Biology Chapter 3,4,5 Macromolecules/Cell Structure and Function
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
Organic Compounds
Contain carbon along with hydrogen, oxygen, and/or nitrogen
Carbon skeleton
Chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule
Functional groups
bond to carbon skeletons and are responsible for most of the chemical properties of a particular organic compound
What can small organic molecules combine into?
Larger macromolecules
Macromolecules
Polymers consisting of many small repeating molecules called monomers
Basic structures of all amino acids is a carbon backbone and…
an amino and carboxyl group
Monomers
Single subunits that make most macromolecules
Polymers
Monomers combine with each other via covalent bonds
Dehydration synthesis
When polymers are being formed, monomers release water molecules as byproducts
“to put together while losing water”
Maltose molecule
Dehydration synthesis of two glucose molecules and requires energy
Hydrolysis
Reaction that uses water to break bonds and energy is released in the process
Enzymes
Used to speed up a process that is sped up with something specific to break down specific types of macromolecules
Carbohydrates
sugars
Functions of carbohydrates
How do carbohydrates help cells
they can provide structural integrity to cells
What does the body do to carbs
Turns them into glucose to give energy to function
What do carbohydrates consist of?
C, H, and O
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars
How long are monosaccharides?
3-7 carbon atoms
Examples of monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose, and deoxyribose
What can monosaccharides be used for?
Can constitute the building blocks of more complex sugars
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides
Examples of disaccharides
Sucrose, lactose, and maltose
How are disaccharides be broken down?
Using hydrolysis
Polysaccharides
Tens or hundreds of monosaccharides joined together
Polymers of glucose
Starch, glycogen dextran, and cellulose
Lipids
Primary components of cell membranes and consist of C, H, and O
Lipid polarity
They are nonpolar and insoluble in water
Saturated fat
No double bonds in fatty acids
Unsaturated fat
One or more double bonds in the fatty acids
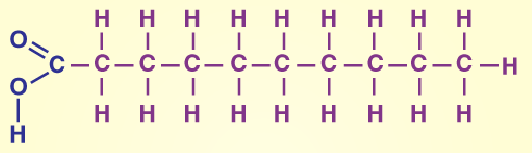
Saturated fat
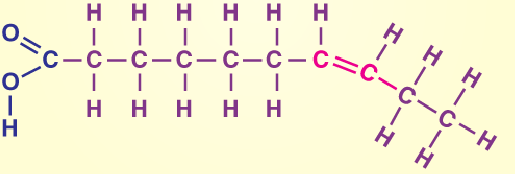
Unsaturated fat
Examples of saturated fat
Fatty meat, butter, cheese, milk, cream, coconut oil, chocolate
Examples of unsaturated fat
Fatty fish, avocado, plant oils, peanut butter, nuts, seeds
Phospholipids
Lipid bilayer
Lipid bilayer
Cell membrane made out of complex lipids
Complex lipids
Contain C, H, and O + P, and/or S
Phospholipids polarity
polar and non polar regions
Polar heads
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic
Water loving
Nonpolar tails
Hydrophobic
Steroids
Signaling molecule, and an important component of cell membrane as it alters fluidity
How are steroids made?
Four carbon rings with an -OH group attached to oone ring
Most common steroid in the body
Cholesterol
Cholesterol
waxy substance in blood, too much means an increased risk of heart disease as it leads to fatty deposits in the blood vessels
Protein
Made of C, H, O, N, and sometimes S: N-C-C-N-C-C-N…
Why are proteins important?
Essential in cell structure and function
Protein examples
Enzyme speeding up chemical reactions. transporter proteins move chemicals across membranes, flagella aid in movement, some bacterial toxins and cell structures
What are proteins made of?
subunits called amino acids
Amino acids
Contain an alpha-carbon that has an attached carboxyl, amino and side group (R)
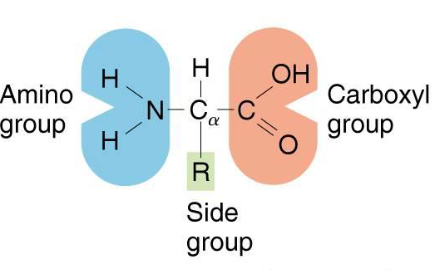
Amino acids structure
Peptide bonds
Type of covalent bond that forms between amino acids via dehydration synthesis reaction to form a chain → peptide → protein
Primary (1 degree) structure
Polypeptide chain
Secondary (2 degrees) structure
Occurs when the amino acid chain folds and coils in a helix or pleated sheet
Tertiary structure
When the helix or sheet folds irregularly, forming a disulfide bridges, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds between amino acids in the chain. Three dimensional structure.
