final exam review new stuff
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
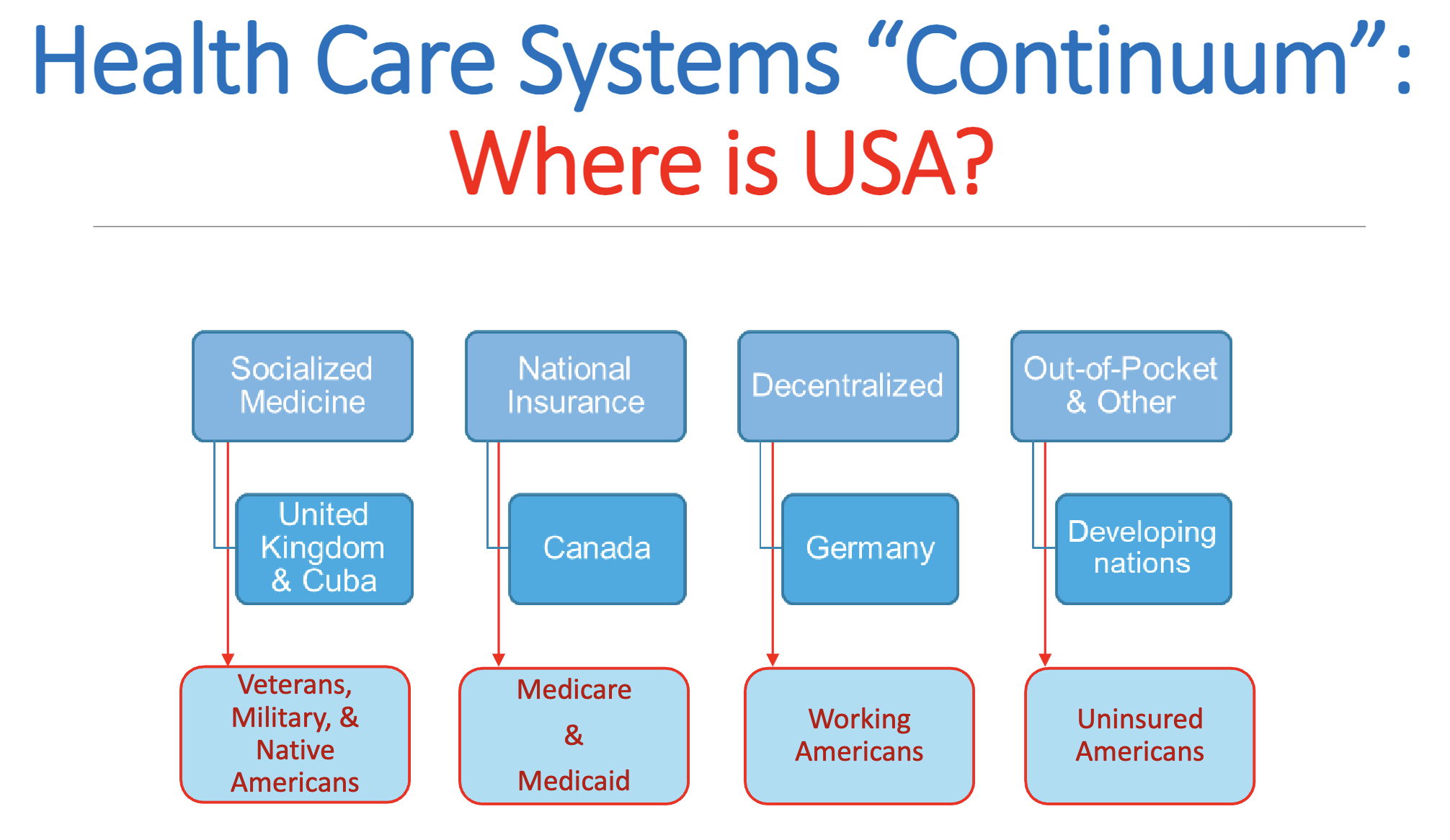
Socialized Programs (aka Socialized medicine or Beveridge model) –
Socialized Programs (aka Socialized medicine or Beveridge model) – government delivers and finances most health care services
National Health Insurance Model (aka Socialized health insurance or Single payer) –
National Health Insurance Model (aka Socialized health insurance or Single payer) – single, government-run insurance program finances healthcare services
Decentralized National Health Program (aka Bismarck model) –
Decentralized National Health Program (aka Bismarck model) – employers and employees are required to obtain private health insurance
Out-of-pocket Model –
Out-of-pocket Model – lack of private health insurance or no government- sponsored healthcare system.
Developed vs Developing nations

