Biomolecules
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
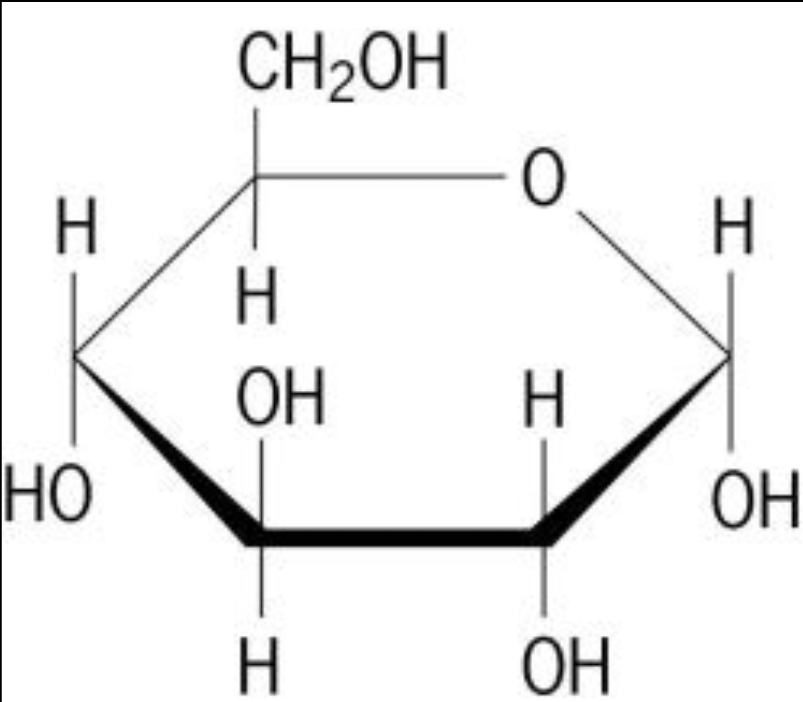
molecules have a chemical formula
identifies what atoms make up a given molecule
Ex: C6H12O6
tells you very little about its actual shape
Where do molecules get their true structure?
from the atoms present and the types of bonds formed amongst them
atoms in molecules are typically held together by covalent and hydrogen bonds
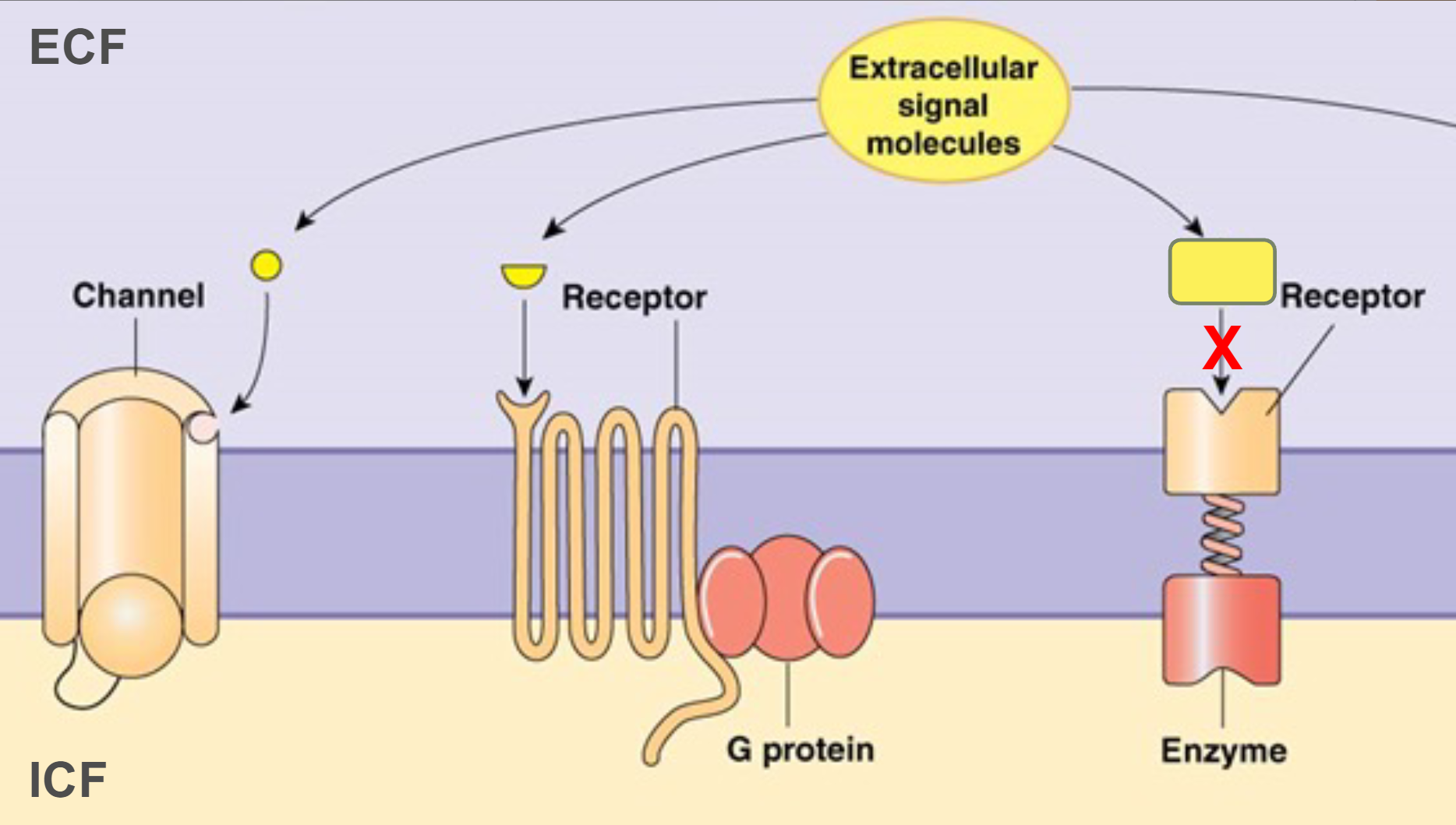
When molecules interact, shape is very important
always remember, STRUCTURE DETERMINES FUNCTION
wrong structure = wrong function

What are biomolecules?
