Chapter 38 Providing Wound Care and Treating Pressure Injuries
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
The nurse clarifies that the first stage of wound healing is:
a. Proliferation.
b. Maturation.
c. Reconstruction.
d. Inflammation.
d. Inflammation
Inflamation is the first stage of wound healing, followed by the proliferation, maturation, and reconstruction stages.
The nurse is taking care of a post-surgical patient and notes the incision is clean and dry, with sutures intact. The nurse further assesses that the wound is healing by:
a. Fourth intention.
b. Third intention.
c. Second intention.
d. First intention.
d. First intention.
A wound with minimal tissue loss, such as a surgical incision, heals by closure, which is first, or primary, intention. Wounds that are not closed heal by either second (secondary) or third (tertiary) intention.
The nurse gives an example of a wound that heals by second (secondary) intention as a:
a. Laceration with edges that do not approximate.
b. Surgical incision closed with staples.
c. Chest wound left open for a closed system.
d. Puncture wound sutured with silk suture.
a. Laceration with edges that do not approximate.
A secondary intention healing occurs when there is a jagged wound whose edges do not approximate.
When the patient complains that he feels he is getting worse because of the increased swelling at his wound site on his leg, the nurse's most helpful response would be that swelling indicates that:
a. An infection is in progress at the wound site.
b. Vessels have dilated and allowed plasma to leak into the wound site.
c. He has lain in one position for such a long time that swelling has occurred.
d. There is probably a deeper injury than what appears on the surface.
b. Vessels have dilated and allowed plasma to leak into the wound site.
As part of the healing process, histamines and prostaglandins have caused small vessels to dilate and leak plasma and electrolytes into the wound site causing swelling, which causes the wound to become reddened and swollen as the phagocytosis cleans up the microorganisms.
The nurse warns the patient that one of the patient's habits has caused the reduction of functional hemoglobin, which limits the hemoglobin's oxygen carrying ability. To improve this situation, the nurse suggests that the patient quit:
a. Drinking.
b. Using marijuana.
c. Smoking cigarettes.
d. Eating excessive fats.
c. Smoking cigarettes.
Smoking reduces the functional hemoglobin which, in turn, reduces the amount of oxygen carried to the cells of the body.
A nurse is assessing a surgical patient for internal hemorrhage, which would be indicated by:
a. Restlessness, rising pulse, and falling blood pressure.
b. Restlessness, falling pulse, and rising blood pressure.
c. Headache, rising pulse, and falling blood pressure.
d. Lethargy, falling pulse, and rising blood pressure.
a. Restlessness, rising pulse, and falling blood pressure.
If hemorrhage occurs, it can lead to hypovolemic shock. Indicators of hemorrhage include restlessness, rising pulse, and falling blood pressure.
The nurse is alert to the indication of possible dehiscence of an abdominal surgical wound, which would be evidenced by:
a. Increased pallor of the surgical site.
b. Complaint of constipation.
c. Excessive gas.
d. Increased serosanguineous drainage from the wound.
d. increased serosanguineous drainage from the wound.
Increase in the serosanguineous drainage from the surgical wound is a common sign of impending dehiscence.
