ACIDS AND BASES
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Bronsted-Lowry acids
proton donors
Bronsted lowry acids release H+ ions when mixed in water
which combine with H2O to form hydroxonium ions H3O+
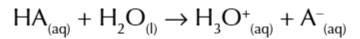
Bronsted Lowry base
proton acceptors
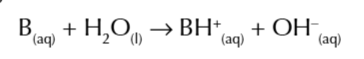
acids and base dissociate in water
acids break up into positive charged ions
bases break up into negative charged ions
the strength of the acid/ base depends on
their ability to dissociate
the stronger the acid/base
the more they dissociate/ ionise in water

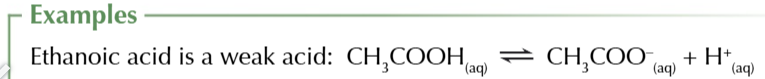
weak acids like carboxylic/citric acids
only very slightly dissociate in water so only number of H+ form
weak acid equilibrium
lies heavily on the left
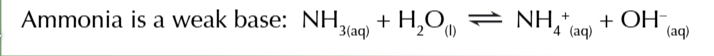
weak bases like ammonia
only slightly dissociate in water
weak base equilibrium
lies heavily on the left
acids can only get rid of protons
if a base is available to accept them
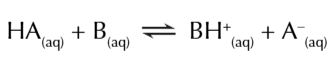
when water is added to acid
water acts as a base
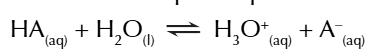
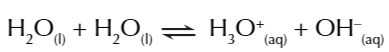
water dissociates into hydroxonium ions AND hydroxide ions
so an equilibrium exists in water
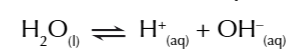
you can write the equilibrium constant expression for the equilibrium of water
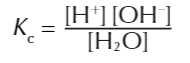
water dissociates in TINY amounts
so thr equilibrium lies HEAVILY on the left
waters concentration is so much larger that the cocnentration of H+ and OH-
that the concentration of water is considered a constant value
ionic product of water Kw
multiplying the Kc expression by the concentration of water produces ANOTHER constant
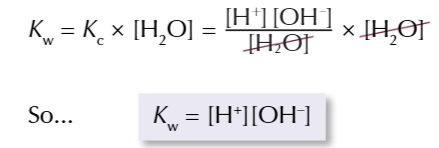
Kw value is the same for an aqueous solution at a certain temperature
FOR EXAMPLE: 298K → 1.00×10-14 mol2 dm-6
the value of Kw changes
as the temperature changes
in PURE water the ration of H+ to OH- is 1:1
so [H+]=[OH-]
![<p>so [H<sup>+</sup>]=[OH<sup>-</sup>]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4f1e913c-5bd6-412a-a4fe-162ef296b520.png)

pH scale
the measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution

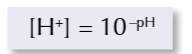
you can calculate the concentration of a solution from the pH
[H+]=10-pH
![<p>[H<sup>+]</sup>=10<sup>-pH</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d21d3a2b-8d41-4d84-853b-268a7cb19351.png)
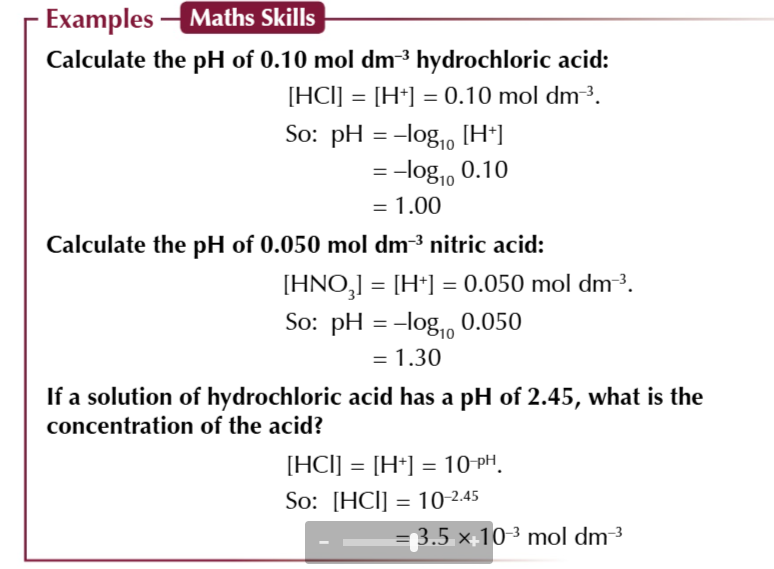
monoprotic acids like HCl and HNO3
each molecule of acid releases 1 proton when it dissociates
each mole of monoprotic acid produces 1 mole of hydrogen ions
meaning the H+ conc is the same as the acid conc
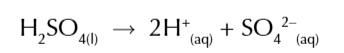
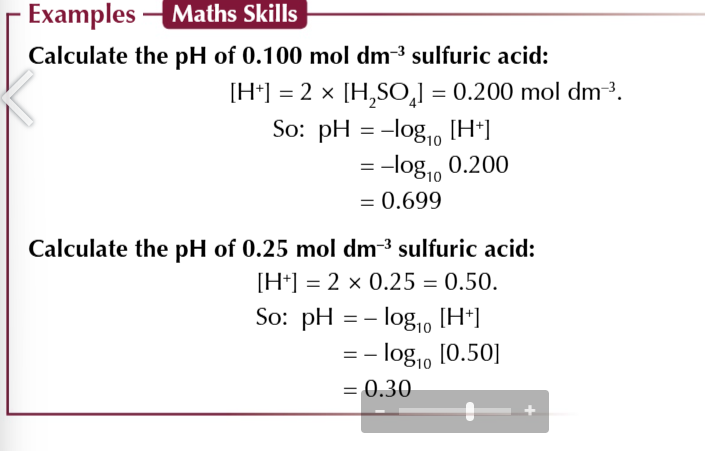
diprotic acids like H2SO4
each molecule of acid will release 2 protons when it dissociates
diprotic acids produce 2 moles of hydrogen ions for each mole of acid
meaning the H+ conc is twice the conc of the acid
STRONG ACID EXAMPLES THAT DONATE 1 MOLE OF OH- PER MOLE OF BASE
sodium hydroxide
potassium hydroxide
![<p>[base]=[OH-]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0282506d-ea02-4c21-9c31-ef334dbf02c4.png)
[base]=[OH-]
0.2 mol dm-3 of sodium hydroxide has 0.2 mol dm-3 [OH-]
if you know [OH- and the Kw value you can calculate the {H+]
find the value of Kw and [OH-]
rearrange the equation to make [H+] the subject
using the [H+] find the pH using: -log10[H+]=pH
![<ul><li><p>find the value of Kw and [OH-]</p></li><li><p>rearrange the equation to make [H+] the subject</p></li><li><p>using the [H+] find the pH using: -log<sub>10</sub>[H+]=pH</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ee13d675-14bf-444e-99be-a38882240d9c.png)
weak acids and bases dissociate only slightly in solution
so the [H+] isn’t the same as the [acid conc]- making it trickier to find the pH
acid dissociation constant
Ka
for weak aqueous acid, HA, you get the equilibrium
HA⇄H+ + A-, where only a small amount of HA dissociates
[HA]»[H+]
[HA at the start]≂[HA at equilibrium]
![<p>[HA at the start]≂[HA at equilibrium]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fb5a2605-73d5-41a7-bec8-5d17a64f8207.png)
when dealing with WEAK acids you can assume H+ ions come from the acid
[H+]≂[A-]
![<p>[H+]≂[A-]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/57ce6090-173f-4b20-9914-fda15ca2bc97.png)
finding the pH weak acids
