A2 Unit 3.2 Photosynthesis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
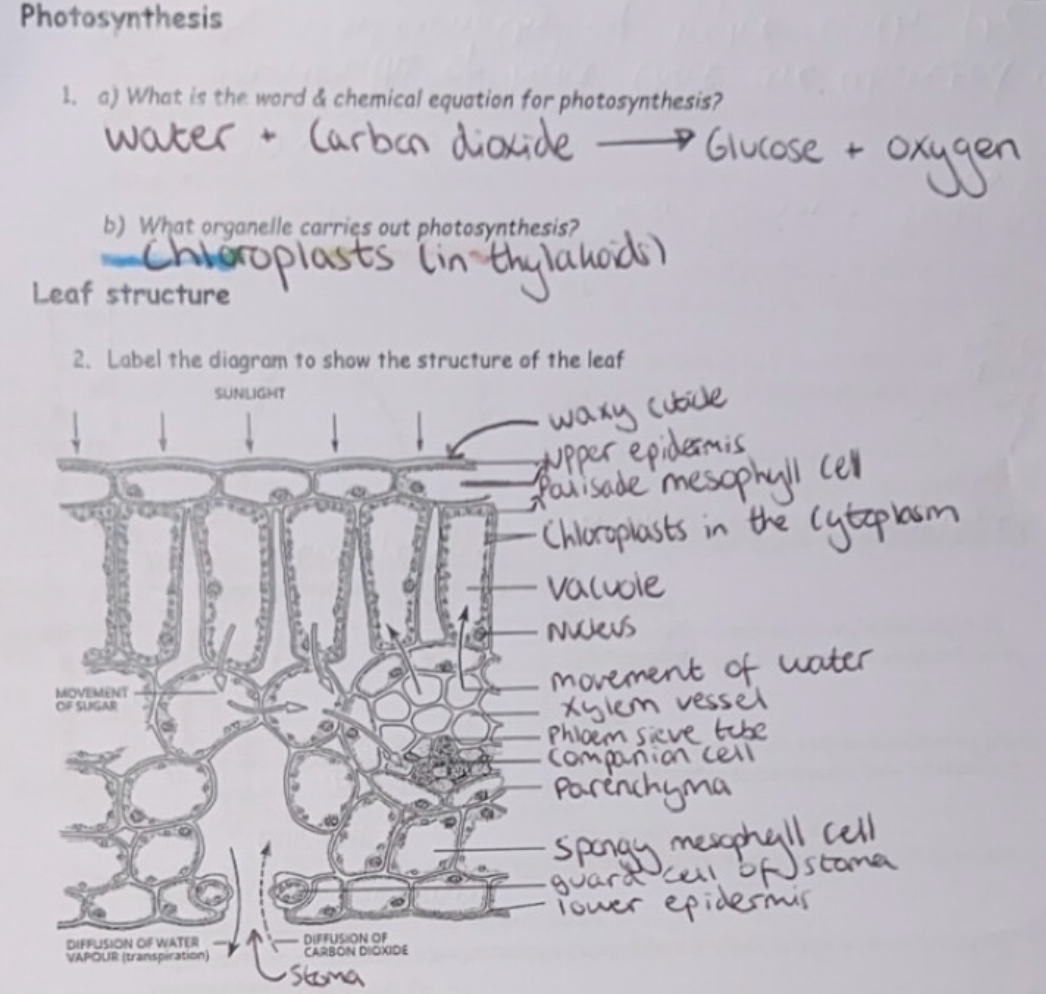
Photosynthesis & Labelled Structure of Leaf - Adaptations
Large surface area of leaf - for maximum absorption of light
Stomata - Allow diffusion of gases (CO2 for photosynthesis & O2 for respiration)
Air spaces between cells (Spongy mesophyll layer) - Allow shorter diffusion distance for CO2 to diffuse to photosynthesising cells
Palisade mesophyll cells arranged vertically - more light can be absorbed as closer to surface than if stacked horizontally
High concentration of Chloroplasts in Palisade mesophyll cells - closer to surface of leaf, so absorb more light
Large surface area of Chloroplasts - for maximum absorption of light
Chloroplasts can move within Palisade cells - can move towards direction of light for maximum absorption of light
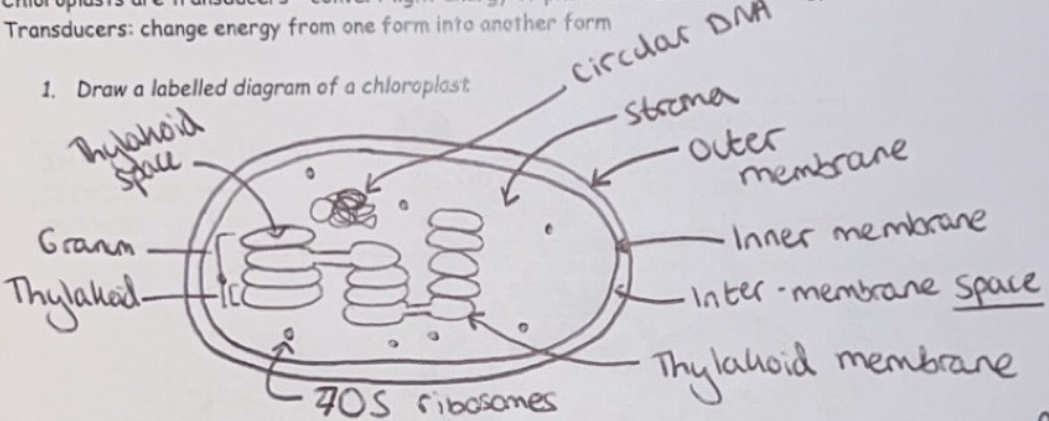
Chloroplasts - Photosynthetic Pigments
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis in plant cells. Chloroplasts are transducers - convert light energy of photons into chemical energy of ATP
Transducers: change energy from one form into another form
Chloroplasts contain different photosynthetic pigments:
- Chlorophyll a and b
- Carotene
- Xanthophyll
Photosynthetic pigments absorb light energy
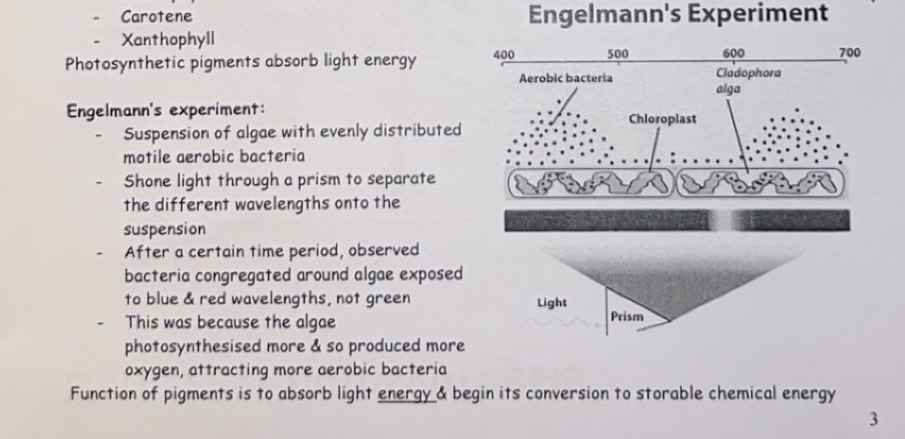
Englemann’s Experiment
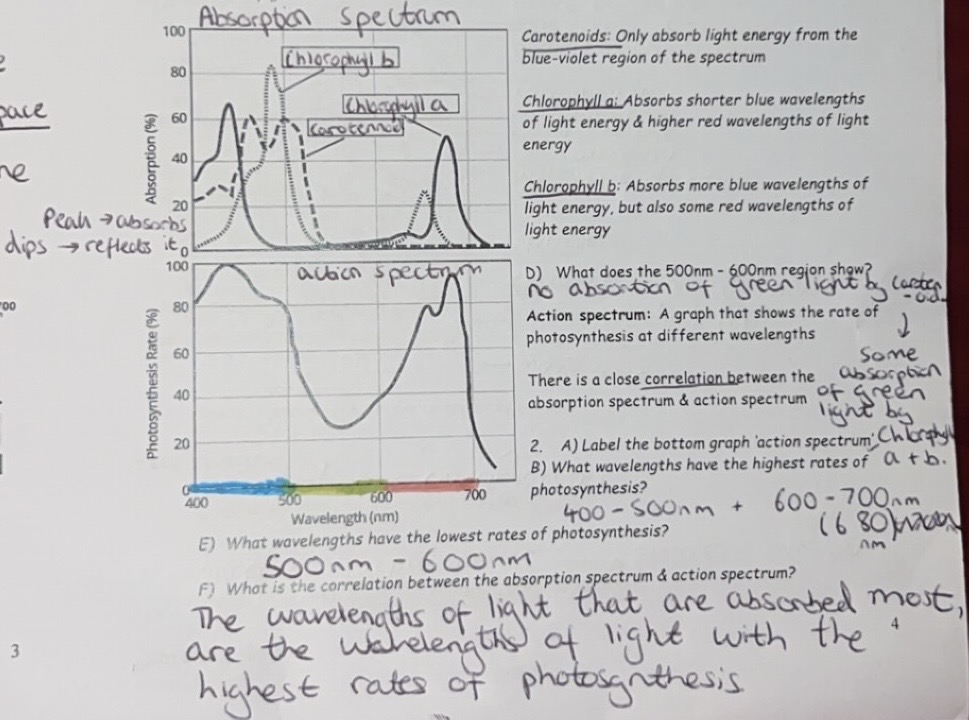
Absorption & action spectrum
Different pigments absorb photons at different wavelengths of light
- Chlorophylls absorb light energy from red & blue-violet regions of the spectrum e.g. chlorophyll a & chlorophyll b
- Carotenoids absorb light energy from the blue-violet region of the spectrum
