Unit 1: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
nature-nurture issue
the longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors. Today's science views traits and behaviors as arising from the interaction of ________ and ________.

natural selection
the principle that the inherited traits enabling an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will (in competition with other trait variations) most likely be passed on to succeeding generations.
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection.
behavioral genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior.
mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change.
environment
every nongenetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to our experiences of the people and things around us
heredity
the genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
genes
the biochemical units of heredity
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism
identical (monozygotic) twins
individuals who developed from a single fertilized egg that split in two, creating two genetically identical organisms

fraternal (dizygotic) twins
individuals who developed from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than ordinary siblings, but they share a prenatal environment.
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems.
Central Neevous System (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
REM Sleep
rapid eye movement sleep; a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active. (Sometimes called R sleep.)
nerves
bundled axons that form neural cables connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sensory organs.
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the body's tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs.
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles. Also called the skeletal nervous system.
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy.
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Reflexes
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response.
neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
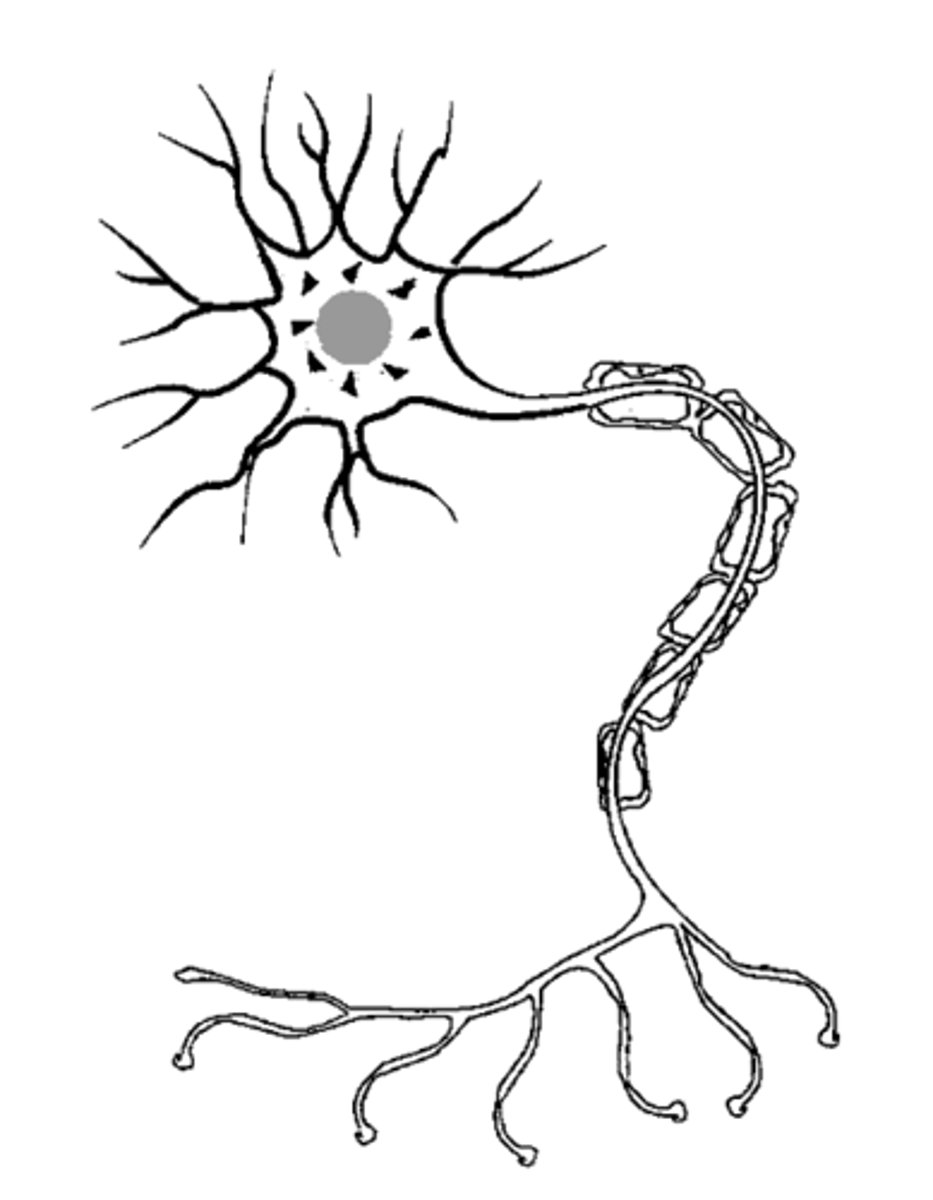
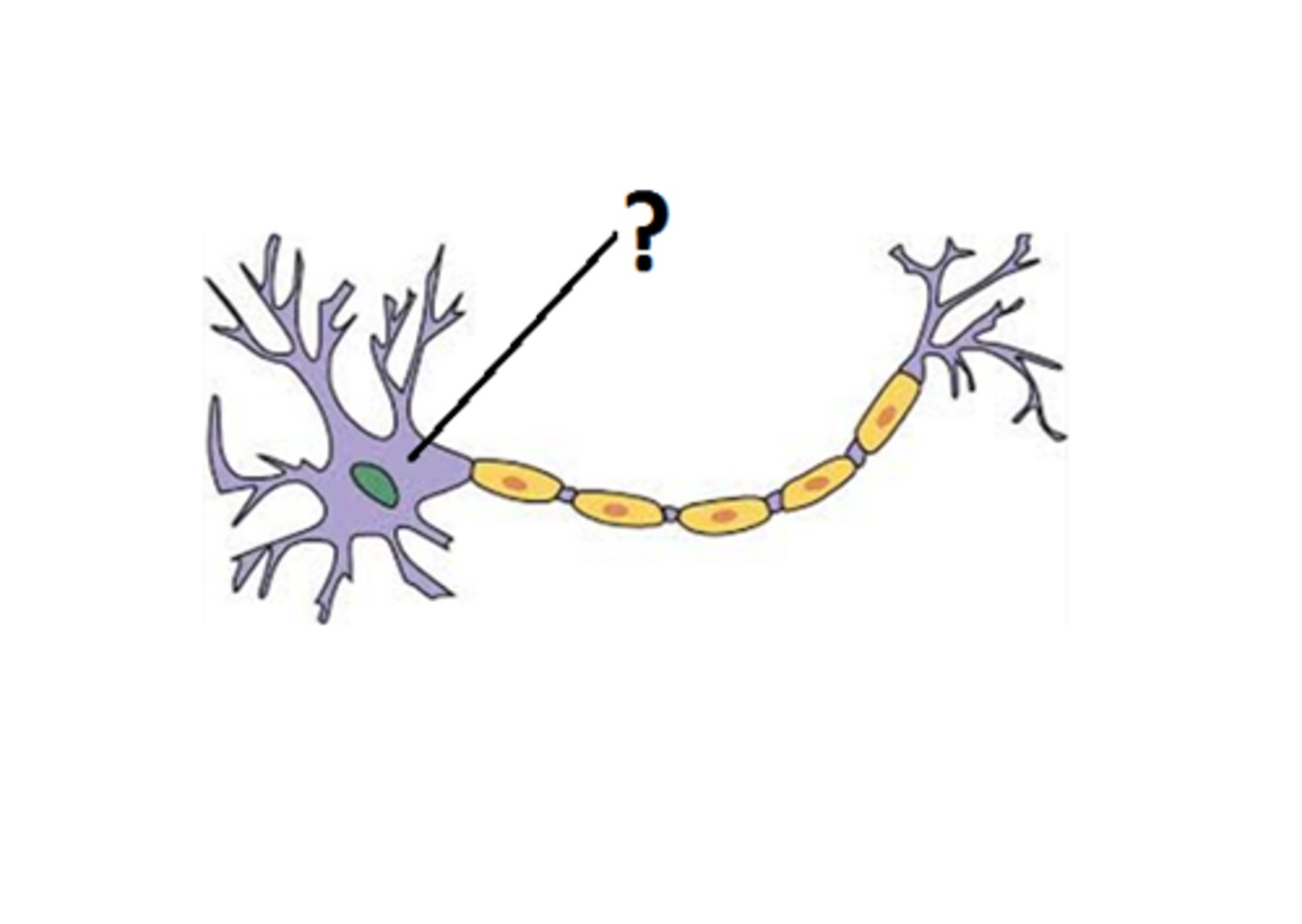
cell body
the part of a neuron that contains the nucleus; the cell's life-support center.
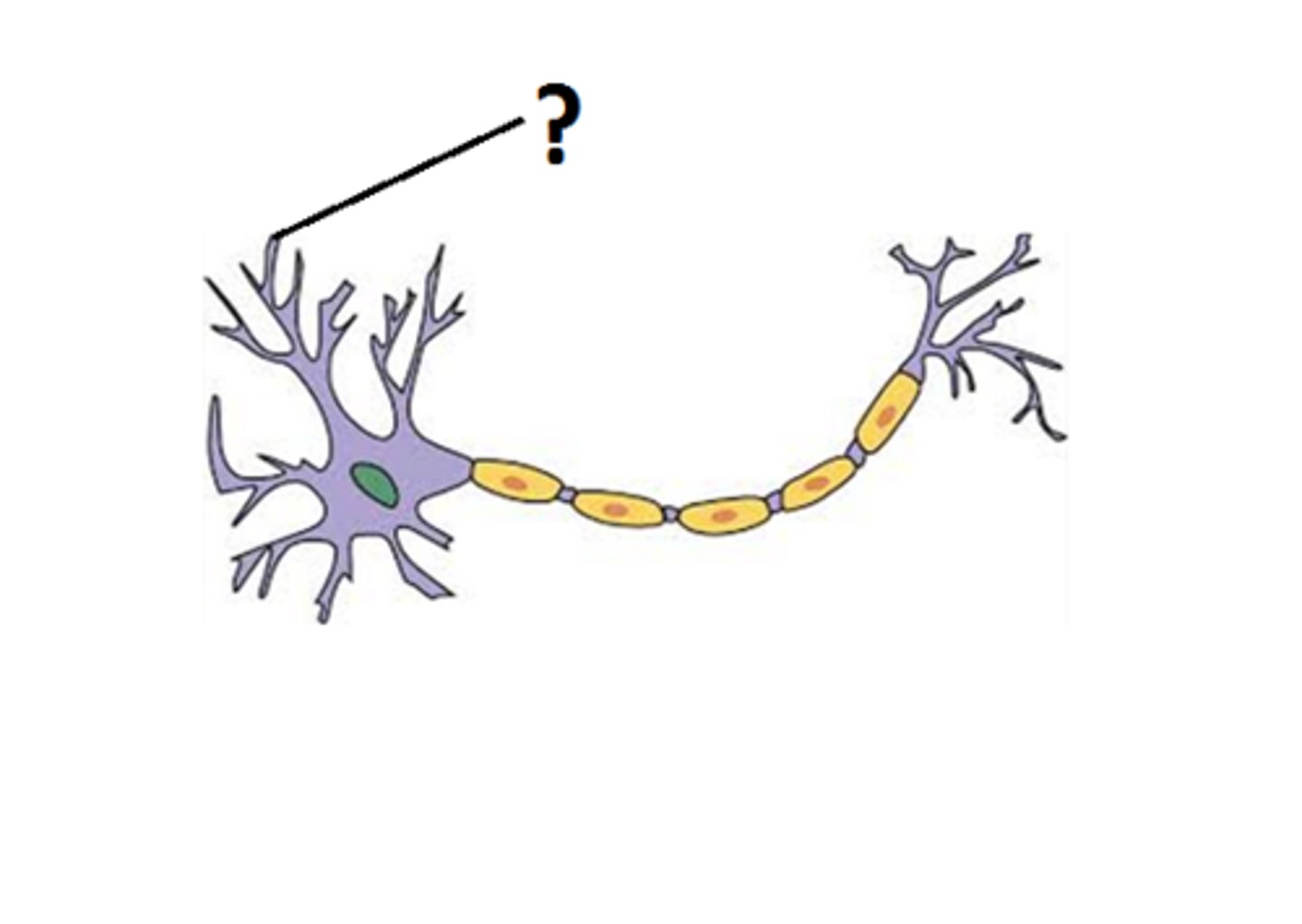
Dendrite
a neuron's often bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body.