Canada
Common nickname
Type of System
Underlying Principles
Structure
Common nickname: Medicare
Type of System: ◦ Socialized health insurance or Single payer (Model = National health insurance)
Underlying Principles ◦ Portability of benefits: coverage is kept, even when the individual is absent from the province.
◦ Comprehensiveness: all necessary physician and hospital services are covered.
◦ Universality: all citizens of a province are entitled to the same services.
◦ Accessibility: reasonable access to services is assured
◦ Public Administration: a nonprofit, public organization accountable to the provincial government runs the plan
Structure ◦ 13 different plans (for ea. province & territory)
◦ Delivery: mostly private (4 % of hospitals belong to the federal government)

UK
Common nickname
Type of System
Underlying Principles
Structure
Common Name: NHS
Type of System: ◦ Socialized Medicine (Model = Socialized Program)
Underlying Principles ◦ Universality
◦ Comprehensiveness
◦ Financing through general taxation with little charge at point of service
◦ Nationalization of hospitals
Structure: ◦ National health plan with 3 major components:
◦ Primary medical and dental: General Practitioners (GPs)
◦ Community services
◦ Hospitals: 2ry & 3ry care ◦ Thus, delivery: mostly public
◦ Private provider services are not reimbursed by the NHS
◦ Unlike Canada, private insurance for services also covered by NHS is available (10.5% of the population in 2015).

Germany
Common nickname
Type of System
Underlying Principles
Structure
Common Name: Sickness Funds
Type of System ◦ Statutory health insurance (SHI) (Model = Decentralized National Health Program)
Underlying Principles ◦ Self-governance: system is administered by a self-managing organization
◦ Social partnership: both the employer and employee have a share in the system
◦ Social solidarity: ensuring equality in health care through some members of society subsidizing other members’ healthcare costs
Structure ◦ Not a comprehensive national health plan
◦ Coverage through:
◦ Sickness funds (SHI) - “private companies under public law”, 88%
◦ Private insurance (PHI) - 10%
◦ Social welfare program - 2%
◦ Delivery: mostly private

Cuba
Common nickname
Type of System
Underlying Principles
Structure
Common Name: Family Physician Program
Type of System: ◦ “Socialist” (socialized) medicine (Model = Socialized Program)
Underlying Principles ◦ Health care is a right
◦ Health care is the responsibility of the state
◦ Preventive and curative services are integrated
◦ Everyone participates in the function of the health care system
◦ Health care activities are integrated with economic and social development
Structure: ◦ National health plan with 3 major components:
◦ 1ry care: Consultorio (consultation office)
◦ Family MD & nurse assigned to specific community
◦ 2ry care: Polyclinics
◦ 3ry care: Hospitals ◦ Thus, delivery: completely public