e.g. beta-carotene & xanthophylls & act as accessory pigments
The presence of several pigments allows the plant to absorb a wider range of wavelengths of light than a single pigment
Absorption spectrum: a graph that shows how much light energy is absorbed at different wavelengths by particular pigments
Pigments & Wavelengths
Plants adapted to living in habitats with different light availabilities produce different proportions of photosynthetic pigments & contain different pigments - maximises light energy absorbed for photosynthesis.
As light passes through water, longer wavelengths of light are absorbed while shorter wavelengths of light can penetrate deeper through water i.e seaweeds growing deeper in water produce more pigments that absorb more light energy of blue-violet wavelengths (shorter wavelengths - penetrate deeper through water) for photosynthesis.
Why do plants growing in shade have higher chlorophyll content & shorter palisade cells with larger chloroplasts
There is less light energy available in shade, so more chlorophyll/ larger chloroplasts to maximise absorption of light energy.
Shorter cells - closer to surface so light doesnt need to penetrate as far to maximise absorption of light energy.
Chromatography
Different photosynthetic pigments can be separated using chromatography.
Pigments (the solute) are ground & dissolve in a solvent, e.g. propanone & are absorbed onto chromatography paper
more soluble pigments travel further (tend to be smaller)
pigments that are absorbed less by the chromatography paper travel further
The further the pigment travels & the larger the Rf value
Rf values can only be equal to or less than 1