axon
the segmented neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
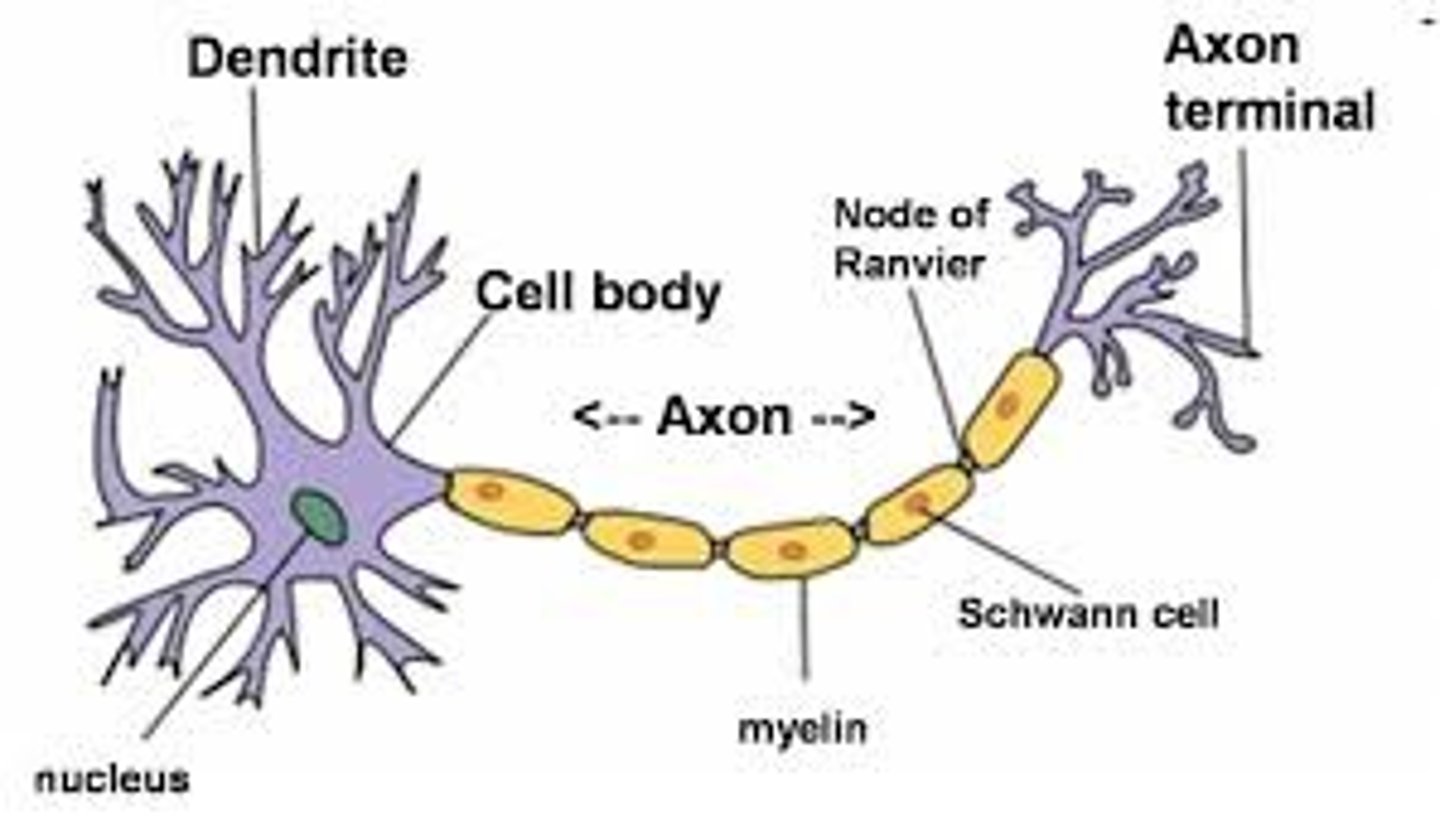
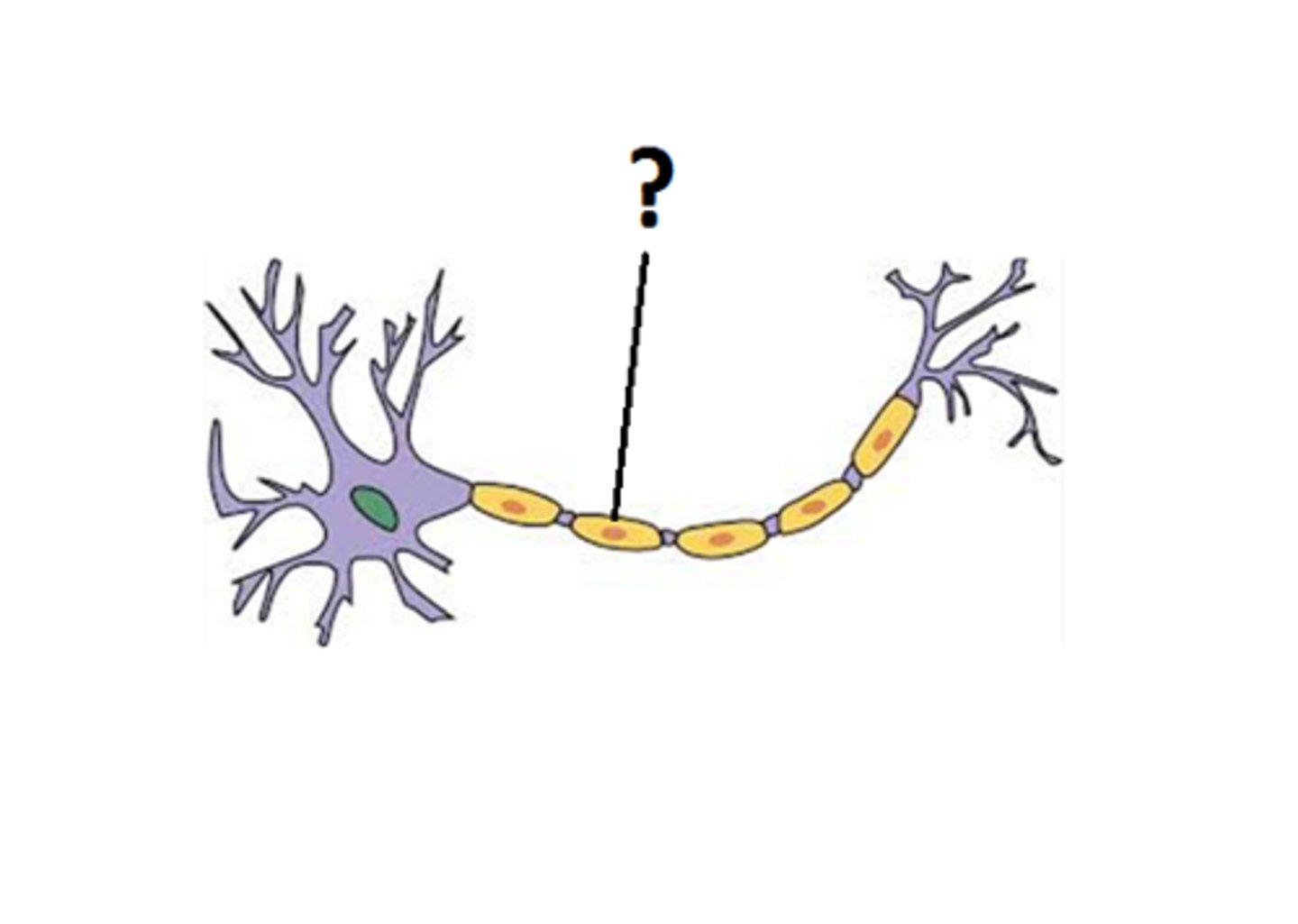
myelin sheath
a fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axons of some neurons; it enables vastly greater transmission speed as neural impulses hop from one node to the next.
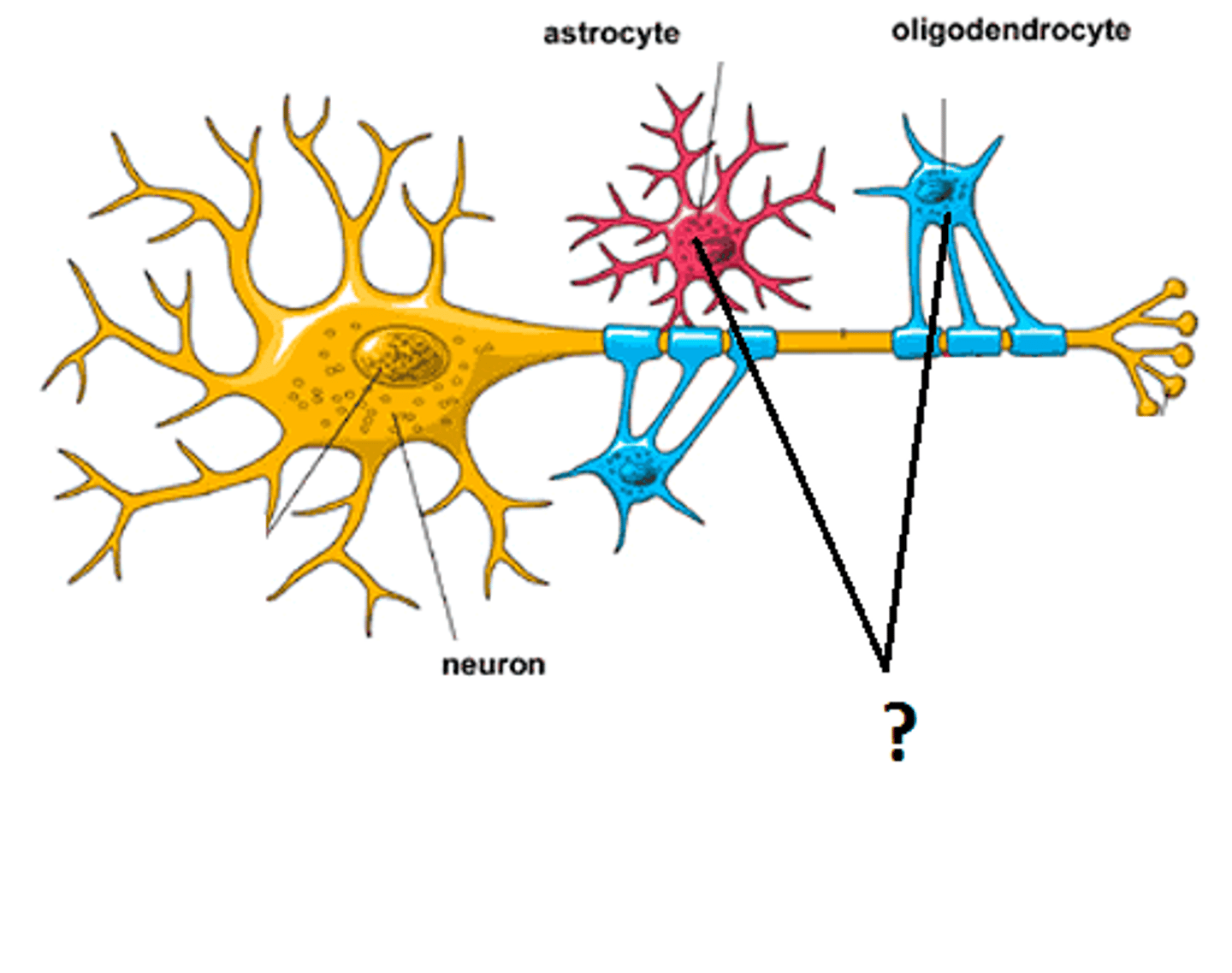
glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons; they may also play a role in learning, thinking, and memory.
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse.
refactory period
in neural processing, a brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired; subsequent action potentials cannot occur until the axon returns to its resting state
all-or-none response
a neuron's reaction of either firing (with a full-strength response) or not firing.
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, ____________ travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse.
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron.
Endorphins
"morphine within" — natural, opioid-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasures.
Agonist
a molecule that increases a neurotransmitter's action
Antagonist
a molecule that inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitter's action

endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands and fat tissue that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues.
psychoactive drugs
a chemical substance that alters the brain, causing changes in perceptions and moods.
substance use disorder
a disorder characterized by continued substance use despite significant life disruption.
depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
barbiturates
drugs that depress central nervous system activity, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment.
Opioids
opium and its derivatives; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety.
stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions.
Hallucinogens
psychedelic ("mind-manifesting") drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input.
near-death-experience
an altered state of consciousness reported after a close brush with death (such as cardiac arrest); often similar to drug-induced hallucinations.
biological psychologists
the scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes. (Some ___________________ call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists.)
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis.
levels of analysis
the differing complementary views, from biological to psychological to social-cultural, for analyzing any given phenomenon.
neuroplasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience.
lesion
tissue destruction. Brain __________ may occur naturally (from disease or trauma), during surgery, or experimentally (using electrodes to destroy brain cells).
electroencephalogram (EEG)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity sweeping across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
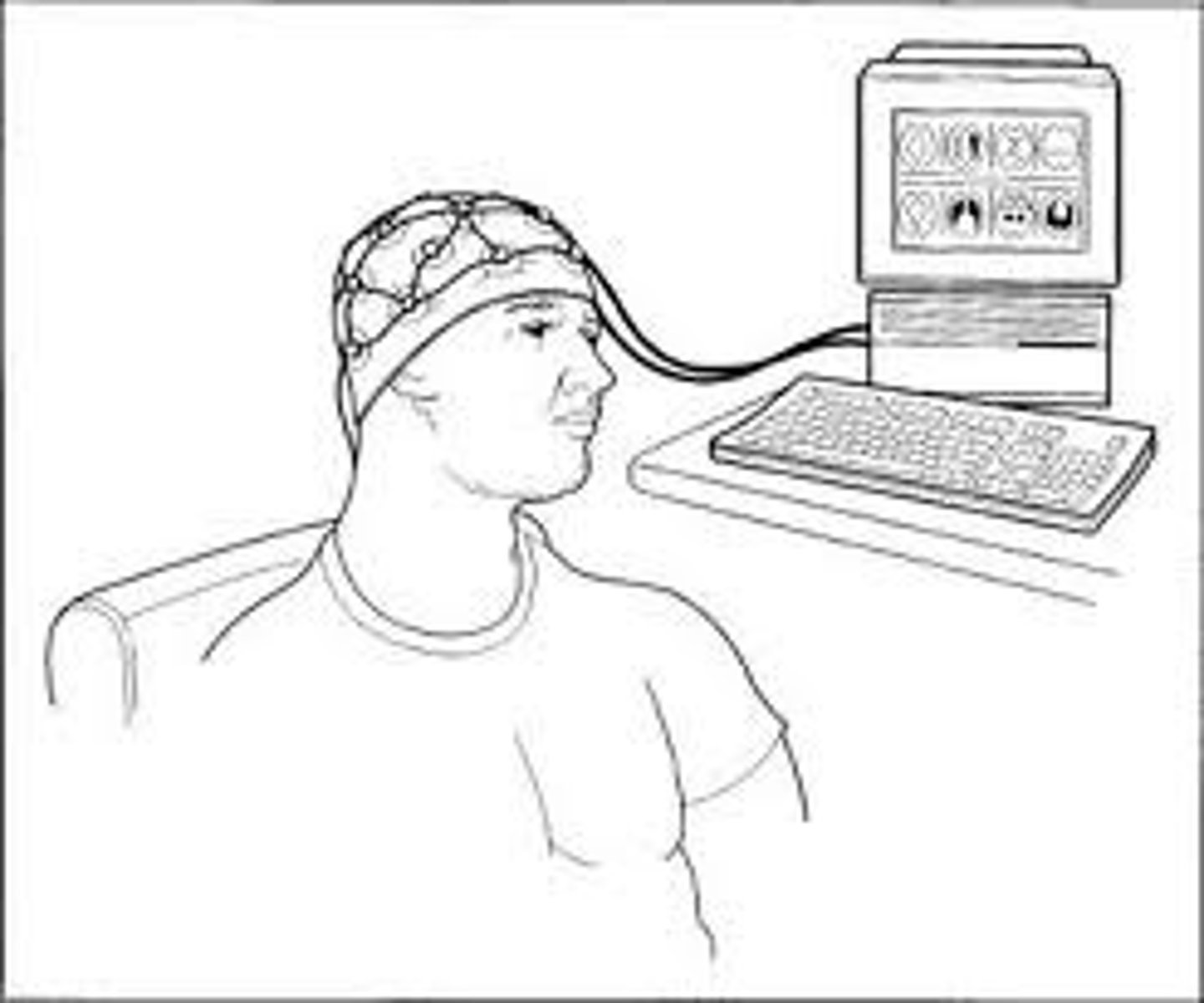
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
a brain-imaging technique that measures magnetic fields from the brain's natural electrical activity.
