Orgo Quiz 3
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 16/17, Chapter 18, & Chapter 19
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
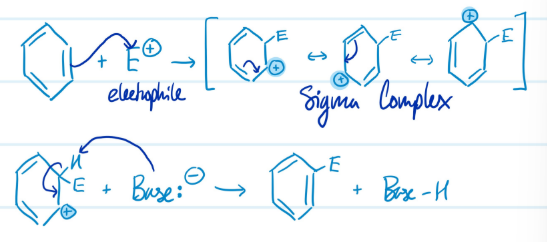
Mechanism
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
1) Benzene ring attacks electrophile, carbocation forms
2) Base attacks H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
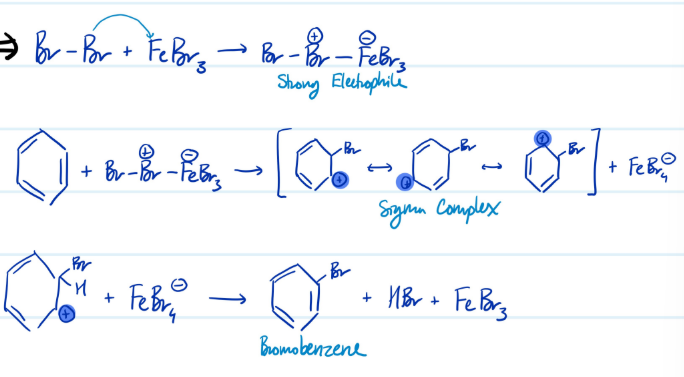
Mechanism
Bromination of Benzene
1) Form a stronger electrophile using FeBr3
2) Benzene ring attacks electrophile, carbocation forms
3) Base attacks H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Bromination of Benzene
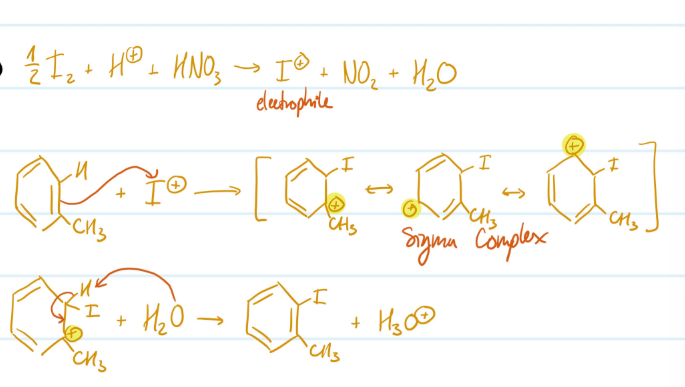
Mechanism
Iodination of Toluene
Pre-steps) Form electrophile (I+ ion)
1) Toluene attacks electrophile, carbocation forms
2) Deprotonation, aromaticity regained
Steps for Iodination of Toluene
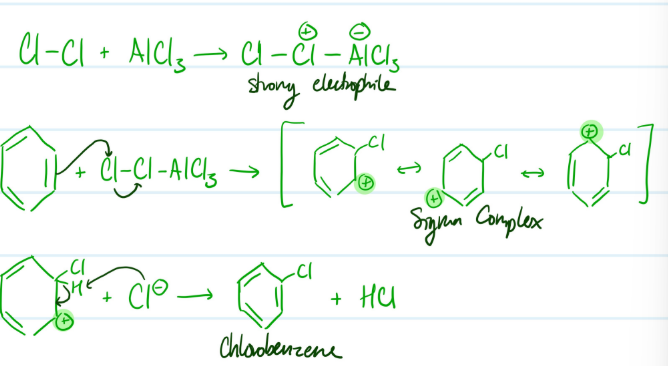
Mechanism
Chlorination of Benzene
1) Form stronger electrophile using AlCl3
2) Benzene attacks electrophile, carbocation
