BLOOD BANK 214-261
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
218-A drug-induced immune hemolytic anemia caused by a drug-independent antibody would have which of the following results?
A- positive direct antiglobulin (DTA) with ig G; positive antibody screen
219-The autoantibody most often implicated in Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria (PCH) is:
A-cold-reactive, IgG, anti-P
220-Intravascular destruction of red blood cells results when:
B- IgM antibodies activate complement to completion
221-Which of the following is likely to result in extravascular red cell destruction?
C-transfusion associated with a delayed transfusion reaction caused by anti-Jk®
222-Indications for an autologous hematopoietic progenitor cell (HPC) transplant include patients who have:
A-Hodgkin lymphoma with high-dose chemotherapy
223-Which of the following statements is correct about hematopoietic progenitor cell (HPC) transplantation?
B- sources for HPC collection include bone marrow, umbilical cord blood (UCB), and mobilized peripheral blood
224-A patient in the immediate post bone marrow transplant period has a hematocrit of 21%. The red cell product of choice for this patient would be:
D-irradiated
225-Which of the following systems plays an important role in Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI), transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD), platelet refractoriness, and Febrile Nonhemolytic Transfusion Reactions (FNHTR) as well as in hematopoietic stem and organ transplantation rejection?
B-HLA
226-Which of the following statements is true about Class Il HLA antigens?
C-HLA-DR, HLA-DQ and HLA-DP are all Class II
227-The most widely accepted QC test to measure probable Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell (HPC) engraftment is:
C-CD34+ cell enumeration
228-To prevent transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease (TA-GVHD) in a patient undergoing HPC transplantation, blood components selected for transfusion should be:
A-irradiated
229-which of the following HPC transplants would be considered an ABO major incompatibility?
C-group B donor to a group O recipient
230-When selecting blood products for transfusion to a patient who is day 1 post ABO major incompatible HPC transplant, which of the following apply?
A-red cell components selected are based on ABO antibodies circulating in the recipient

231-The blood typing results shown in this table are noted on a patient's sample:
Whatis the patient's likely ethnicity?
C-Black
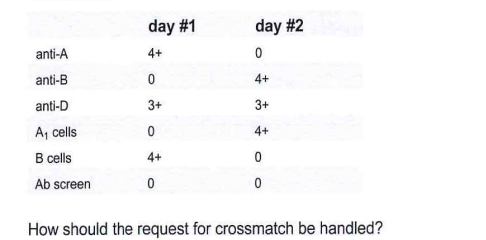
232-Samples from the same patient are received on 2 consecutive days. Test results are summarized in this table:
D-collecta new sample and repeat the tests
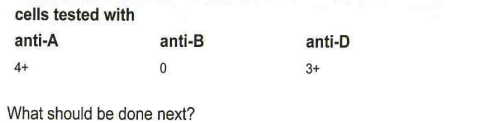
233-Test results are shown in this table for a unit of blood labeled group A, Rh-negative:
cells tested with
anti-A anti-B anti-D
4+ 0 3+
What should be done next?
C-notify the collecting facility

234-In what patient population may we observe the results shown in this table?
C-2-year-old pre-surgical patient
235-A patient is a subgroup of A (Ag,), Rh-positive with Anti-A1 in their serum. How many units would you have to screen to find 1 unit that is compatible with the patient's Anti-A1?
A-5
236-A patient is group A, Rh-positive but is receiving a Group O, bone marrow transplant (BMT) on Friday. After the transplant, what hemagglutination pattern will the patient demonstrate when the patient's red cells are tested with anti-A?
D-mixed-field
237-A group B, Rh-negative patient has a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Which of the following situations would occur?
B-the weak D test and control would be positive
38-The reaction results shown in this table are obtained:
cells tested with serum tested with
ant-A anti-B anti-AB A,cells B cells
4+ 3+ 4+ 2+ 4+
The technologist washes the patient's cells with saline, and repeats the forward typing. A saline replacement technique is used with the reverse typing, and obtains the results shown in this second table:
cells tested with serum tested with
anti-A antiB antiA1B A1cells Bcells
4+ 0 4+ 0 4+
Based on these results, a likely diagnosis for the patient may be:
C-multiple myeloma
239-What ABO type is found in group A1 individuals following deacetylation of their A antigens?
A-acquired B
240-The Rh-negative phenotype results from the complete deletion of what gene(s)?
C-RHD
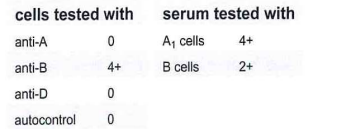
241-The results shown in this table are obtained on a patient's blood sample during routine ABO and Rh testing:
Select the course of action to resolve this problem:
D-perform antibody screening procedure at immediate spin and AHG using group O cells
242-The test for weak D is performed by incubating patient's red cells with:
B-anti-D antiserum

