UF PPA Lecture 3.2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
the _____ valve is between the left ventricle and aorta
aortic
the ______ valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle
tricuspid
the ______ valve is between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
pulmonary
the ______ valve is between the left atrium and left ventricle
mitral
true or false
valves can open in both directions
false!
one or the other
the tricuspid and mitral valves open and close due to changes in pressure in the ________ and _______
atria, ventricle
the aortic and pulmonary valves open and close due to changes in pressure in the ________ and _______
ventricle, artery
normal opening and normal flow produce no ________
sound
S1 (lubb) is a result of
mitral/tricuspid valve closure
S2 (duub) is a result of
aortic/pulmonary valve closure
__________ is left ventricle contraction and _________ is left ventricle dilation
systole, diastole
S3 sounds are heard during ________ phase and can be in __________ hearts or _________ heart
early diastole (rapid filling)
normal, large
pathological
S4 sounds are heard during ________ phase and are in __________ hearts and are always _________
late filling (slow filling phase)
hypertrophic
abnormal
_________ is a stiff valve where it does not completely open and reduces the flow through the valve
stenosis
stenosis is a ______ issue
systole
________ is a valve closing problem where it does not completely close and results in backflow or regurgitation
insufficiency
backflow is a ________ issue
diastole
the opening of the mitral valve is caused by ________ pressure in the LV
decreased
What are the three things we want to know about each valve?
what murmurs occurs with each defect?
what is the consequence?
-does it increase pressure or volume work?
-does it affect atria or ventricle more?
what diseases make progression of disease worse?
___________ is the thickening and calcification of the _______ valve making it so that it cannot completely open when it is supposed to
mitral stenosis
mitral
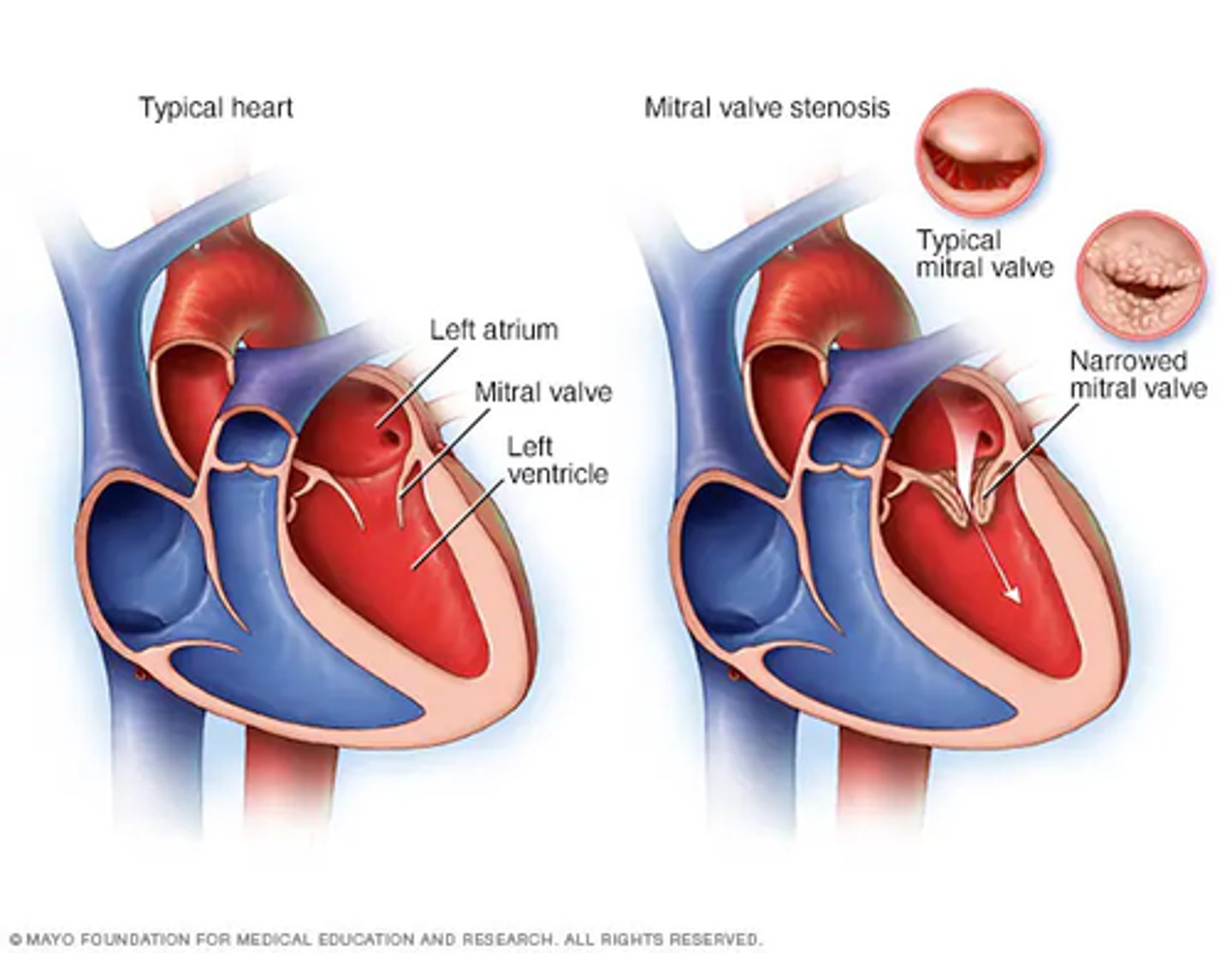
thickening and shortening of chordae tendinae is caused by ________ fever and _______ infection
rheumatoid
strep
mitral stenosis is a ________ murmur/rumble with a loud _____ sound
diastolic
S1
mitral stenosis leads to pressure overload in the ________ because there is blood that it cannot get rid of
left atrium
mitral stenosis can lead to which of the following?
a. left atrial enlargement
b. atrial arrhythmias
c. thrombus formation
d. pulmonary edema
e. possible right heart failure
f. heartburn
g. brain damage
a, b, c, d ,e
________ is when the valve does not close completely when it supposed to
mitral insufficiency
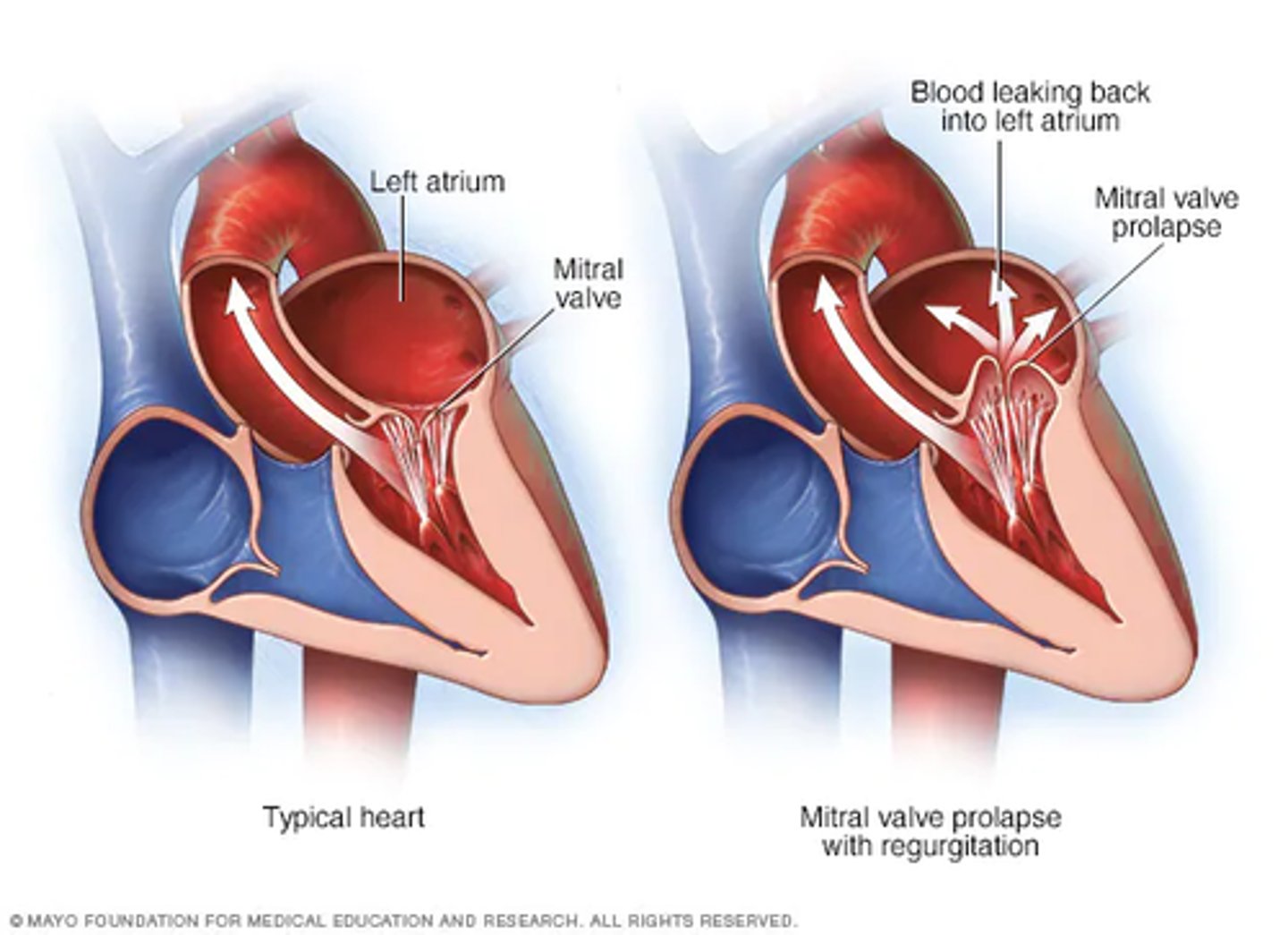
true or false
mitral valve prolapse can be asymptomatic
true
