Physics A Level OCR A
1/391
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
392 Terms
2 forces are on an object, and the object is in equilibrium, what must be true?
What about 2+ forces?
The forces have equal magnitudes
The forces act in opposite direction
Their vectors must resolve to 0
What is a projectile?
An object with an initial velocity that moves freely under gravity.
What is drift velocity?
The average velocity of electrons in the direction of the wire.
Rules to help solve projectile motion problems
Horizontal and Vertical components in motion are independent.
The horizontal velocity will remain constant
Vertical velocity will decelerate at 9.81ms-2
At the highest point the vertical velocity of the projectile is 0
The 2 types of friction, depending on the things interacting
2 types of friction, often used in calculations
Contact friction - This is between 2 surfaces in contact
Fluid friction / Drag - This is between a solid object and a fluid (liquid or gaseous)
Static & Dynamic (also known as kinetic) Friction
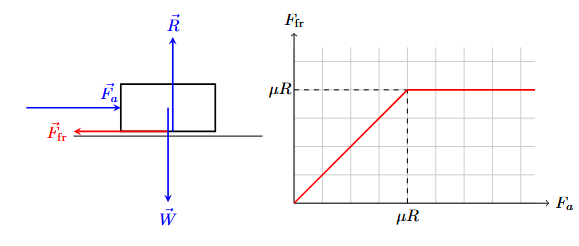
Important stuff about drag (x3)
It increases as the object’s force increases
It is impacted by the shape and size of the object
Drag can never cause an object to accellerate
What is voltage / p.d.?
Voltage (potential difference) is the work done per unit charge, transferred from the electrical potential energy of the charges.
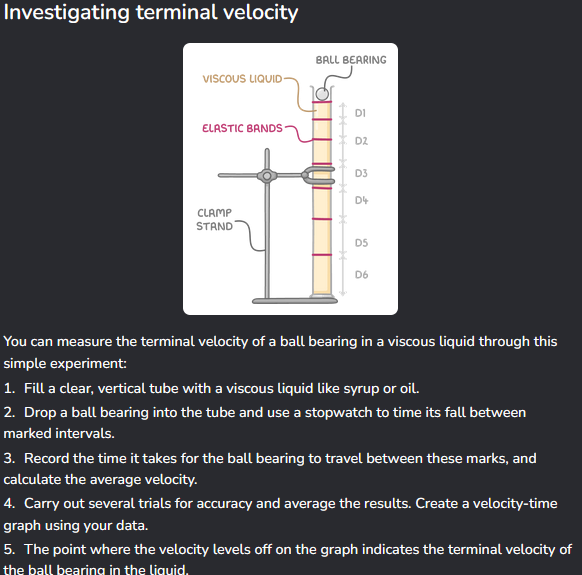
Experiment to investigate terminal velocity.
What is a moment?
Torque, turning effect generated when a force is applied at a distance from a pivot.
What is a couple and how do you calculate them?
They are 2 equal and opposite forces acting in the same direction, but seperated by a distance, creating torque and inducing rotation.
T (Nm) = F x d
F = magnitude of one of the forces
d = distance between the forces
T = torque
What is the pressure in a fluid?
gravity (N/kg) x density of fluid (kg/m3) x depth (m) = Pressure (N/m²)
What is upthrust?
When an object is partially or fully in a fluid, it experiences an upward force.
This results from the pressure difference between the top and the bottom of the object.
Archimedes’ Principle?
Upthrust = Weight of the water displaced
= density of fluid x volume of fluid x gravity
