W12- Protein Synthesis (Translation)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the purpose of translation?
To make a polypeptide that corresponds to the sequence in the mRNA
What is an mRNA?
Messenger RNA which is a type of RNA molecule that is single -stranded and carries genetic information from DNA in order to synthesized protein
What are ribosomes?
Ribosomes are particles that are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
What is the structure of ribosomes?
They consists of 2 subunits a large and small subunit.
In eukaryotes, what is the large subunit denoted as?
60S
In eukaryotes, what is the small subunit denoted as?
40S
In eukaryotes, what is is the total ribosome consisting of two subunits denoted as?
80S
In eukaryotes, where are the subunits of the ribosome assembled in?
Nucleolus
Once the subunits of the ribosome are assembled where do they move to?
Cytoplasm
When do the subunits of the ribosome come together?
Only when translation occurs, otherwise they are found free in the cytoplasm
What is tRNA?
Transfer RNA is a type of RNA molecule.
It is a carrier of amino acids as it binds to a specific amino acid and brings it to the mRNA based upon the appropriate codon.
There is a specific tRNA molecule for each amino acid
What are the 3 tRNA binding sites?
A site
P site
E site
What is the full form of the A site?
aminoacyl-tRNA binding site
What is the full form of P site?
peptidyl-tRNA binding site
What is the full form of E site?
Exit site
List the components of a ribosome ready for translation
mRNA
Ribosomes
tRNA
What is an anticodon?
A nucleotide triplet that base-pairs with a complementary sequence on the mRNA
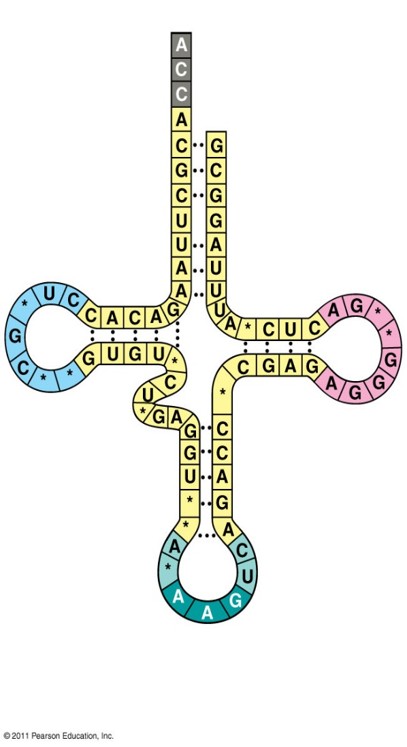
What amino acid will this tRNA bring in and what is the anticodon?
tRNA brings in the anticodon 5’-AAG-3’. This anticodon will code for the 5’-UUC-3’ genetic code of the mRNA. This amino acid codes for Phe.

A tRNA with the anticodon 3’CGG5’ will carry which amino acid?
Codes for 5’GCC 3’ which codes for the amino acid Ala
What is aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
An enzyme that is responsible for attaching the correct amino acid to its corresponding tRNA molecule
How many different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are there?
