standards to maintain patient care
Identify areas for improvement (e.g. patient feedback)
Implement evidence-based practices and protocols
Provide ongoing training and professional development
Mentor and coach staff to enhance their clinical skills
Advocate for the role of occupational therapy
What can the role of an occupational therapy manager be described as?
Multifaceted, requiring a combination of clinical expertise, leadership skills, and business acumen
What do occupational therapy managers play a vital role in?
Improving patient outcomes
Advancing the field of occupational therapy
What term can be described as measures or indicators of successful and safe performance that verifies that the individual has necessary knowledge, skills, and abilities to perform a task?
Competency statements
Competency Statements
Measures or indicators of successful and safe performance that verifies that the individual has necessary knowledge, skills, and abilities to perform a task (e.g. fabricate an orthosis, complete Hoyer lift transfer)
What are the necessary competencies of an occupational therapy manager?
What is the managerial role at a small firm?
Spokesperson (high)
Entrepreneur, figure head, leader (moderate)
Disseminator (low)
What is the managerial role at a large firm?
Resource allocator (high)
Liaison, disturbance handler, negotiator (moderate)
Entrepreneur (low)
What should occupational therapy managers become familiar with?
Technology (e.g. physical agent modalities, simulators)
Business (e.g. analytical software, data, virtual meetings)
Information and communication
What is the managerial philosophy and method?
Creating an organization that wants continuous improvement in their quality of services (e.g. leadership support, resource allocation, organizational learning)
What does continuous quality of improvement identify?
Improvement opportunities
What does continuous quality of improvement analyze?
Problems
Continuous Quality of Improvement Tools
Fishbone diagram
Checklist
Pareto chart
Plan-do-study-act cycle
Process flowchart
Run chart
What 2 factors influence the role of an occupational therapy manager?
1. Company size
2. Managerial level
Are occupational therapy managers often top, middle, or line-level managers?
Middle-level
Which two of the four major management function often take precedence for occupational therapy managers; planning, directing, organizing, and controlling?
Directing and controlling functions
What should occupational therapy managers possess in addition to occupational therapy clinical competencies?
Relevant managerial competencies
Does a leader or a manager create a vision that empowers, motivates, and influences people in an organization for change?
Leader
What do leaders focus on?
Vision of the organization
Vision
Represents an ideal model of the future that implies change and challenges organizations to transcend the status quo
Do leaders have adaptive or restrictive decision making styles?
Adaptive
What do leaders challenge?
Status quo
How do leaders inspire others?
By enthusiastically communicating a clear and compelling vision that influences actions toward the achievement of organizational goals
Does a leader or a manger perform preplanned tasks on a regular basis with the help of their team/subordinates?
Manager
What do managers focus on?
Setting and meeting organizational goals
How many key management functions are managers responsible for?
4
What do managers encourage?
Productivity
What is the authority of a manager conferred with?
Professional title outlined with a list of responsibilities
What do managers oversee?
Employees' work toward the achievement of predictable and short-term objectives
What are managers mainly concerned with?
Individual performance and measurement of outcomes that are focused on operations
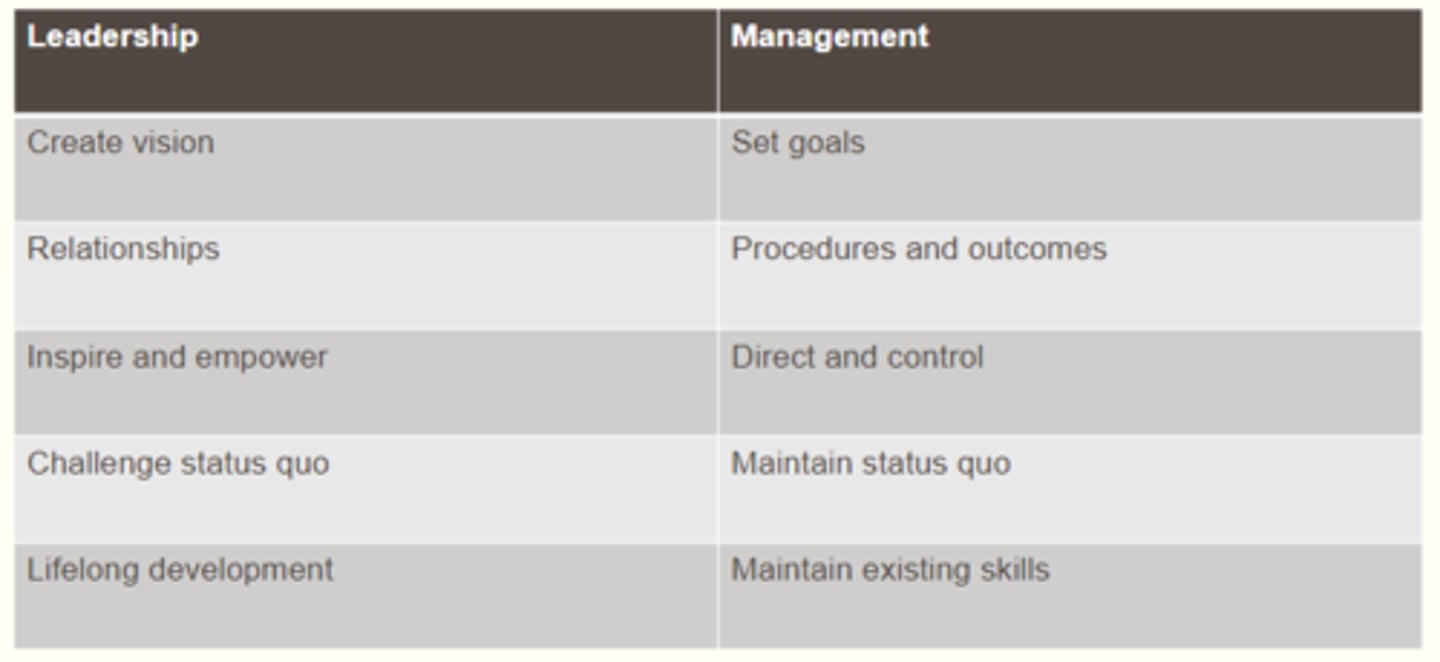
Leadership vs. Management
Leadership:
Create vision
Relationships (know how best to serve them)
Inspire and empower by clearing the path of obstacles
Challenge status quo (encourage risk taking)
Lifelong development (development is never complete)