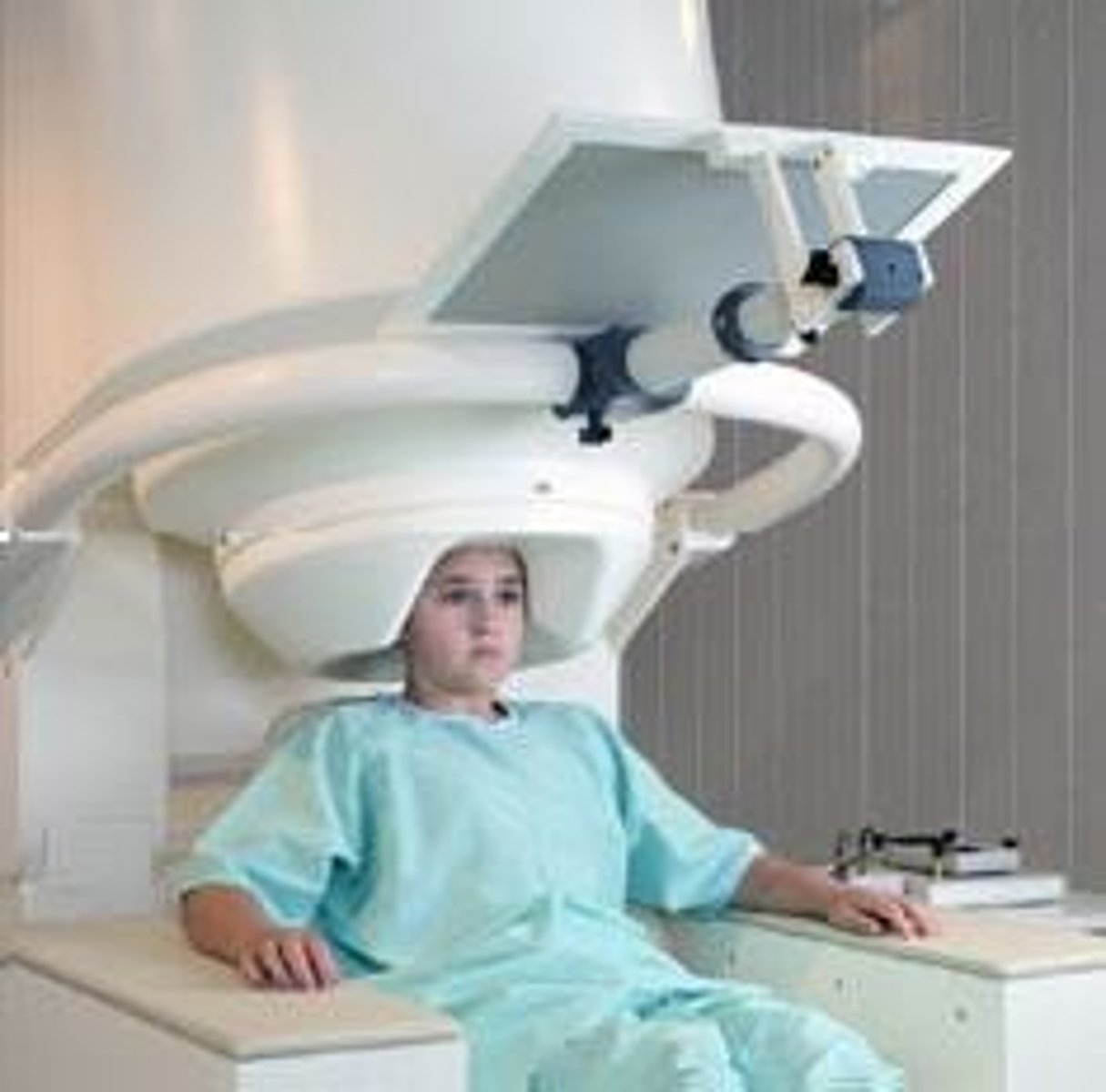
CT (computed tomography) scan
a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice of the brain's structure.
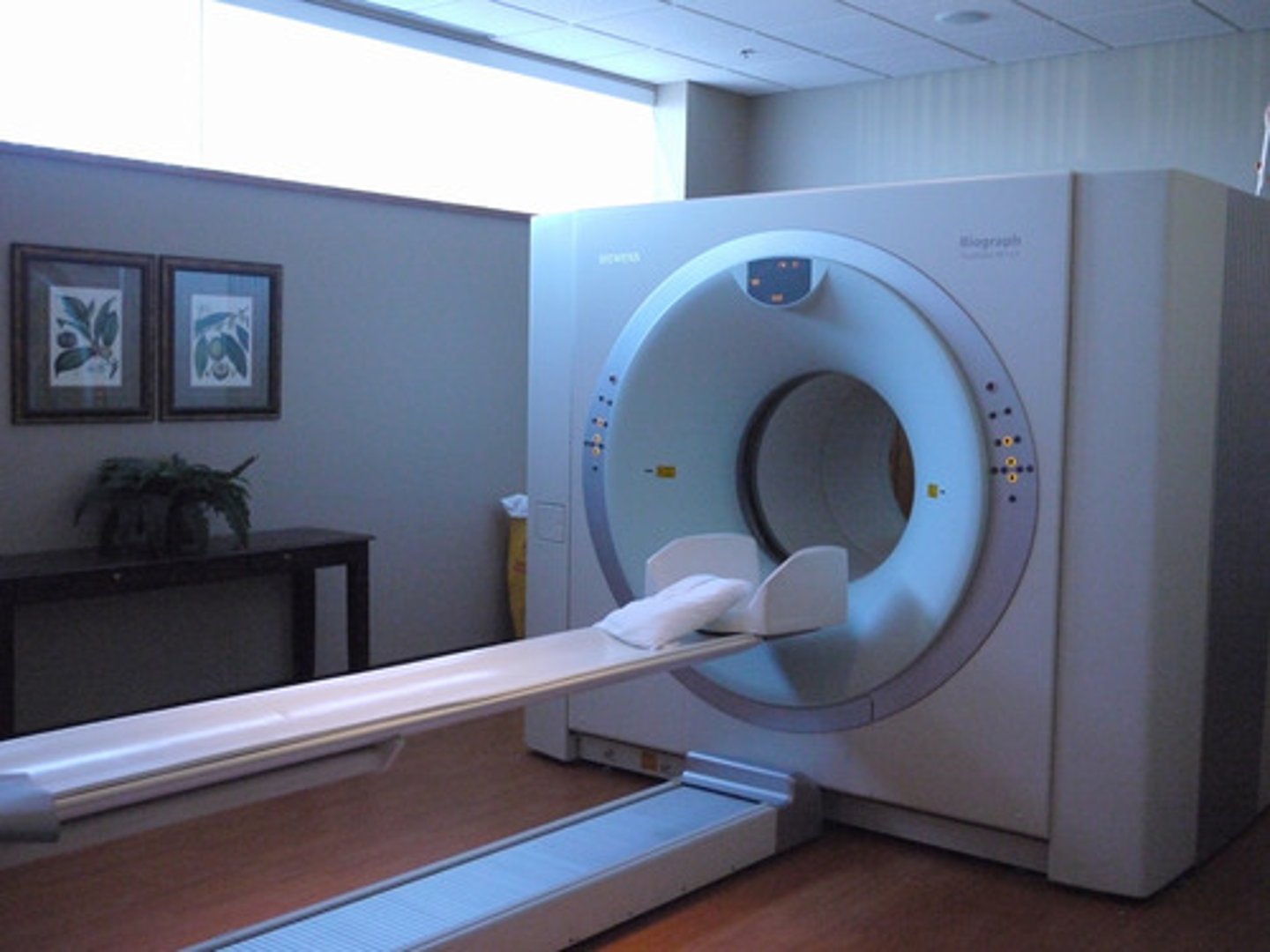
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
technique for detecting brain activity that displays where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task.

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. _________ scans show brain anatomy.
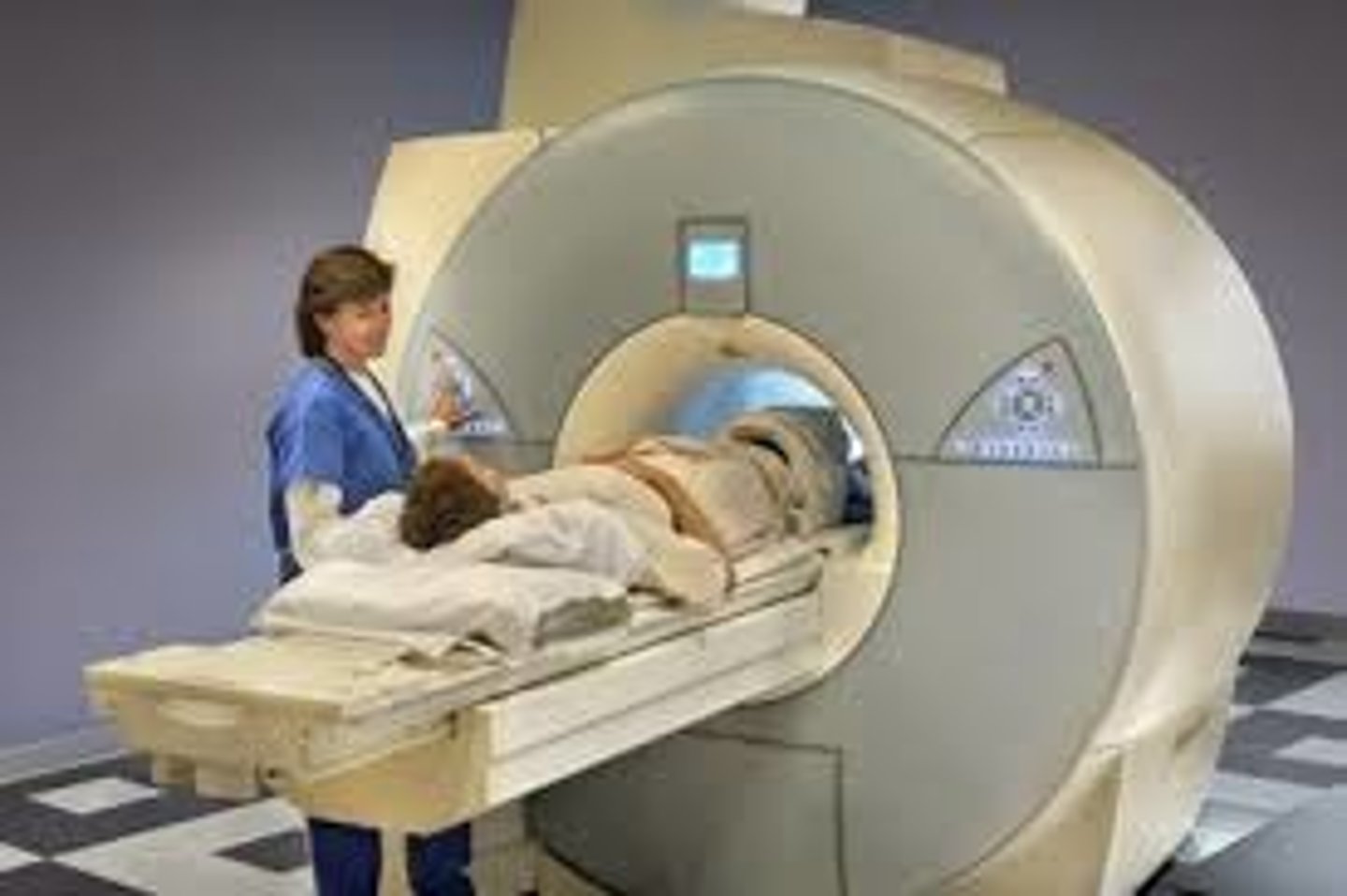
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
a technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. ___________ scans show brain function as well as structure.