20 different for each amino acid
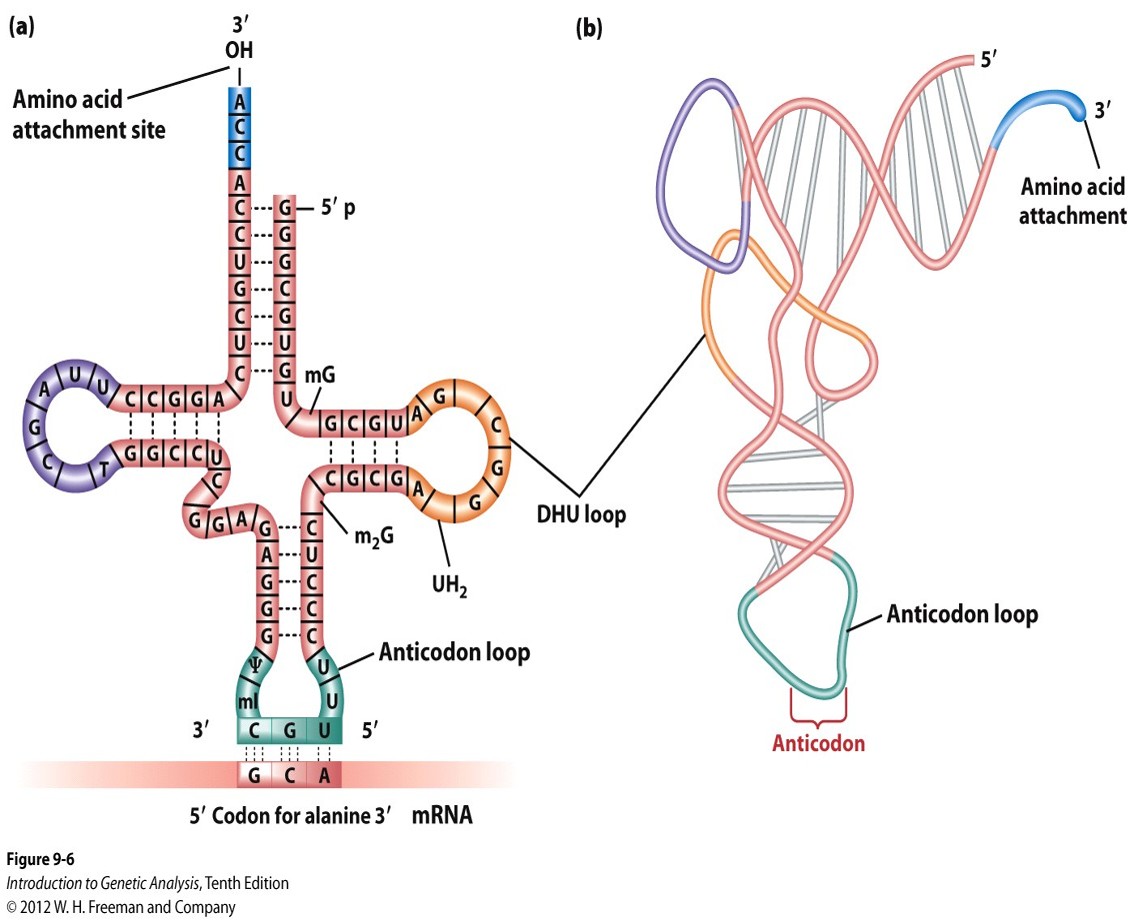
Where is the amino acid linked to of the corresponding tRNA?
At the free 3’-OH group of the terminal adenine molecule
How does it attach an amino acid to its tRNA?
CHECK HOPW IT IS IN WORDS
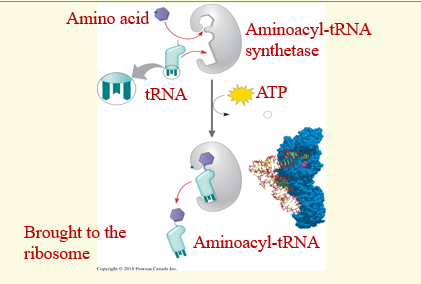
After an amino acid gets attached to the tRNA, forming an aminoacyl-tRNA, what is the state of the tRNA now?
The tRNA is ‘charged’.
What are the stages of translation?
Initiation
Elongation
Aminoacyl-tRNA binding
Transpeptidation
Translocation
Termination
What are various protein factors required for in translation?
Required for initiation, elongation and termination
What is the translation initiation codon?
5’-AUG-3’
What does every newly synthesized polypeptide start with?
It starts with the amino methionine
What does initiation assembly require?
mRNA
Small ribosomal subunit
Initiator tRNA (met)
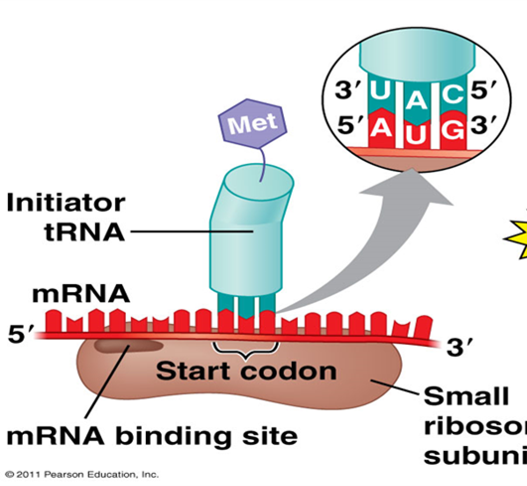
Once the 3 components required for initition are assembled, what is the complex called?