Management:
Set goals
Operational procedures (getting work done through people)
Direct and control, delegating responsibilities
Maintain status quo (avoid risk of failure)
Maintain existing skills (rely on existing skill sets)
Is the following scenario an example of leadership or management: A company contracted with multiple skilled nursing facilities to provide rehabilitation services is appointing an occupational therapist to review the recently published Medicare changes and develop administrative processes to ensure organizational sustainability?
Management
Is the following scenario an example of leadership or management: In response to the recently proposed Medicare changes, an occupational therapist who works in a facility decides to a drive a campaign on how the changes may negatively affect the stakeholders. She solicits case vignettes from fellow therapists and service recipients to make a case?
Leadership
Do contemporary organizations need leaders, managers, or both?
Both
What can management without leadership be described as?
Bureaucratic
What do bureaucratic managements have high rates of?
Employee dissatisfaction
What does leadership without management result in?
Low productivity
Inefficiency
Complimentary Process Differences Between Leaders and Managers

What are management and leadership considered when taken together? Why?
Transformational because they prompt both leaders and followers to adhere to higher levels of ethical aspirations and conduct when pursuing a shared purpose toward organizational change
When is a transformational approach necessary? Why?
When organizations implement strategic change in response to new policy mandates and diverse payer models to maintain high engagement and forward momentum
What is the focus of the Triple Aim of Health Care Reform?
Interprofessional primary health care, new models for payment, and an emphasis on value as demonstrated through improved outcomes
What can the beliefs around management and leadership be construed and misconstrued through?
Different assumptions based on power (e.g. influence, control, or authority over others)
What are the differences between management and leadership primarily
based on?
Intention and behaviors
What is leadership determined by?
Person's behavior and overall effectiveness while guiding others toward the achievement of organizational goals
What approach do managers often use in a hierarchical organizational structure? Why?
Authoritative approach to achieve short-term organizational goals, directing others through a specific chain of command
What type of process is leadership?
A highly relational and ethical process that inspires individuals to work together to create necessary changes that effectively move an organization toward an ideal model of the future despite challenges
The difference between leadership and management is based on; values and power, intentions and behavior, control and budgeting, or directing and planning?
Intentions and behavior
In hierarchical organizational structures, managers often take what approach to the achievement of short-term organizational goals; organized, repetitive, authoritative, or friendly?
Authoritative
A vision represents an ideal model of the future that implies; progress, change, status quo, or acuity?
Change
What is the American Occupational Therapy Association Vision of 2025?
Maximize health, well-being, and quality of life for all people, populations, and communities through effective solutions that facilitate participation in everyday living
Where do occupational therapy practitioners have opportunities to develop their leadership skills?
Serving on interprofessional health care teams
Interprofessional Health Care Teams
Comprise individuals from multiple health care disciplines who agree to share their point of view and expertise and are open to learning and sharing in a trusting environment to help solve organizational problems
True or False: Leadership can be developed in any context of life and often occurs when one has very little awareness that it is happening.
