4. Internal Economies and Diseconomies of Scale.
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Define internal economies of scale.
Advantages that arise for a firm because of its larger size, or scale of operation.
What do internal economies of scale lead to?
A fall in average costs.
State the types of internal economies of scale.
1. Purchasing bulk.
2. Technical.
3. Managerial.
4. Marketing.
5. Financial.
6. Risk bearing.
7. Social and welfare.
Explain how purchasing bulk is an economy of scale.
Buying raw materials in high quantity can reduce price.
Explain how technical factors are economies of scale.
Larger firms can invest in new technology to produce faster/ cheaper and increase efficiency.
Explain how managerial factors are economies of scale.
Firms have the ability to hire specialist managers to run business functions, leading to better planning and decision making.
Explain how marketing factors are economies of scale.
Firms have access to larger scale promotion.
Explain how financial factors are economies of scale.
Firm has a wider range of finance options available and may be able to negotiate a lower rate with the lender.
Explain how risk bearing is an economy of scale.
Firm can have a more diversified product range, giving them more resilience.
Explain how social and welfare factors are economies of scale.
Firm can give more benefits to staff and therefore attract + retain good employees.
What will all internal economies of scale have an impact on?
- Average costs
- Quantity produced e.g. productivity
Define internal diseconomies of scale.
Inefficiencies that can arise when a firm operates on a larger scale.
What do internal diseconomies of scale lead to?
A rise in average costs.
Give examples of internal diseconomies of scale.
1. Lack of motivation
2. Poor communication
3. Co-ordination
Explain how lack of motivation is an internal diseconomy of scale.
- Workers can feel underappreciated or not valued as individuals.
- Can be more difficult for managers in larger firms to develop relationships with employees.
- If motivation falls, productivity may fall.
Explain how poor communication is an internal diseconomy of scale.
- Harder for larger firms to communicate with staff in a personal way.
- Likely to be greater use of written notes over personal explanations.
- Messages can remain unread or misunderstood and staff not informed properly.
Explain how co-ordination is an internal diseconomy of scale.
- Large business requires organising.
- Requires increase in meetings and planning to ensure that all staff know what they're supposed to be doing.
- New layers of management may be required, increasing costs and creating more inefficiency.
Draw an internal economies and diseconomies of scale diagram.
Q* = Minimum efficient scale.
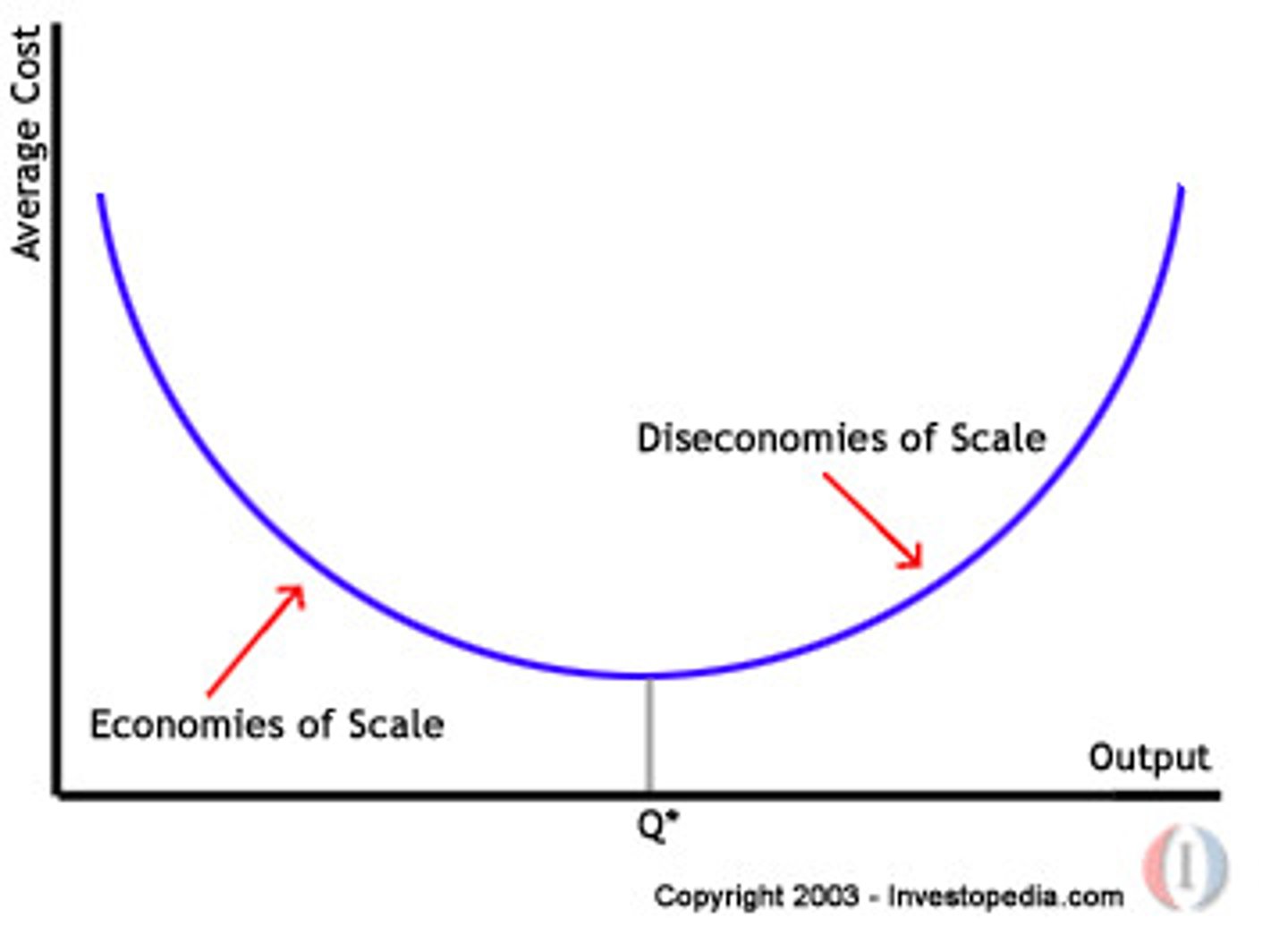
What is the minimum efficient scale?
The lowest point on the curve at which economies of scale still occur and the firm can produce goods or services at the lowest possible average cost.
When do internal economies and diseconomies of scale occur?
In the long run only.