3) Base attacks H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Chlorination of Benzene
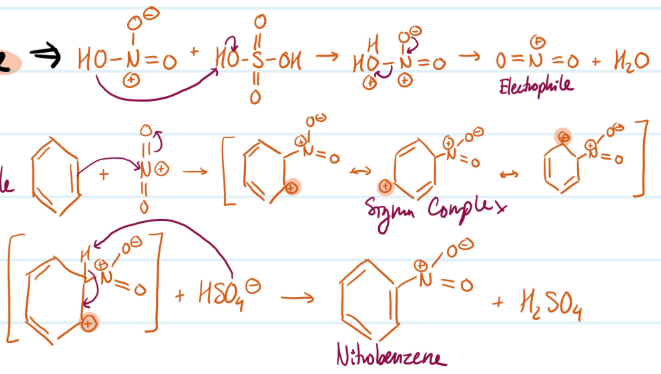
Mechanism
Nitration of Benzene
Pre-steps) Form electrophile (+NO2)
1) Benzene attacks electrophile, carbocation forms
2) Base attacks H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Nitration of Benzene
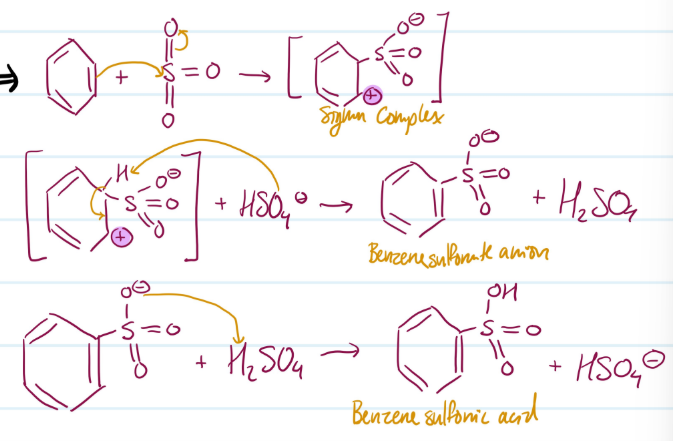
Mechanism
Sulfonation of Benzene
1) Benzene attacks electrophile (SO3), carbocation forms
2) Base attacks H
3) Protonation
Steps for Sulfonation of Benzene
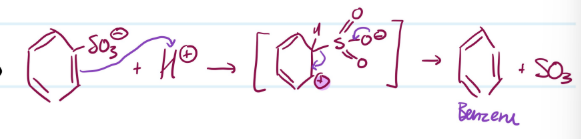
Mechanism
Desulfonation of Benzene
Activating Groups do what?
Speed Up Reactions
Activating groups are what?
Electron Donating Groups
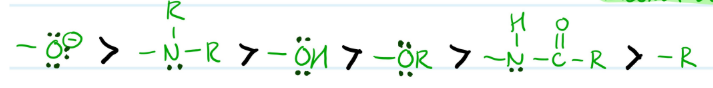
Example of What?
Ortho and Para Directing Substituents
Deactivating Groups do what?
Slows Reaction
Deactivating Groups are what?
Electron Withdrawing Groups
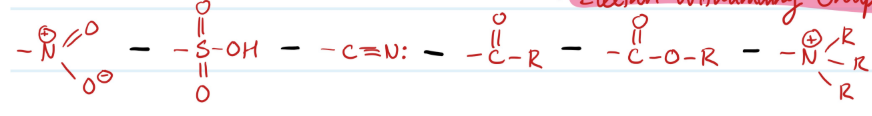
Examples of What?
Meta Directing Substituents
Halobenzenes are what?