Rf Value Example Question

Rf Values
When Rf values are stated, the following information is needed:
The solvent used for extraction
The solvent used to carry out the chromatogram
The type of chromatogram (e.g. chromatography paper or TLC)
Temperature

Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis involves 2 stages:
Light dependent stage - light energy is converted into chemical energy as the photolysis of water releases protons & electrons which produce ATP via photophosphorylation & reduce the coenzyme NADP
Light independent stage (Calvin cycle) - ATP & NADPH from the light dependent stage reduce carbon dioxide to produce glucose
Photophosphorylation: synthesis of ATP from ADP & Pi (inorganic phosphate) using light energy
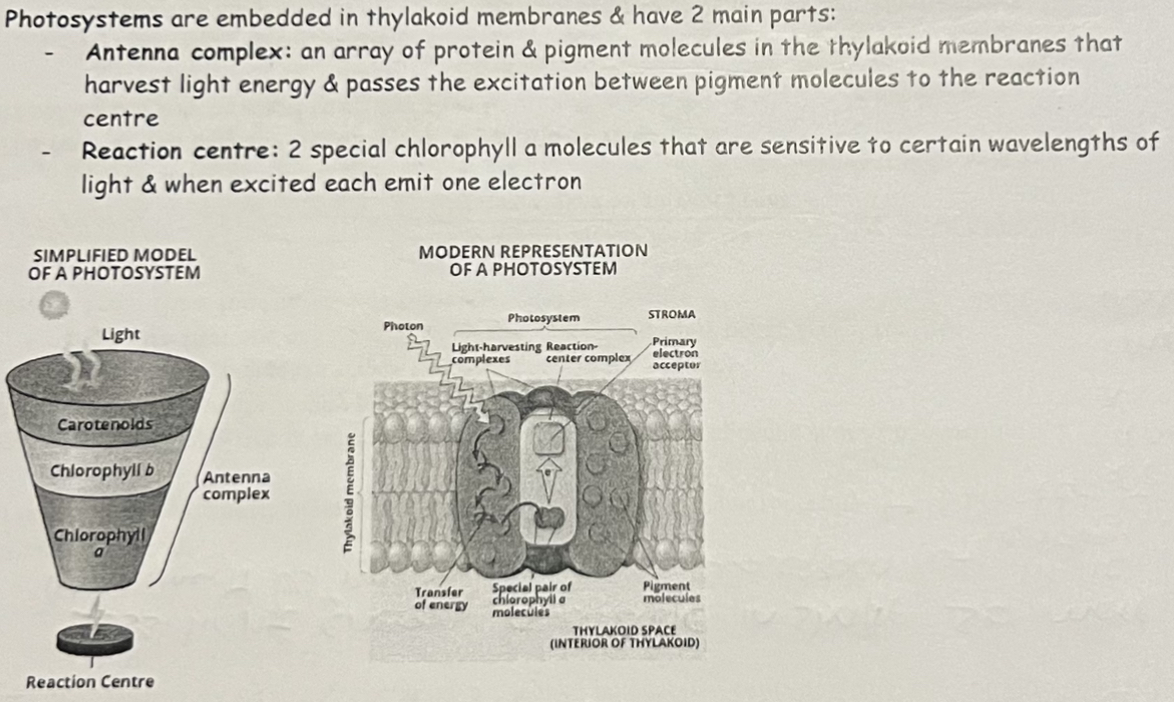
Light Dependent Reactions & Photosystems Structure
Light Dependent Reactions depend on photosynthetic pigments absorbing light energy.
Pigments are arranged in collections of molecules called photosystems.
Photosystems || + |

Types of Photophosphorylation
The light dependent stage involves an electron transport chain to produce ATP & there are two pathways that electrons can follow:
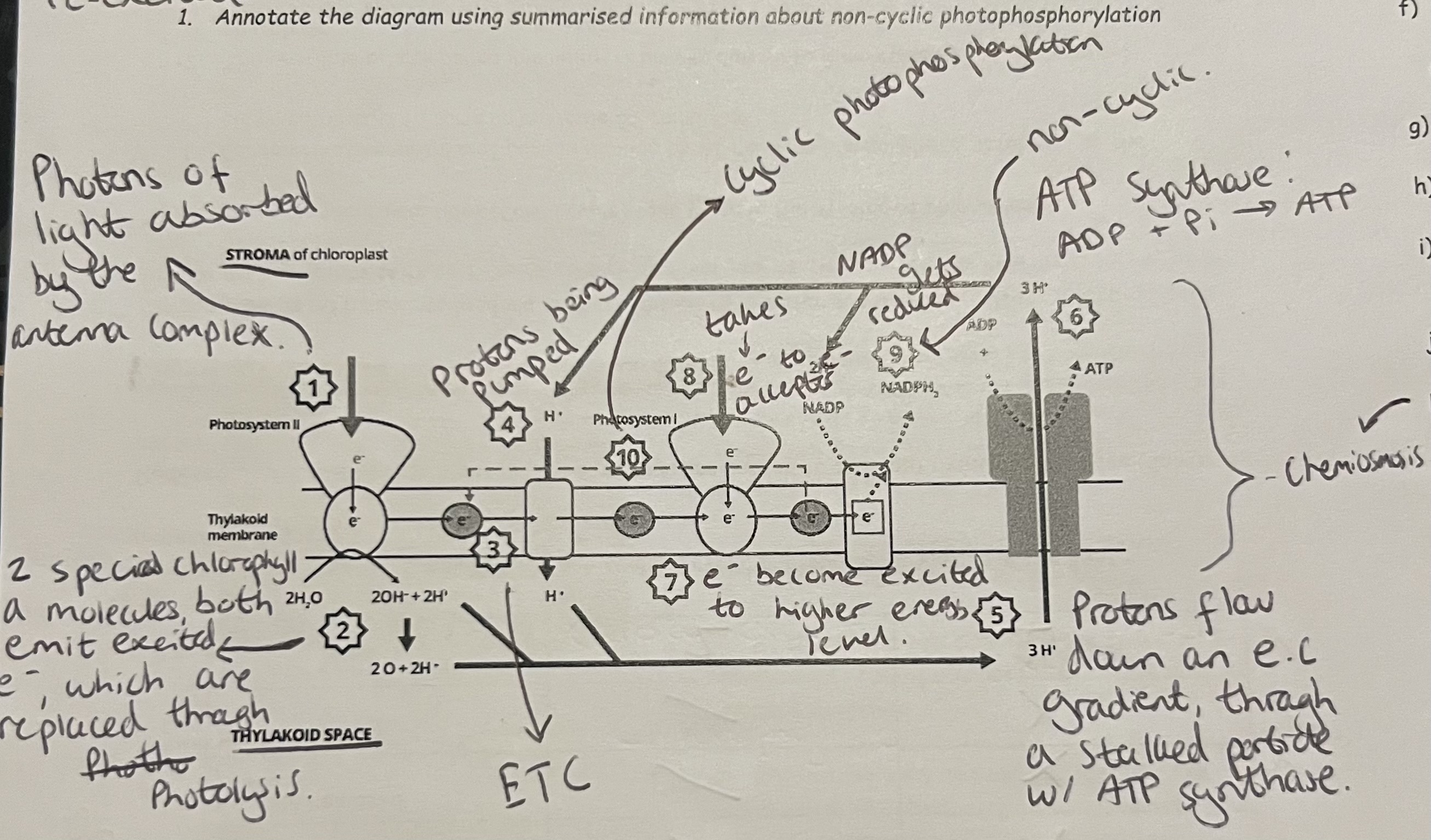
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
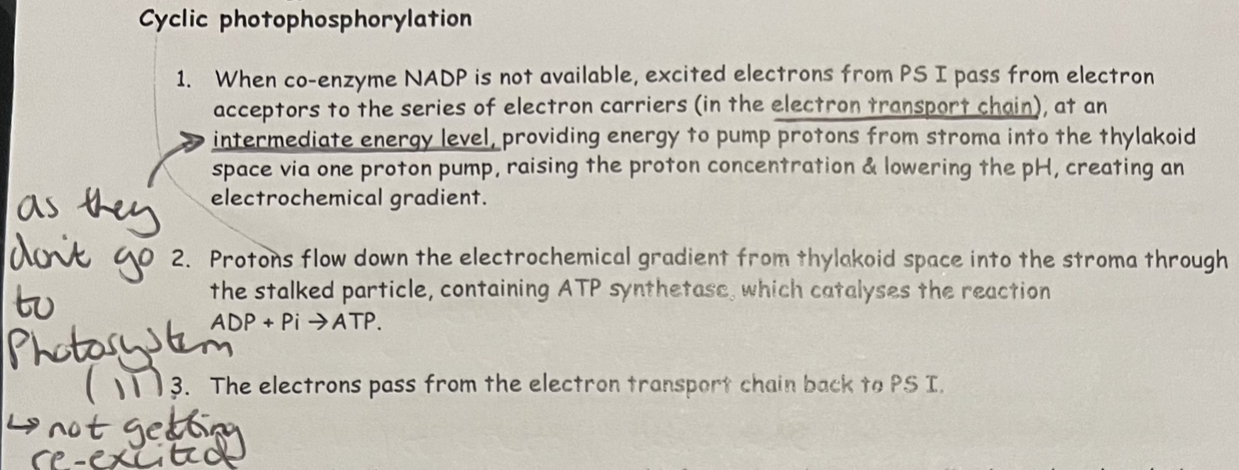
Cyclic photophosphorylation
Non-cyclic & cyclic photophosphorylation are sources of electrons for the electron transport chain.
Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation

