Animal Diversity LAB - Week 3
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
4 mechanisms by which evolution occur
mutation, genetic drift, natural selection, gene flow
Microevolution
evolutionary change within a species over a shorter period of time
Macroevolution
origin of new species and divisions of taxonomic hierarchy above species level
3 disadvantages to multicellularity
harder to take nutrients, higher energy requirements, harder to distinguish self from others
How is multicellularity characterized?
juvenile/adult life stages, division of labor (apoptosis), determinant growth, adhesion between cells
Clade Porifera is
the sponges
Porifera cellular level of organization
no true tissues or germ layers
Internal skeleton made of…
spicules
mesohyl
gelatinous matrix in sponge
Suspension feeders
system of pores and canals
Asexual reproduction in Porifera
formation of buds/gemmules
Sexual reproduction in Porifera
free-swimming ciliated or flagellated larvae
Sponge body types
ascon, sycon, leucon
Ascon body type
small and simple with tube shaped body
Sycon body type
tube shaped body with thickened, folded walls
Leucon body type
complex, larger in overall body size, thickest walls
osculum
where filtered water is pushed out of
spongocoel
filtered water collects here (central cavity)
choanocytes
specialized cells lining radial canals, trap small food particles with flagella through phagocytosis
pinacocytes
cells making up outer layer of sponge
amoebocyte
mobile cells that carry food to other cells and can turn into any other cell needed (use pseudopodia)
porocyte
elongated, doughnut-shaped cells that channel water to radial canals
ostia
pores on body surface of sponge
Clade Cnidaria is
radiate animals
Cnidaria tissue level of organization
diploblastic
mesoglea
non-living, jelly-like connective tissue containing few cells
Gastrovascular cavity
both mouth and anus, central digestive cavity
polymorphism
more than one morphology (polyp and medusa)
Polyp
attached to substrate, typically asexual
Medusa
free-floating, typically sexual
nerve net
connects uniformly distributed sensory cells and motor neurons to enable limited number of coordinated movements
bud
product of asexual reproduction
cnidocyte
stinging cells
testes
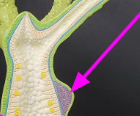
bud
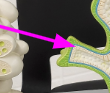
ovary
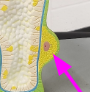
gastrovascular cavity
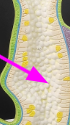
nematocyst

cnidocyte

planula larvae
free swimming, ciliated larvae
hydranth
specialized feeding polyp
gonangium
specialized reproductive polyp
medusa
product of asexual reproduction, released from gonangium when mature
Obelia life cycle
medusae release sperm and egg, forms zygote, forms blastula, matures into planula, budding forms new colony, gonangium forms medusa buds, medusa buds released, medusa buds mature into medusae
oral disc
raised portion of mouth
tentacles
defense and prey capture
mouth
ingestion of food and elimination of indigestible particles
pharynx
muscular portion of gastrovascular cavity for pulling in prey
pedal disc
attaches organism to rocks; can be used for locomotion
ostium
pore that allows circulation of fluids between adjacent body sections
retractor muscles
expand and contract body
gonads
organs for sexual reproduction
radial canal
extension of gastral pouch that radiates out and brings nutrients to rest of body
circular canal
circular extension of gastric pouch that distributes nutrients to outer rim of body
gastric pouch
one of four divisions for gastrovascular cavity for digestion of food
oral arms
defense and prey captures
Aurelia life cycle
medusae release sperm and egg, forms zygote, matures into planula larvae, schyphistoma, matures into strobilia, strobilation (budding process), free swimming ephyra, matures into medusa
Cnidarian Clades
Anthozoa, hydrozoa, schyphozoa, cuboza