The United States does not have a single health care model; it has elements of all four!
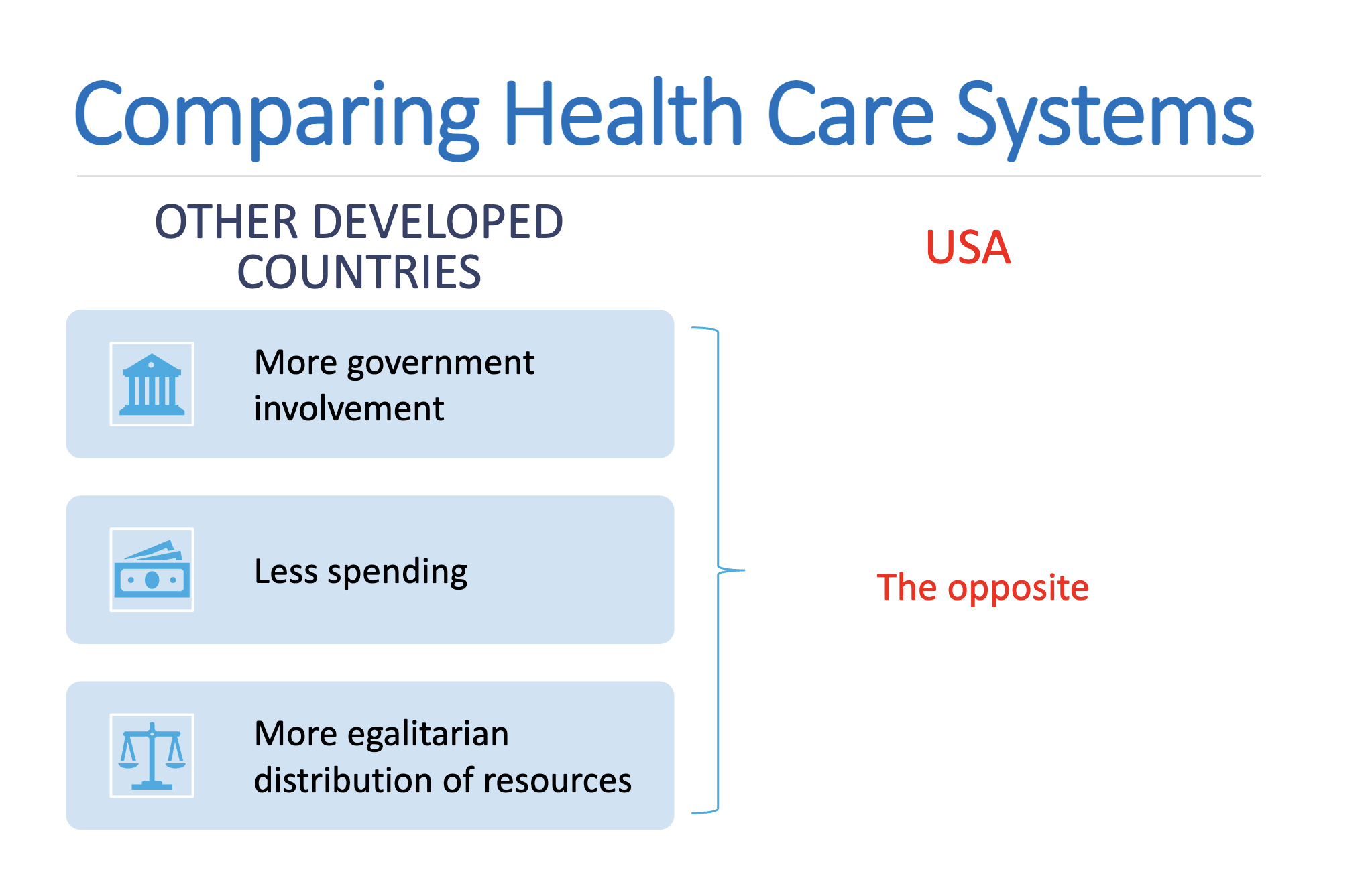
We spend more than everyone else
Increased expenditures doesnt mean better results though
Comparing health care systems
IOM
The degree to which health care services for individuals and populations increase the likelihood of desired health outcomes and are consistent with current professional knowledge. ~IOM
AHRQ
Doing the right thing for the right patient, at the right time, in the right way, to achieve the best possible results
Components of quality (IOM)
• Safety
• Timeliness
• Patient-centeredness
• Effectiveness
• Efficiency
• Equity
Factors that affect quality
• Providers
• Patients
• Information technology
• Coordination
• Financing/reimbursement
• Organization
Measuring quality