Why is efficiency important?
Conserves resources
Reduced environmental impact
Reduces costs
What are newton’s 3 laws?
An object’s velocity will not change, unless a resultant force acts on it.
F = ma
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
What are the two types of collisions?
Elastic: KE is conserved
Inelastic: KE is lost (heat or sound)
How to deal with a two-dimensional collision?
Split into x and y components.
Apply the conservation of momentum law to each separately.
Plastic vs Elastic deformation
Elastic deformation: material returns to original size and shape, once the stress is removed
Plastic deformation: material does not return to original size and shape, once the stress is removed.
Equation for spring constant in series
\frac{1}{k_\text{eq}} = \frac{1}{k_1} + \frac{1}{k_2} + \frac{1}{k_3} + \cdots + \frac{1}{k_n}
Equation for spring constants in parallel
K1 + K2 + K3 + … + Kn
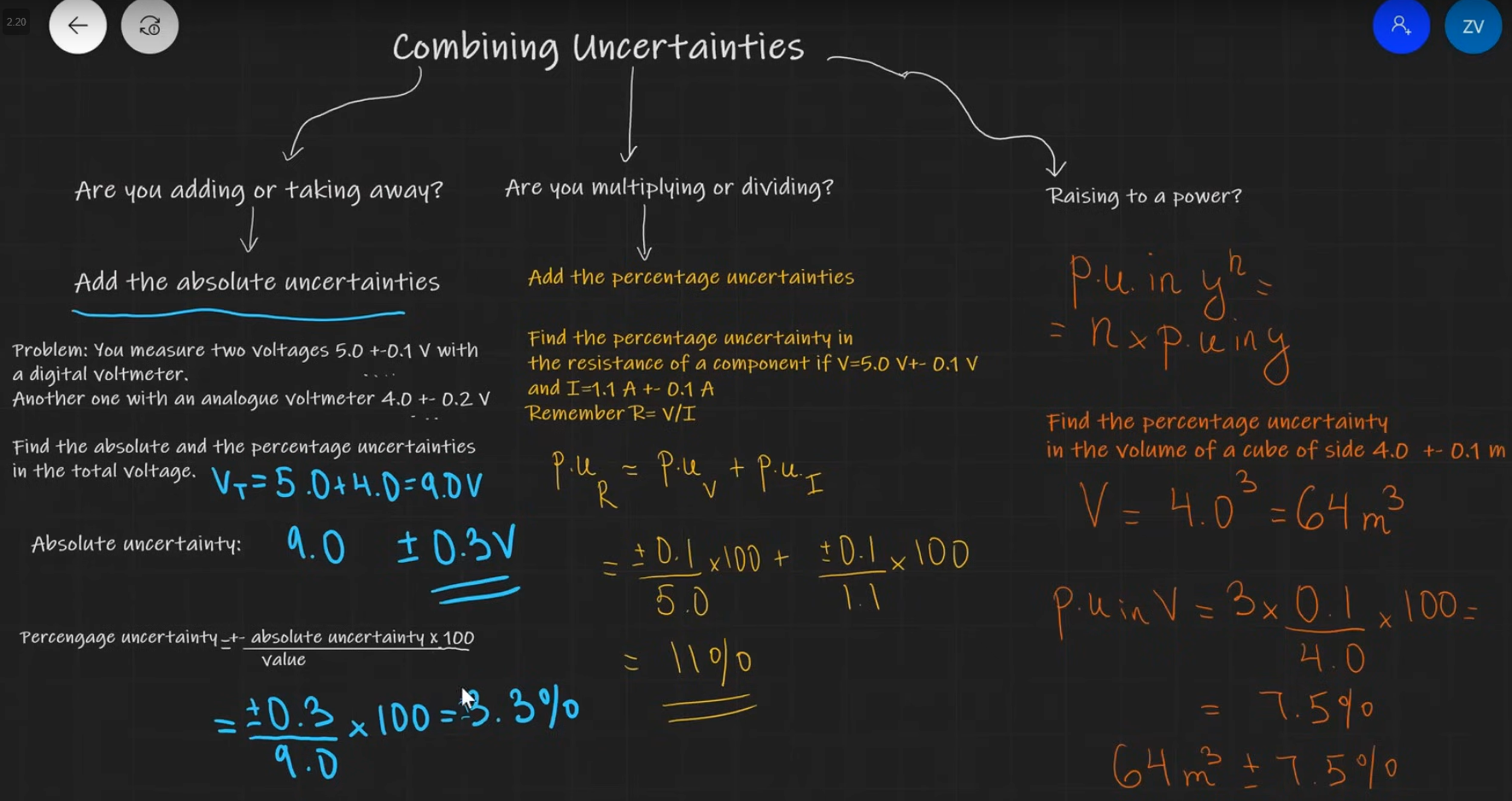
How are uncertainties handled in physics?
Equation for stress?
Force (N) / Area (m²)
Stress’s Force Unit
Equation for strain?
Extension (m) / original length (m)
Strain’s Deformation Unit
What is Young’s Modulus?
What is it also called?
Stress / Strain
Stiffness
Facts about Young’s Modulus
This will remain directly proportional until the material reaches its breaking point.
What is UTS?
Ultimate tensile strength.
The maximum amount of load or stress a material can handle until it fractures and breaks.
What is breaking stress?
How is this different from UTS?
The stress level at which a material fractures, all the fibres break.
This is different to UTS, which is the maximum force a material can take without breaking.
Elastic potential energy equation (in relation to Young’s Modulus)
Work done = Average force x distance
EPE = Final force x 0.5 x extension
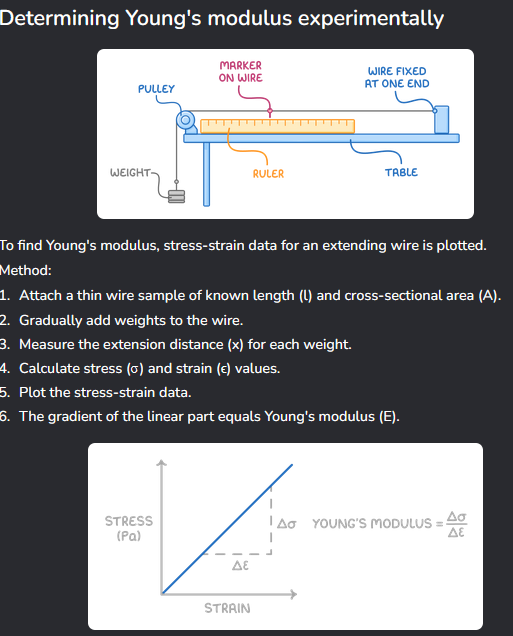
How to determine Young’s Modulus in a common experiment.
How will the stress/strain graph of a ductile material look?
There will not be a sudden change (a breaking point) in gradient, but it will be gradual, this signifies that the material is ductile.
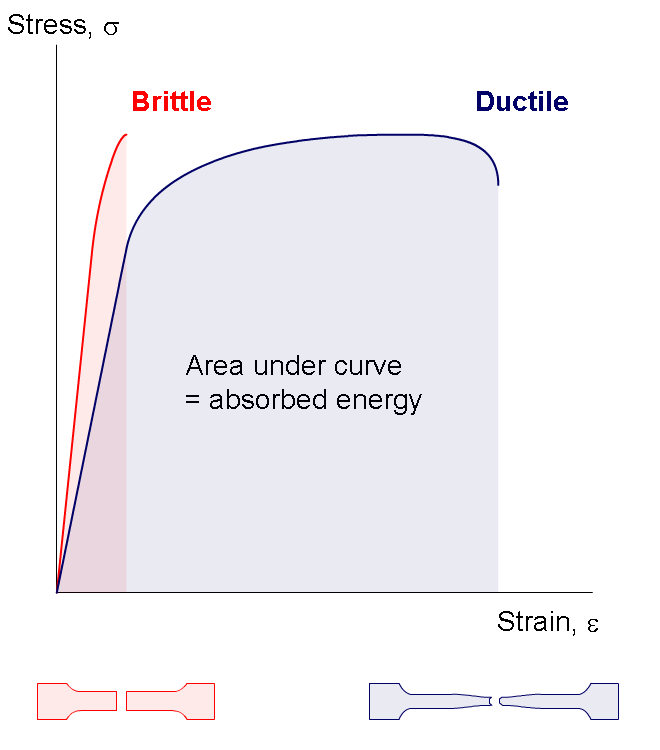
What properties can you deduce from a Stress/Strain graph?
Max height is the strength of the material.
The gradient shows how stiff the material is.
