OCR A Level Biology - Cell Structure
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
DESCRIPTION:
Similar to RER but with no ribosomes. (System of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space called cisternae. )
FUNCTION:
-Synthesises and processes lipids.
SER contains enzymes that catalyse reactions involved with lipid metabolism such as:
-synthesis of cholestrol
What is rRNA made by
Nucleolus
Prokaryotic cells
-Extremely small (less than 2 um diameter)
-DNA is circular
-No nucleus (DNA is free in the cytoplasm)
-Cell wall is made of a polysaccharide but not cellulose or chitin
-Few organelles and no membrane bound organelles eg.mitochondria
Flagella made of the protein flagellin, arranged in a helix
Small ribosomes
Example: E. Coli bacteria
- has 70s ribosomes
Prokaryotic cell organisms
- cell wall
-cell surface membrane
-mesosomes
-flagella
-bacterial chromosomes
-plasmids
- ribosomes
-glycogen granules
-lipid droplets
Cell wall details and function in prokaryotic cell
wall composed of a mix of carbohydrates and polypeptides . The material is murein or peptidoglycan.
provides rigidity and maintains the shape of the cell.
Provides physical protection against mechanical danger .
Prevents the bursting of cell.
Cell surface membrane details and function - details and structure (prokaryotes )
Details: composed of a phospholipid Bilayer and proteins.
Function: to control the entry or exit of small molecules into the cell.
Mesosomes (Prokaryotes)- details and function
Details-
- a type of unfolding of the cell membrane
.
Function- generates ATP via chemiosmosis , site of respiration.
Flagella details and function (prokaryotes)
Function- much simpler then ones found in eukaryotes. Their role is to propel in organisms through the environment by moving in a clockwise or anti-clockwise manner .
Plasmids details and function
Details- short loops of DNA which only carry a few genes for special metabolical processes
Function- vectors , In genetic engineering
Capsule
The capsule is a slimy layer made of protein.
This prevents the bacteria from desiccating (drying out) and protects the bacteria against the host's immune system.
Lipid droplets ( prokaryotes )
prokaryotes store energy as lipids and glycogen. The glycogen a carbohydrate is stored in a granules and the lipid, fat or oil , is stored as a droplet
Function- food storage
Eukaryotic cells
Larger cells (about 10-199 um diameter)
DNA is linear
Nucleus present (DNA inside)
No cell wall in animals, cellulose cell wall in plants, or chitin in fungi
Many organelles
Flagella made of microtubule proteins
Larger ribosome
Animal cell (11)
Plasma membrane
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Lysosomes
Ribosome
Nuclear envelope
Golgi apparatus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondrion
Plant cell (14)
All the same organelles as animal cells par lysosomes and plus a few extra:
Cell wall with plasmodesmata
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Description of Plasma membrane
The membrane found on the surface of animal cells and inside the cell wall of plant cells and prokaryotic cells. It's made mainly of lipids and proteins.
Function of Plasma membrane
Regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. Also has receptor molecules of which allow it to respond to chemicals like hormones
What are Plasma membranes made of?
It's made mainly of lipids and proteins.
description of Cell wall
Rigid structure that surrounds plant cells, it's is made mainly of the carbohydrate cellulose
function of cell wall
Supports plant cells
what are cell walls made of?
made mainly of the carbohydrate cellulose
structure of Nucleus
large organelle surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double membrane) which contains many pores.
The nucleus contains chromatin (which is made from DNA and proteins) and the nucleolus
The nucleus contains a cytoplasm like substance called nucleoplasm
function of nucleus
Controls cells activities (by controlling the transcription of DNA)
DNA contains instructions to make proteins.
Pores allow substances (eg. RNA) to move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm,
(nuclear pores allows substances to exit/enter)the nucleolus makes ribosomes.
what is the nucleus composed of?
the nucleolus
the nuclear envelope
chromatin
what is chromatin composed of?:
DNA and histone proteins
what is rRNA made by?
rRNA is made by the nucleolus
what are sections of DNA that codes for a polypeptide?
gene
structure of Lysosome
round organelle surrounded by a membrane, with no clear internal structure.
function of Lysosome
lysosomes contain and isolate digestive enzymes - they are needed to prevent the rest of the cell being digested by these enzymes .
Lysosomes Can be used to digest invading cells or break down worn out components of the cell and return the digested components to the cell to reuse.
lysosomes are vesicles filled with _______ enzymes used to ________ unwanted material
hydrolytic (digestive)
-engulf
structure of Ribosome
in cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
made up of proteins and RNA.
A ribosome is composed of two subunits that combine to carry out protein synthesis .
It's not surrounded by a membrane.