Cyclic Photophosphorylation
Labelled Diagram
Energy levels of Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation (Z Scheme)
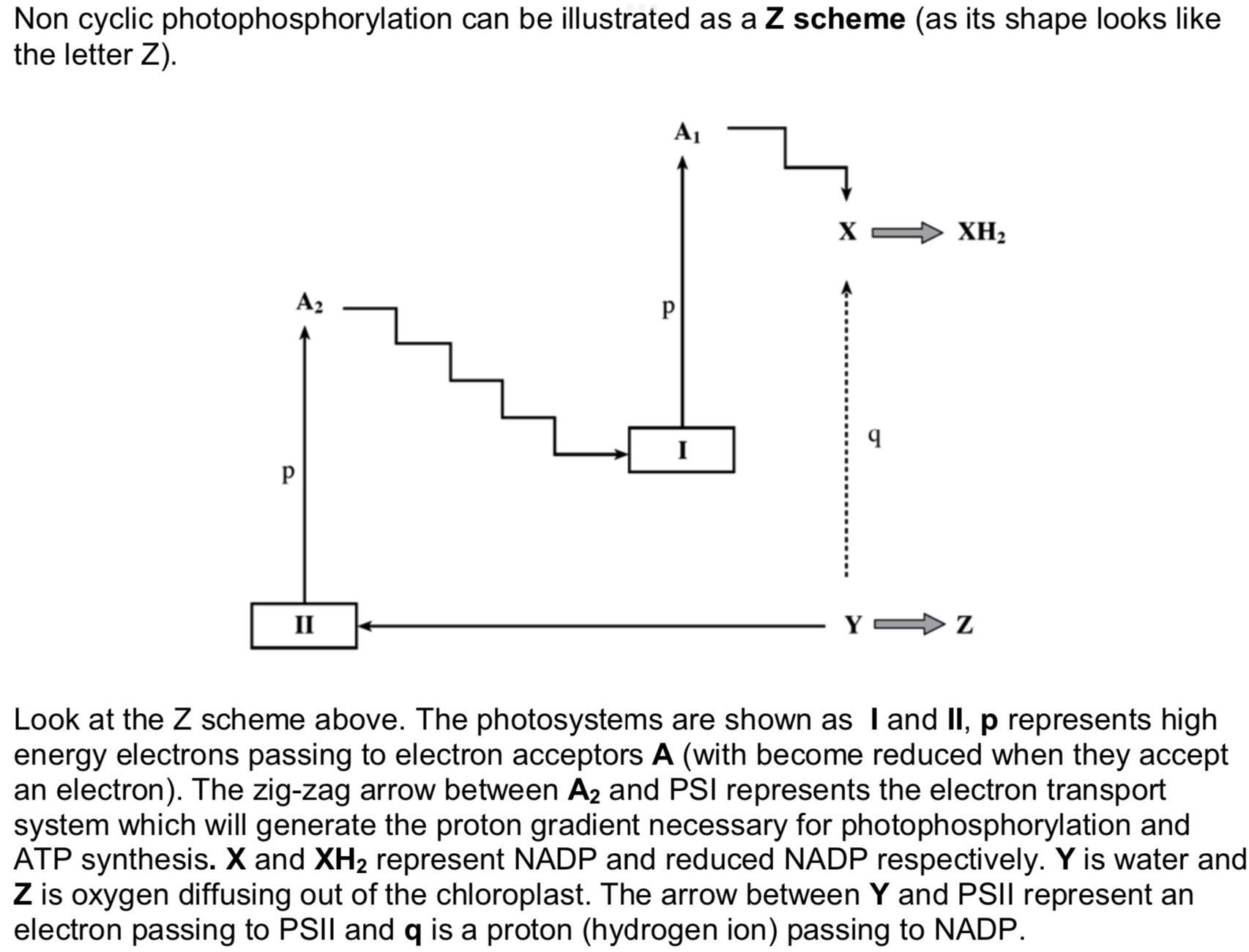
Comprehension questions

