Physics IGCSE - Nuclear Physics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
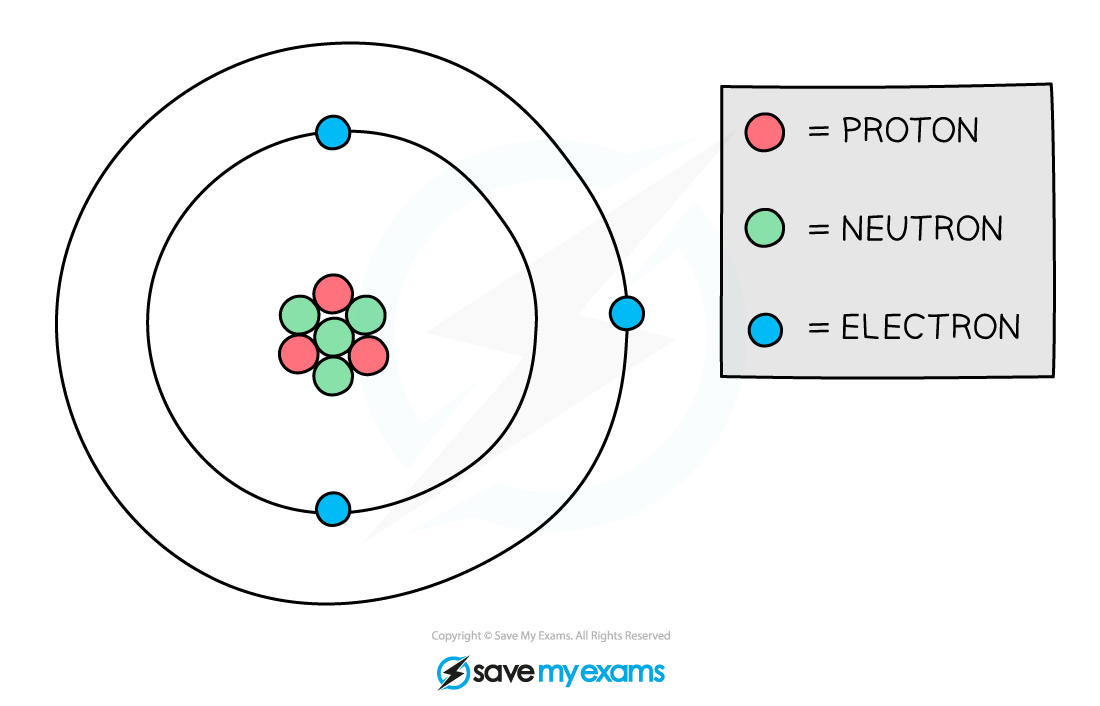
Composition of nucleus
Protons and neutrons
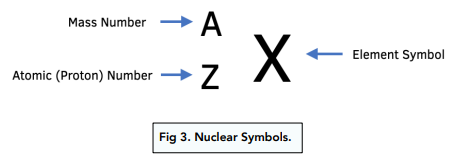
Proton number (Z)
no. of protons
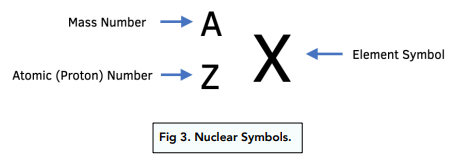
Nucleon number (A)
total no. of protons + neutrons
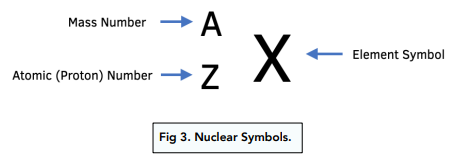
Number of neutrons
A - Z
An element may have more than 1 isotope
Some isotopes are radioactive
Relationship between proton no. + relative charge on nucleus
Nucleus relative charge is 1+
Nuclear fission
A large unstable nucleus splits into smaller stable nuclei → releases energy and neutrons
Nuclear fusion
2 small nuclei join → form larger nucleus → releases energy
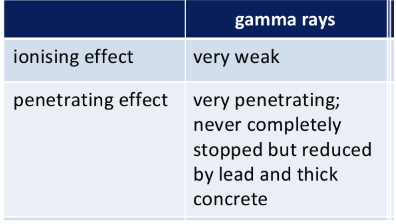
Ionising nuclear radiation
Radiation that removes electrons from atoms → turns them into ions