80S- large ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells
70S- smaller ribosome found in prokaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Function of Ribosome
the site of protein synthesis .
what do ribosomes contain?
Contains proteins and RNA.
structure of Rough endoplasmic reticulum
system of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space called cisternae.
The surface is covered with ribosomes.
the rough endoplasmic reticulum is made up of flattened sacs called...
cisternae
the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane is continuous with the...
nuclear membrane
what is the rough endoplasmic reticulum coated with?
-the rough endoplasmic reticulum coated with ribosomes which is responsible for protein synthesis ( provides a large surface area for ribosomes.
-RER is the Intracellular transport system
function of Rough endoplasmic reticulum
folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes . ( protein synthesis)
structure of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
-A system of membranes, containing fluid-filled cavities (cisternae) which are continuous with the nuclear membrane.
- similar to RER but Has no ribosomes on its surface.
function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
lipid synthesis
the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for _______ synthesis
lipid
Vesicle
DESCRIPTION:
A small fluid-filled sac in the cytoplasm, surrounded by a membrane
FUNCTION:
Transports substances in and out of the cell (via the plasma membrane) and between organelles.
Some are formed by the Golgi apparatus or the endoplasmic reticulum, while others are formed at the cell surface.
Golgi apparatus structure
DESCRIPTION:
A group of fluid filled, membrane bounded flattened sacs. Vesicles are often seen at the edges.
Golgi apparatus function
- to chemically process proteins
-to package proteins for secretion
-to produce glycoproteins
-to transport and store lipids
-to form lysosomes
Mitochondrion structure and function
STRUCTURE:
Usually oval shaped. Is a double membrane bound structure - the inner membrane is called the cristae. Inside is called the mitochondrian matrix which contains enzymes involved in respiration.
Contain 70s ribosome .
FUNCTION:
-Site of aerobic respiration
-therefore its a site of ATP production.
They're found in large numbers in cells that are very active and require a lot of energy.
There is DNA to code for enzymes needed in respiration.
In mitochondria why is the inner membrane folded
To increase its surface area
Why do mitochondria have different shapes
As it depends on the way the slide is produced
what does the inner mitochondria membrane folds to make structures called?:
cristae
what does cristae increase the surface area for
These increase the surface area of the membrane and help make the mitochondrion more efficient
Chloroplast
DESCRIPTION:
small, flattened structure found in plant cells.
Chloroplasts are surrounded by a double membrane known as the chloroplast envelope
Inside is a colour matrix - the stroma
Floating in the stroma are thylakoids, these stack together to form a Granum. Grana can be interconnected by tubular extensions called intergranal lamella .
also present are starch grains which act as temporary stores for the carbohydrates formed during photosynthesis.
FUNCTION:
The site where photosynthesis takes place. Some parts of photosynthesis happen in the grana and other parts happen in the stroma (a thick fluid found in chloroplasts)
Centriole
DESCRIPTION:
Small, hollow cylinders made of microtubules (tiny protein cylinders). Found in animal cells but only some plant cells.
Centrioles arise from a region of the cytoplasm called the centrosome and consist of 2 hollow cylinders .
FUNCTION:
Involved in the separation of chromosomes during cell division. - at cell division they migrate to opposite poles of the cell and produce the microtubules of the spindles that pull chromosomes apart .
What happens during cell division to the centrioles
The centrioles replicate
Cilia structure and function
STRUCTURE:
Small, hair like structures found on the surface membrane of sine animal cells. In cross-section they have an outer membrane and a ring of nine pairs with protein microtubules inside with two microtubules in the middle.
mobile cilia help move substances in a sweeping motion.
The microtubules allow the cilia to move. This movement is used by the cell to move substances along the cell surface.
stationary cilia are important in sensory organs such as the nose
cilia and unudulipodia are used for____
the movement of mucus
Flagellum
DESCRIPTION:
On eukaryotic cells are like cilia but longer. They stick out from the cell surface and are surrounded by the plasma membrane.
Made of a spiral protein called flagellin attached to a spinning protein disc.
FUNCTION:
The microtubules contract to make flagellum move. Flagella are used like outboard motors to propel cells forward (eg. when a sperm cell swims)
- The flagella rotates to enable the bacteria to move
Protein production
proteins made at ribosomes
ribosomes on Rough ER make proteins that are excreted or attached to the cell membrane. The free ribosomes in the cytoplasm make proteins that stay in the cytoplasm.
new proteins produced at the rough ER are folded and processed in the rough ER
then they're transported to the Golgi apparatus in vesicles
at the Golgi apparatus the proteins undergo further processing
the proteins enter more vesicles to be transported around the cell e.g. glycoproteins (found in mucus) move to the cell surface and are secreted.