SPO (structure process outcome)
Structure

SPO (structure process outcome)
Process

SPO (structure process outcome)
Outcome

Quality Measurement
Quality can also be measured at various “levels”
– Institution/facility
– Health plan
– Provider
• Variations in quality and lack of information (or transparency) are some identified problems with the US health care “system”
• Important way to increase transparency of health care operations
• Reporting may be voluntary or legally mandated
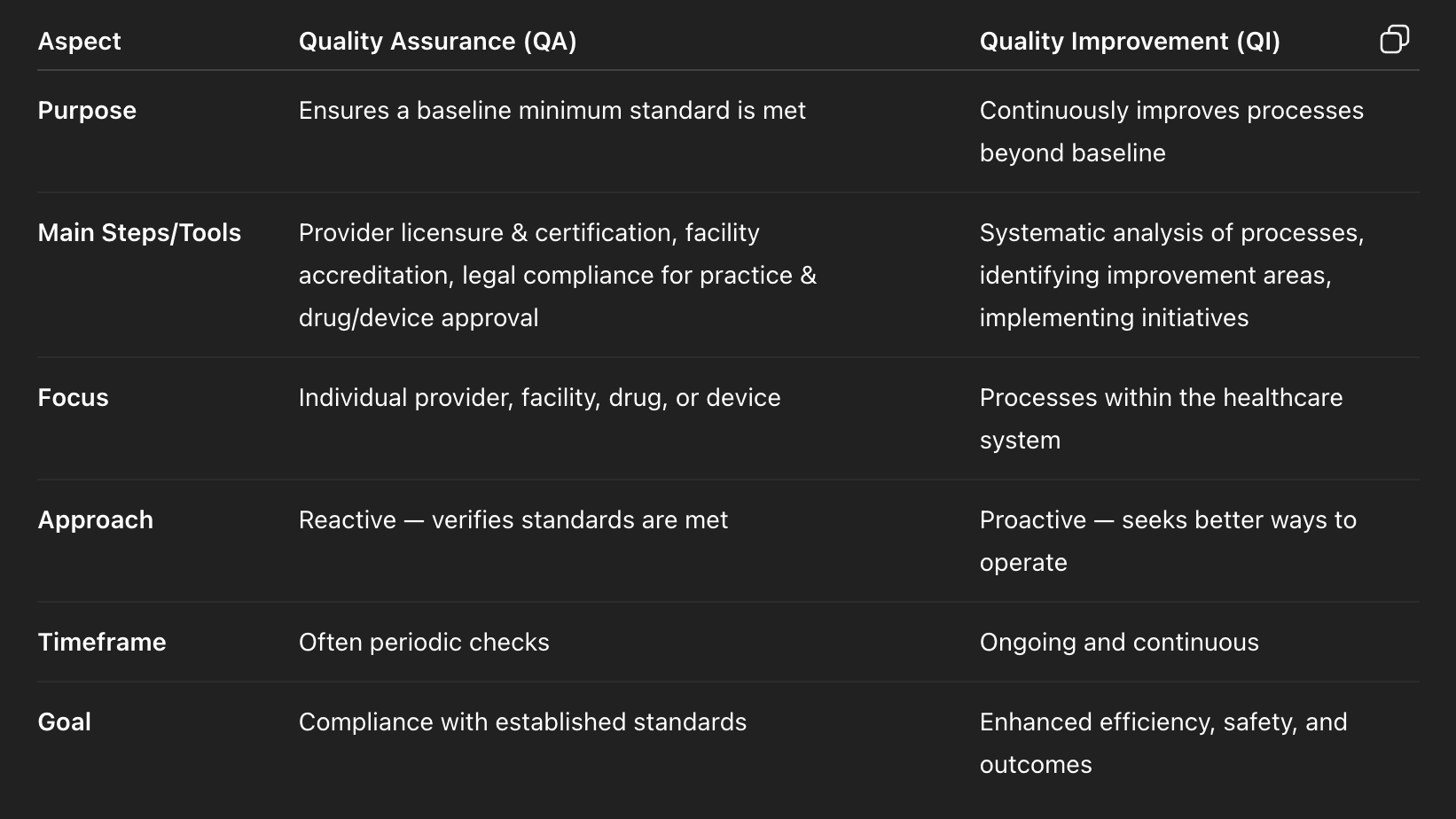
Quality assurance vs quality improvement
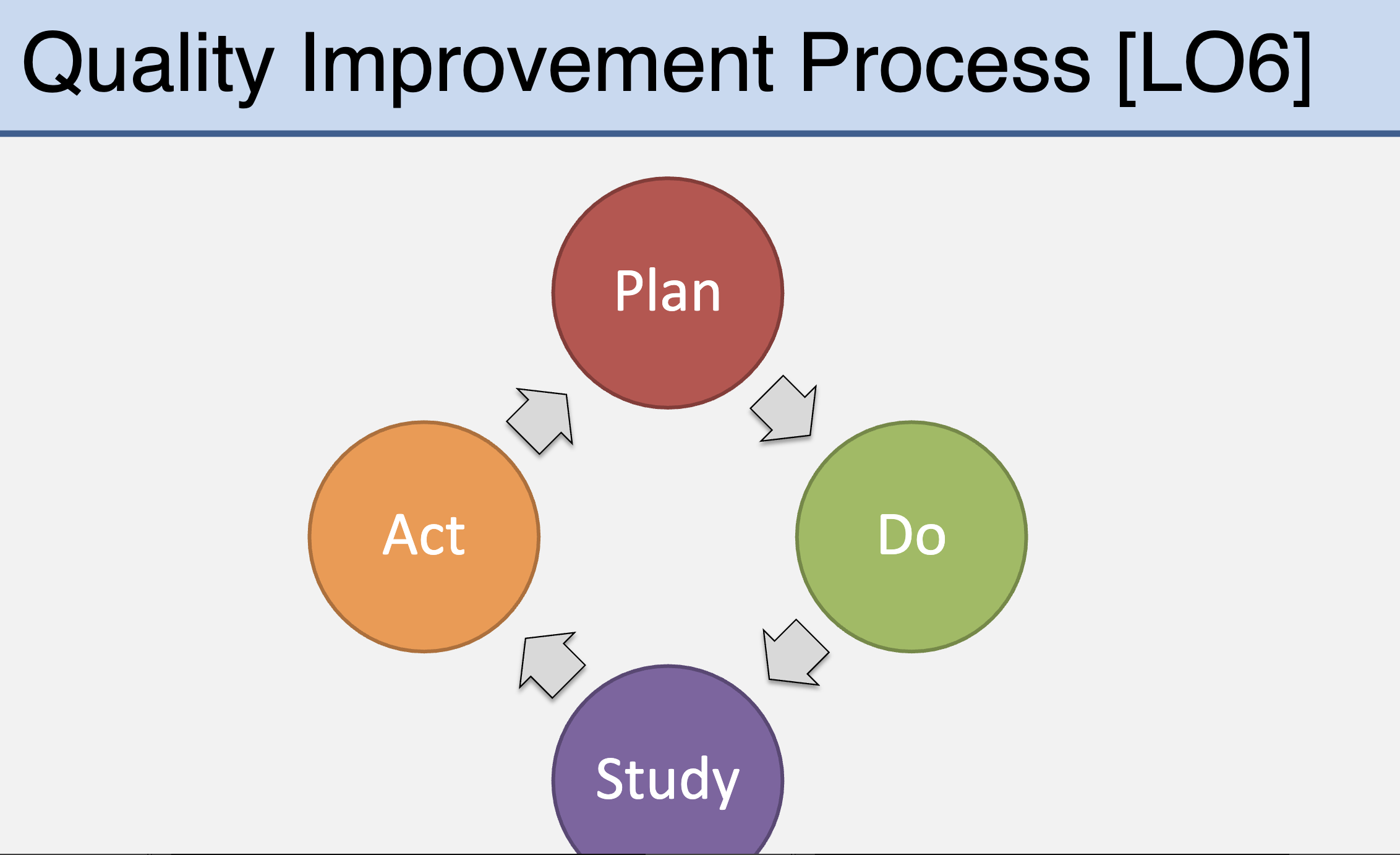
Quality improvement process
Describe the role of evaluation in clinical practice as it relates to quality improvement
• Periodic review of practices is important to determine whether the care being provided is optimal