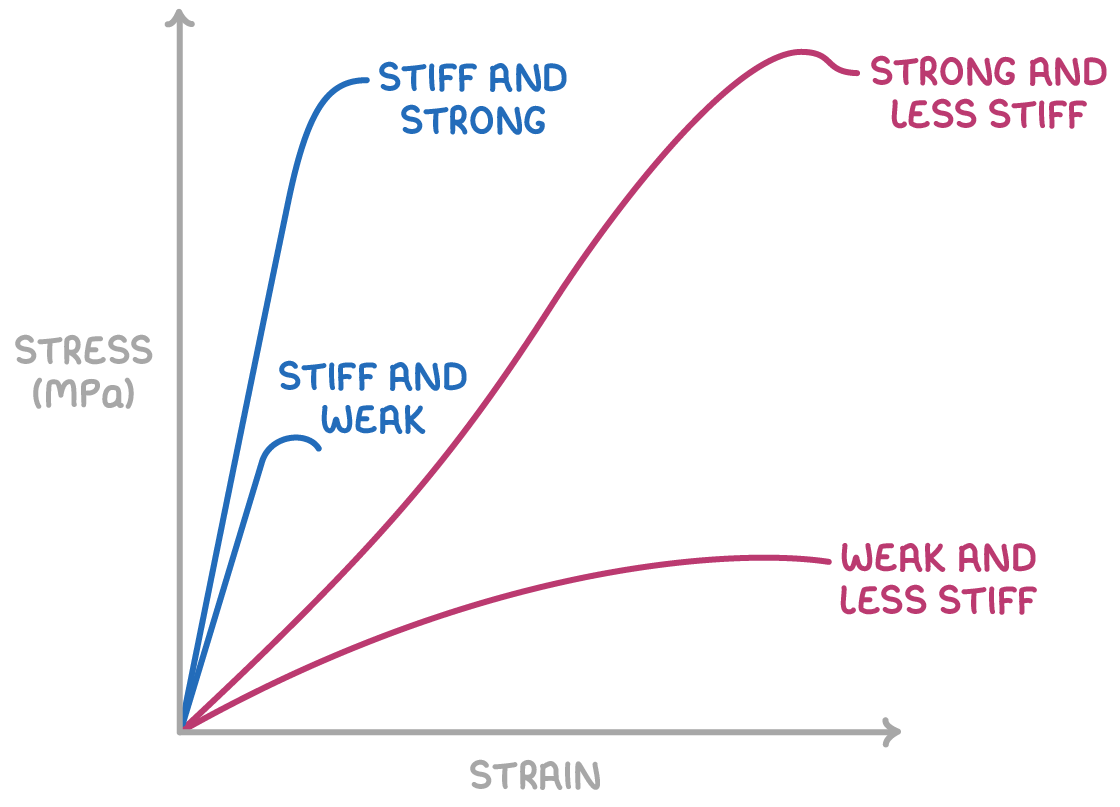
What does the Stress/Strain graph for rubber and other polymers look like?
Name of these types of graphs?
Polymeric stress-strain graphs
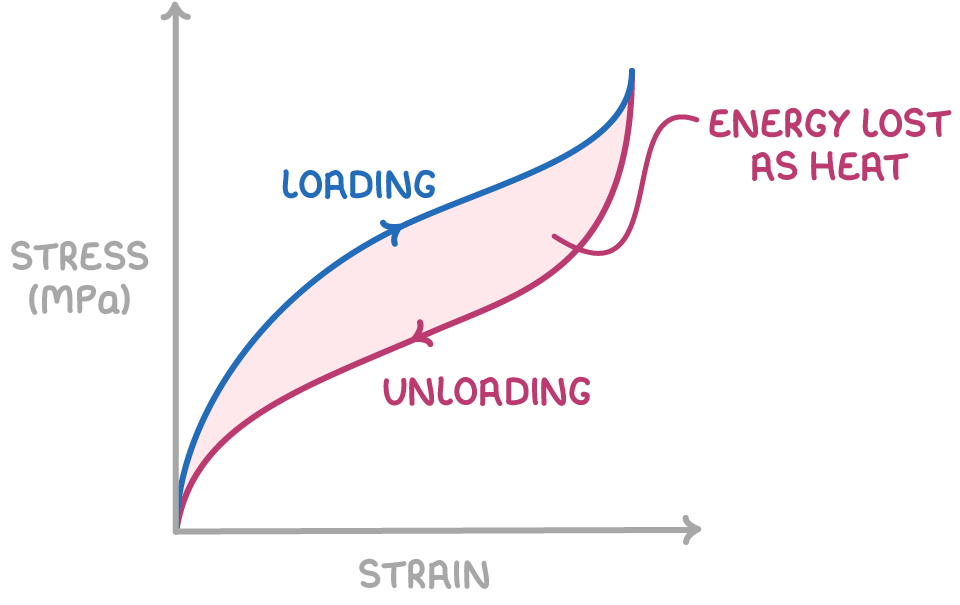
The unloading is different due to the energy which is lost as heat.
If a wire was a pipe carrying water, what would each electrical property map to?
Voltage (V) = pressure difference pushing water.
Current (I) = flow rate of water (litres/s).
Charge (C) = total water that flowed (litres).
Mean drift velocity = average speed of the water drifting through the pipe.
Resistance (R) = pipe roughness/narrowness, slowing the flow.
Internal resistance = resistance inside the pump itself.
Number density (n) = how many molecules per volume of water.
Charge per carrier (q) = "size" of each water parcel (same for all).
Cross-sectional area (A) = thickness of the pipe.
Equation for mean drift velocity?
v=\frac{I}{A\cdot n\cdot q}

2 important points about charges.
They move randomly, but tend to drift in one direction.
The mean drift velocity is the average of these velocities.
Compare charge carriers in metals
In metals, there are many delocalised electrons, this means that there is a high density of charge carries, so metals conduct electricity very well.
Compare charge carriers in semiconductors
In semiconductors, there are fewer charge carriers, so a higher drift velocity is needed to reach the same current.
Compare charge carriers in insulators
In insulators, there are very few or no free carries, meaning that they are poor conductors of electricity.
Compare charge carriers in ionic solutions, or molten ionic compounds.
In ionic solutions or molten ionic compounds, both the negative and positive ions act as charge carriers, so electricity is conducted decently well.
