Geography geological hazards (tectonics)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Crust -
Thin outer layer of the Earth. It is made up of giant sections called tectonic plates . These drift slowly on top of the mantle as a result of convection currents
Mantle
The thickest layer. Due to a high temperature it is semi-liquid. The upper layer of the mantle is called the asthenosphere which has convection currents which move the Lithosphere/Crust.
Outer Core
Liquid layer. As the earth rotates, the outer core spins and creates the Earth’s magnetic field.
Inner Core
Hottest layer. There is so much pressure that it doesn’t melt and is a solid layer. Inner core is the hottest layer of the earth and this heat decreases as you move from the inner core to the crust.
Plates in the lithosphere (types of crust)
Oceanic and continental crust
Oceanic crust
Thin layer ● Forms Ocean Bed - 6-8 km thick ● Mainly Basaltic - Dense igneous rock
Even if its thinner, the higher density makes it go under the continental.
Continental crust
Thick layer ● Sits on top of the oceanic crust ● Forms the continents - 30-50 km thick ● Mainly Granite - A low density igneous rock
4 Plate boundaries
Constructive
Destructive subduction
conservative
Destructive collision
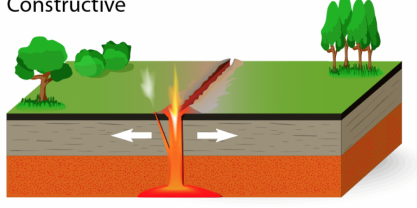
Constructive
Usually 2 oceanic plates - They move away from each other creating fissures/faults - Magma seeps through the fissures and instantly cools, forming solidified rock - Fissure and Shield Volcanoes are formed from this - Example: Mid-Atlantic Ridge
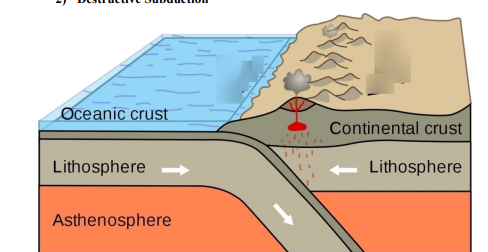
Destructive subduction
The oceanic and continental plates move towards each other and the oceanic plate subducts as it is denser. - The denser oceanic plate then melts in the mantle creating viscous, andesitic lava with high silica content which makes it very dangerous as a lot of energy will be needed to make the volcano explode. - This creates Strato/Composite volcanoes (E.g. Pacific Ring of Fire.)
2 types of crust scientific thing
Lithosphere, Asthenosphere
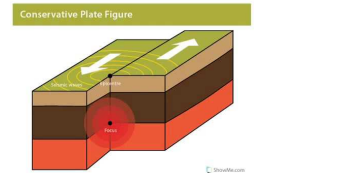
Conservative
This occurs when 2 plates move alongside each other. - It causes only earthquakes. - They can be moving in the same direction at different speeds or in the opposite direction. - Example: San Andreas Faultline.
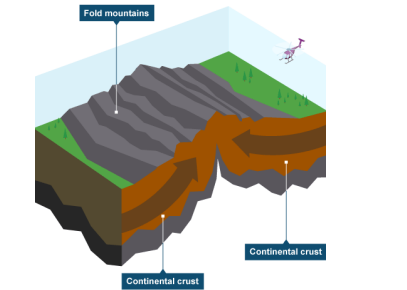
Destructive collision
When 2 plates of the same density move towards each other, they buckle up creating fold mountains. - Examples: Mount Everest, The Alps
usually continental continental
What is a hotspot?
Areas of the earth’s crust which are significantly hotter than its surroundings which is linked to volcanic activity.
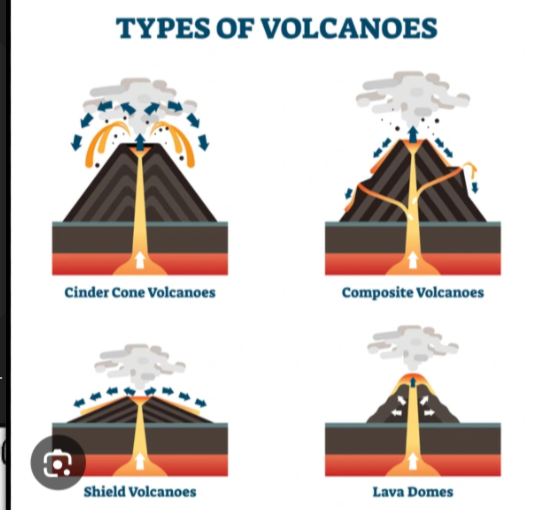
Types of volcanoes
Composite, Shield, fissure, caldera
Composite volcano
- Very explosive - Less frequent explosions - High viscosity, andesitic lava with high silica content - Steep sided, cone shaped - Destructive Plate Boundary - Pacific Ring of Fire
example: Mount Fuji
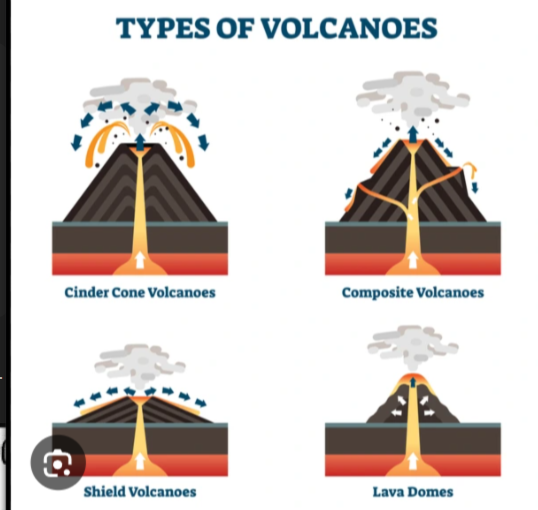
shield volcanoes
Not very explosive - More frequent explosions - Low viscosity, basaltic lava with low silica content - Constructive plate boundaries - Basaltic Lava
example: Mauna Kea/Loa
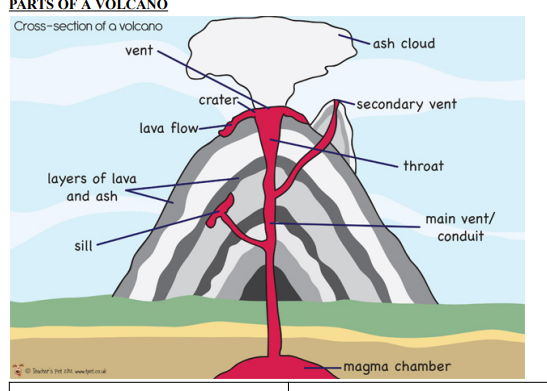
Parts of volcano?
Advantage of volcano