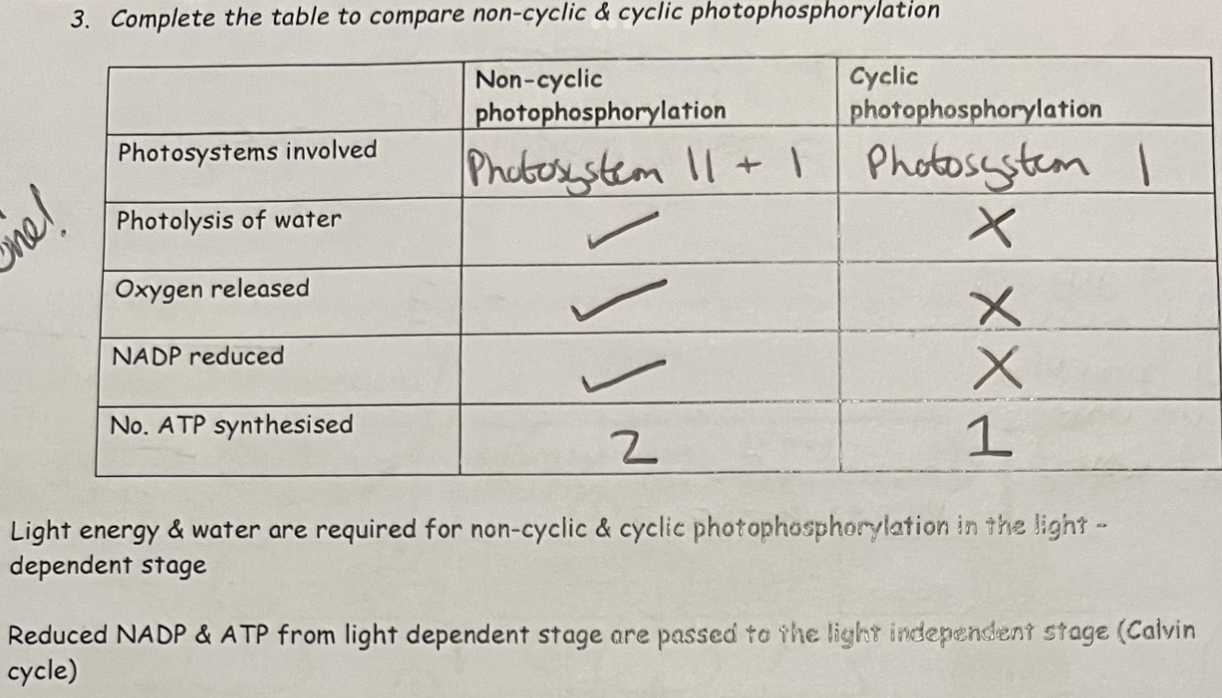
Comparing non-cyclic & cyclic photophosphorylation
Light Independent Reactions - Calvin Cycle

Calvin Cycle Labelled Diagram
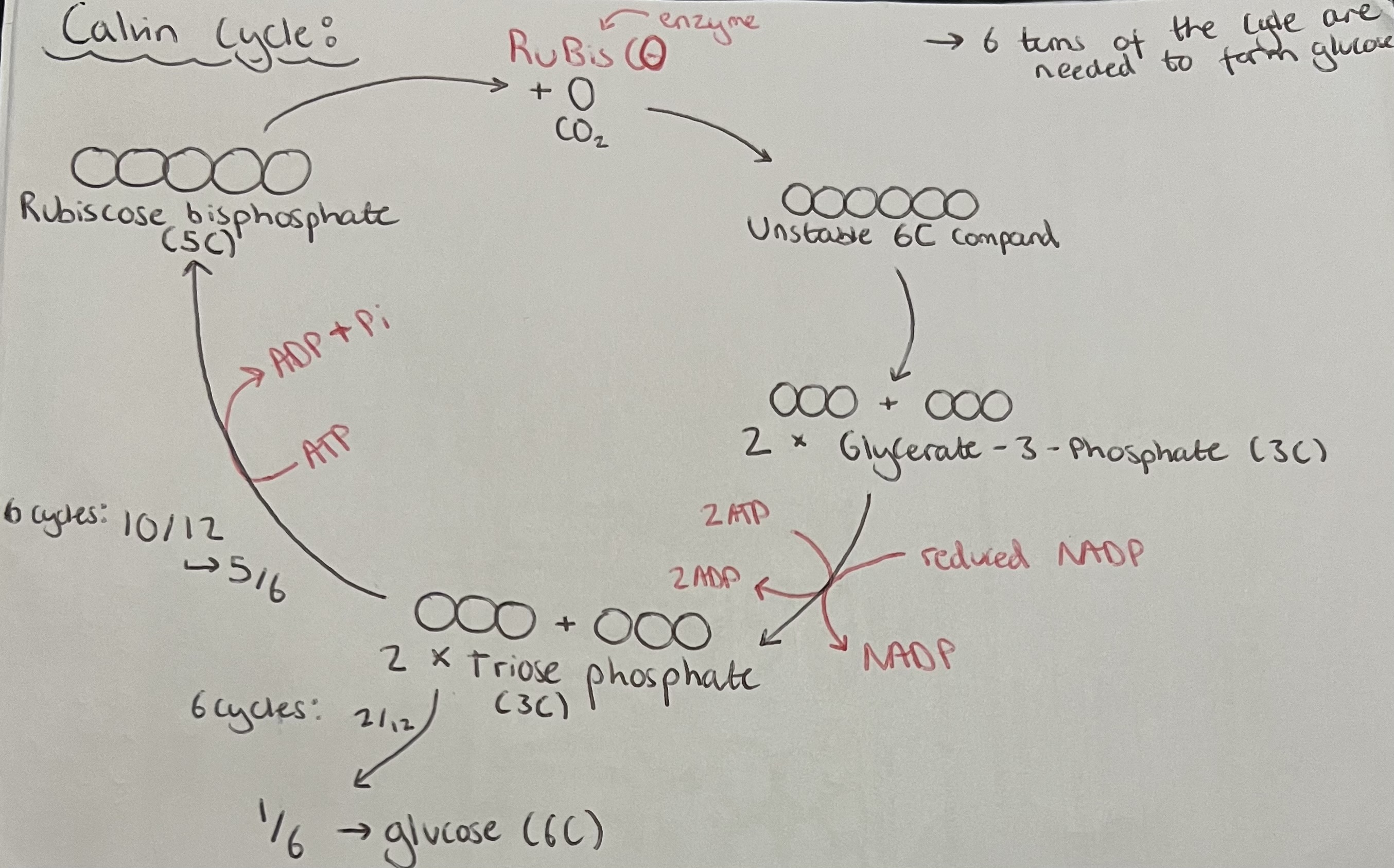
Key concept questions