True
When does the engagement in leadership often start?
When one's personal core values align with those of others who are also motivated to make a positive difference toward a greater good
What is the ability to lead not based on?
Position or title (can be developed by anyone at any time)
Leaders and managers must have a complementary skill set and adopt what type of approach; forced, visionary, blended, or controlled?
Blended
Transformational leadership can be described as all of the following except; inspiring, engaging, visionary, or preventing change?
Preventing change
Who should assume leadership of the profession of occupational therapy; AOTA board members, members of professional associations such as
state occupational therapy associations and AOTA, AOTA employees, or everyone?
Everyone
Health Care System
Organization of resources, institutions, and people that deliver health care services to meet the health needs of populations
What is the goal of health care systems?
Value-driven care
Value-Driven Care
The best clinical outcomes for patients with the best customer service
What are examples of agencies who monitor and guide health care systems in providing quality care in an efficient manner?
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
National Quality Forum
The Joint Commission
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
Federal agency that provides health care coverage for beneficiaries, works with state governments to administer Medicaid and other health care coverage, and provides standards for quality improvement initiatives
Health care costs in what country are among the highest in the world?
United States
What efforts has the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) led to reduce health care costs?
Bundled payments
Readmission penalties
Quality payment programs
Bundled Payment for Care Improvement (BPCI)
An initiative addressing performance and accountability for an episode of care, with the aim to improve coordination of care across providers and care environments
What has the bundled payment for care improvement initiative resulted in?
Decreased length of stay
Increased discharge to home
Stable readmission rates
Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program (HRRP)
A risk-standardized readmission rate for Medicare beneficiaries who were hospitalized in an acute care hospital and experienced an unplanned readmission for any cause to an acute care hospital within 30 days of discharge
What is an important component for maximizing cost containment?
Providing efficient care in all phases of care from acute to post-acute
The concept of what is at the center of Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) initiatives?
Value = (Quality + Outcomes)/Cost
Levels of Care
Acute care (e.g. treatment provided in a hospital setting)
Skilled nursing or subacute rehabilitation
Acute inpatient rehabilitation (e.g. receive 3 hour services)
Long-term acute (e.g. provides specialized care)
Day rehabilitation (e.g. intensive individualized rehabilitation)
Home health services
Primary care (e.g. basic medical care in an outpatient setting)
Outpatient rehabilitation
What is a key tenet of effectively navigating health care systems?
Care coordination
What is developed in order to structure the care provided to facilitate discharge for a specified length of stay within the hospital?
Clinical pathways
What is an important metric in healthcare systems that has financial implications?
Throughput
Throughput
Moving the client through the episode of care while achieving all of the clinical milestones
If a hospital has a shorter length of stay for the entire episode of care then does the healthcare system have greater or lesser efficiency and financial return?
Greater
What is a metric used in many healthcare systems?
Productivity
Productivity
Efficiency in the delivery of care against an established standard
What is productivity for therapy services often measured through?
Billable time for financial purposes and patient visits as a measure of throughput
Benchmarking
A standard by which others may be measured or judged and can be used for comparison
2 Forms of Benchmarking
1. Internal
2. External
Internal Benchmarking
Compares best practices within an organization as well as evaluating performance of the organization over time
External Benchmarking
Assesses performance in comparison to other organizations whose strategies have proven effectiveness
Patient/Client Satisfaction
Type of outcome that measures an individual's perception and attitudes of the care provided and received
The use of what provides clinicians with a standard approach to care, leading to fewer medical errors and more efficient care delivery?