Quaternary structure
Consists of two or more polypeptides and is the relationship between these several folded polypeptide chains to form a protein
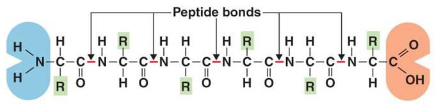
Example of a primary 1 structure
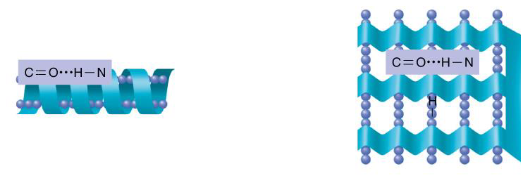
Examples of secondary structures
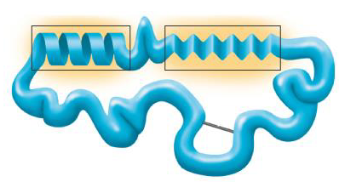
tertiary structure example

Quaternary structure example
Nucleic acids
Nucleosides, and nucleotides
Nucleosides
Pentose sugar with a nitrogen-containing base (purine or pyrimidine)
Nucleotides
Five carbon pentose sugar, nitrogen-containing base, and a phosphate group
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Contains a deoxyribose (pentose sugar), Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
How to the nitrogen bases connect?
They use hydrogen bonds
What do the nitrogen containing bases do?
Forms genetic instructions of the organism
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Ribose (sugar), adenine bonds with uracil as it substitutes for all thymines
RNA structure
Single-stranded
RNA types that play specific roles in protein synthesis
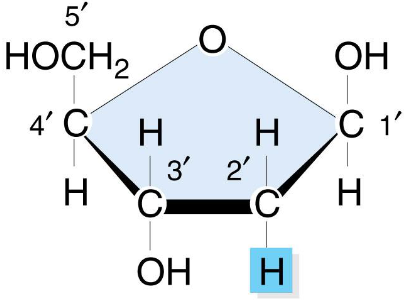
Deoxyribose
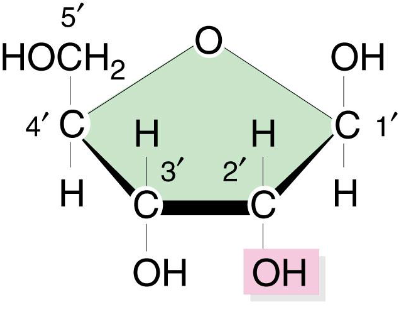
Ribose
Purine
Adenine, and Guanine
Pyrimidine
Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Made of ribose, adenine, and three phosphate groups
What does ATP do?
Stores chemical energy released by some chemical phosphate reactions and is the main carrier in cells
When is ATP made?
Generated during cellular respiration
Cell theory
Cells are fundamental structural and functional units of all living organisms
Cell Function
nutrient uptake waste removal, energy use, and reproduction
Prokaryote
Pre-nucleus and there is no membrane bound nucleus or organelles
What falls under prokaryote?
Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryote
True nucleus, and has a membrane bound nucleus organelles such as the ER, mitochondria, Golgi, etc
What falls under eukaryote?
Plants, animals, fungi, and protozoa
Glycocalyx
External to the cell wall and is viscous/gelatinous due to being made out of polysaccharides (sugar), and/or polypeptides
What is the purpose of the glycocalyx?
Capsule type of Glycocalyx
Neatly organized and firmly attached to prevent phagocytosis (ingestion) and helps in the formation of biofilms (microbial communities)
Flagella
Propels bacteria (locomotion) as it is filamentous appendage(s) and made out of flagellin
Chemotaxis
Movement of an organism (towards or away from) a chemical stimulus
What is unique about the kinds of flagellar proteins?
They can be used to distinguish between different serovars of bacteria
Serovar
Distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus
Axial Filaments
Endoflagella
Where are axial filaments found?
In bacteria called spriochetes
Structure of axial filaments
Fimbriae
Bristle-like, short appendages that allow for attachment
Pili
Long hair-like appendages involved in motility (like crawling on a surface)
Conjugation (sex) pili
Involved in the transfer of DNA from one cells to another
Bacterial Cell Walls
Protects the cell membrane and prevents osmotic lysis
What do bacterial cell walls contain?
Peptidoglycan
Cell walls of bacteria can contribute to what?
Pathogenicity
Pathogenicity
Potential or ability of an organism to cause disease in a host
Gram-Positive Cell Walls