Product Synthesis & Inorganic Nutrients
The following substances may be manufactured from triose phosphate:
Glucose (actually fructose bisphosphate converted to glucose or combined with glucose to produce sucrose) & other carbohydrates (e.g. alpha glucose stored as starch or beta glucose forms cellulose)
Lipids (phospholipids need a source of phosphorus)
Amino acids (need a source of nitrogen & sulphur)
Nucleic acids (need a source of nitrogen & phosphorus)

Specified Prac & Calvin’s Experiments

Calvin’s Experiments - Key Concepts
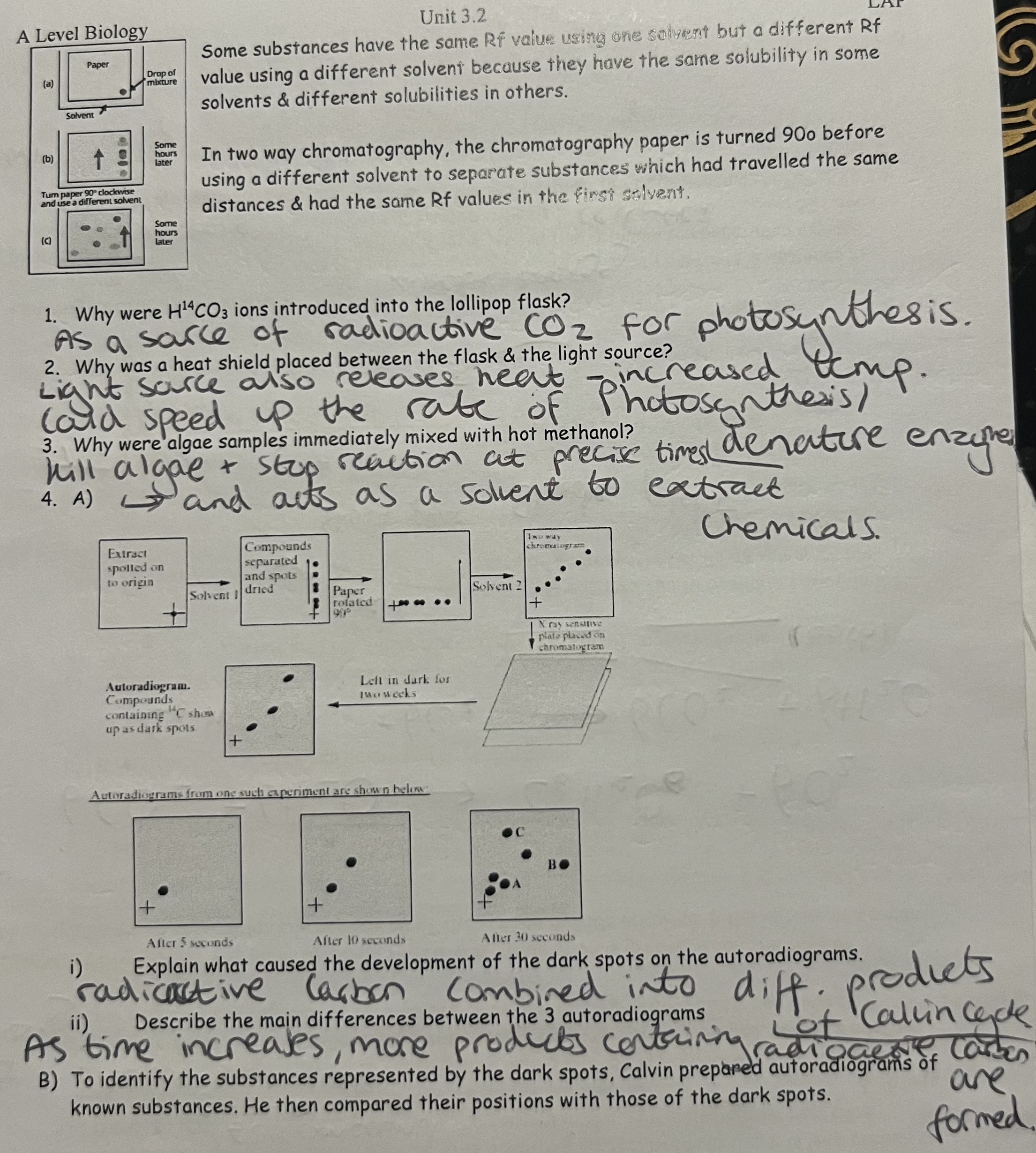
Calvin’s Experiments Questions

Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
Limiting factor: factor in shortest supply which limits the rate of a physiological process
Any change in the level of a limiting factor will affect the rate of reaction
Rate limiting step: the slowest reaction in a sequence & so determines the overall rate of reaction.

Limiting Factor: Light Intensity
Decreasing light intensity means that less ATP & NADPH2 are made during the light dependent reactions, so less glycerate-3-phosphate is reduced to triose phosphate in the light independent reactions.
This means less ribulose bisphosphate is regenerated to continue the Calvin cycle & less glucose is produced so the rate of photosynthesis is reduced.