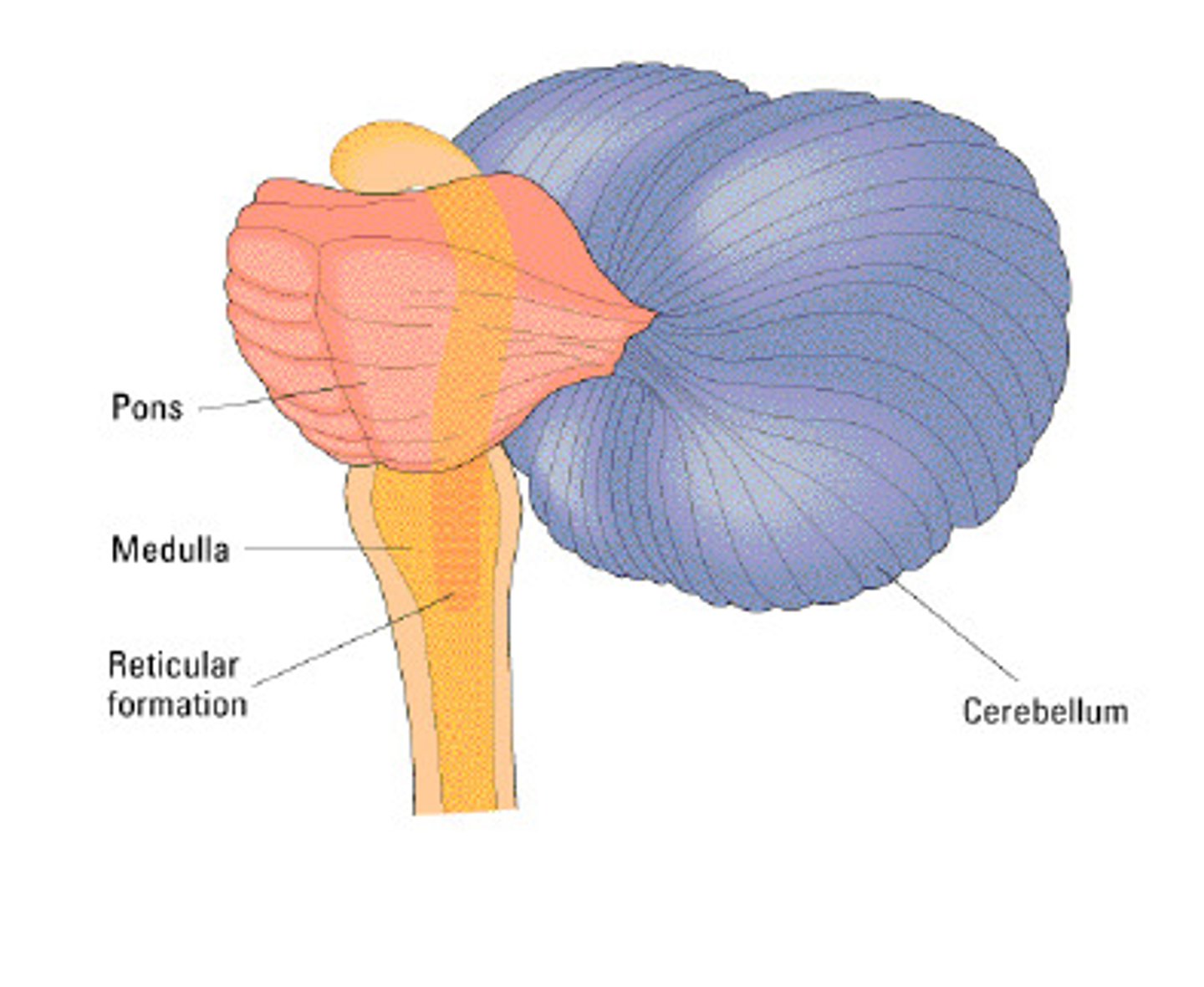
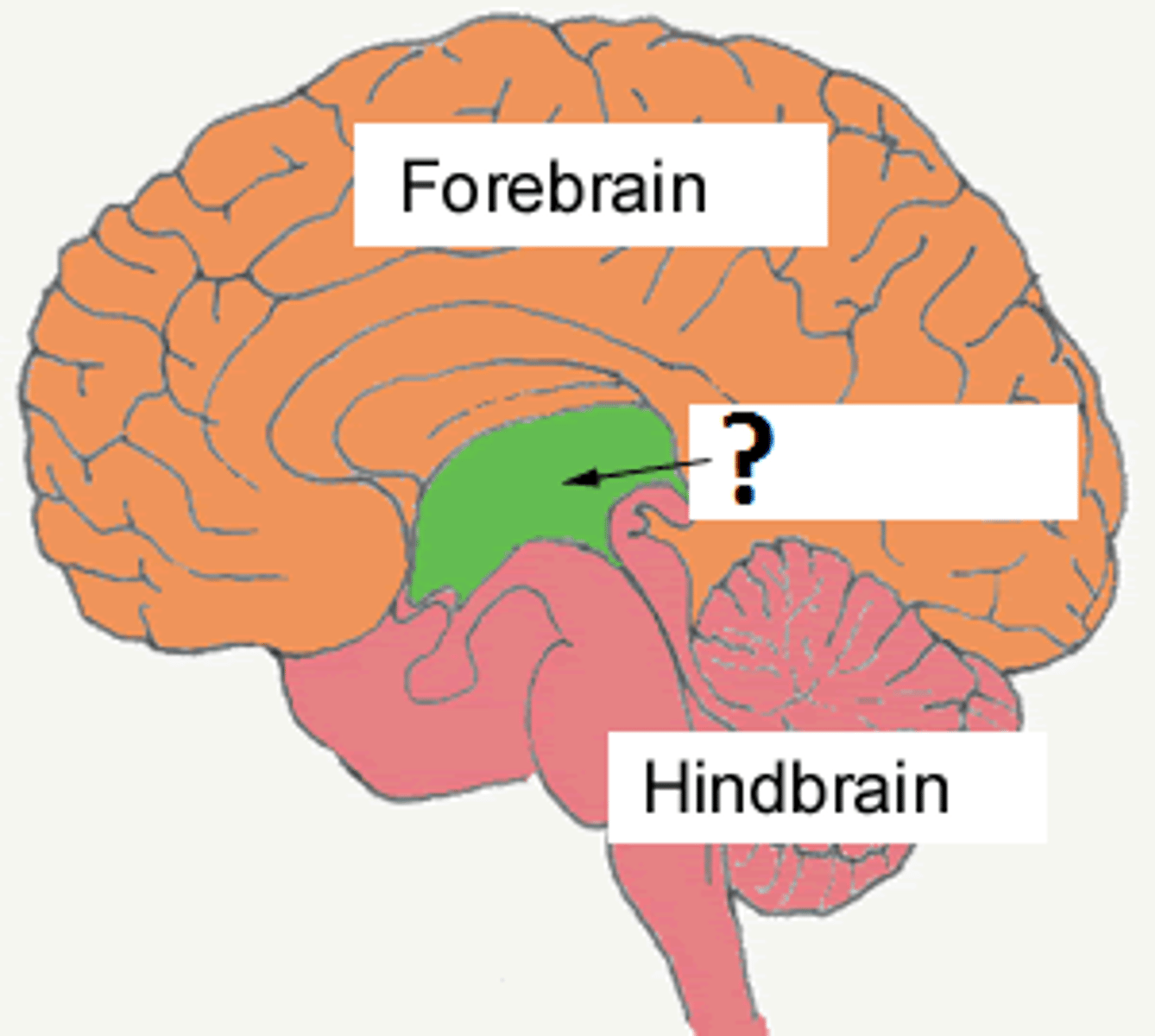
hindbrain
consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum; directs essential survival functions, such as breathing, sleeping, and wakefulness, as well as coordination and balance.
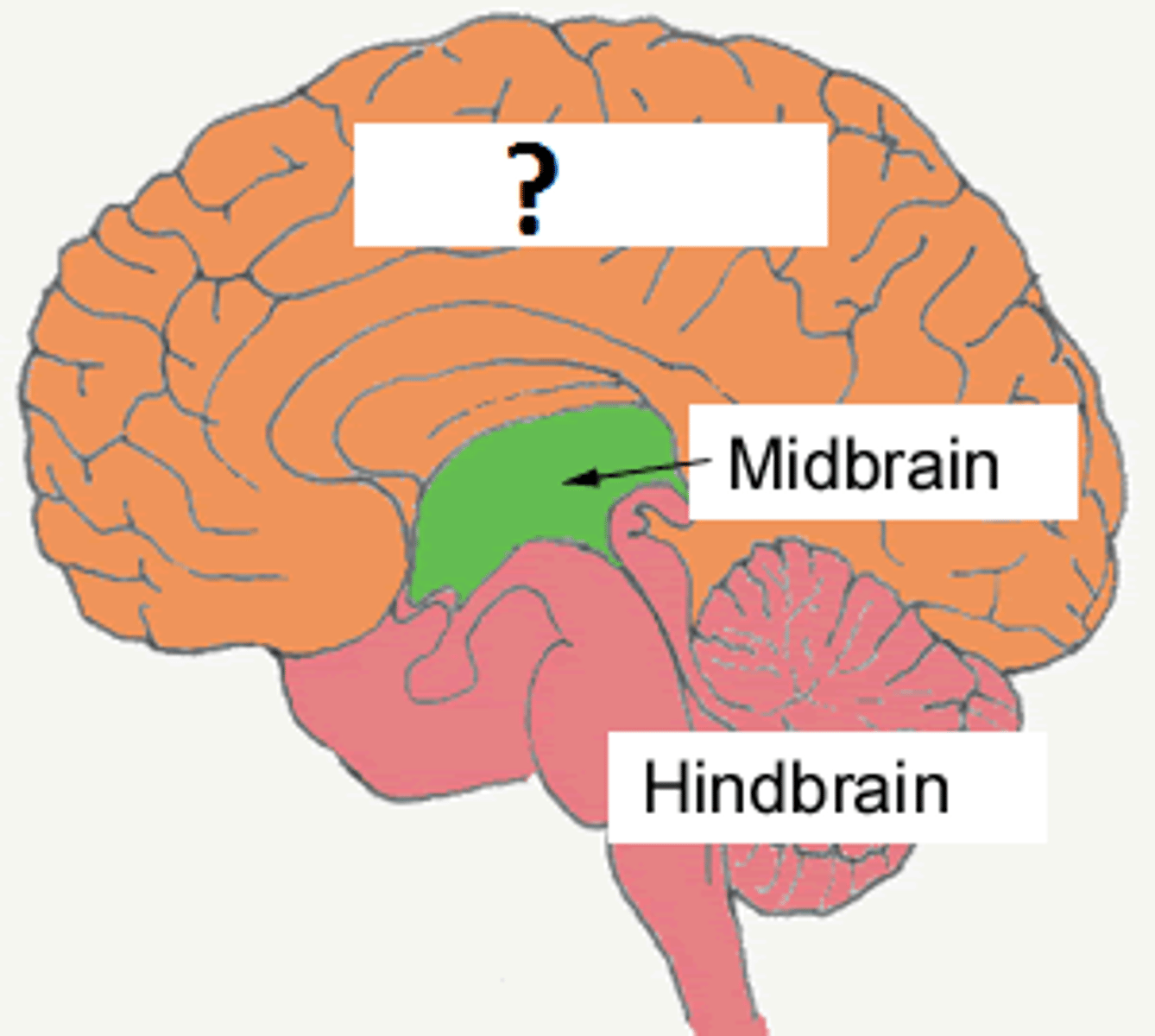
midbrain
found atop the brainstem; connects the hindbrain with the forebrain, controls some motor movement, and transmits auditory and visual information.
forebrain
consists of the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus; manages complex cognitive activities, sensory and associative functions, and voluntary motor activities.
branstem