Compare charge carriers in gases
In gases, the lack of carrier ions means that they cannot usually carry charge, but they can become conductive when they get ionised.
What is p.d.?
Work done per unit of charge.
What is the charge of an electron?
1.6 × 10-19 C
What is the mass of an electron?
9.11 × 10-31 kg
Why is saving energy important?

Examples of how to save energy
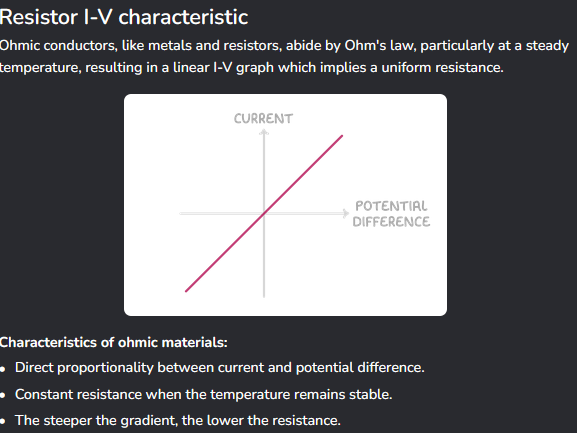
An ohmic resistor.
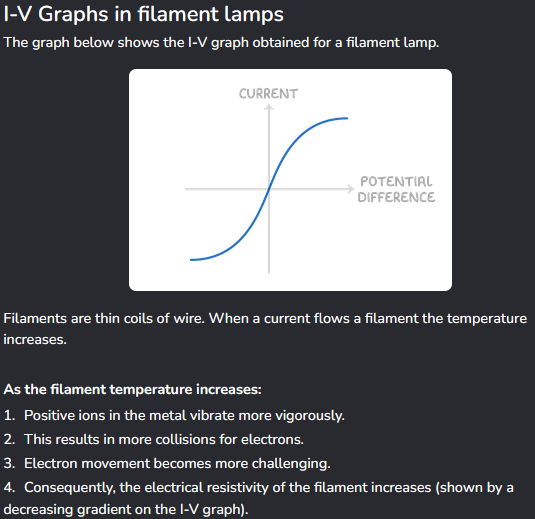
A filament lamp
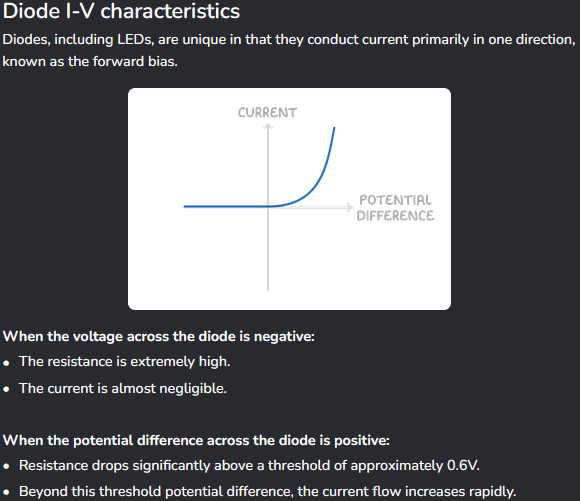
A diode
What is resistivity?
This is the resistance encountered in a material that is 1m long, and has a cross-sectional area of 1m².
It allows us to compare the resistance of different materials without a dependence on size or shape.
Its units are ohm-metres (Ωm).
Equation for resistivity?
\rho=\frac{RA}{L}

Experiment to determine resistivity of a wire.
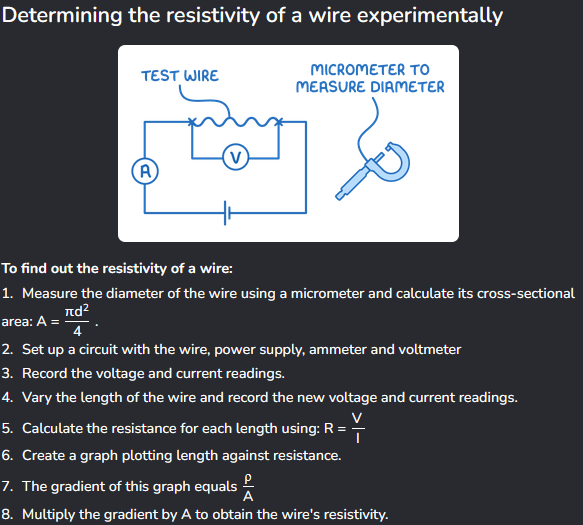
Kirchhoff’s First Law
‘The sum of currents entering a junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving that junction.'
Basically, charge is conserved
Kirchhoff’s Second Law
'The total e.m.f. in a closed loop is equal to the sum of potential differences across each component in that loop.'
Equation for resistance of components in series.
R1 + R2 + R3 + … + Rn = Rtotal
Equation for resistance in parallel.
\frac{1}{R_\text{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} + \cdots + \frac{1}{R_n}
How many base units are there?
What are they?
7
Length — meter (m)
Mass — kilogram (kg)
Time — second (s)
Electric current — ampere (A)
Thermodynamic temperature — kelvin (K)
Amount of substance — mole (mol)
Luminous intensity — candela (cd)
Line of best fit and worst fit.
Percentage uncertainty from this.