Limiting Factor: CO2 Concentration
At low concentrations of carbon dioxide, it is a limiting factor, because there is less carbon to be fixed, so less 6C Compound is formed in the light independent reactions, meaning less glycerate-3-phosphate is formed, so less is reduced to triose phosphate & so less ribulose phosphate is regenerated & less glucose is produced, so the rate of photosynthesis is reduced.
Above 0.5% the rate of photosynthesis plateaus, because another factor becomes limiting. Above 1% stomata close, preventing uptake of carbon dioxide.
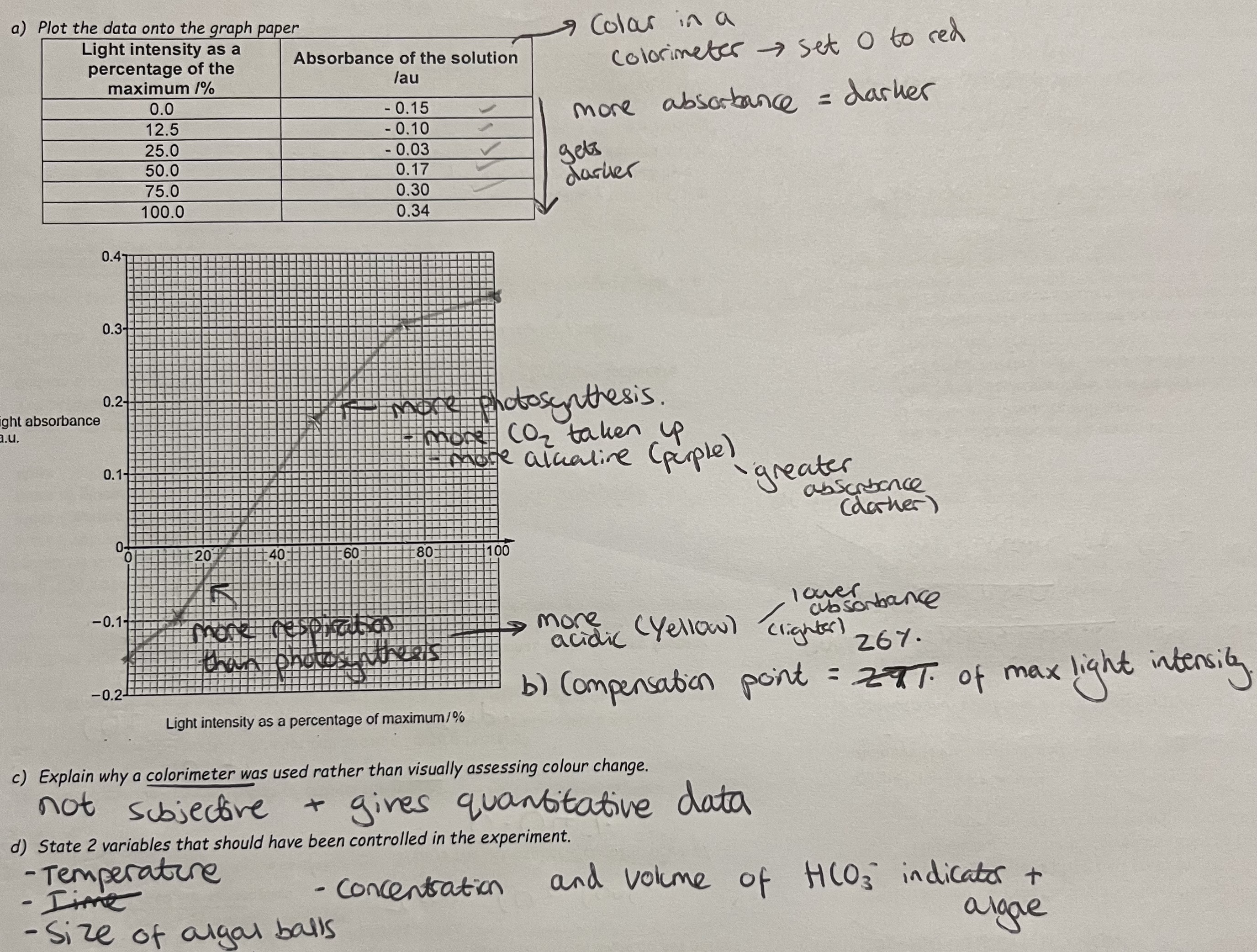
Compensation Point + Graphs for respiration & photosynthesis
Compensation point: The point up which the rate of respiration is greater than the rate of photosynthesis, so respiration can provide all of the carbon dioxide required & the uptake of carbon dioxide is zero.
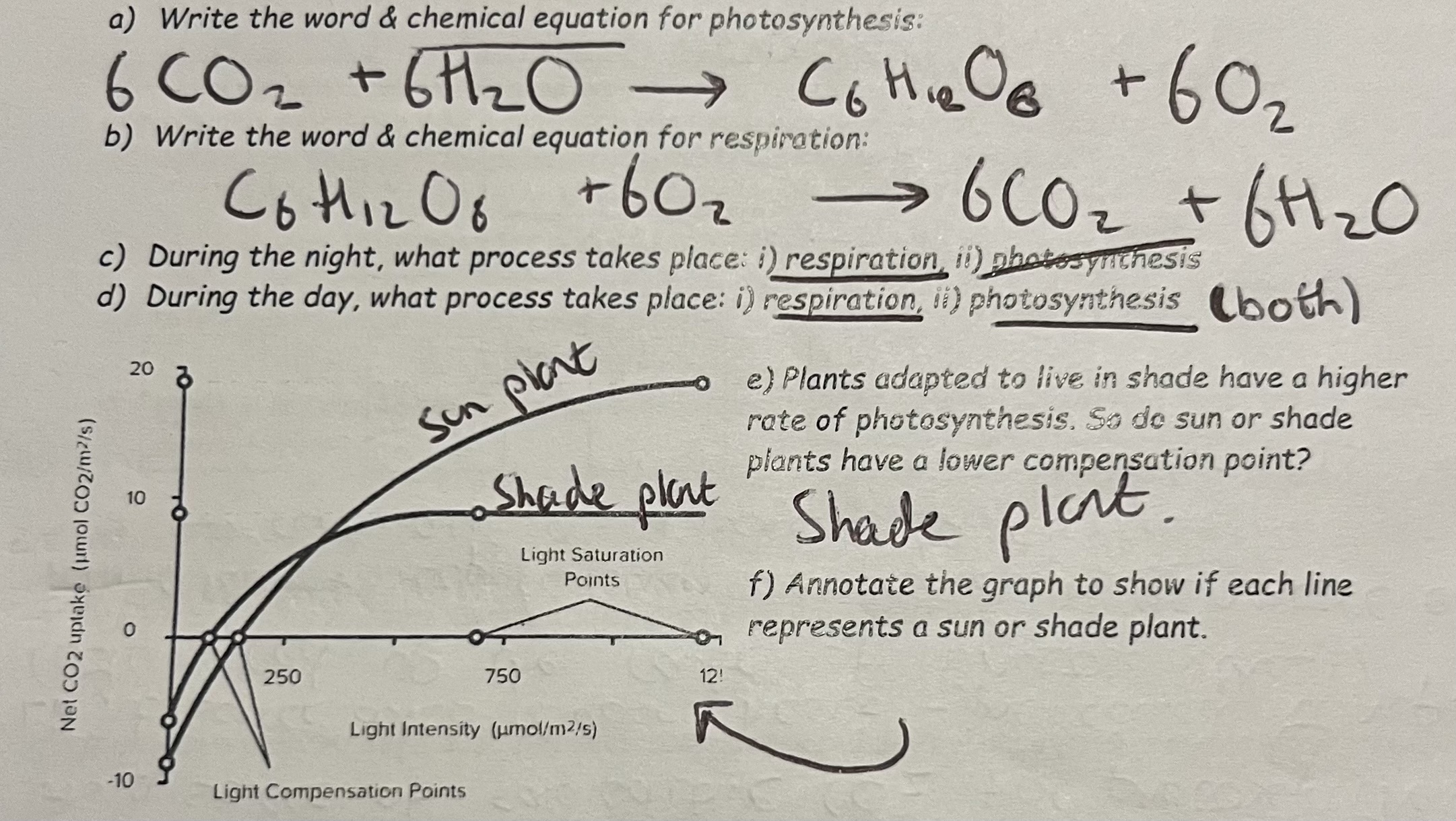
Limiting Factor: Temperature
Increasing temperature increases the kinetic energy of reactants & enzymes in photosynthesis, increasing the rate of photosynthesis.
Above the optimum temperature enzymes begin to denature, so the rate of photosynthesis reduces & it does not plateau.
The optimum temperature is higher in species adapted to hot environments.