the central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the ___________ is responsible for automatic survival functions.
medulla
the hindbrain structure that is the brainstem's base; controls heartbeat and breathing.
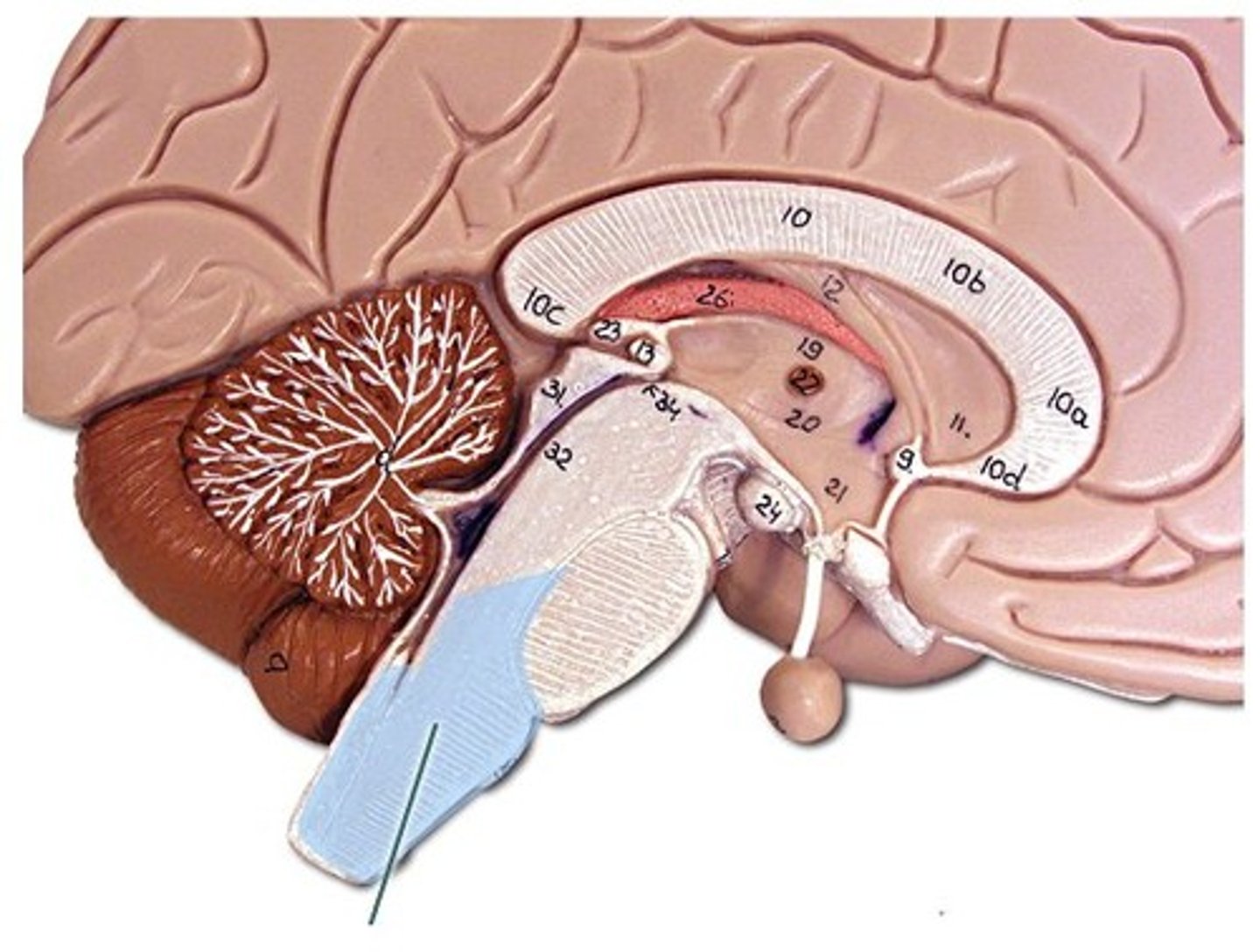
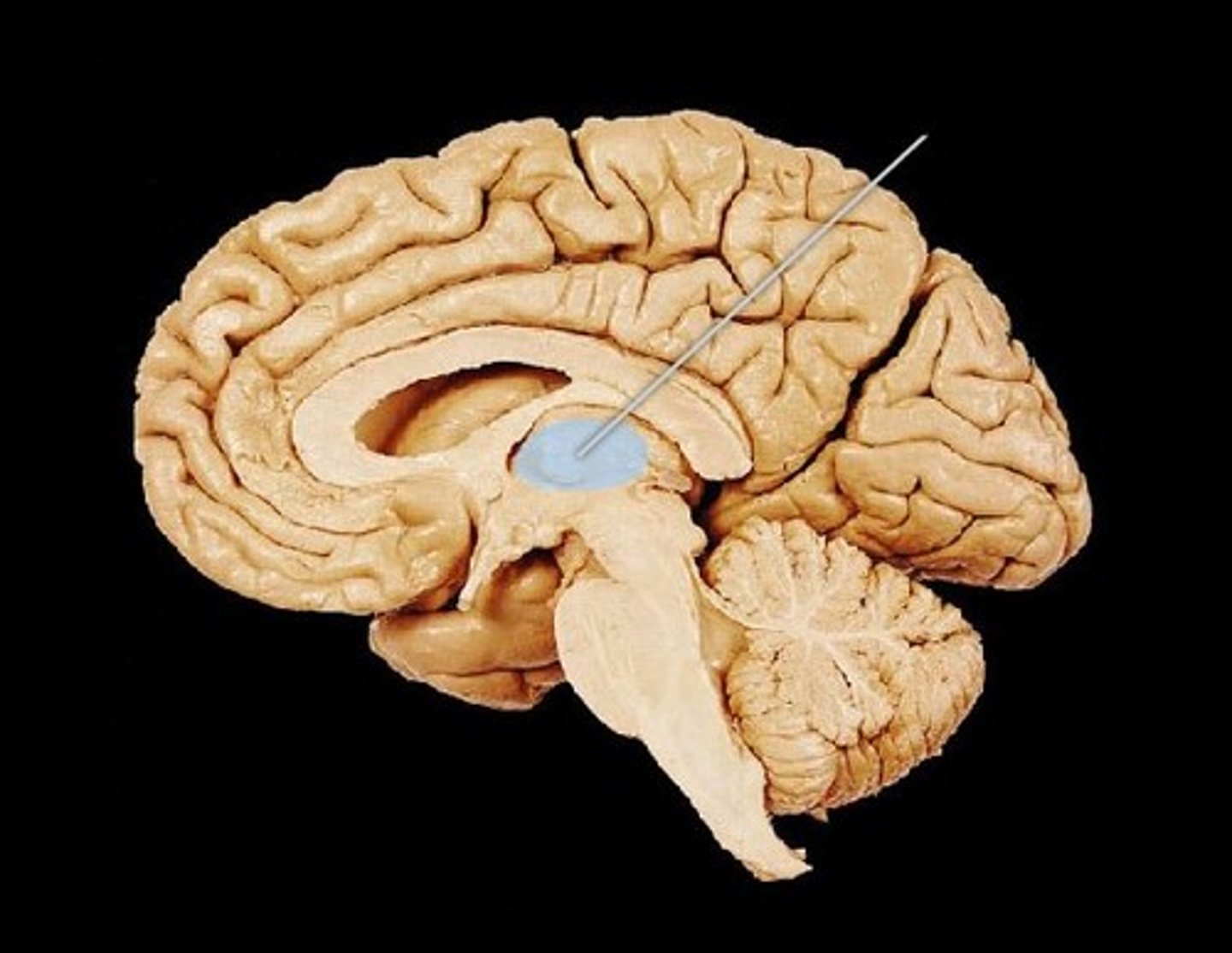
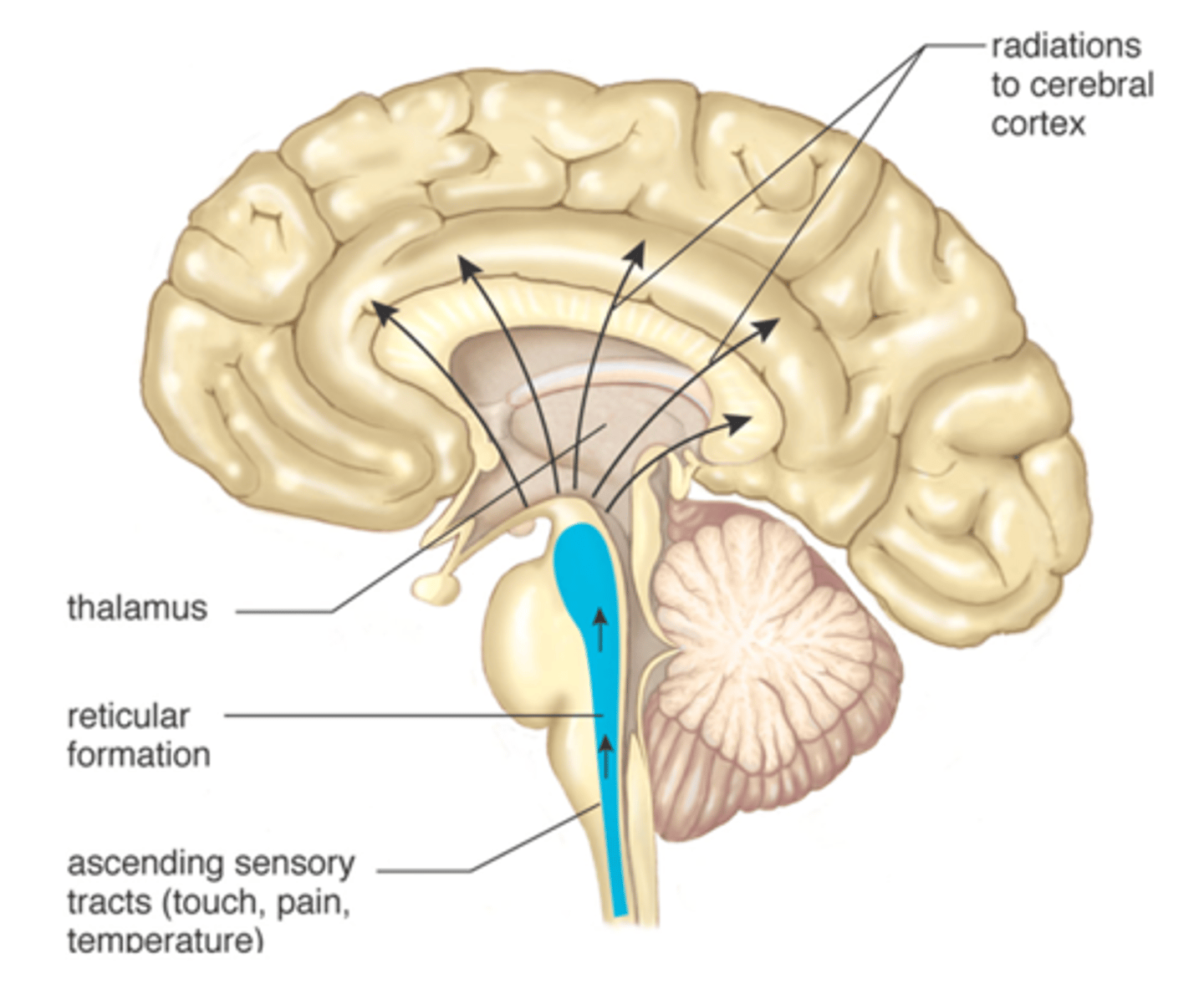
thalamus
the forebrain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla.
reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; it filters information and plays an important role in controlling arousal.
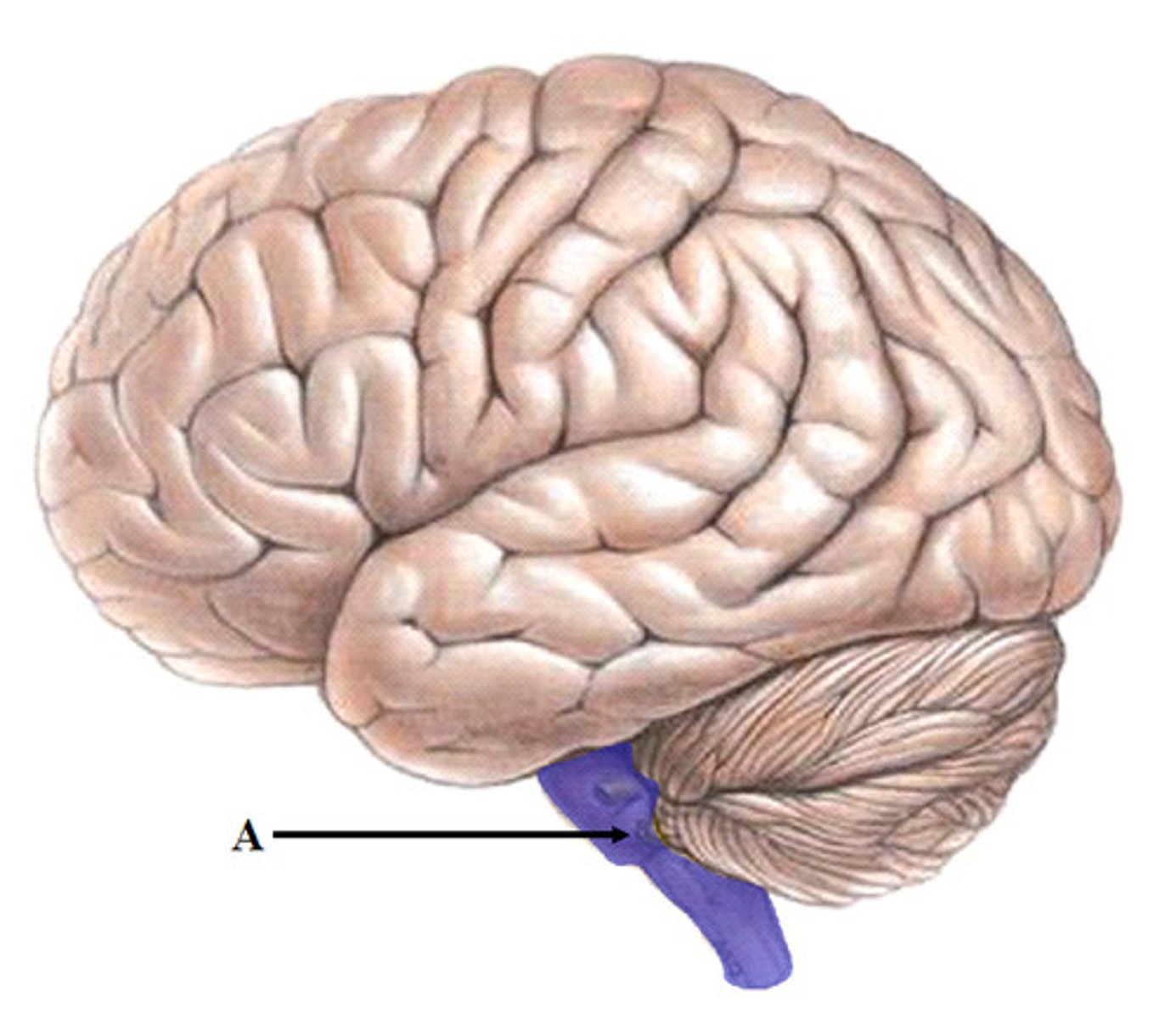
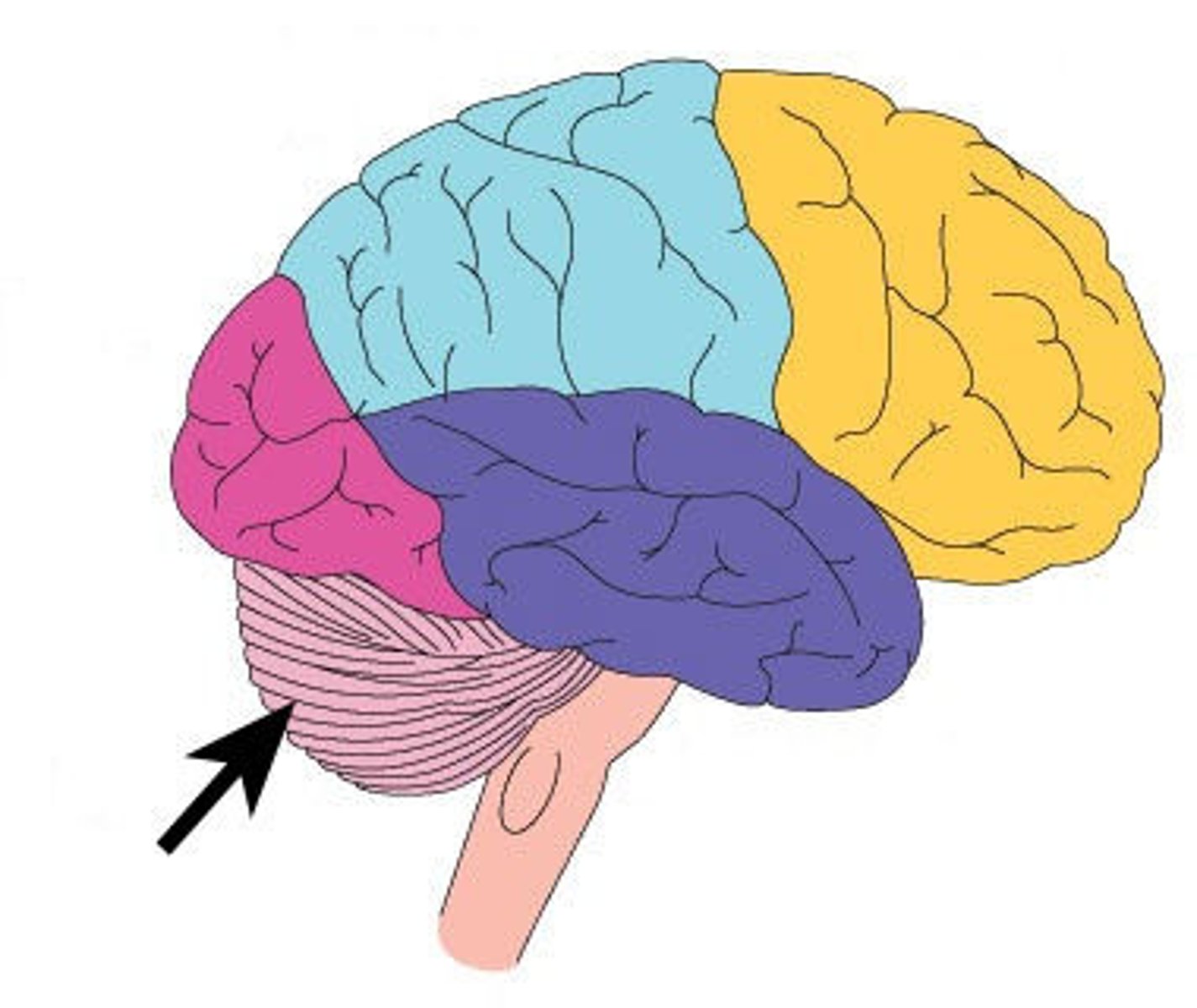
Cerebellum
the hindbrain's "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; its functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory.