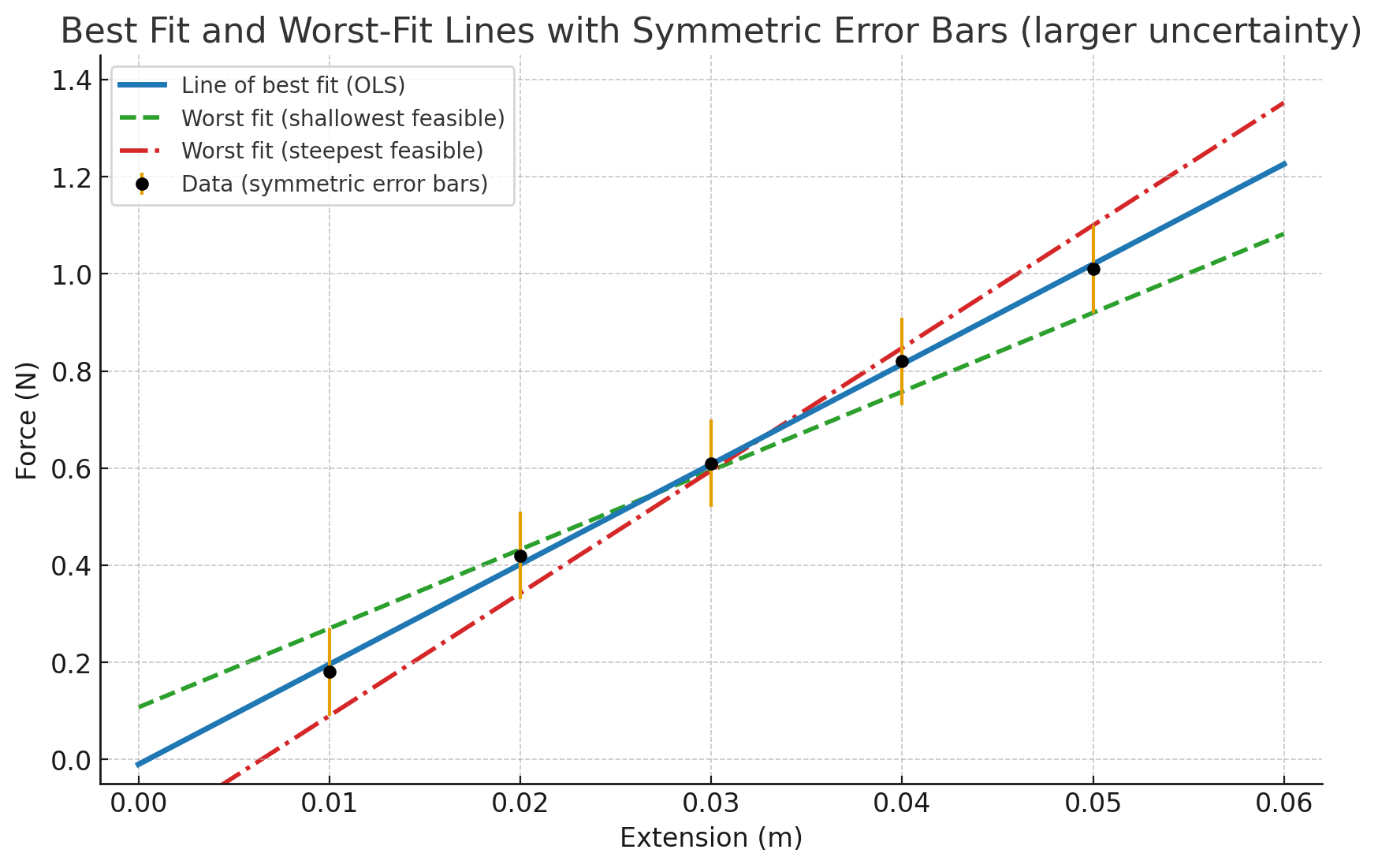
Uncertainty bars show the absolute uncertainty.
% uncertainty = uncertainty / gradient of line of best fit x 100
What is internal resistance?
Very battery has its own resistance, this is caused mainly by the collisions of electrons as they move through the material of the battery.
This can cause the battery to heat up.
The symbol is often “r”
What is the definition of resistance?
The ratio of p.d. across a component to the current through it.
From V = IR
What is Ohm’s Law?
This states that for an ohmic component, the current through it is directly proportional to the p.d. at constant temperature.
What is load resistance?
This is the total resistance outside the battery.
The symbol is often “R”
What is EMF?
Electromotive Force (E)
This is the total energy per unit charge of a battery, measured in volts.
The EMF of a supply is the energy gained per unit charge by charges passing through the supply, when a form of energy is transferred to electrical energy carried by the charges. Units V or J/C.
What is Terminal Potential difference?
The actual potential difference across the terminals of a power source, measured in volts.
What are lost volts?
Without any internal resistance, the EMF would equal the load potential difference.
But the presence of internal resistance, means there is a loss of energy per unit charge.
The symbol is often “v”
EMF equation.
EMF = I(R + r)
EMF = V + v
Special note with EMF?
With not current flowing, there will be no lost volts, so just a voltmeter in parallel will read the battery’s EMF.
EMF in series?
The EMF of each cell adds up.
This is because each cell contributes to the pushing of the charge.
EMF in parallel?
The EMF will not change, but the current will increase.
Experiment to determine EMF and internal resistance?
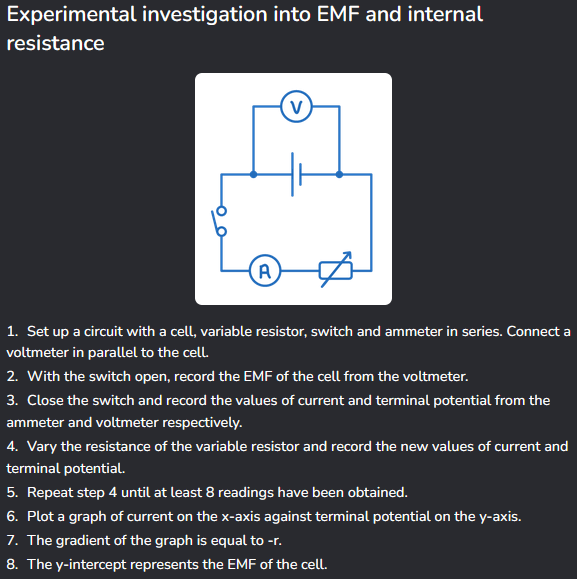
How does this EMF experiment work?
EMF = V + Ir
So as current increases, the contribution of Ir (lost volts) increases.
Rearranging into y = mx + c gives
V = -rI + EMF
So the y-intercept (when current is 0) will be the EMF, and the gradient will be -r.
Compare semiconductors to metals, and what happens when you add more current.
They have greater resistivity than metals, and become more conductive as energy is added.
This is because the density of charge carries increases, as more energy means more electrons are released, allowing charge to be better conducted: reducing resistance.