Measuring the rate of Photosynthesis
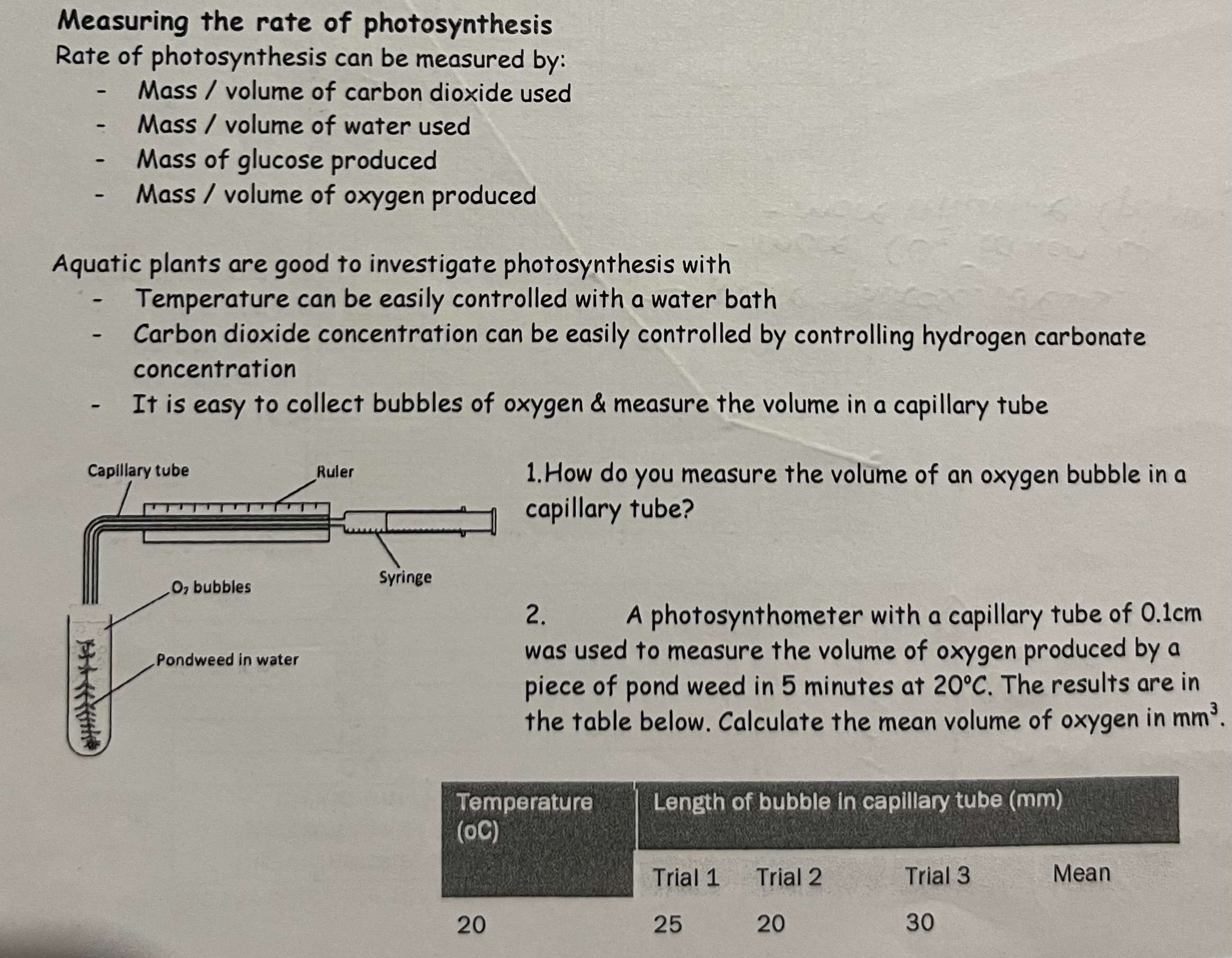
Specified Prac & Questions

Further Questions