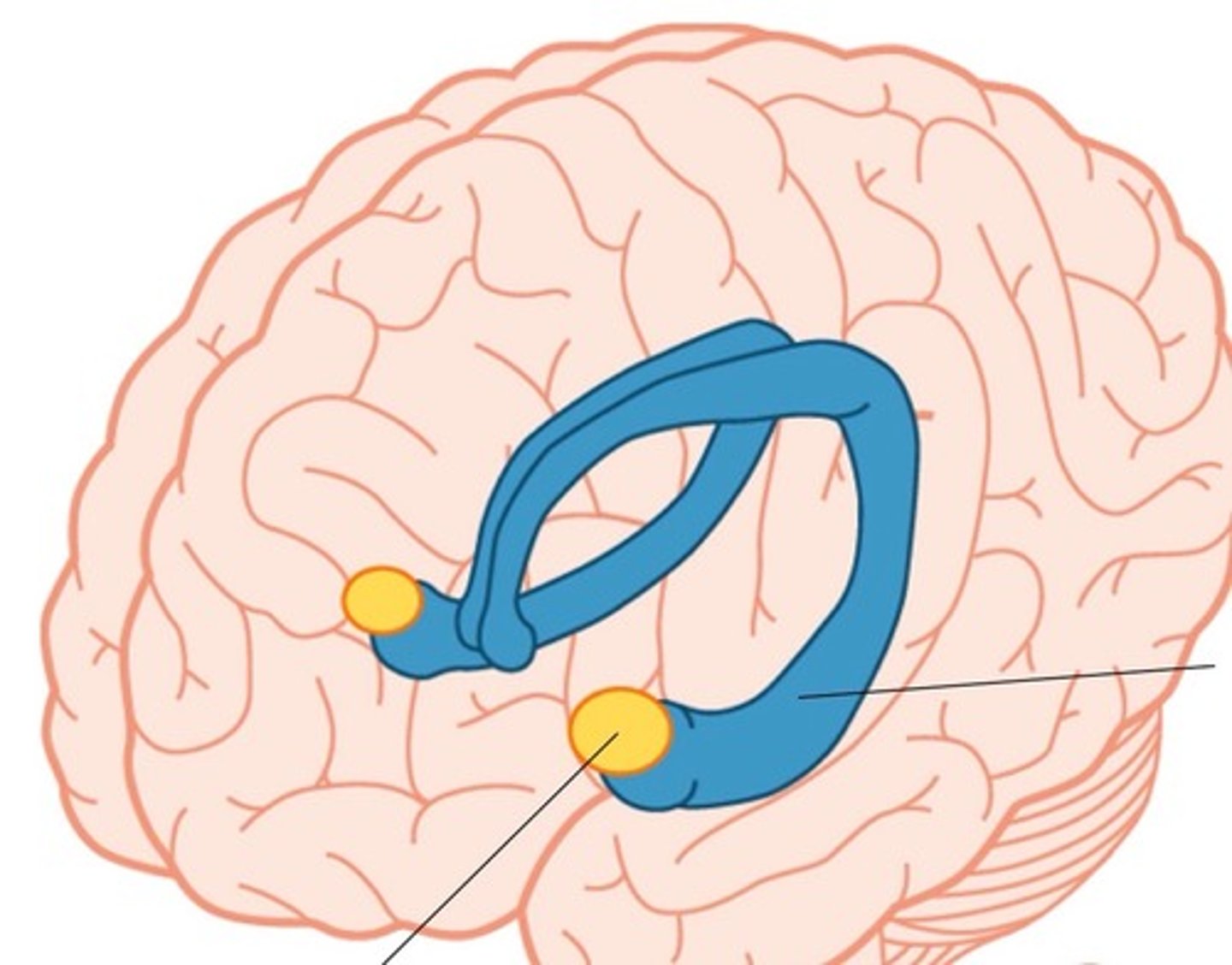
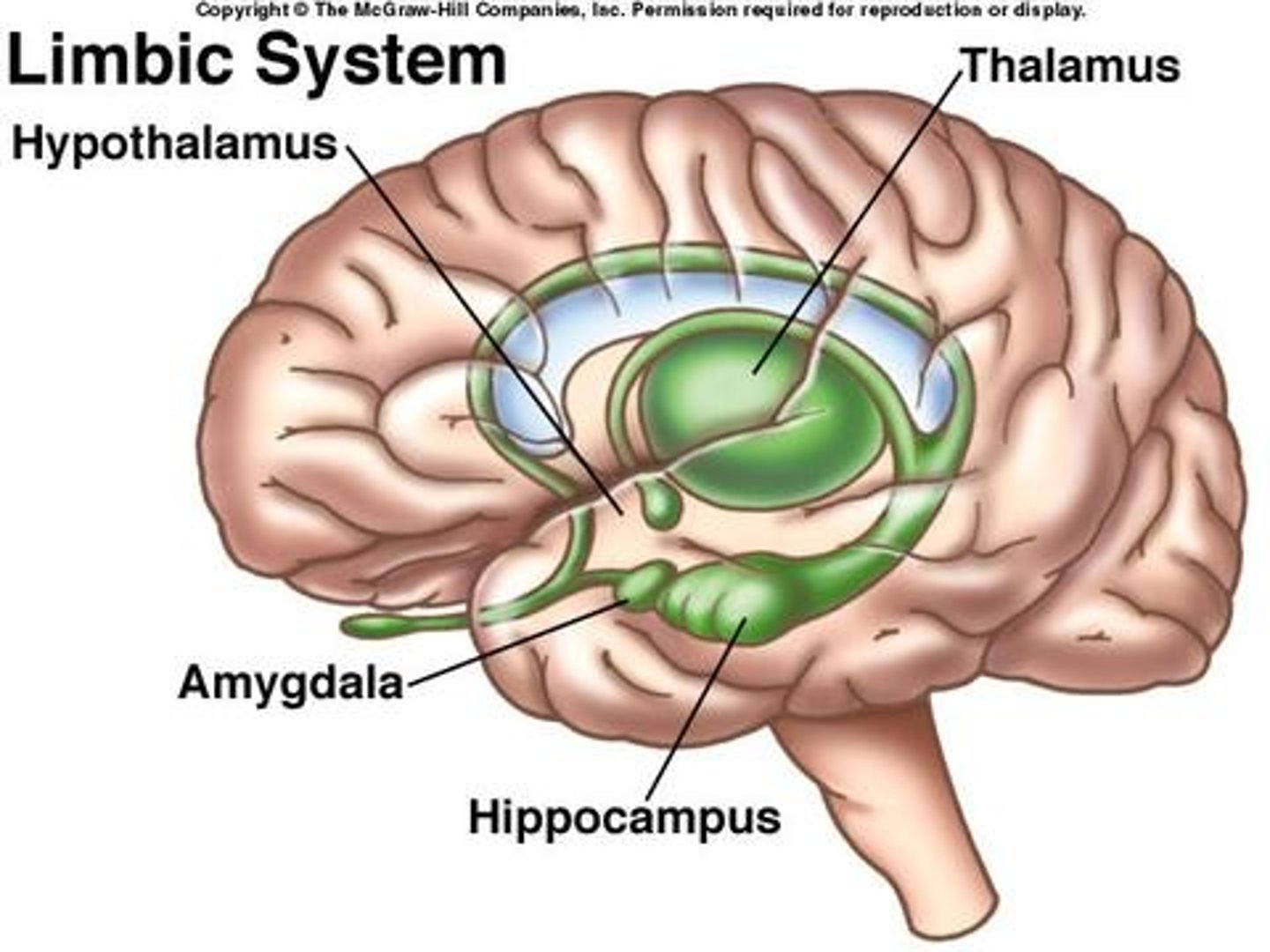
limbic system
neural system located mostly in the forebrain — below the cerebral hemispheres — that includes the amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and pituitary gland; associated with emotions and drives.
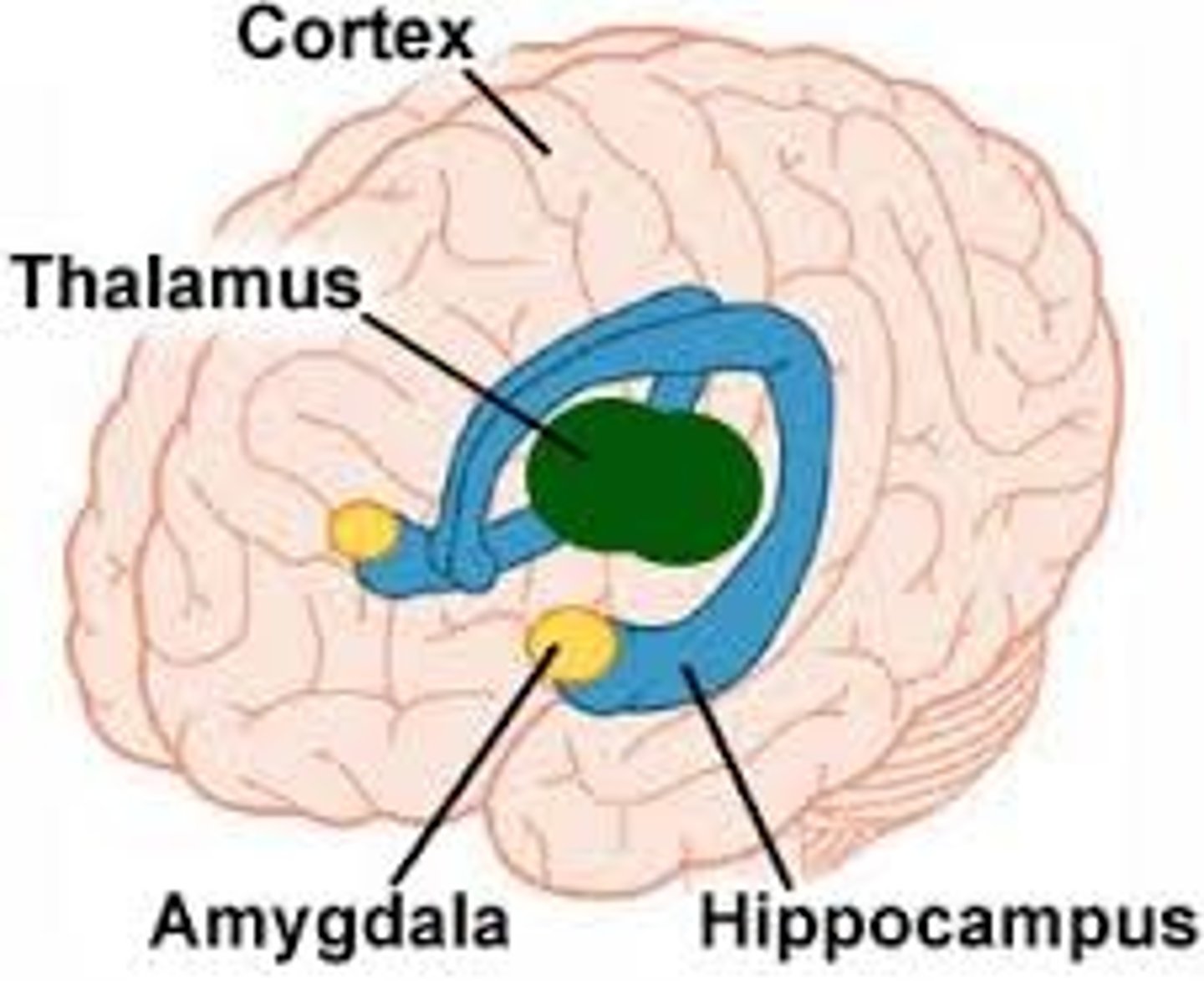
Amygdala
two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
Hypothalamus
a limbic system neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system; helps process explicit (conscious) memories — of facts and events — for storage.
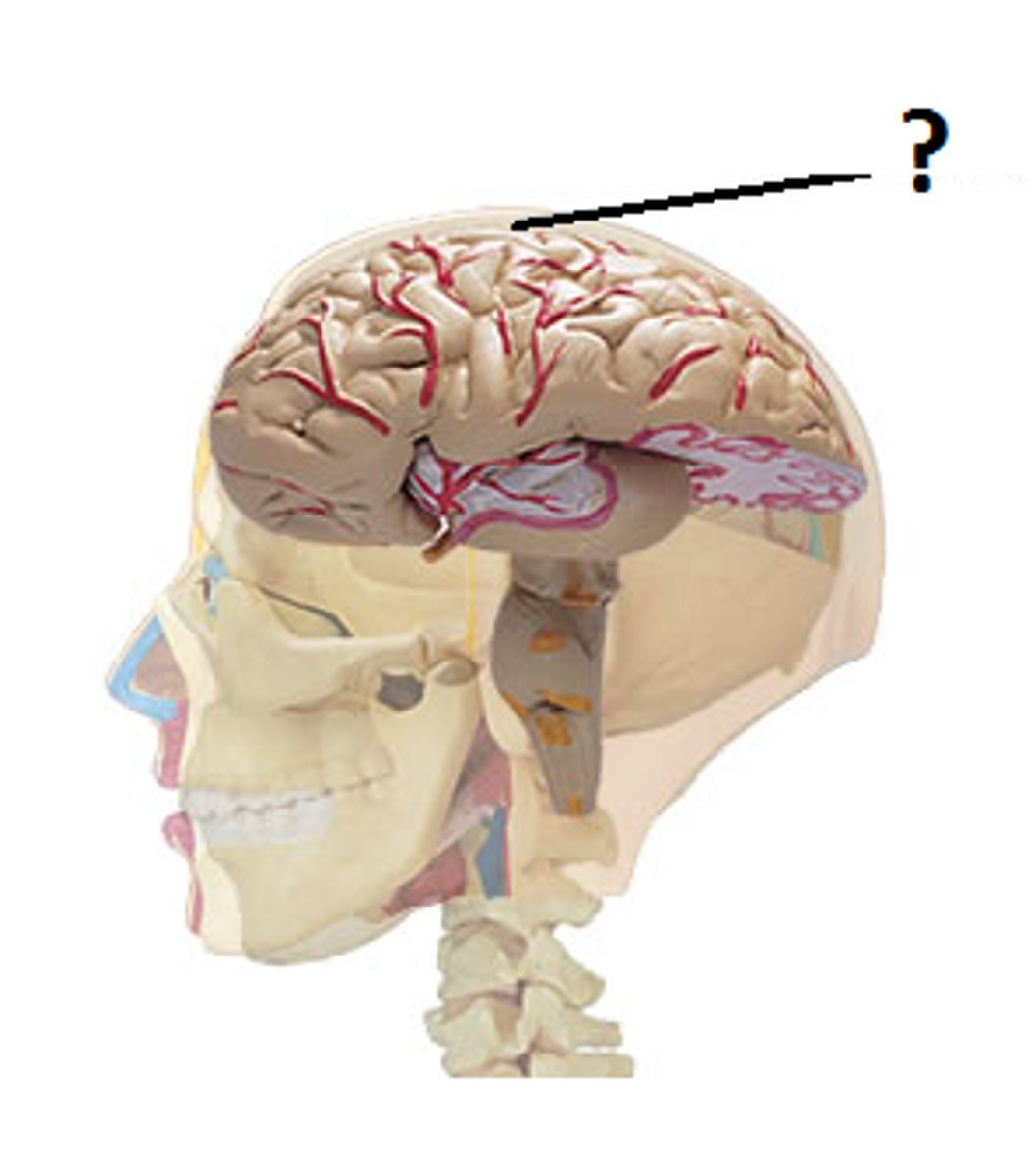
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the forebrain's cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
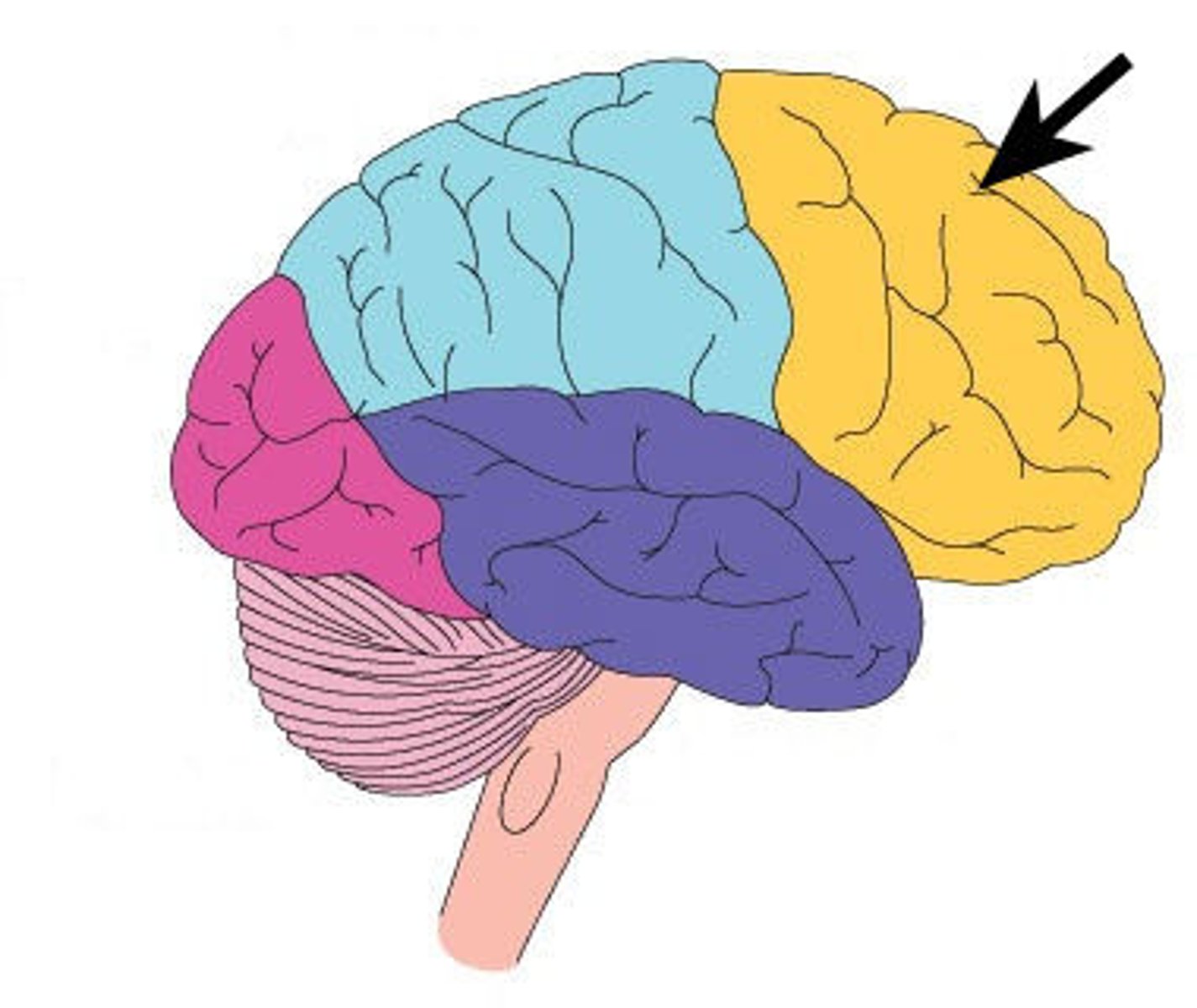
frontal lobe
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead. They enable linguistic processing, muscle movements, higher-order thinking, and executive functioning (such as making plans and judgments).