What is an NTC?
Key points?
Type of thermistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient).
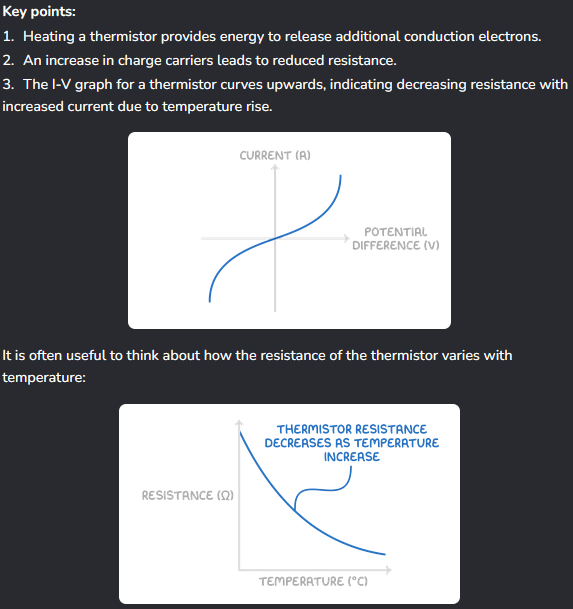
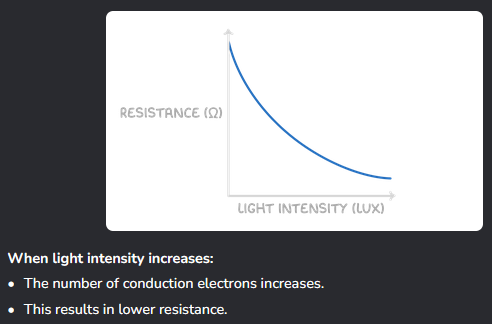
How do LDRs work?
Light causes resistance to decrease because energy is provided to release more electrons to carry the charge.
Tell me about centre of mass
Definitions
Centre of Mass (CoM) → Point where all mass is assumed to be concentrated.
Centre of Gravity (CoG) → Point where all weight is assumed to act.
Relation → CoM and CoG coincide in a uniform gravitational field.
Calculations & Modeling
Uniform beams/rods → CoM located at geometric centre; Weight vector drawn downwards from midpoint.
Non-uniform objects → CoM not at geometric centre; Must be found experimentally or given.
Solving Moments → Treat object's total weight as single force acting at CoM.
Experiment: Irregular Lamina
Setup → Suspend lamina freely from pin; Hang plumb line from same pin.
Action → Mark vertical line defined by plumb line.
Repeat → Suspend from different point; Mark second line.
Result → Intersection of lines = CoM.
Stability & Toppling
Stable → Line of action of weight (vertical from CoM) falls inside base area.
Toppling → Line of action of weight falls outside base area; Moment created causes rotation.
Critical limit → Line of action passes exactly through pivot point/edge.
To increase stability → Lower CoM OR Widen base.
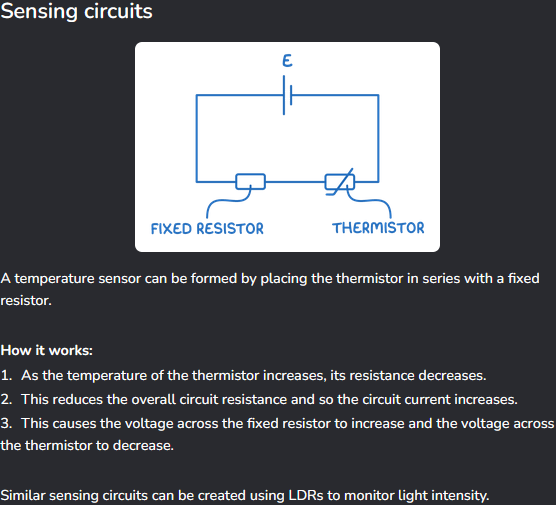
How does a sensing circuit work?
What can waves be categorised as?
Progressive: A wave where energy is transferred from one point to another, without transferring matter.
Stationary: A wave where there is no net energy transfer
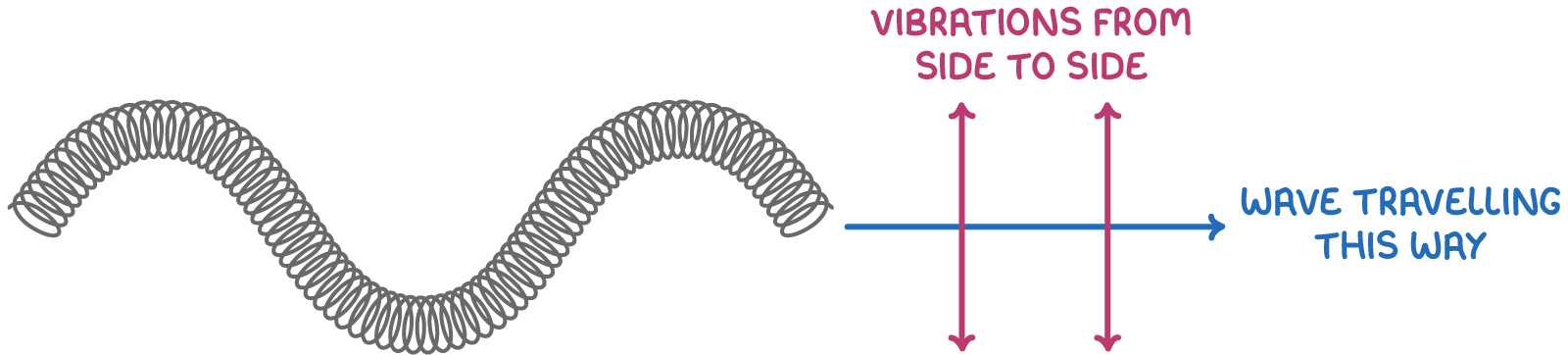
What are transverse waves?
Examples?
A wave where the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy travel.
Light, Water waves (at the top), Earthquake S-Waves
What are longitudinal waves?
Examples?
A wave where the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy travel.