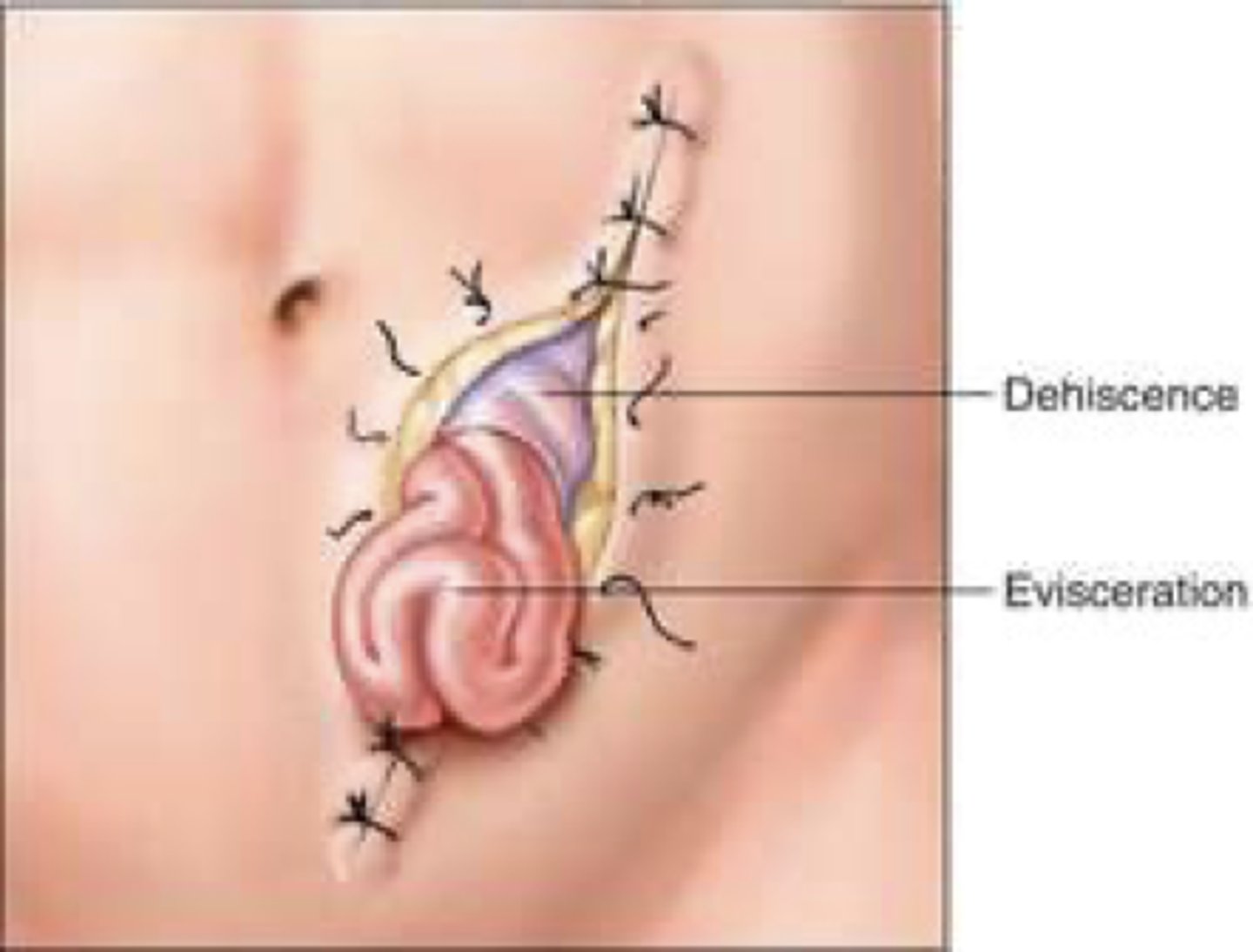
A nurse is ambulating a patient in the hall a few days after abdominal surgery and the patient says, "I think something just let go." The initial intervention by the nurse should be to:
a. Seat the patient in a nearby chair.
b. Assist the patient in a supine position.
c. Ask someone to quickly get an abdominal binder.
d. Instruct the patient to pant to reduce abdominal tension.
b. Assist the patient in a supine position.
The patient is likely experiencing wound dehiscence and should immediately be assisted into a supine position. This eliminates the force of gravity from putting additional stress on the suture line and possibly causing evisceration.
A patient who underwent removal of a breast must be discharged home with a Jackson-Pratt wound drain in place. As the patient demonstrates the procedure for emptying it, the nurse should correct her if she:
a. Uses one alcohol wipe to clean both the spout and the plug.
b. Compresses the device in the hand before closing.
c. Refrains from touching the drainage spout with the hand.
d. Points the device away from herself while opening it.
a. Uses one alcohol wipe to clean both the spout and the plug.
Separate alcohol swabs should be used to clean the spout and the plug.
The nurse chooses a nonadherent dressing to apply to a wound because the nonadherent dressing:
a. Is smaller and less bulky and will absorb more drainage.
b. Retains sterility longer than plain gauze.
c. Allows drainage to seep through the barrier and be absorbed on the other side.
d. Does not require the use of tape to make it adhere to the skin.
c. Allows drainage to seep through the barrier and be absorbed on the other side.
Telfa dressings have a shiny, nonadherent surface; the shiny side is applied to the wound to prevent the dressing from sticking to the skin. The drainage seeps through the barrier and is absorbed on the other side. It does require some sort of adhesive or binder to keep the pad in place.