243-The results shown in this table are obtained when testing a sample from a 20-year-old, blood donor:
D-weak subgroup of
244-A mother is Rh-negative and the father Rh-positive. Their baby is Rh-negative. It may be concluded that:
C- the father is heterozygous for D
245-Some blood group antibodies characteristically hemolyze appropriate antigen-positive red cells in the presence of:
complement

246-Review this set of instructions:
The next step would be to:
B-identify the cause of the agglutination
248-A patient has an order for a type and screen and 6 units of Red Blood Cells are requested for surgery. At the indirect antiglobulin (IAT) phase of testing, both antibody detection cells and 2 of 6 crossmatched units are incompatible. What is the most likely cause of the incompatibility?
A-Recipient alloantibody
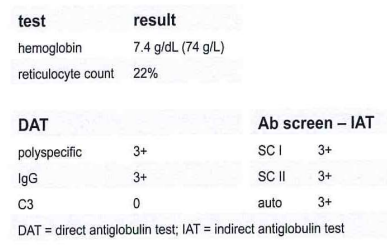
249-Which clinical condition is consistent with the lab results shown in this table?
test result:
B-warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
250-Based on the results in this table, what is the next step in determination of the patient's ABO/Rh type?
anti-A anti-B anti-D A cells B cells
4+ 4+ 4+ 0 0
C-repeat ABO red cell typing and include a control
251-The major crossmatch will detect a(n):
D-recipient antibody directed against antigens on the donor red cell
252-Which of the following would most likely be responsible for an incompatible antiglobulin crossmatch?
D-donor red cells have a positive direct antiglobulin test
253-In the process of identifying an antibody, the technologist observes 2+ reactions with 3 of 10 cells atimmediate spin (1S) and room temperature (RT). There are no reactions at 37°C or with antihuman globulin (AHG). What is the most likely antibody?
B-anti-Lea room temperature
255-A 29-year-old male is hemorrhaging severely. He is AB, Rh-negative. Six units of blood are required STAT. Of the following types available in the blood bank, which would be most preferable for crossmatch?
B-A, Rh-negative
256-A patient is group A;B, Rh-positive and has an antiglobulin-reacting anti-A1 in his serum. He is in the operating room bleeding profusely and group A;B Red Blood Cells are not available. Which of the following blood types is first choice for crossmatching?
A-B, Rh-positive b B, Rh-negative
257-A10% red cell suspension in saline is used in a compatibility test. Which of the following would most likely occur?
D-false-negative result due to antigen excess
58-A patient received 4 units of blood 2 years previously and now has multiple antibodies. He has not been transfused since that time but is now in need of additional blood transfusions. While determining the specificities for these antibodies, it would also be helpful to:
A-phenotype his cells to determine which additional alloantibodies may be produced
259-A utoantibodies demonstrating blood group specificity in warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia are associated more often with which blood group system?
A-Rh
260-, An antibody that causes in vitro hemolysis and reacts with the red cells of 3 out of 10 AHG crossmatched donor units is most likely:
A-anti-Lea

261-An antibody identification study is performed with the 5-cell panel shown in this table:
An antibody against which of the following antigens could not be excluded?
A-1
214-A 40-year-old man with autoimmune hemolytic anemia due to anti-E has a hemoglobin level of 10.8 g/dL (108 g/L). This patient will most likely be treated with:
D-No transfusion
215-Pathologic cold autoantibodies differ from benign cold autoantibodies in:
C- antibody titer
216-The direct antiglobulin test (DAT) in a patient with warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia (WAIHA) is most often positive for:
D- IgG and C3
217-What is the most important consideration for a patient requiring red cell transfusion due to severe anemia when their serum contains a warm autoantibody?
C- determine the presence of underlying alloantibody(ies)
254-DNA arrays evaluate the encoding genes for common blood groups. These technologies detect small differences in the membrane proteins after amplification of what amino acid residues of genomic DNA?
C- SNP