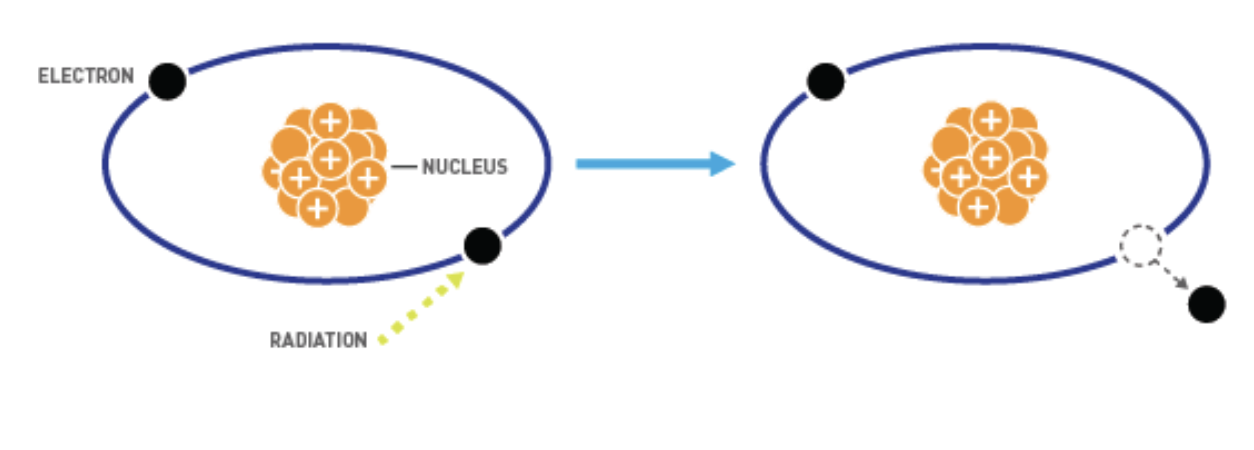
Background radiation
Naturally occurring ionising radiation from environment
Things that make a big contribution to background radiation
radon gas (in air)
rocks + buildings
food + drink
cosmic rays
How ionising nuclear radiation is detected
A Geiger-Müller tube connected to counter
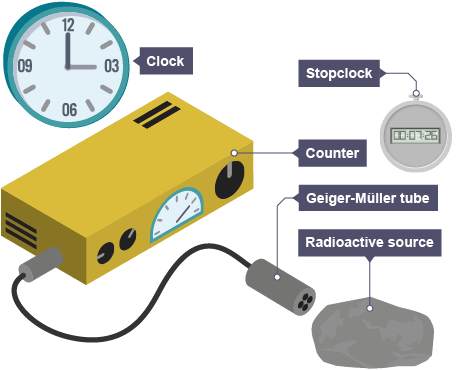
Unit count rate measured in
Counts per second
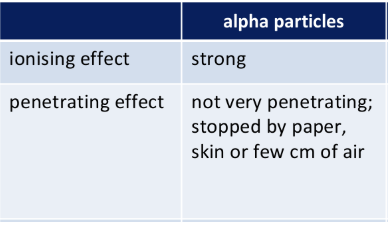
Nature of alpha particle

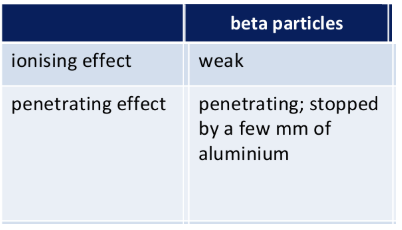
Nature of beta particle

Nature of gamma particle

Alpha particle
Beta particles
Gamma particles
Radioactive decay
spontaneous and random change in unstable nucleus → result in emission of α particles or β particles and/or γ radiation
Change in nucleus due to α decay or β decay
Nucleus changes into different element → due to change in proton no.
