Medical Interventions 3.2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
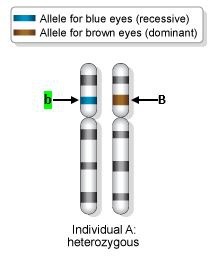
Allele
Any of the alternative forms of a gene that may occur at a given locus
Dependent variable
The measured outcome of a study; the data
Independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied
The dependent variable in the skin cancer lab
Amount of yeast growth
The independent variable in the skin cancer lab
Sunscreen or fabric
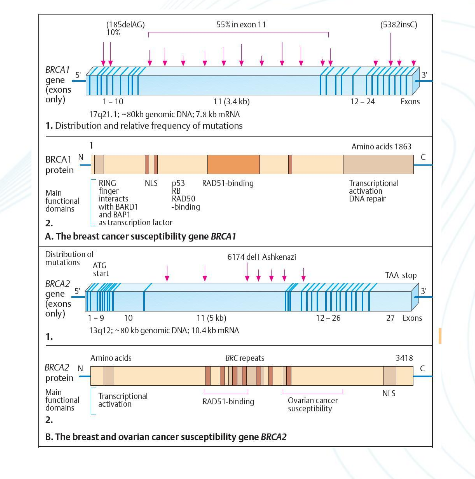
BRCA
Either of two tumor suppressor genes (BRCA 1 and BRCA 2) that in mutated form tend to be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers and especially breast and ovarian cancers
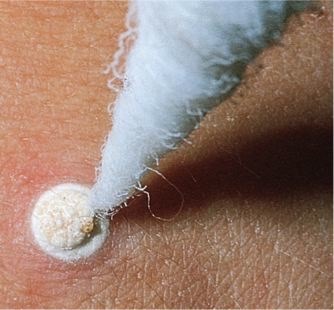
Cryosurgery
Surgery in which diseased or abnormal tissue (such as a tumor or wart) is destroyed or removed by freezing (by the use of liquid nitrogen)
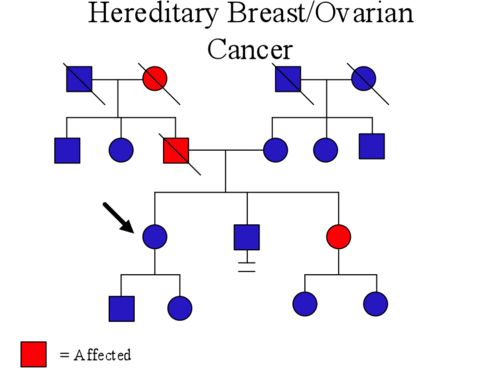
Familial cancer
Cancer that tends to occur in families, often indicating a genetic predisposition or inherited mutations.
Genetic marker
Alteration in DNA that may indicate an increased risk of developing a specific disease or disorder
Hereditary cancer
Cancer that is passed down through generations in families, often linked to specific genetic mutations.
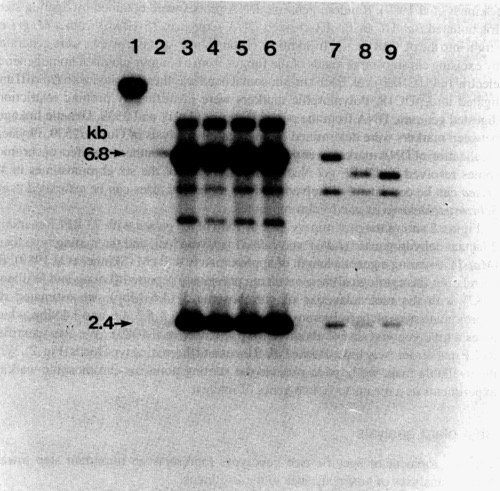
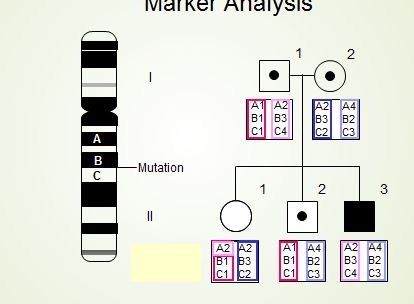
Marker analysis
A genetic technique whereby the sequence of the gene is not directly analyzed, but the mutant copy (allele) of the gene is inferred through analysis of a genetic marker
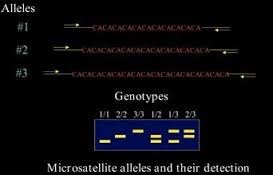
Microsatellite (also known as Short Tandem Repeats -STRs)
Any of numerous short segments of DNA that are distributed throughout the genome, that consist of repeated sequences of usually two to five nucleotides, and that are often useful markers in studies of genetic linkage because they tend to vary from one individual to another
Melanoma
A tumor of high malignancy that starts in melanocytes of normal skin or moles and metastasize as rapidly and widely
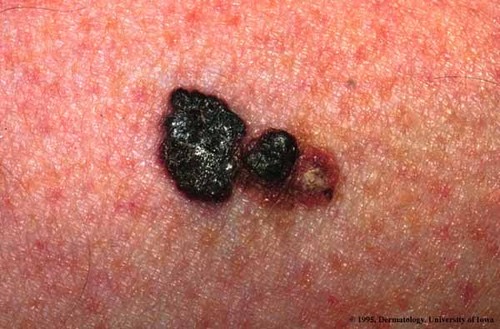
Model system
An organism chosen to study broad biological principles

Screening
To test or examine for the presence of something (As a disease)
Sporadic cancer
Cancer occurring occasionally, singly, or in scattered instances
Virologist
A specialist in virology, the branch of science that deals with viruses
Biological risk factors
Reduce these risks by being screened often and getting vaccinations (age, infections, sex)
Genetic risk factors
A gene can be inherited from parents that increases risk of cancer; (hereditary and familial cancer)
Environmental risk factors
Pollution, UV radiation, radiation
Behavioral risk factors
Diet, smoking, excessive sun exposure
BCC
basal cell carcinoma; forms in the lower layers of the epidermis