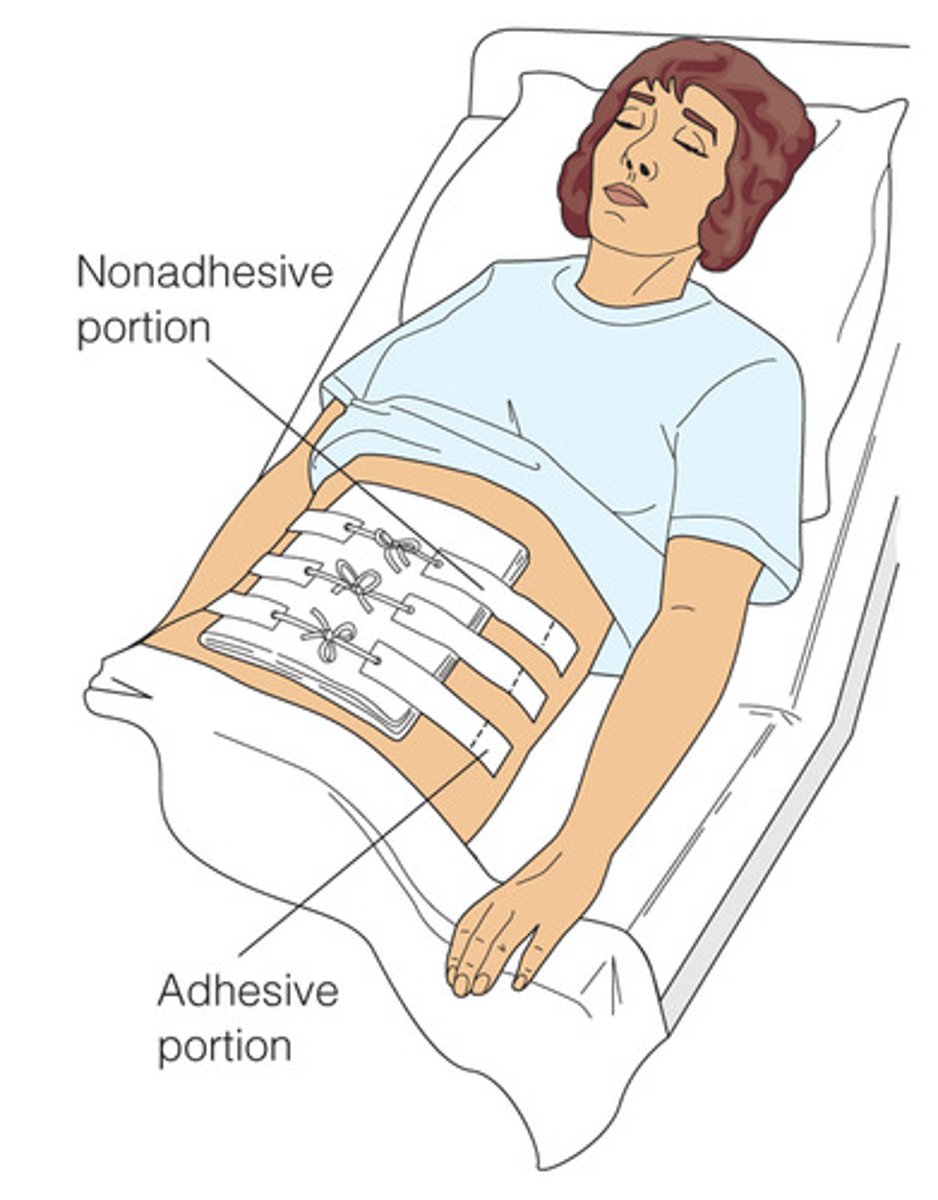
Because the patient with an abdominal dressing requires frequent dressing changes, the abdomen is beginning to show skin irritation from repeated tape removal. The nurse would change the dressing procedure in order to use:
a. Paper tape.
b. Montgomery straps.
c. Karaya paste.
d. Elastic adhesive tape.
b. Montgomery straps.
Montgomery straps allow the dressing to be changed without constantly applying and removing tape.
A nurse caring for a patient with a Stage I pressure ulcer would most appropriately select:
a. Nonocclusive dressing.
b. Exudate absorbing dressing.
c. Hydrocolloid dressing.
d. Thin film dressing.
d. Thin film dressing.
Thin film dressings are used on Stage I ulcers to protect them from shearing forces and to keep them moist.