Translation initiation complex
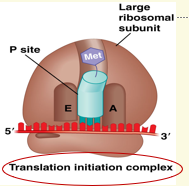
What position is tRNAmet in?
In the P site
Right before elongation occurs, where is the tRNAmet and which site is open next for the elongation process to start?
tRNAmet is in the P site
The A site is open for elongation phase of translation
What occurs during the aminoacyl-tRNA binding phase of Elongation?
An incoming aminoacyl-tRNA is brought to the A site of the ribosome
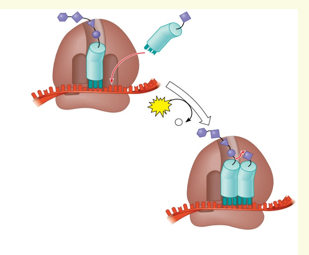
What is the ribozyme?
An RNA based enzyme
What is peptidyl transferase?
It is a ribozyme which catalyzes the transpeptidation reaction and is found in the large (60S) ribosomal subunit
Explain how peptidyl transferase catalyzes Transpeptidation reaction?
It catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between amino group of the new amino acid in the A site and the carboxyl group of the amino acid on the growing chain.
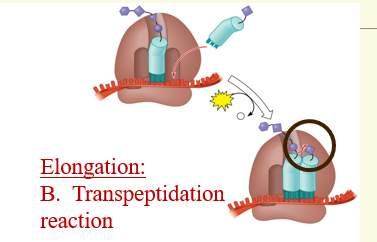
Following the Transpeptidation phase of an amino acid, where is the polypeptide found?
Polypeptide is in the A site
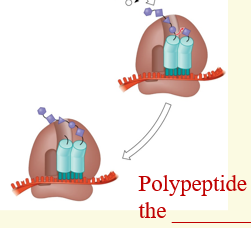
What occurs during the Translocation phase of the elongation stage?
The ribosome moves down one codon along the mRNA strand, causing the polypeptide attached to the tRNA to move to the P site. The empty tRNA is in the E site and then exits. A site is not unoccupied.
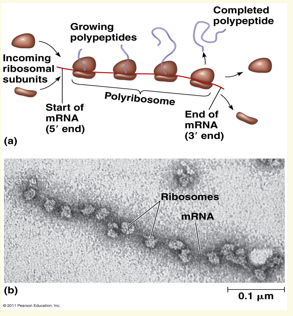
What are a polyribosomes?
String of ribosomes along the mRNA which enables the cell to make many copies of a polypeptide very quickly
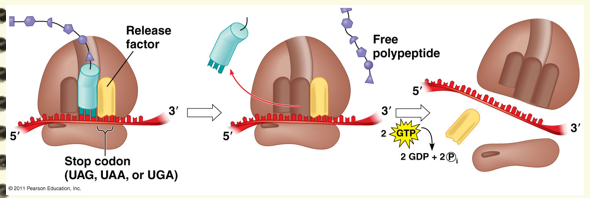
When does termination occur/ When does ribosome know when to stop?
Elongation proceeds until one of three possible stop codons is reached.
When occurs during the termination stage?
When any of the stop codons are in the A site, there is no tRNA for these codons. These stop codons are recognized by release factors, proteins that bind to the codon and trigger the release of the polypeptide from the tRNA. The tRNA is released and the small and large subunits dissociate.
After termination process is done, what happens to the polypeptide?
The released polypeptides are then folded into their 3D conformation, and the correct folding is aided by proteins called molecular chaperons.
What is a release factor?
A protein that comes in to the A site of ribosome signaling the end of translation, which is the process of creating a new polypeptide chain from mRNA.
What are molecular chaperons?
Proteins that assist other proteins in folding correctly, but they do not become part of the final protein structure.
Protein vs Polypeptide
A polypeptide refers to the immediate polymerization of amino acids and a protein is a polypeptide (or several) that has folded into a functional conformation.