• This goal-setting and reviewing is an important part of professional development
• Practice evaluation may be focused on the local site but can provide a framework to help those at others
• New services can be identified and developed as part of QI initiatives
Describe the relationship between financing/reimbursement and quality in health care
• Fee-for-service
• Per diem
• Episode of care/Episode of illness
• Capitation
• Pay for performance
Describe the role of the government in assuring quality health care
• Oversees basic licensing and accreditation requirements
• Requires reporting of quality measures (e.g., Medicare, mortality rates, etc.)
• Supports the development and dissemination of clinical practice guidelines (e.g., AHRQ and USPSTF, National Guidelines Clearinghouse, etc.)
• Coordinates or supports quality measurement efforts (e.g., AHRQ, HRSA, etc.)
• Supports research efforts (e.g., AHRQ, NIH, VA, etc.)
• Supports service development (e.g., Patient Safety and Clinical Pharmacy Services Collaborative [PSPC]) 36
Discuss why health care reform is an ongoing topic in the United States
Health care reform is ongoing in the U.S. because it lacks universal coverage, leaving many uninsured or underinsured, despite very high spending; access is shaped by insurance status plus age, ethnicity, and income disparities, creating ongoing debates over cost, equity, and rights.
Determinate of healthcare (people less likely to be insured):
Age (adults)
Ethnicity (people of color)
Income gaps (working poor)
Describe how the United States has the best and worst health care system when compared to other industrialized nations