Earthquake P-Waves, Sound waves
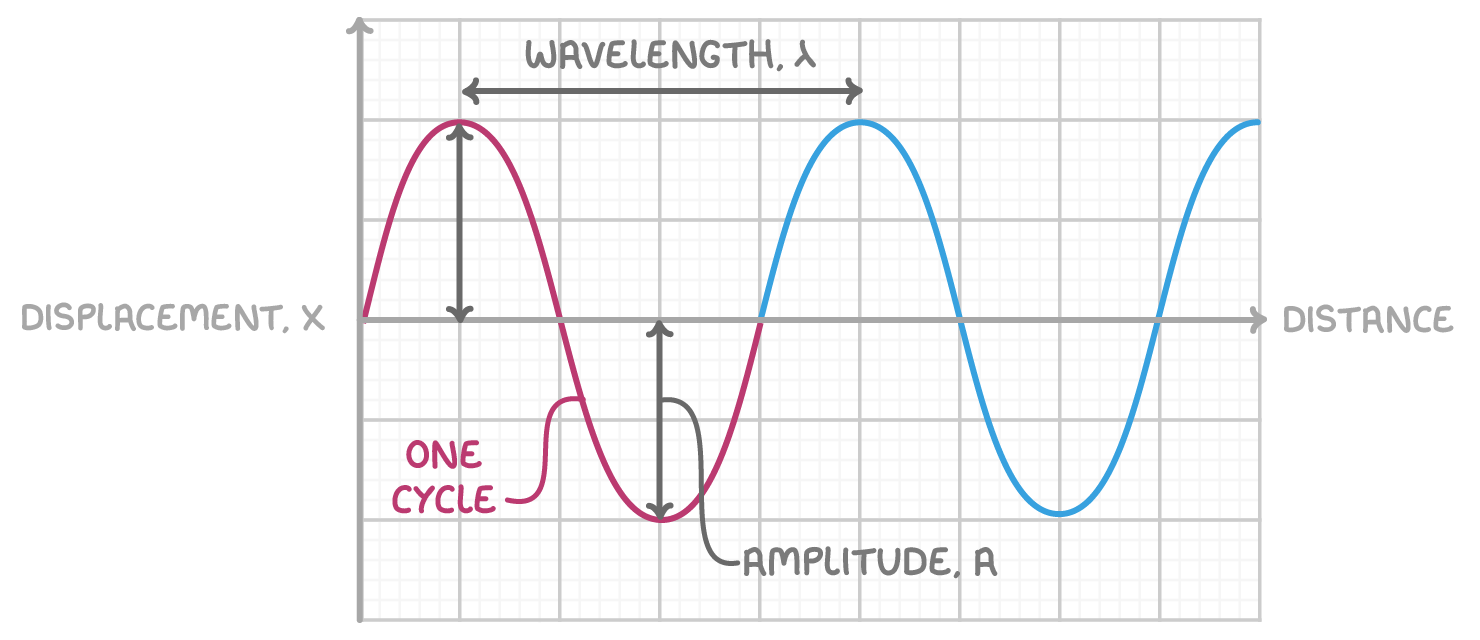
Features of a transverse wave (graphed on paper)
Features of longitudinal waves (drawn on paper)
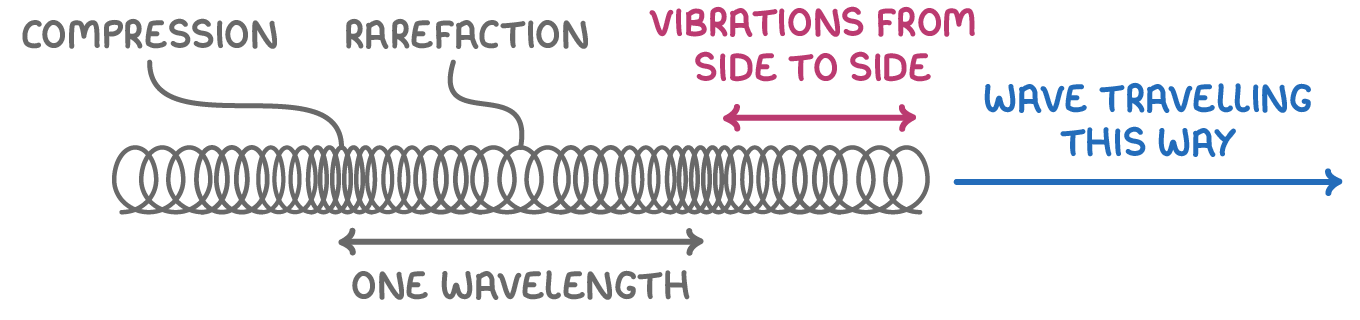
Wavelength is measured from the centre of one compression to the centre of the next.
What is wave intensity?
It is a measure of energy a wave conveys through a unit of area, perpendicular to its direction of travel, per second.
It is the “brightness” of light, or the “loudness” of sound.
Equation for wave intensity.

Relationship between wave intensity and amplitude.
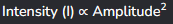
So if amplitude doubles, intensity quadruples.
How to work out the intensity when the object is spherical.
I=\frac{P}{4\pi r^2}
Where:
I = Intensity
P = Power
r = Radius between object and emitter.
This is a special case when the object emitting is spherical, like the sun.
What is Malus’ Law?
I=I_0cos^2\theta
Where:
I is the output intensity
I_0 is the original intensity
\theta is the angle between the waves
What is polarisation of waves?
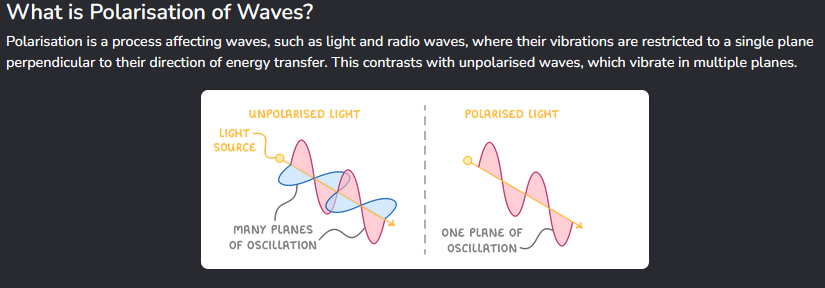
What does plane polarised mean?