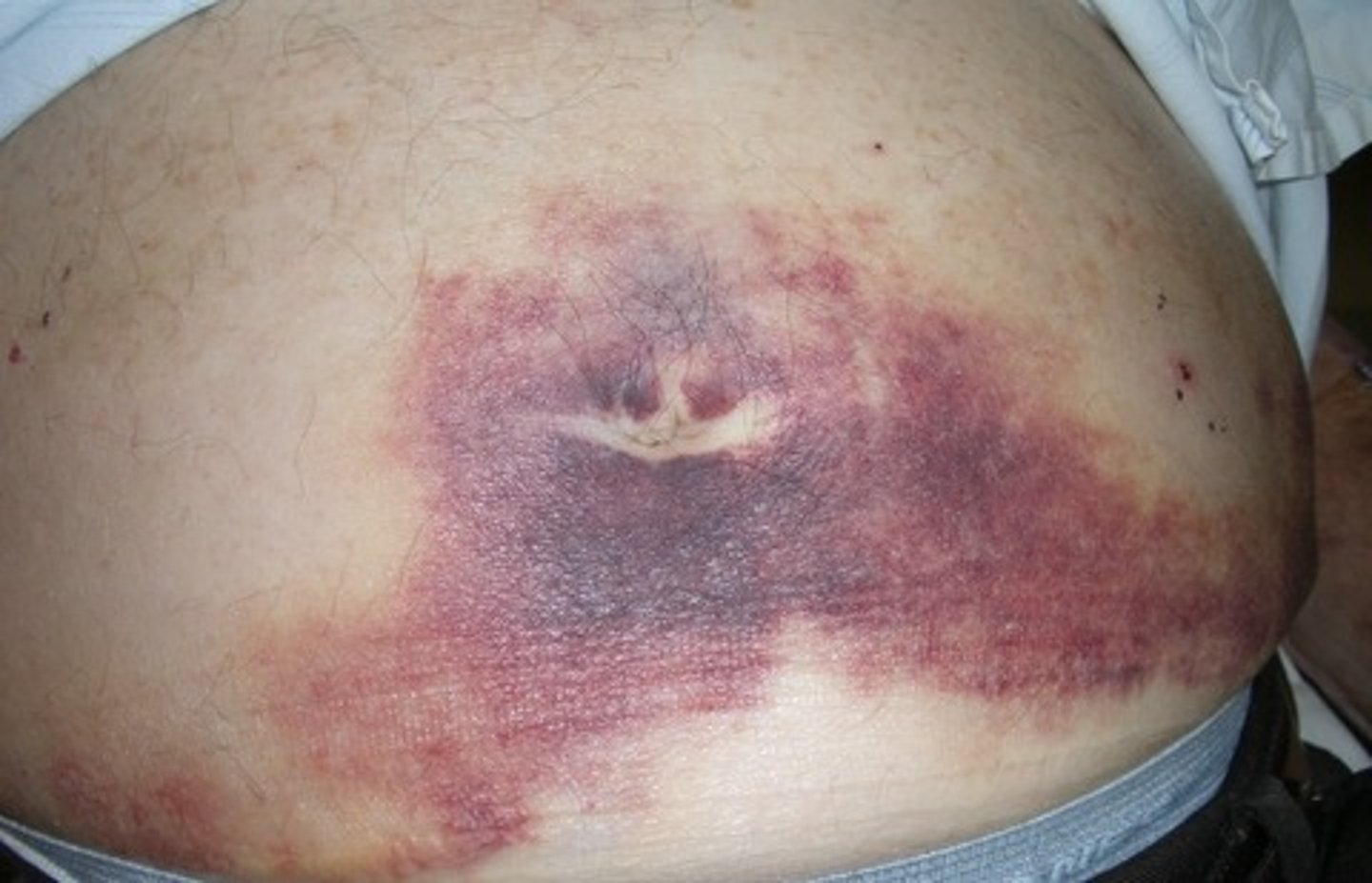
A patient has a pooling of blood under unbroken skin of the hip after a fall. The nurse should document that this patient has a(n):
a. Abrasion.
b. Laceration.
c. Hematoma.
d. Avulsion.
c. Hematoma.
A hematoma is a pooling of blood under unbroken skin. An abrasion is a scraping away of skin tissue. A laceration is a torn, ragged, or mangled wound, and a contusion is a bruise.
The nurse is performing a dry sterile dressing change for an abdominal wound. The nurse should use a swab to clean:
a. From the outer abdomen toward the wound.
b. In a circular motion around the wound circling to the outside.
c. From the left to the right across the wound.
d. Directly over the wound.
b. In a circular motion around the wound circling to the outside.