Describe previous landmark reform efforts in the US
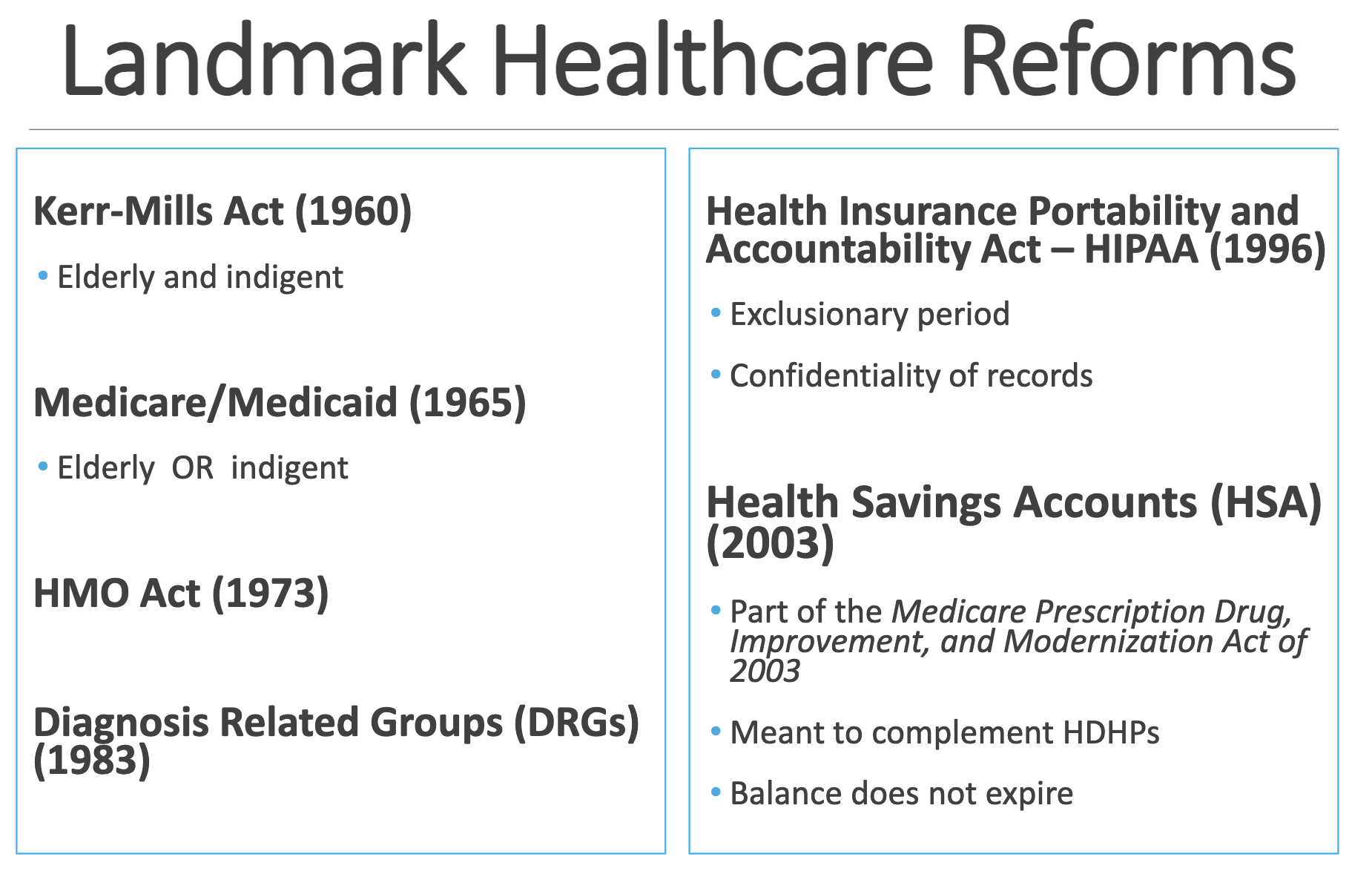
Kerr-Mills Act (1960) •
Medicare/Medicaid (1965) •
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act – HIPAA (1996)
• Part of the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003
Kerr-Mills Act (1960) • Elderly and indigent
Medicare/Medicaid (1965) • Elderly OR indigent
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act – HIPAA (1996)
• Exclusionary period
• Confidentiality of records
Health Savings Accounts (HSA) (2003)
• Part of the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003
• Meant to complement HDHPs
• Balance does not expire
Compare and contrast various reform proposals/models
Single Payer