Evidence-based practice guidelines
Evidence-Based Practice Guidelines
Provide practice guidelines for specific topics to support decision making that promotes a high quality health care system
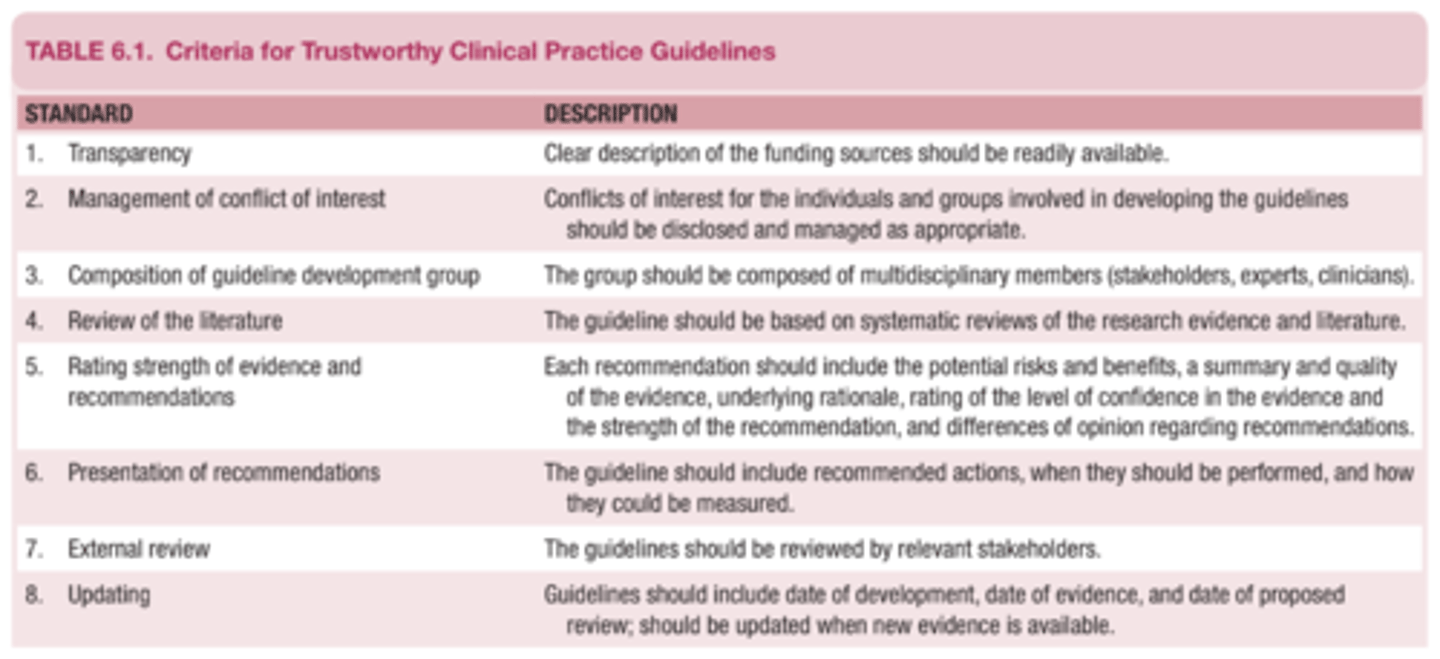
8 Criteria for Trustworthy Evidence-Based Practice Guidelines
1. Transparency
2. Management of conflict of interest
3. Composition of guideline development group
4. Review of the literature
5. Rating the strength of evidence and recommendations
6. Presentation of recommendations
7. External review
8. Updating
Value-based programs were implemented to: improve coordination of care, improve quality of care, reduce health care costs, or all of the above?
All of the above
Strategies to improve care transitions include all except: a coordinated individualized discharge plan including the client and caregivers, follow-up telephone call to reinforce discharge education and respond to concerns, medication reconciliation and education, discharge planning assigned to a single provider, or providing clients with follow-up appointments at the
time of discharge?
Discharge planning assigned to a single provider
Benchmarking in healthcare systems: benchmarking allows comparison in performance with other similar organizations for improvements in different areas of measurement, external benchmarking allows comparisons of best practices within an organization, internal benchmarking assesses performance with other organizations, or benchmarking sets up competition between organizations for financial gain?
Benchmarking allows comparison in performance with other similar organizations for improvements in different areas of measurement
In what manner must occupational therapy care be provided to provide positive clinical outcomes for clients?
In a manner reflecting the core belief that occupational therapy practice is anchored in the meaningful, necessary, and familiar activities of everyday life
What has an individual’s functional level been shown to affect?
Hospital readmissions (e.g. individuals with unmet ADL needs were more likely to be readmitted to a hospital within a year; 1 in 4 Medicare beneficiaries were discharged with unmet ADL needs)
Case Management
A collaborative process that assesses, plans, implements, coordinates, monitors, and evaluates the options and services required to meet the client's health and human service needs
Occupational therapy leaders can facilitate the role of occupational therapy providers in reducing hospital readmissions by: assisting in optimizing client participation in medication management, collaborating for the implementation of coordinated mobility and early intervention programs, facilitating self-management in establishing health routines that promote healthy lifestyles, participating in the development and evaluation of clinical pathways, or all of the above?
All of the above
Opportunities for occupational therapy providers to demonstrate leadership roles in care transitions include all except: advocating for client needs when resources may be limited, assessing and evaluating functional abilities and identifying barriers for discharge, completing medication reconciliation to ensure no potential concerns for discharge, or communicating recommendations for appropriate level of care with the interprofessional team?
Completing medication reconciliation to ensure no potential concerns for discharge
Tools used by occupational therapy managers to measure efficiencies in healthcare systems include: length of stay, productivity, clinical outcome measurements, or all of the above?
All of the above
Emerging Areas of Practice (Non-Traditional Practice Areas)
Areas in which the occupational therapy role has not been established