A circular motion around the wound toward the outside keeps the wound area cleanest.
A patient is due for a wound dressing change for a horizontal lower abdominal incision. In which direction should the nurse pull to remove the tape from the old dressing?
a. From left to right across the abdomen
b. From right to left across the abdomen
c. From the top of the wound to the bottom
d. From each of the four sides toward the wound
d. From each of the four sides toward the wound
The tape should be removed by pulling it off toward the wound. This helps prevent alteration of the wound.
A nurse explains that the major purpose of the use of a hydrocolloid dressing is to:
a. Keep the wound dry.
b. Help destroy microorganisms in an infected wound.
c. Occlude air and promote breakdown of necrotic tissue.
d. Leave the dressing in place for 10 days.
c. Occlude air and promote breakdown of necrotic tissue.
Hydrocolloid dressings are air occlusive dressings used on noninfected wounds that provide a moist environment for wound healing. They can be left in place for up to 7 days.

The nurse changing a wet to dry normal saline dressing for a patient with an ulcer on the heel finds that the old dressing is stuck to the wound bed. The nurse's most beneficial intervention would be to:
a. Add normal saline to loosen it.
b. Pull it off using slow, steady pressure.
c. Leave it in place and cover it with new, wet dressings.
d. Moisten it with povidone iodine.
a. Add normal saline to loosen it.
If the dressing sticks to the wound, normal saline should be added to loosen it. Pulling loose a stuck dressing damages new tissue. Leaving it in place does not promote a clean wound. Povidone iodine must be ordered.
A nurse performing a right eye irrigation will position the patient:
a. Upright with the head hyperextended.
b. Upright with the head tilted toward the left eye.
c. Supine with the head hyperextended.
d. Supine with the head tilted toward the right eye.
d. Supine with the head tilted toward the right eye.
The patient should be positioned supine with the head tilted toward the affected eye. This position allows the irrigation solution to drain away from the eye and not contaminate the other eye.
A nurse removing wound staples would engage the staple puller and squeeze the handles completely and:
a. Pull to the right.
b. Pull outward.
c. Pull to the left.
d. Rotate.
b. Pull outward.
The handles should be squeezed together all the way. This depresses the center of the staple and allows it to be lifted outward from the skin.
The nurse clarifies that a vacuum-assisted closure supports healing of a wound by:
a. Drawing the wound edges together by negative pressure.