write expression for Ka
rearrange the equation and substitute values known to find [H+]
take the SQUARE ROOT of the number to find [H+]
substitute [H+] into -log10 [H+] to find the pH
![<ul><li><p>write expression for Ka</p></li><li><p>rearrange the equation and substitute values known to find [H+]</p></li><li><p>take the SQUARE ROOT of the number to find [H+]</p></li><li><p>substitute [H+] into -log10 [H+] to find the pH</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/777c87a7-1230-4471-8d1b-285dbcf48949.png)
finding the concentration of weak acids
substitute the pH value into 10-pH to calculate [H+]
write expression for Ka
rearrange the equation to give the conc of the acid
substitute the value of Ka and [H+] into the equation and solve it
![<ul><li><p>substitute the pH value into 10<sup>-pH</sup> to calculate [H+]</p></li><li><p>write expression for Ka</p></li><li><p>rearrange the equation to give the conc of the acid</p></li><li><p>substitute the value of Ka and [H+] into the equation and solve it</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/965fcc1c-ca8e-4e12-bd90-5be83c0e0899.png)
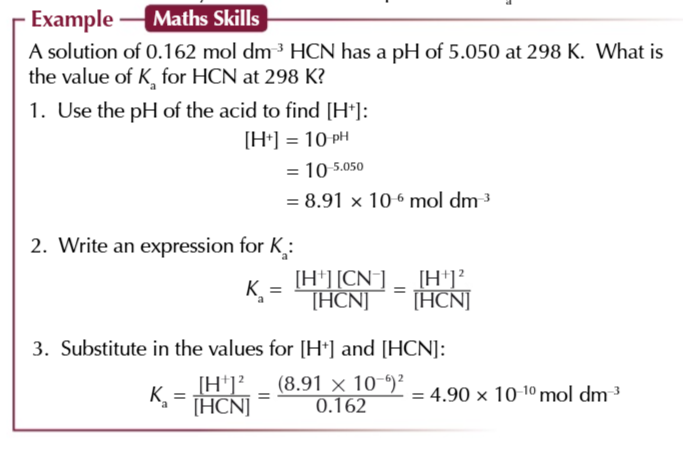
find the Ka of weak acids
if you know the concentration and the pH you can sue them both to find Ka of a weak acid
the value of Ka varies massively between acids
sometimes its easier to find the Ka value from its logarithmic constant pKa

pKa=-log10Ka
Ka=10-pKa
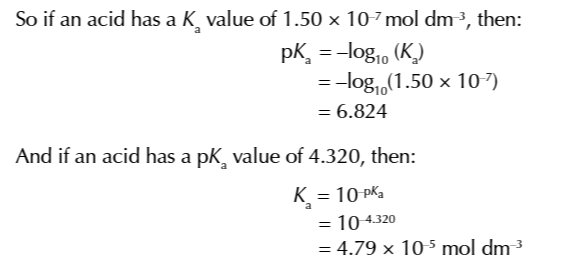
questions may ask to calculate the pH of a weak acid and give the concentration of acid and the pKa value

things to ensure your titration results are as accurate as possible:
measure the neutralisation volume as precisely as you possibly can to the nearest 0.05cm3
its a good idea to repeat the titration at least 3 times to get a mean titre value
don’t use anomalous results, must be within ∓0.1cm3
a pH curve of the titration can be drawn if you find the pH using a pH probe/meter
the pH of the solution is the equivalence point/ midpoint
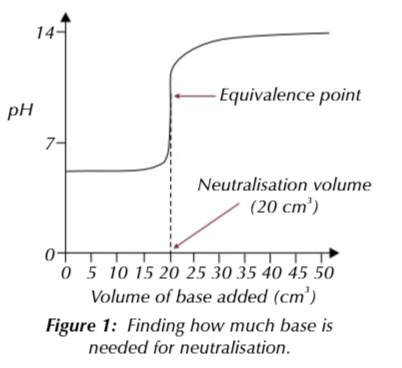
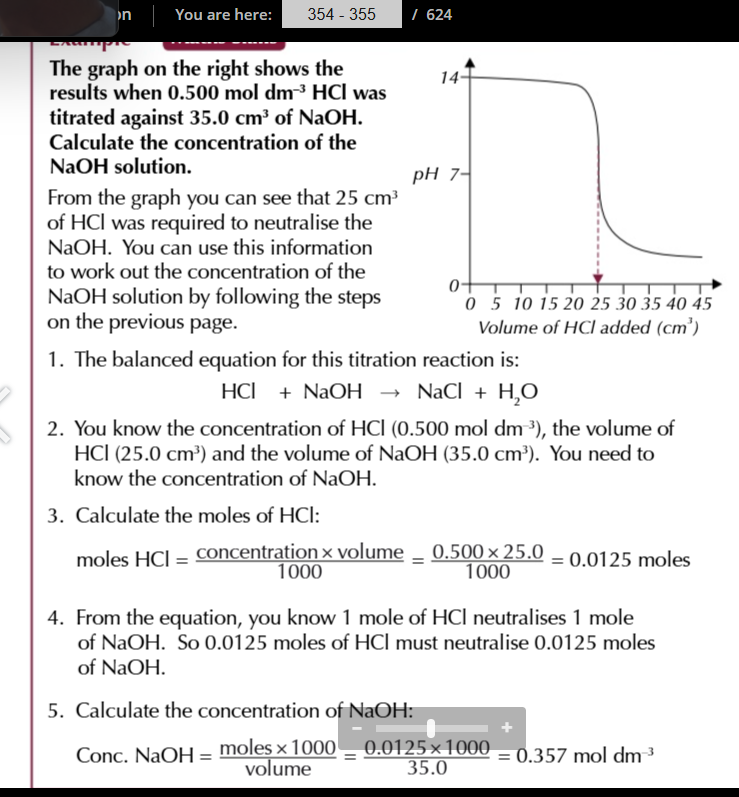
calculating concentration of monoprotic acids
write balanced equation for the titration reaction