___________ occurs if leaflets are enlarged or chordae tendinae are too long
mitral valve prolapse
mitral valve prolapse may cause ______ clicks or late _______ murmur or chest palpitations
mid-systolic
systolic
complications of mitral valve prolapse include the progress to ________ or the rupture of chordae tendinae to cause sudden ________.
other complications include infective _________, ________ formation due to _______ blood flow and ________ arrhythmias.
regurgitation, regurgitation
endocarditis, microthrombus, irregular, atrial or ventricular
________ is caused by the rupture of chordae tendinae or structural abnormality or damage to valve caused endocarditis, ischemic heart disease, structural abnormality of valves or papillary muscles, LV enlargement, and calcification
mitral regurgitation
mitral regurgitation causes a ________ or ________ murmur
holosystolic
pan systolic
mitral regurgitation causes overload of ventricle and atrium which can lead to ________ and ________ enlargement, ________ arrhythmias, ______ sound and left heart failure
LA LV, atrial, S3
acute and severe back flow into the left atrium leads to ____________ left atrial pressure, followed by ________ edema, and difficulty breathing
increased, pulmonary
_________ is a rigid valve due to fibrosis or calcification
aortic stenosis
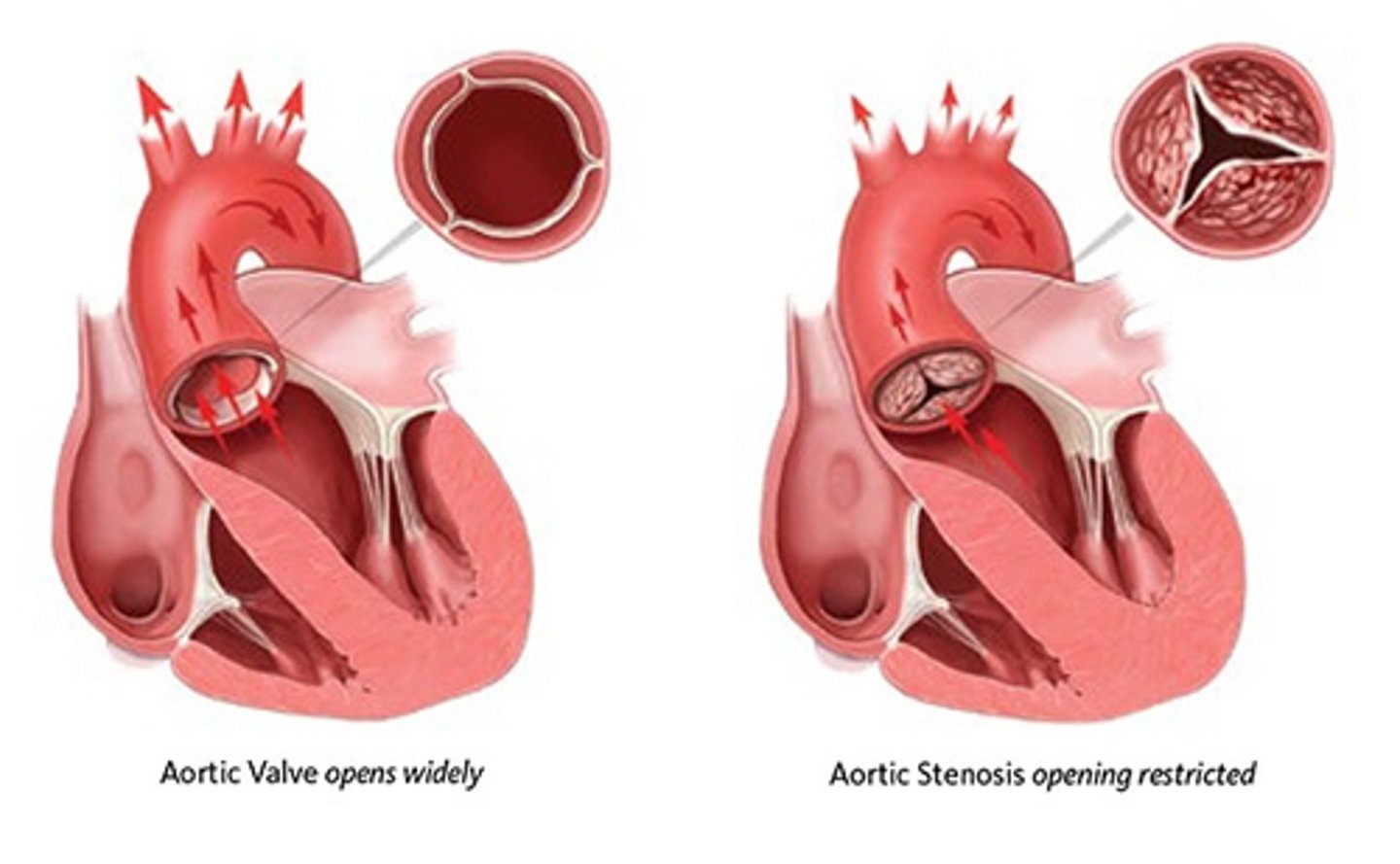
__________ causes both fibrosis and/or calcification which causes aortic stenosis
rheumatic heart disease