b. Interrupting the proliferation of bacteria in the wound.
c. Strengthening the wall of the wound.
d. Making an air occlusive cover for the wound.
a. Drawing the wound edges together by negative pressure.
A vacuum-assisted dressing that is accomplished by a special dressing and vacuum device applies negative pressure to the wound, which increases blood flow, increases oxygenation, and improves the delivery of nutrients to the wound.
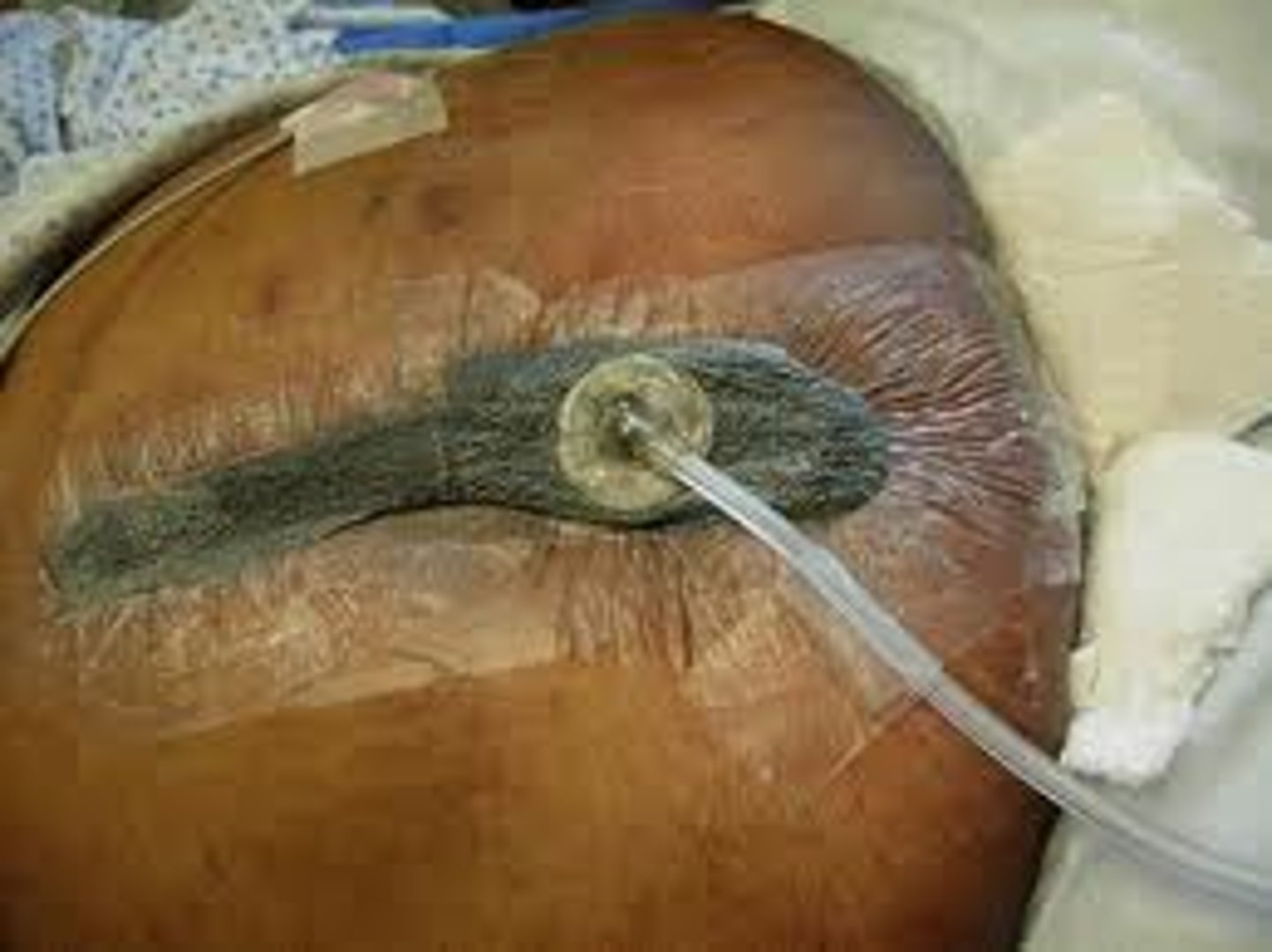
The nurse is aware that the only necrotic wound for which debridement is not recommended is a pressure ulcer located on the:
a. Scapula.
b. Sacrum.
c. Heel.
d. Femoral head.
c. Heel.
Debridement is not recommended for treatment of a pressure ulcer on the heel because of the small amount of tissue available at that site.
____________ drainage contains dead phagocytes, bacteria, and tissue and is thick in consistency.
Purulent
Purulent drainage contains dead phagocytes, bacteria, and tissue and is thick in consistency. It occurs when an infection is present.
Which phase of healing begins about 3 weeks after injury?
a. Proliferation
b. Reconstruction
c. Inflammatory
d. Maturation
d. Maturation
The final stage of healing, maturation, begins about 3 weeks after injury. Scar maturation, or remodeling, is the process of collagen lysis and collagen synthesis by the macrophages to produce the strongest scar tissue possible. The proliferation phase begins on the third or fourth day after injury. The inflammatory phase begins immediately after injury. The reconstruction phase is the same as the proliferation phase.
Platelet aggregation, formation of fibrin, and phagocytosis occur during which phase?
a. Proliferation
b. Healing
c. Maturation
d. Inflammatory
d. Inflammatory
The inflammatory phase begins immediately after injury and lasts about 4 days. Hemostasis, clot formation, and phagocytosis occur during the inflammatory phase, not the proliferation or maturation phases. Healing is not a phase of wound healing.
An abdominal wound left open for drainage and then later closed is an example of healing by
a. Tertiary intention.
b. Fourth intention.
c. First intention.
d. Second intention.
a. Tertiary intention.
Tertiary intention is known as delayed or secondary closure and occurs when there is delayed suturing of a wound. Healing by second intention occurs when the wound is left open and fills with scar tissue. Fourth intention is not a type of wound closure. Healing by first intention occurs when a wound has little tissue loss.
Which factor will promote wound healing?
a. Steroids
b. Increased adipose tissue
c. Added protein
d. Limitation of activity
c. Added protein
A diet rich in protein is needed for wound healing.