SCC
Squamous cell carcinoma; most common form of skin cancer; forms in the upper layers of the epidermis
Basal cell carcinoma
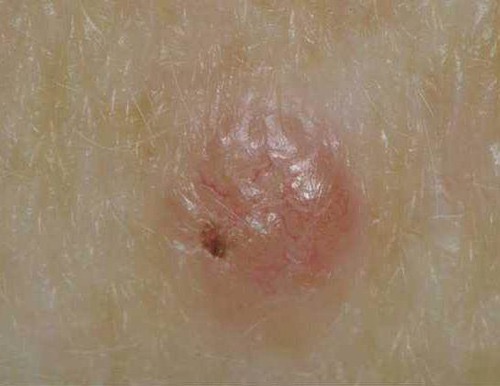
Squamous cell carcinoma
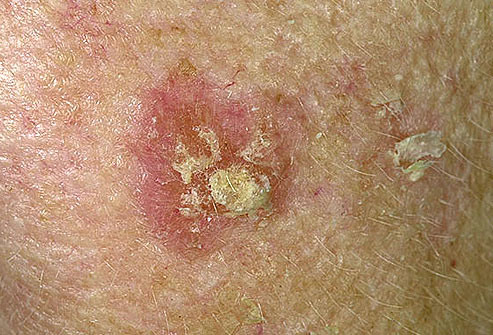
A
Asymmetry; ½ does not match the other ½
B
Border irregularities (no uniform edges)
C
Color: multi-colored
D
Diameter: greater than ¼ inch (pencil eraser)
E
Evolving: change in size and appearance over time
Pyrimidine antagonists
Inhibit the enzyme that makes pyrimidines (thymine, uracil, cytosine), which stops the production of DNA and RNA in skin cancer (sun sensitivity)
Genetic markers
Located in front of the gene in question; also known as STRs; identified with gel electrophoresis
Molecular tests/genetic markers
identify people w gene for cancer
Conduct marker analysis on family members
Identify STR sizes using standard curve
Compare STRs and identify alleles
Analyze allele to see if there is a genetic connection
Breast cancer prevention
Prophylactic surgery (mastectomy and hysterectomy); hormone therapy to reduce estrogen; physical activity to strengthen immune system; nutrition to increase antioxidant levels and prevent cells from forming
How can viruses cause cancer?
Inject DNA into cells and cause infection —> prolonged infection leads to mutation —> mutation leads to cell immortality
HBV, HCV
hepatitis B/C virus; may lead to liver cancer
EBV
Epstein-Barr virus; cause of mononucleosis; may cause stomach cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, nasopharyngeal cancer
HPV
Human Papillomavirus; may cause cervical cancer
MCV
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus; rare type of skin cancer
HTLV-1
Human T-lymphotrophic Virus, type 1; may cause a type of leukemia
Mammography
X-ray image of the breasts to detect the presence of tumors or precancerous cells; women age 40; performed annually
Colonoscopy
Examination of the colon using a flexible colon scope to detect cancer or precancerous polyps; men and women age 45; performed every 5-10 years
PSA
Prostate-specific antigen blood test to detect the presence of prostate cancer; men age 55; performed every 2-3 years
Visual Screeninf Test
Exam for skin cancer (performed by you or a provider); men and women at any age; performed annually
Pap test
Examination of cells taken from the cervix; women age 21; performed every 3 years
Low does CT scan
1/5 of the radiation of a standard CT scan for lung cancer; men and women age 50 who are smokers; performed every year
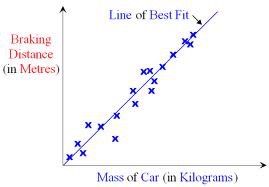
Standard curve graph
Used to quantify an unknown using a standard data set
African Americans are at a greater risk for
Colon cancer, prostate cancer
The greatest risk factor for cancer is
Age
Diet is a risk factor for
Stomach, colon, and prostate cancer