________ calcification can cause aortic stenosis
senile
___________ valve can cause aortic stenosis
congenital bicuspid
aortic stenosis results in a __________ murmur and causes ________ heart sound due to the heart working overtime and becoming thick and big
systolic ejection
S4
aortic stenosis causes reduced outflow into aorta which leads to decreased _________ but increased ______________
aortic pressure
left ventricle pressure
the pressure overload in the ventricle due to aortic stenosis can lead to which of the following:
a. chest pain, syncope, fatigue
b. left heart failure
c. dizziness with exercise
d. fatigue, dyspnea, cyanosis
all of the above
floppy valve leaflets or deformed aortic root is caused by _______ disease, ________ defect, ________, ________ dilation, and ________
rheumatic
congenital valve
endocarditis
aortic root (marfan syndrome, aneurysm syphilis)
hypertension
aortic regurgitation leads to _______ murmur
diastolic
aortic regurgitation leads to ________ into the left ventricle which leads to an abnormal __________
backflow
aortic P (water hammer pulse)
volume overload of the ventricle can lead to:
______ dilatation
______ arrhythmias
fatigue, excerise intolerance, angina
_______ edema
_______ with progression
LV
ventricular
pulmonary
dyspnea
the dilated left ventricle can be caused by
a. mitral stenosis
b. mitral regurgitation
c. aortic regurgitation
c. aortic regurgitation