The microorganism most frequently present in wound infections is
a. Proteus vulgaris.
b. Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
c. Staphylococcus aureus.
d. Escherichia coli.
c. Staphylococcus aureus.
The microorganism most frequently present in wound infections is Staphylococcus aureus.
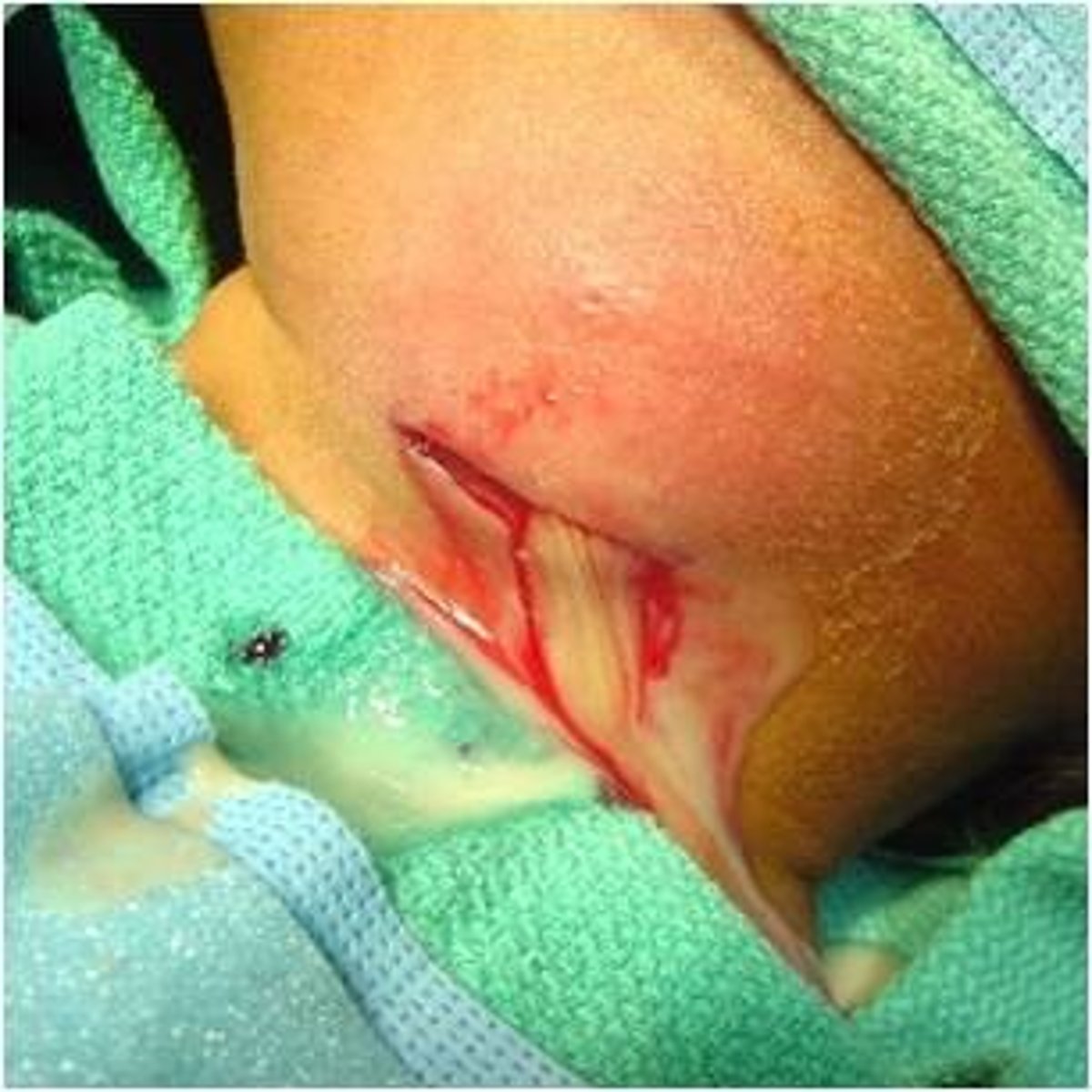
A nurse finds an increased amount of serosanguineous drainage into the patient's abdominal wound dressing and the patient reports "something has given way." What has likely occurred?
a. Evisceration
b. Dehiscence
c. Fistula
d. Abscess
b. Dehiscence
Dehiscence is the spontaneous opening of an incision. Evisceration is the protrusion of an internal organ through the incision.