decide what you know already and what you need to know, usually you’re given 2 volumes and a concentration and you’ll need to work out the other concentration
for one reagent, you’ll know both the concentrations and volume so you can calculate the number of moles
use the molar ratios in the balanced equation to find out how many moles of the other reagent reacted
calculate the unknown concentration using conc=(Mol×1000)÷volume
diprotic acids release 2 protons in a solution like ETHANEDIOIC ACID (HOOC-COOH) the reaction happens in 2 stages because 2 protons are removed from the acid separately,
this means when you titrate ethanedioic acid with a really strong base you get a pH curve with 2 equivelance points
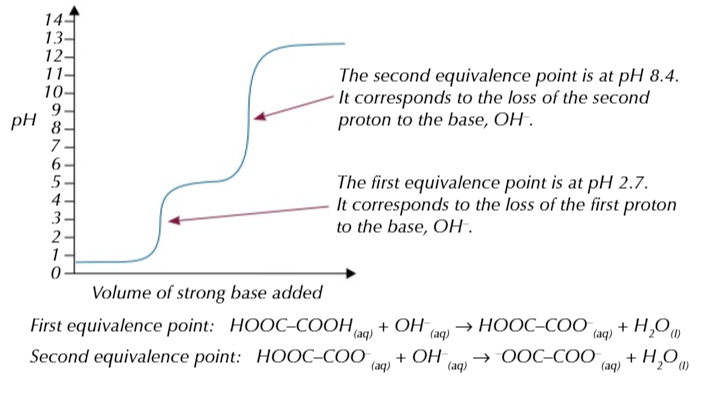

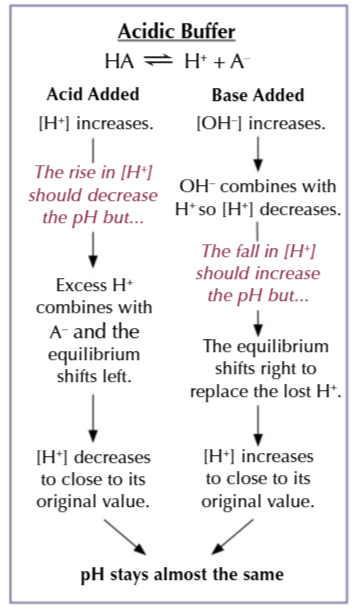
buffer
a solution that resists changes in pH when a small amount of acid/alkali is added
there are 2 types of buffers
acidic buffer
basic buffer
acid buffers pH is less that 7
they contain a mixture of a weak acid with one of its salts
acid buffers resist pH change when
either a base/acid is added to the solution
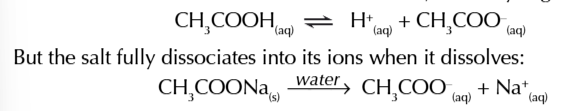
a mixture of ethanoic acid + sodium ethanoate is an example of a buffer solution
in the solution there will be loads of undissociated ethanoic acid molecules CH3COOH and ethanoate ions CH3COO- from the salt
altering the concentration of H+/OH- means the equilibrium is able to shift to counteract the change
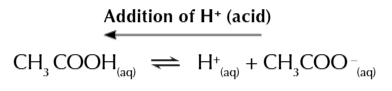
resisting an acid
the large amount of CH3COO- ensure the buffer can cope with the addition of acid
more CH3COOH is produced as the equilibrium shifts left to reduce the concentration of H+ so the pH doesn’t change
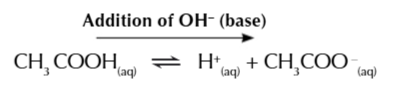
resisting a base
the large amount of CH3COOH ensure the buffer can cope with the addition of a base
CH3COOH dissociates to form H+ IONS SHIFTING THE EQUILIBRIUM RIGHT
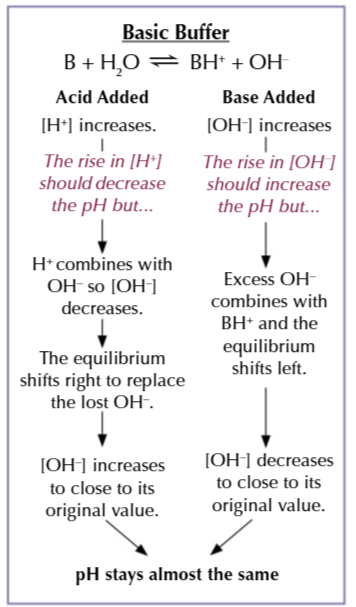
basic buffers have a pH greater than 7
they contain a mixture of weak bases with its salt and can resist the addition of acids/base
a mixture ammonia as a weak base and ammonia chloride as a salt of ammonia is an example of a basic buffer
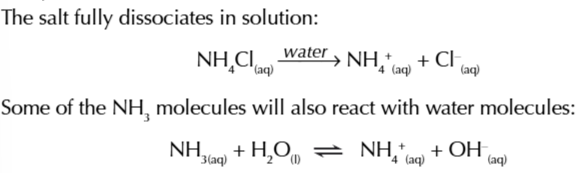
Basic buffer resisting an acid