Cytoskeleton structure and function
DESCRIPTION:
Network of protein threads. In eukaryotic cells the protein threads are arranged as microfilaments (small solid strands) and microtubules (tiny protein cylinders)
FUNCTION:
the microfilaments and microtubules support the cells organelles keeping them in position
strengthen the cell and maintain its shape
responsible for movement of materials within the cell. Eg. The movement of chromosomes when they separate during cell division depends on contraction in microtubules in the spindle.
moved organelles around cytoplasm (also moves cytoplasm , e.g: during phagocytosis, cytokinesis when cell divides). movement requires energy in the form of ATP.
the proteins of the cytoskeleton can also cause the cell to move. E.g. the movement if cilia and flagella is caused by the cytoskeletal protein filaments that run through them. So in the case if single cells that have a flagellum (eg.sperm cells) the cytoskeleton propels the whole cell
The cytoskeleton diagram
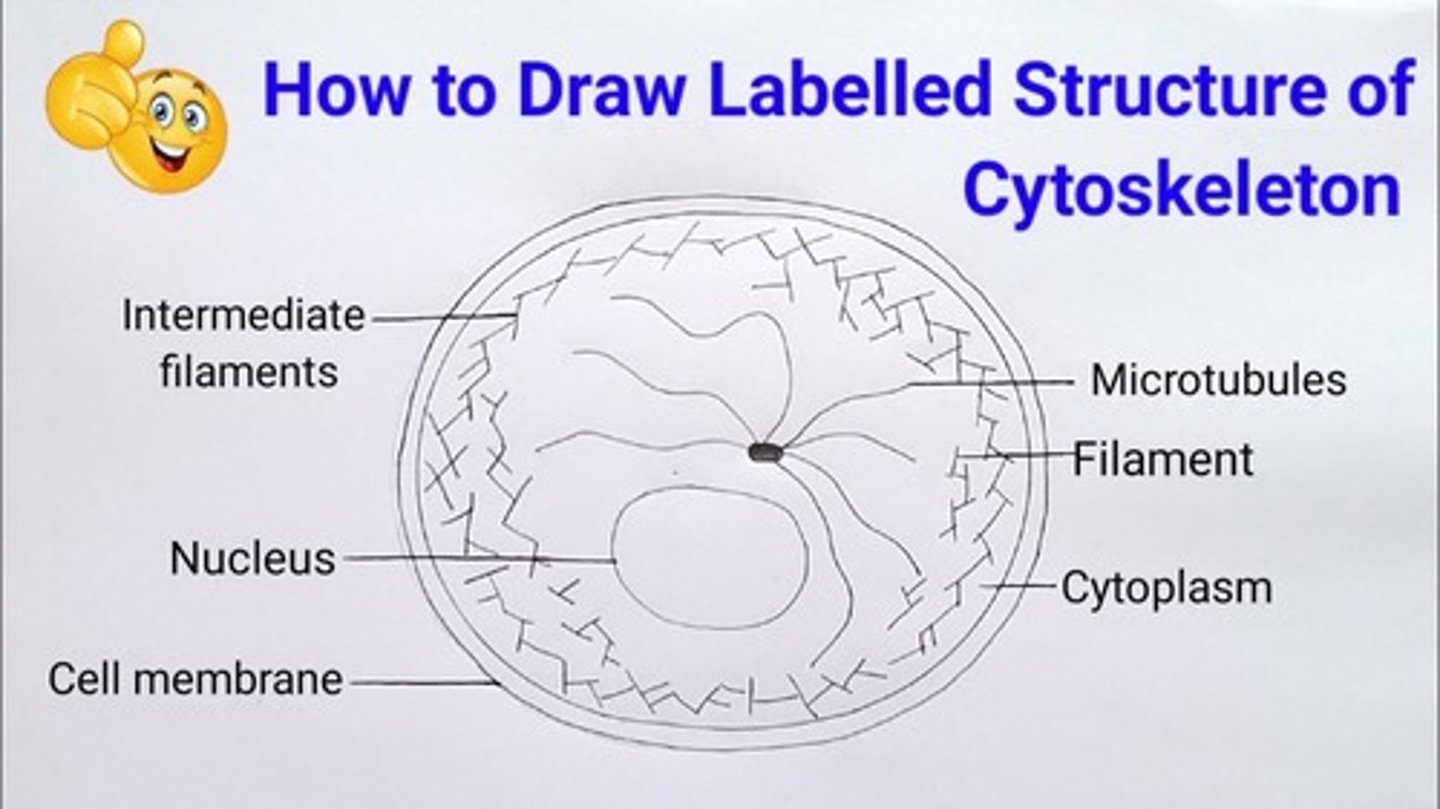
what are three fibres the cytoskeleton is composed of
- actin filament
-intermediate filament
-microtubes
plant cell
Contains:
- Cellular cell wall
-plasmodesma (single) plasmodesmata( plural)
- vacuole membrane
-permanent vacuole
-Golgi body
-SER
-chloroplasts
-mitochondria/ mitochondrion
- ribosomes
-protein filaments
-microtubules
-plasma membrane
Vacuole
-The vacuole is a large fluid filled sac
- it is surrounded by a membrane called the Tonoplast
-it functions as a storage site and provides support for plant cells by creating a pressure potential through osmosis .