Which type of debridement uses the body's enzymes to break down nonviable tissue in the uninfected wound?
a. Enzymatic
b. Chemical
c. Autolytic
d. Sharp
c. Autolytic
Autolytic debridement is a longer process that uses the body's enzymes to break down nonviable tissue in the wound. It is best used on small, uninfected wounds.
What nursing diagnosis is applicable for the goal/expected outcome Pain will resolve when infection is cleared?
a. Acute pain related to an infected wound
b. Acute pain related to a healed wound
c. Impaired skin integrity related to trauma
d. Anxiety related to the need to perform wound care
a. Acute pain related to an infected wound
Acute pain related to an infected wound is the most applicable to the stated goal/expected outcome.
Which factors affect wound healing in the older adult? (Select all that apply.)
a. Atherosclerosis
b. Improved immune function
c. Reduced liver function
d. Peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
a. Atherosclerosis
c. Reduced liver function
d. Peripheral vascular disease (PVD)
Your patient has had abdominal surgery for a ruptured appendix and requires postoperative care and dressing changes. The wound has been left open, and irrigations are ordered. When irrigating a wound, it is most important to:
1. Irrigate slowly to prevent discomfort.
2. Ensure the solution reaches the depths of the wound.
3. Prevent wetting of the bed and covers.
4. Use vigorous irrigation flow from the syringe.
2. Ensure the solution reaches the depths of the wound.
If wound irrigation is not performed correctly, it increases the risk of severe peritonitis in this type of wound management because the exudate is not removed effectively.
If a wound appears infected, you should:
1. Cleanse it with an antiseptic solution.
2. Obtain an order for a culture to be performed.
3. Apply an antibiotic ointment.
4. Change the dressing every 2 hours.
2. Obtain an order for a culture to be performed.
In order to ensure the correct treatment is prescribed, it is important to obtain a wound culture prior to the start of any type of antimicrobial agent. This also minimizes the risk of the patient developing a multidrug resistant organism.
The assessment of the wound indicates that healing is occurring when:
1. The center tissue is white.
2. Bleeding has stopped.
3. There is no further drainage from the wound.
4. Pink granulation tissue is visible.
4. Pink granulation tissue is visible.
Newly formed, healthy tissue is typically pink, regardless of skin tone; all other options are signs of infection.
When caring for a pressure injury, you know that:
1. Eschar usually must be removed before the wound will heal.
2. Pink granulation tissue should be cleansed with antiseptic solution.
3. Keeping the wound dry and covered will aid healing.
4. Heat treatments hurt new tissue and slow healing.
1. Eschar usually must be removed before the wound will heal.
By allowing dead tissue to remain in the wound bed, it increases the risk of infection and minimizes the ability of the tissue to heal, because the nutrients needed for healing to take place can be significantly impaired if the wound bed is not kept clean.
Proper technique for removal of sutures is to:
1. Clip the suture below the knot.
2. Assure the patient that suture removal does not hurt.
3. Refrain from pulling an exposed suture through the wound.
4. Apply a Steri-Strip before removing the suture.
3. Refrain from pulling an exposed suture through the wound.
If the exposed sutures have not been cleansed prior to their removal, and if poor technique is used to remove them, it can introduce pathogenic microorganisms into and along the suture line.
Cold packs applied during the first 24 hours after injury decrease swelling by:
1. Increasing vasodilation so that blood flow will carry away excess fluid.
2. Causing vasoconstriction and decreasing bleeding from damaged blood vessels.
3. Decreasing circulating blood volume so that swelling cannot occur.
4. Dulling pain and thereby reducing cellular enzyme release.
2. Causing vasoconstriction and decreasing bleeding from damaged blood vessels.
If the blood and other fluids are restricted from being able to get to the injury, it can aid in minimizing pain and significant swelling and possible long-term complications.
Your patient with a leg wound asks about NPWT. You answer their question based on your knowledge that NPWT:
1. Decreases cellular proliferation.
2. Is contraindicated in infected wounds.
3. Can sometimes speed wound healing.
4. Minimizes mechanical stretch of cells.
3. Can sometimes speed wound healing.
NPWT has been shown to speed healing in some wounds. It increases cellular proliferation, is useful in infected wounds, and assists with mechanical stretch of cells, which promotes development of new granulation tissue.