the large amount of ammonia ensure the buffer can resist the addition of acid
when H+ is added to a solution it can react with OH- to make water
this shifts the equilibrium right to replace the OH- used up
water reacts with ammonia to produce NH4+ and OH-
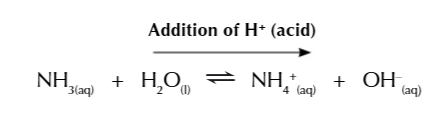
basic buffers resisting a base
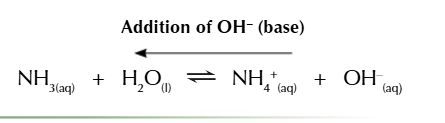
a large amount of ammonium chloride ensure the buffer resist the addition of a base
the extra OH- reacts with the NH4+ to form ammonia and water
the equilibrium shifts left to remove OH- from the solution
acidic and basic vuffers also resist pH change when diluted by water
water slightly dissociates so the extra H+ and OH- puh the equilibrium the same amount in both directions leaving it unchanged
alkaline conditions makes hair rougher
shampoos have a pH around 5;5 to keep hair smooth and shiny
buffers are in shampoo to maintain the pH while washing hair
biological washing powders contain buffers
they maintain the pH at the right level for enzymes to work best
its vital blood stays at a pH near 7.4
so our system contain buffers
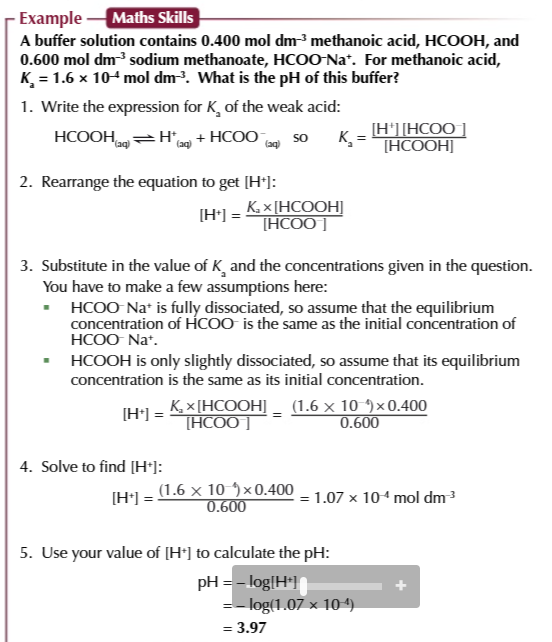
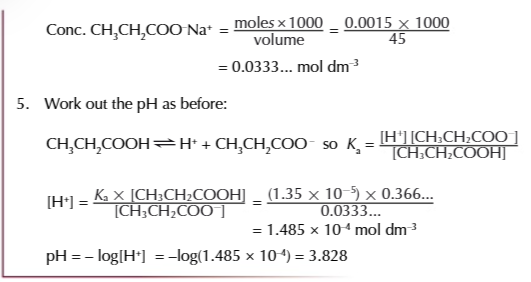
if given the Ka and concentration of the weak acid and its salt you can calculate the pH of an acidic buffer
write expression for Ka
rearrange the equation to give an expression for [H+]
substitute the value of Ka and the concentration of the acid and its salt into the equation
solve the equation to find a value for [H+]
substitute the [H+] into -log10[H+]
other ways to make buffers
mixing a weak acid and a small amount of alkali to that some of the acid is neutralised is salt while some is left unneutralised
this reaction mixture would contain a weak acid and its salt to technically it is still an acidic buffer so you can work out its pH
write out neutralisation equation
calculate number of moles of acid/base at the start of reaction
use the molar ratios in the equation to work out the moles of acid and salt left at the end of the reaction
calculate the conc of the acid and salt in the buffer solution by dividing the moles at the end of the reaction by the volume of the solution
then calculate the pH using Ka