biomolecules are a subset of organic molecules (containing carbon) that are important in living organisms
“building blocks” that help maintain homeostasis
what elements make up biomolecules
they must contain carbon to be considered organic, but also typically contain hydrogen and oxygen
some also have nitrogen and phosphorus
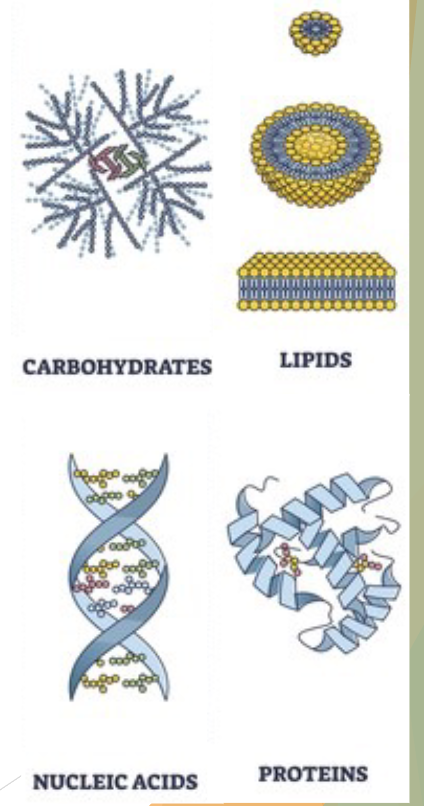
What are the 4 categories of biomolecules?
carbohydrates
lipids (fats and oils)
nucleotides/nucleic acids
proteins
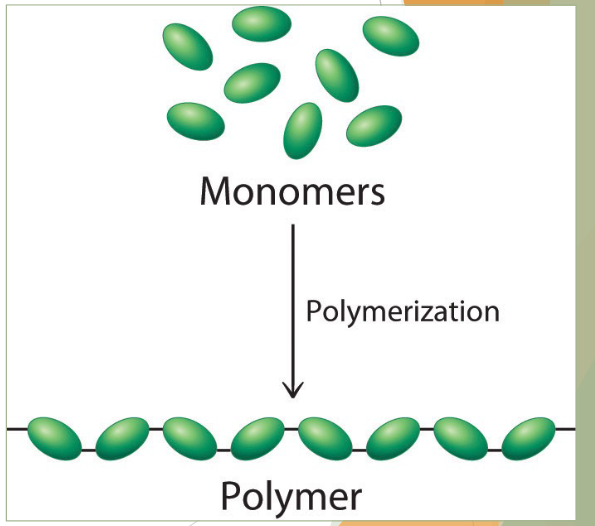
what is a monomer?