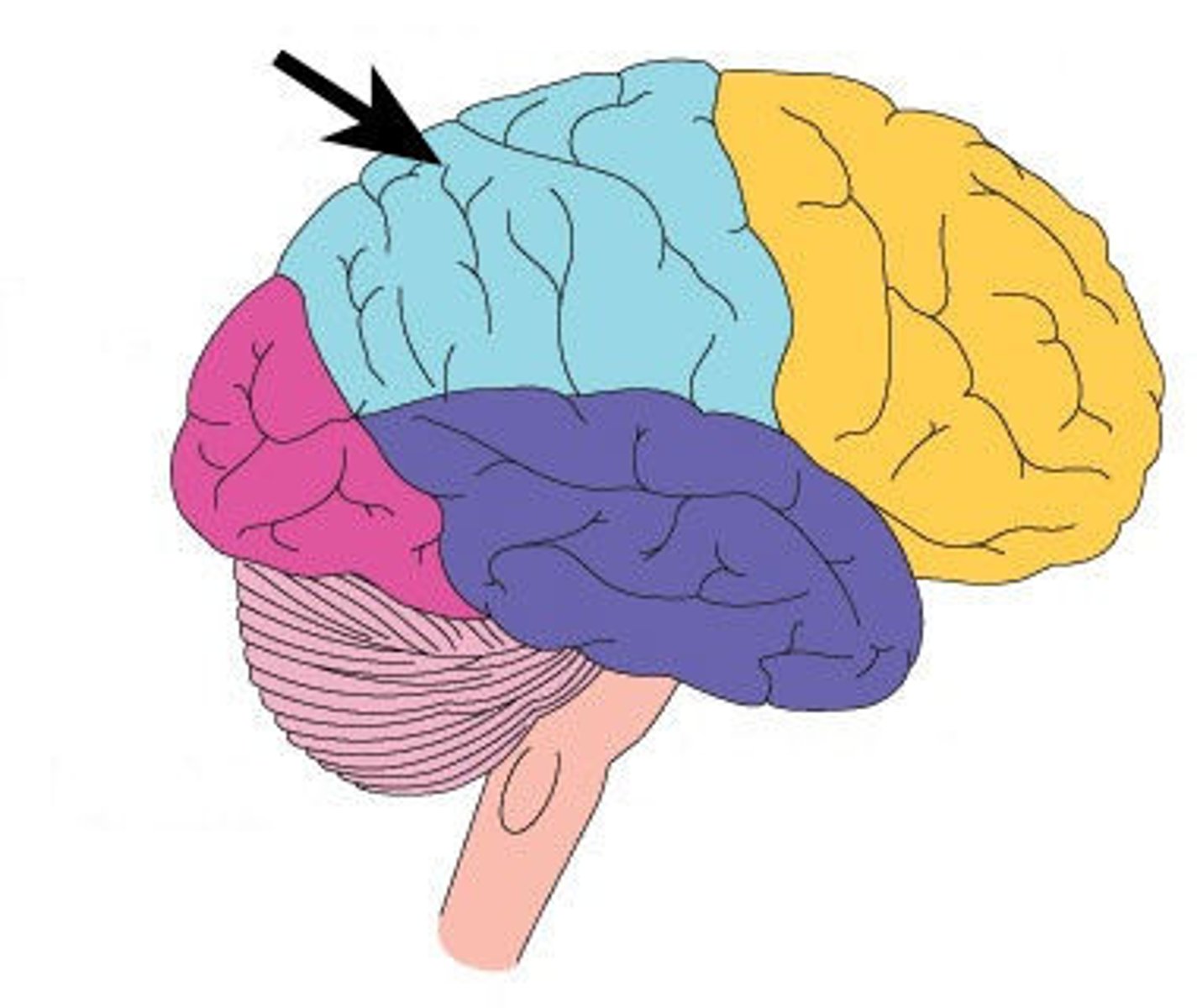
parietal lobe
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; it receives sensory input for touch and body position.
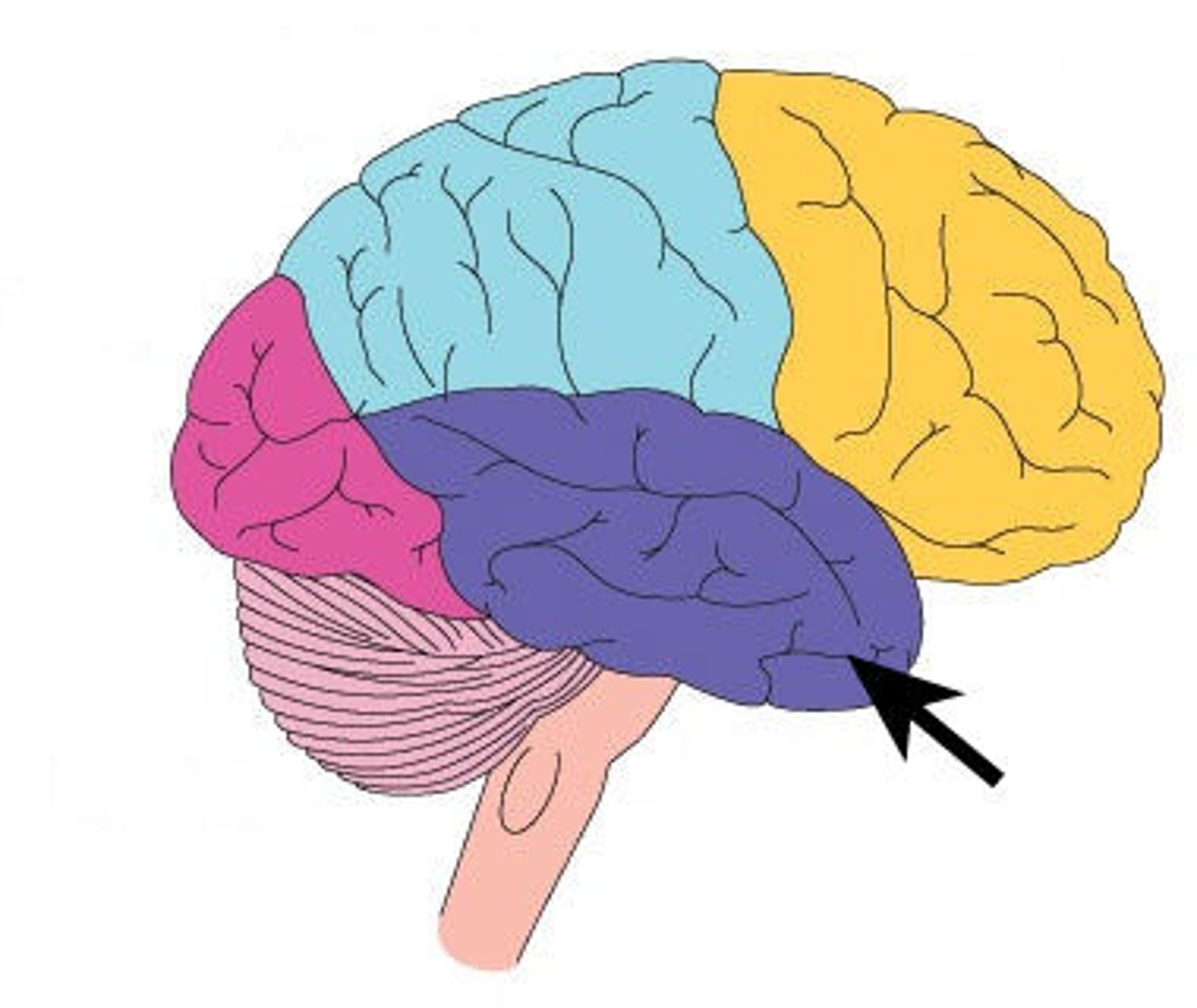
occipital lobe
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; it includes areas that receive information from the visual fields.
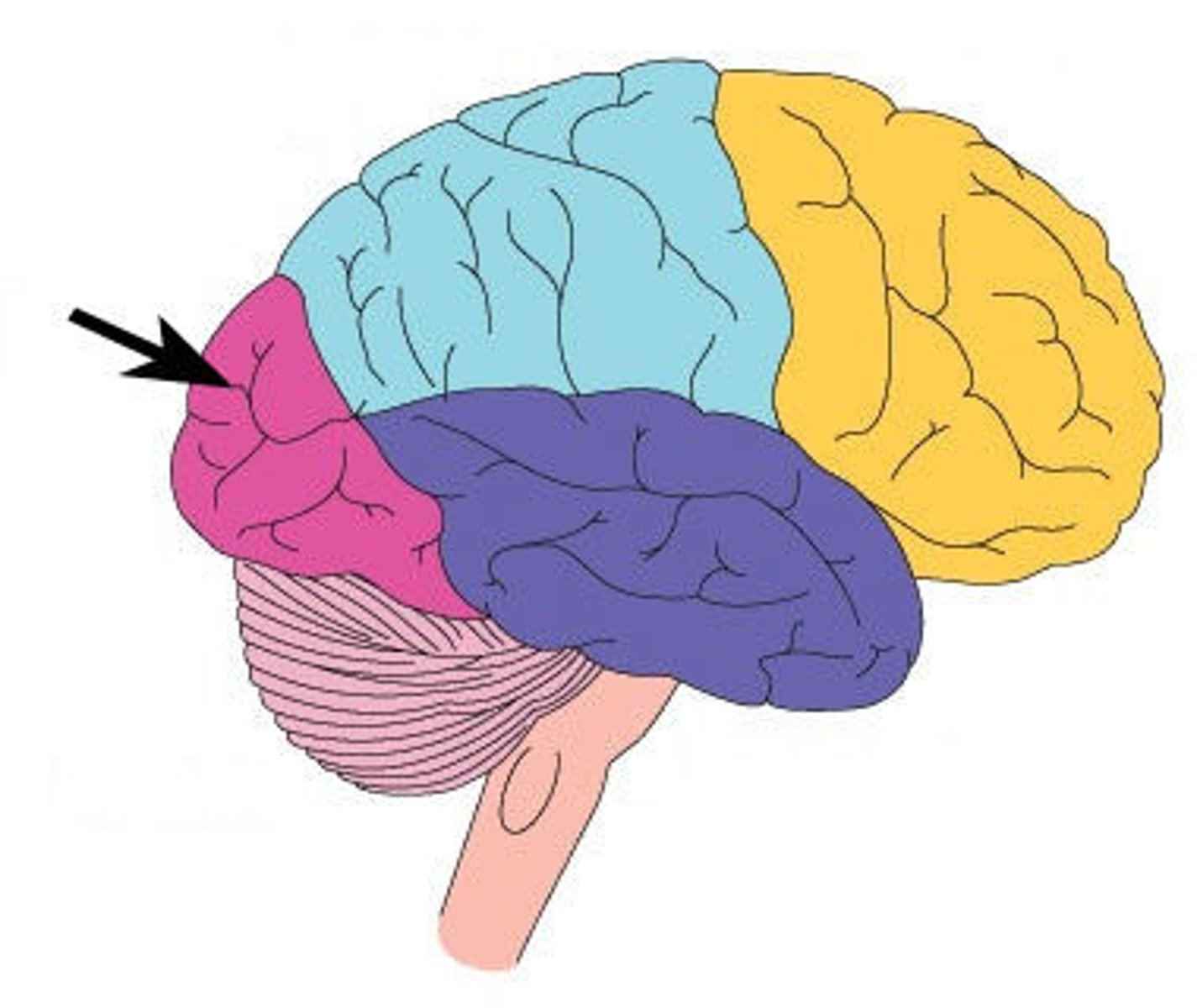
temporal lobe
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; it includes the auditory areas, each of which receives information primarily from the opposite ear. They also enable language processing.