These types of waves are waves that oscillate exclusively in one direction.
This can only be done to transverse waves.
Natural light has many planes of vibration.
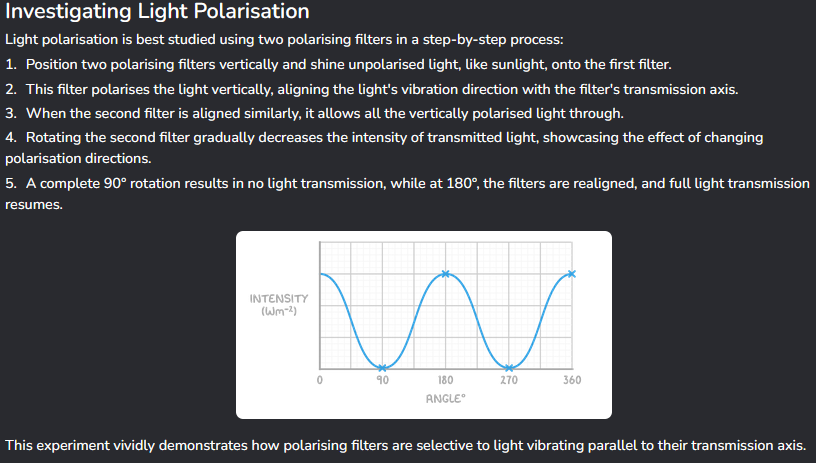
What is a polarising filter?
How to prove this?
This selectively transmits waves parallel to its alignment axis, but reflects or absorbs waves in other orientations.
When placing two filters at 90° against one another’s alignment, nothing is transmitted. But at 180°, polarised light is transmitted, proving the alignment idea.
How do sunglasses work?
Light reflected from a dielectric surface is partially plane-polarised (or linearly polarised).
The polarising filters (or polarisers) in the sunglasses absorb the electric field vector component that is orthogonal (or perpendicular) to the filter's transmission axis.
Investigating visible light’s polarisation experiment
Explain what is meant by a coherent source of sound.

Why would two waves interfere constructively?
the distance for the waves to travel there is equal / the difference is an integer in the number of wavelengths. Mention path difference.
State the principle of superposition.

Experiment with microwave’s polarisation.
Microwaves can be polarised using a grid, where the wires are parallel to each other.
The wires can be connected to a voltmeter to get readings
The maximum transmission will be when the grille is perpendicular to the microwaves’ polarisation direction. Resulting in a very low voltmeter reading.
The minimum transmission will be when the grille is parallel to the microwave’s polarisation direction. This is because the wave is travelling down the wires’ length, thus is absorbed then remitted in random directions, so in the original direction there are hardly any microwaves.
This shows that metal grilles are like polarisation filters but work on microwaves, not visible light.
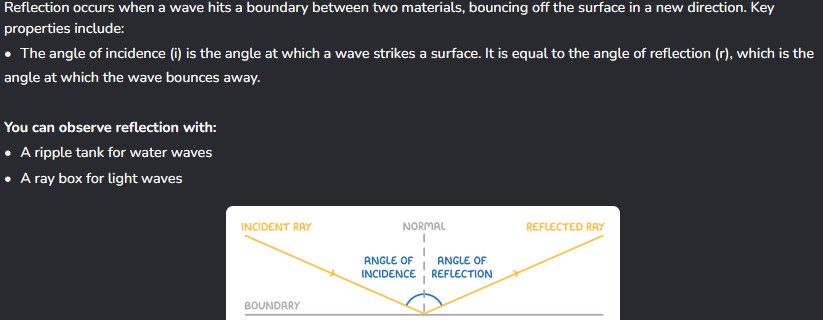
Tell me about reflection
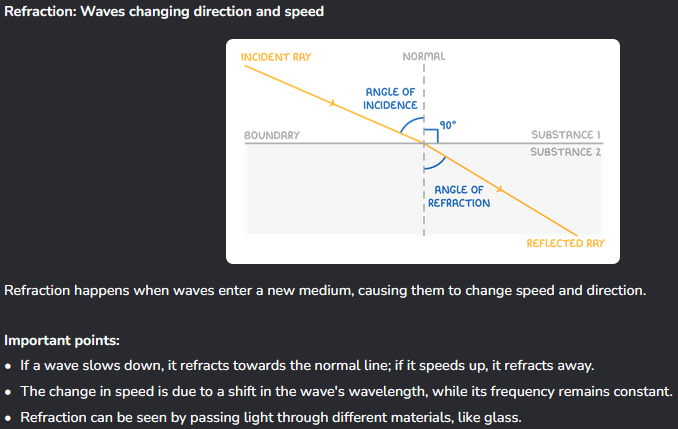
Tell me about refraction
How to calculate refractive index.
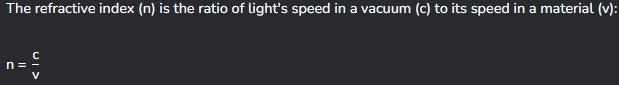
This cannot be less than or equal to 1, because light travels fastest in a vacuum.
Snell’s Law
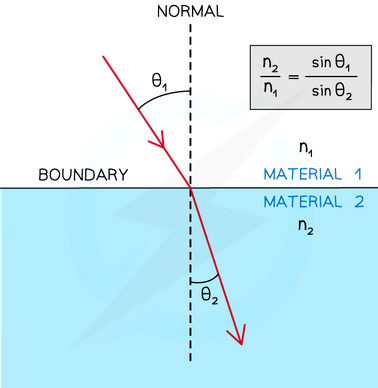
2nd over 1st, 1st over second
Tell me about total internal reflection.
This happens when the incident ray is above a critical angle.
At a certain angle, you will get 90° as the emergent ray.
Beyond, you will get a maths error. This means that there is no emergent ray. Then, there will simply be an internal reflection in the denser medium.
What is superposition?
This is when two or more waves overlap, resulting in a combined wave.
The superposition principle states that the combined wave’s displacement is the vector sum of the individual wave’s displacement.