Employer Mandate

Individual Mandate

Tax Credits Vouchers

The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (2010)
A.K.A.: Affordable Care Act (ACA) Obamacare “Most significant regulatory overhaul of the U.S. healthcare system since the passage of Medicare and Medicaid in 1965.” Signed by President Obama on March 23, 2010.
The law put in place comprehensive health insurance reforms that rolled out over four years (2010-14) and beyond: ◦ “private health insurance plans are required to include young adults up to age 26 under their parents’ policies. The ACA also eliminates caps on total insurance benefits payouts, prohibits denial of coverage based on preexisting conditions, and limits the extent of experience rating...”
ACA – Goals

ACA employer mandate
Employer mandate: employers with 50 or more full-time employees face a financial penalty if... their employees are not enrolled
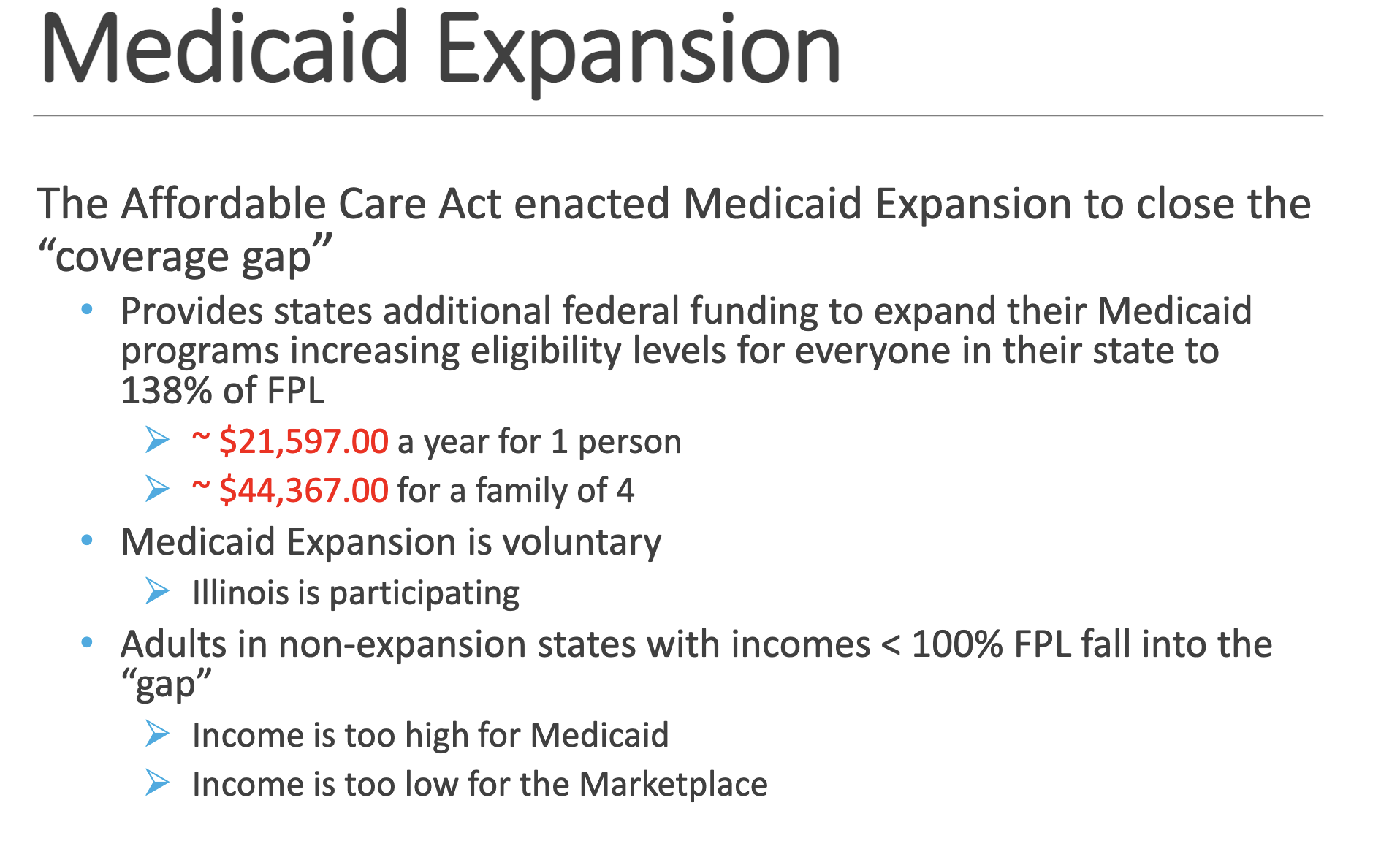
Medicaid Expansion
know 138%
Health Insurance Marketplace

Health Insurance Marketplace Timeline

Current status of ACA:
Most people favor it - 65%