Change in nucleus occurs during β emission
Neutron changes into proton + electron
Neutron → proton + electron
Decay equation for emission of α particles
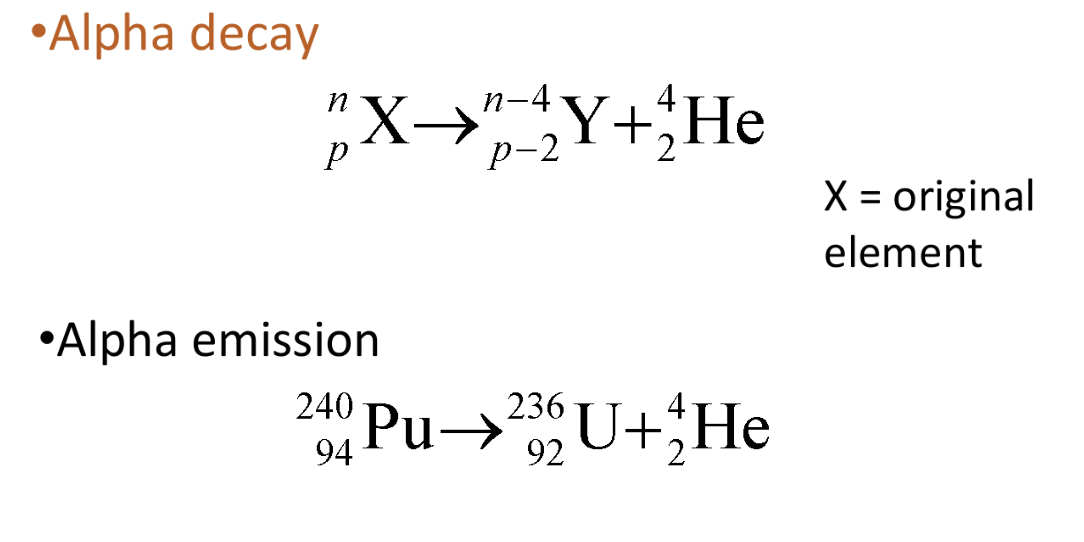
Decay equation for emission of β particles
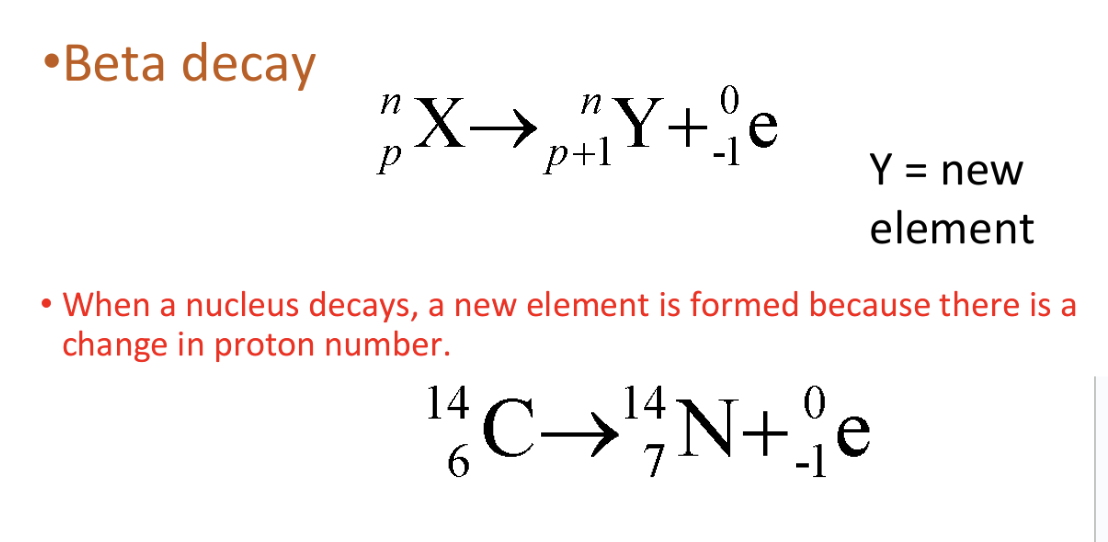
Half life
time taken for half the nuclei of that isotope in any sample to decay
Calculating half life in graphs
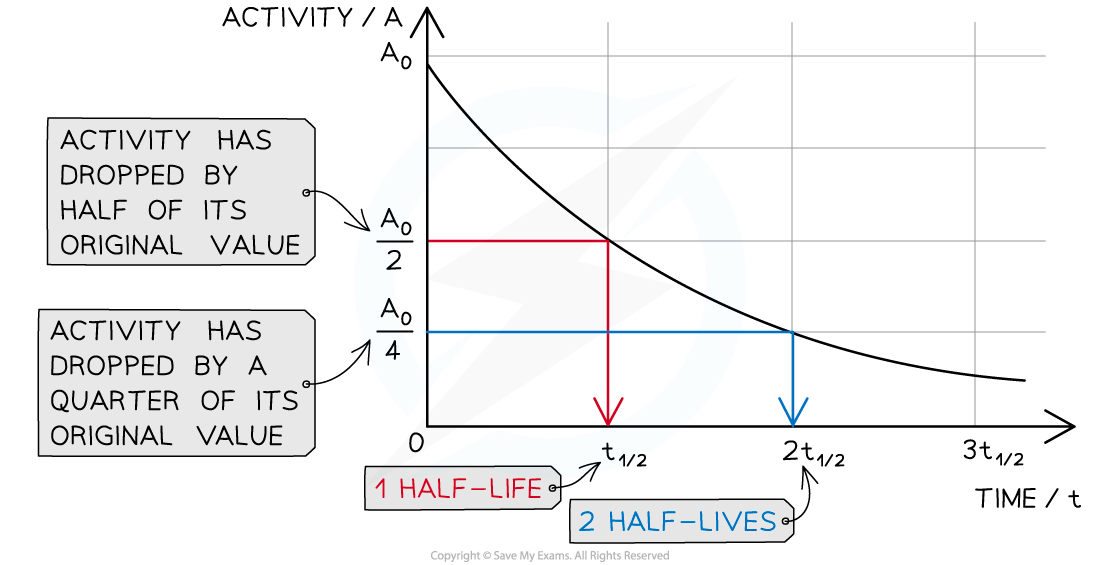
Half life undecayed population equation
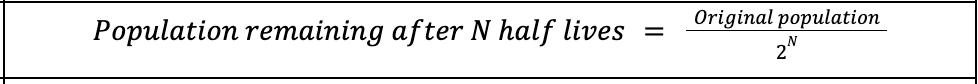
Half life equation (count rate population)
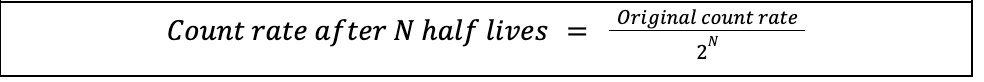
Applications for radioactivity
(a) household fire alarms
(b) irradiating food → kill bacteria
(c) sterilisation of equipment using gamma rays
(d) measuring + controlling thicknesses of materials → less detection = thicker material
(e) diagnosis + treatment of cancer using gamma rays
Effects on ionising material on living things
Cell death
Cell mutation
Cancer
How radioactive materials are handled safely
Time → minimize exposure time
Distance → stay away from source
Shielding → use lead or concrete barriers