simplest form (or unit) of a biomolecule
“building blocks” that assemble into larger, more complex forms
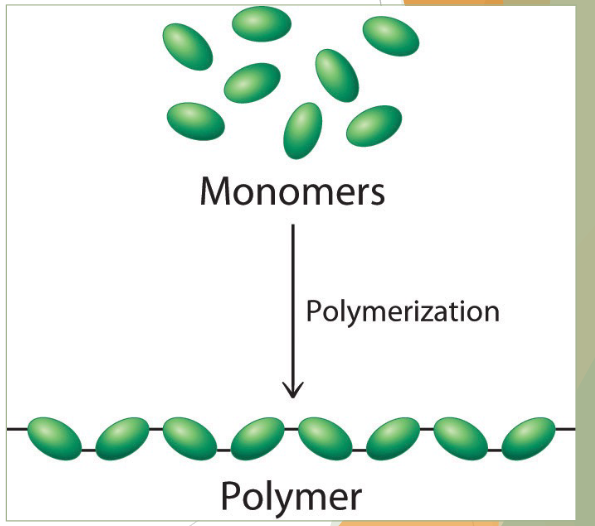
what is a polymer
chain of two or more biomolecule monomer
typically, many hundreds or thousands of monomers linked together
a neat and tidy way for cells to store molecules and energy for later usage storage
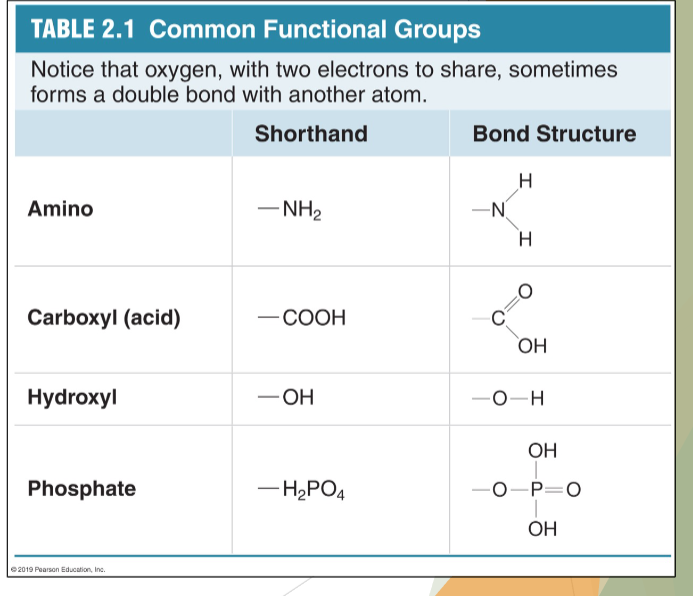
biomolecule monomers link up through reactions between functional groups
they are the “reactive” parts of biomolecules
where one biomolecule joins chemically with another using a covalent bond
Can also be transferred from molecule to molecule as a single unit
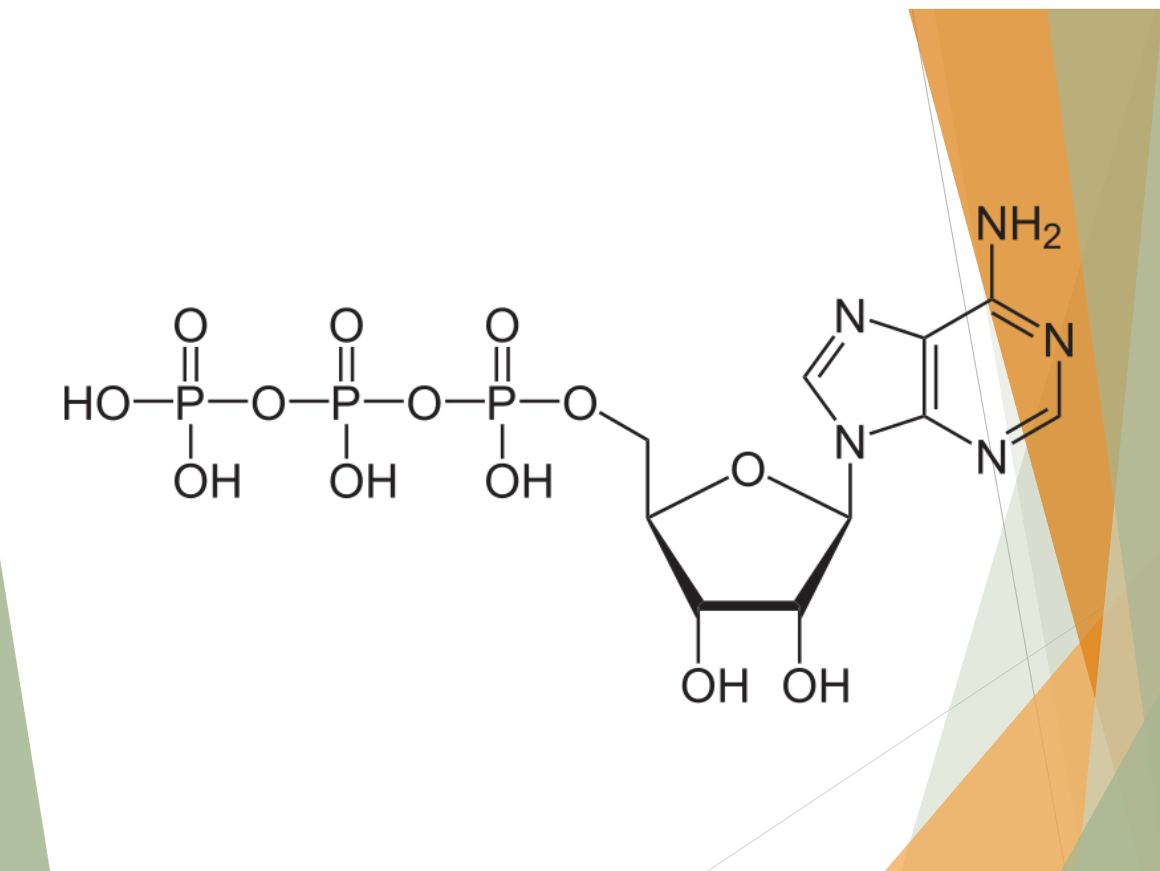
what molecule is this?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)!
3 phosphate groups