the vacuole is surrounded by a membrane called the________ only plants cell have a __________ vacuole
tonoplast
permanent vacuole
Magnification
How much bigger the image is than the specimen
Magnification = image size/actual size
What is the difference between magnification and resolution
MAGNIFICATION - increasing the size of an image. Up until the limit of resolution, an increase in magnification = an increase in detail.
RESOLUTION = minimum distance apart that two objects can be for them to appear as separate items.
Resolution
the ability to distinguish two objects
Light microscopes
-use light
-have a lower resolution than electron microscopes due to the long wavelength of Light- max.resolution of about 0.2 micrometers.
-max.useful magnification of a light microscope is about x1500
-living samples can be examined
- a colour image is obtained
- has a long wavelength of beam
- max.resolution of about 0.2 micrometers
-maximum useful magnification - 1500 x
Why use stains?- contrast
2D or 3D image- 2D
Pros of Light Microscope
-Cheap
-observes living or dead specimens,
-no vacuum required,
-observed in natural colour or stain
-portable, easy to transport
- has a 1500 x magnification
Cons of light microscope
- has a low/ lower resolution compared to electron microscopes
Electron microscope
Use electrons instead of light to form an image. They have a higher resolution than light microscopes, so give more detailed images. There are two kinds of electron microscopes.
Pros of electron microscope
-can magnify effectively to about 500,000 times the size of the actual specimen
Cons of electron microscope
Expensive and hard to use
-there is no O2 in vacuums ( which is what electron microscopes use) so living cells can't survive ,therefore are dead cells.
-no colour visible
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
high magnification and resolution, but they can only be used on thin specimens.
electrons pass through the specimen to create an image
Denser parts of the specimen absorb more electrons, which makes them look dark on the image you end up with.
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Scan of beam of electrons across the specimen. This knocks off electrons from the specimen, which are gathered in the cathode ray tube to form an image. The images produced show the surface of the specimen and can be 3-D. But they give lower resolution images and TEMs.
- high magnification and resolution
- electrons bounce off the surface of the specimen to create an image (3D image)
Staining samples for light microscopes
Common stains include methylene blue and eosin.
The stain is taken up by some parts of the object more than others-the contrast mix different part show up.
Different stains is to make different things show up. For example, eosin is used to stain cell cytoplasms. Methylene blue stains DNA.
More than one stain can be used once.
Staining samples for electron microscopes
Objects are dipped in a solution of heavy metals (like lead). The metal ions scatter the electrons, again creating contrast-some parts of the object show up darker than others.
Dry mount (preparing a slide)
-Take a thin sample your specimen so light can get through it easily
-use tweezers to pick up your specimen and put it in the middle of the clean the slide.
-Pop a coverslip (a square of tin, transparent plastic or glass) on top.
Wet Mount
-Start by putting a small drop of water onto the slide. Then use tweezers to place the specimen on top of the water drop.
-To put the cover slip on, stand the slip up right on the slide, next to the water droplet. Then carefully tilt and lower it to so that covers the specimen. Try not to get any air bubbles under there- they'll obstruct the view of the specimen.
-once the coverslip is in position, you can add a stain. Put a drop of stain next to one edge of the coverslip. Then put a bit of paper towel next to the opposite edge. The stain will get drawn under the slip, across the specimen.
How to use a light microscope to view a specimen
Start by clipping the slide containing the specimen onto the stage
Select the lowest power of objective lens
Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the objective lens down to just above the slide.
Look down the eyepiece and adjust the focus with the fine adjustment knob, until you get a clear image
If you need to see the side with greater magnification swap to a higher powered objective lens and refocus
Scanning (SEM) microscope
3D views of specimens - used to view external surfaces of specimens
- wavelength of beam- short
- resolution (units)- 1-20 nano meters
Maximum useful magnification - 1 million x
Why use stains? - contrast
- example of stain?- metal
-living or non living specimen observed - non living
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the internal structure of thinly sectioned specimens.
-wavelength of beam - 0.04
-resolution (units)- 0.002 micrometers
-maximum useful magnification- x 1 million
Why use stains- contrast
-examples of stain- metal
Living or non living specimen observed- non living
2D or 3d image- 3D