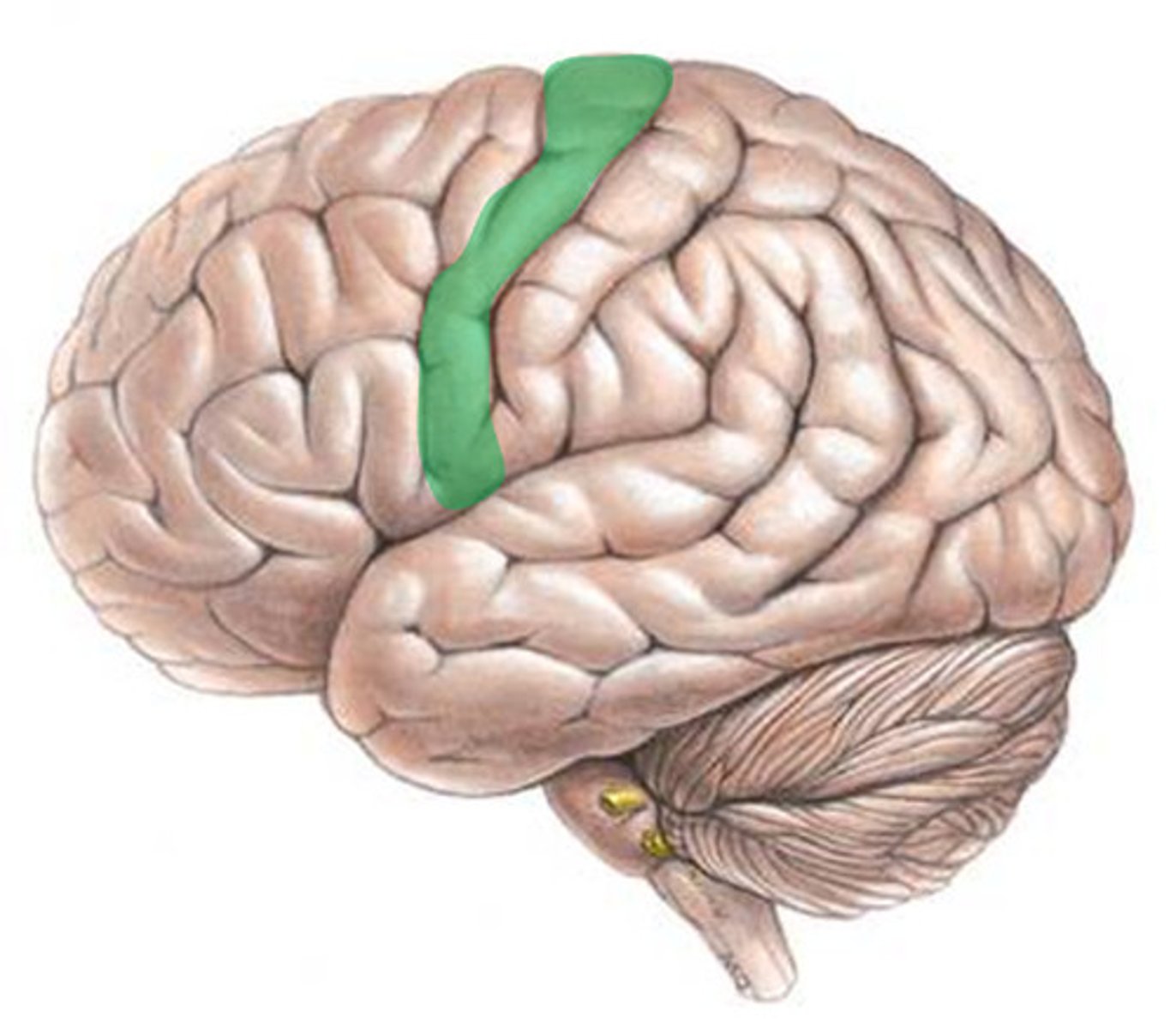
motor cortex
a cerebral cortex area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
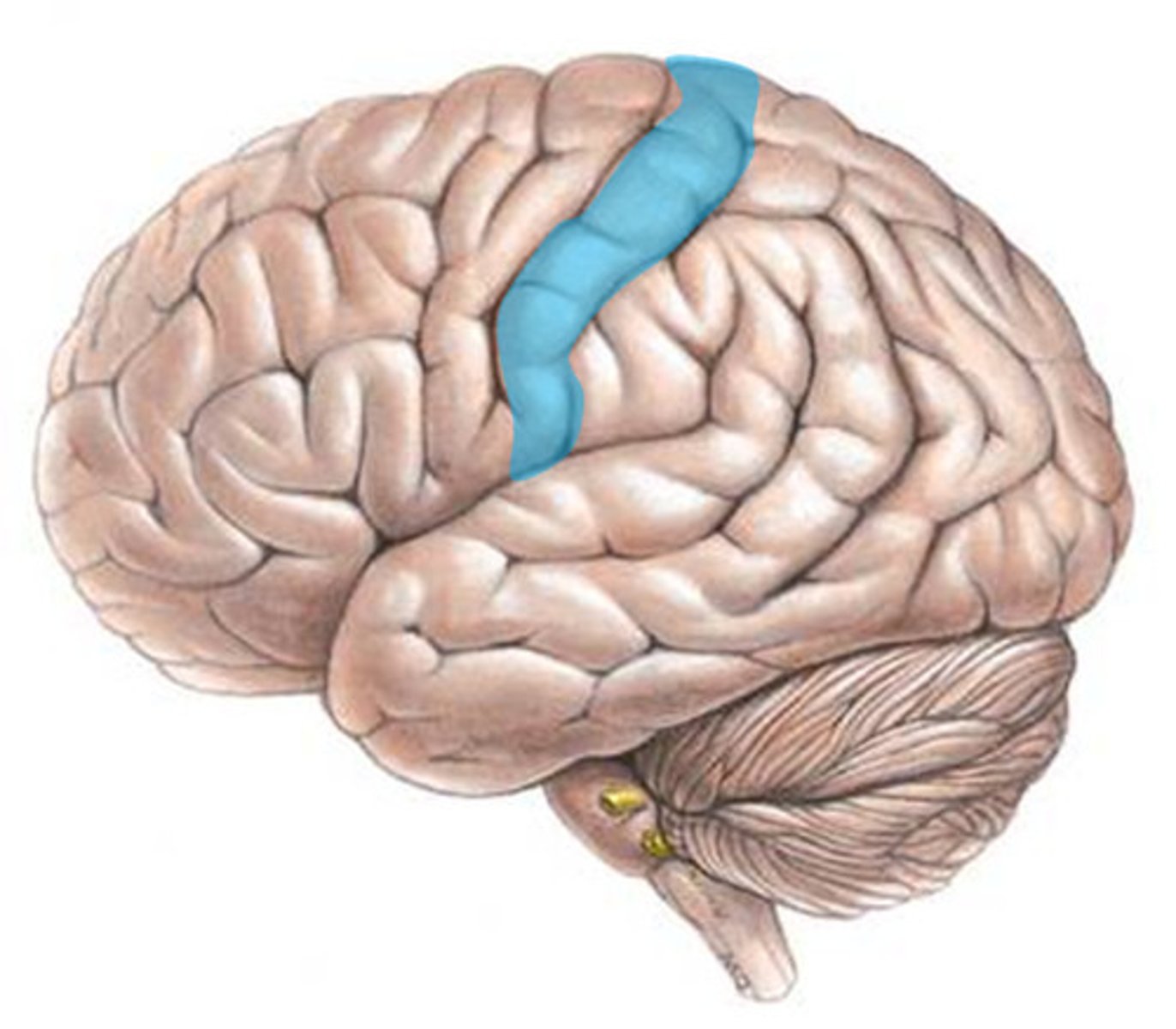
somatosensory cortex
a cerebral cortex area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations.
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them.
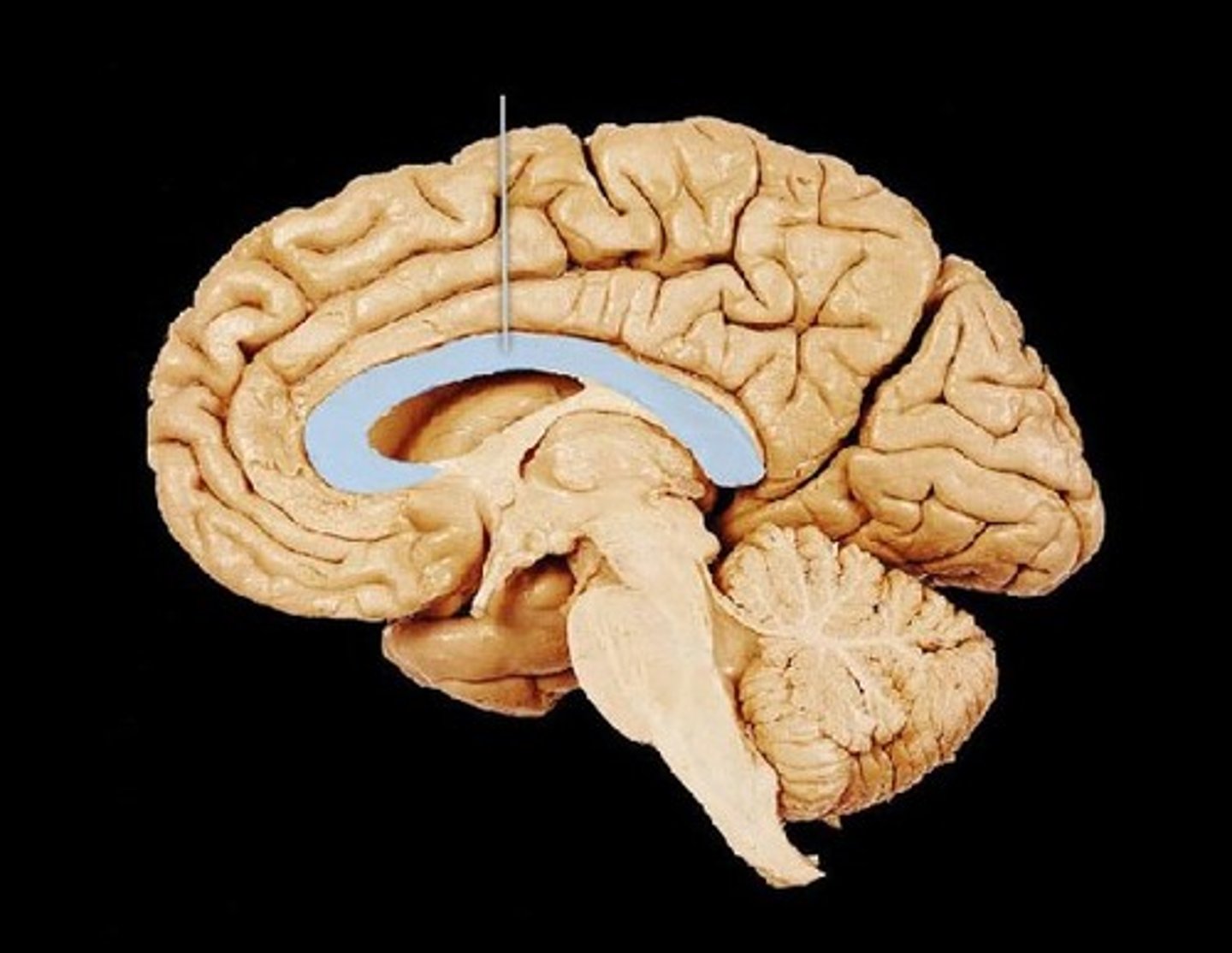
split-brain syndrome
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them.
Consciousness
our subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment.
cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition.
blindsight
a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing it.
parrallel processing
processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously.
sequential processing
processing one aspect of a stimulus or problem at a time; generally used to process new information or to solve difficult problems.
sleep
a periodic, natural loss of consciousness — as distinct from unconsciousness resulting from a coma, general anesthesia, or hibernation.
circadian rhythm
our biological clock; regular bodily rhythms (for example, of temperature and wakefulness) that occur on a 24-hour cycle.
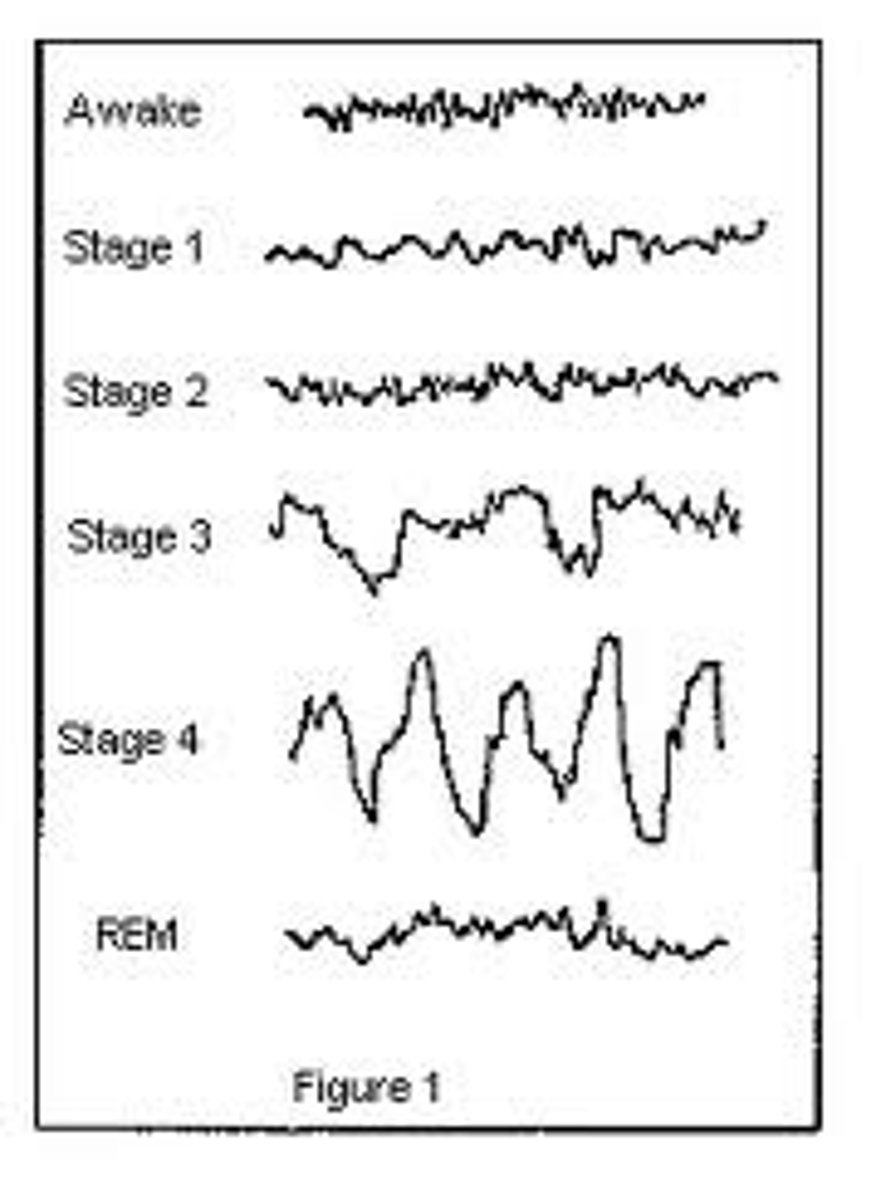
alpha waves
the relatively slow brain waves of a relaxed, awake state.
NREM Sleep
non-rapid eye movement sleep; encompasses all sleep stages except for REM sleep.
hallucination
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus.
hypnagogic/hypnic sensations
bizarre experiences, such as jerking or a feeling of falling or floating weightlessly, while transitioning to sleep.
delta waves
the large, slow brain waves associated with deep sleep.
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
a pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm. In response to light, the _______ adjusts melatonin production, thus modifying our feelings of sleepiness.
isomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep.
narcolepsy
a sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The affected person may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times.
sleep apnea
a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
REM sleep behavior disorder
a sleep disorder in which normal REM paralysis does not occur; instead, twitching, talking, or even kicking or punching may occur, often acting out one's dream.