Ortho and Para directing BUT deactivating
Activating Groups in relation to Deactivating Groups
Stronger Directing Effect
Mechanism
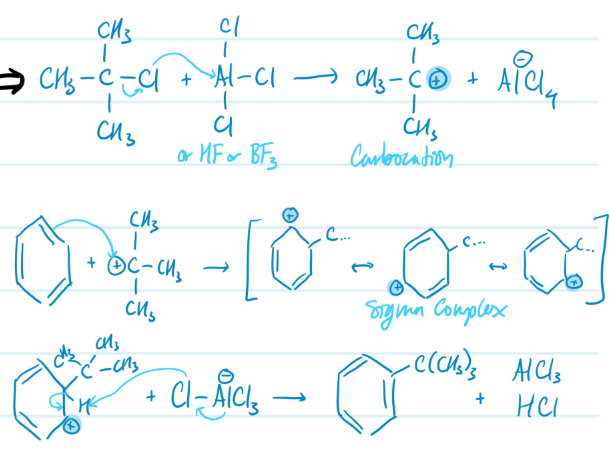
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
1) Form carbocation using AlCl3 or HF or BF3
2) Benzene ring attacks carbocation, sigma complex forms
3) Base attacks H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Limitations of Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
Only works with benzene, activated benzenes, and halobenzenes; rearrangements are common; polyalkylation is possible
Mechanism
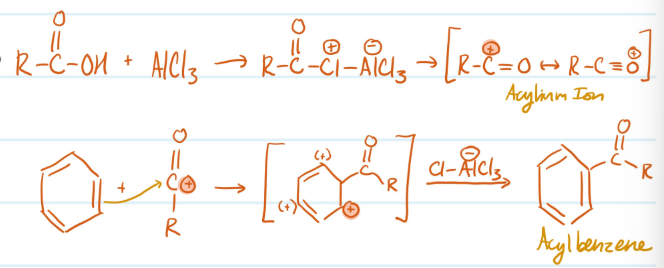
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
1) Form electrophile (R-C+=O)
2) Benzene attacks electrophile, carbocation forms
3) Base attacks H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Friedel-Crafts Acylation
Mechanism
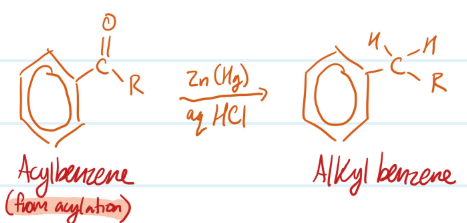
Clemmensen Reduction
1) Reduces acylbenzene using Zn (Hg) and aq HCl
2) Produces alkylbenzene
Steps for Clemmensen Reduction
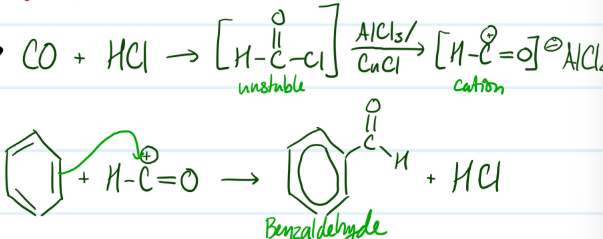
Mechanism
Gatterman-Koch Formylation
1) Form electrophile (H-C+=O)
2) Benzene ring attacks electrophile
Steps for Gatterman-Koch Formylation
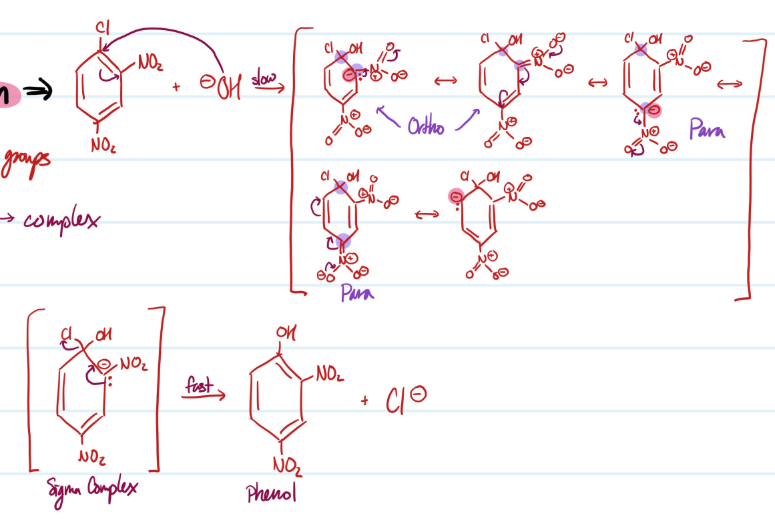
Mechanism
Addition-Elimination
1) Nucleophile attacks benzene ring, sigma complex
2) Loss of leaving group, aromaticity regained
Steps for Addition-Elimination
Condition for Addition-Elimination Reaction
Requires benzene ring with strong electron withdrawing group
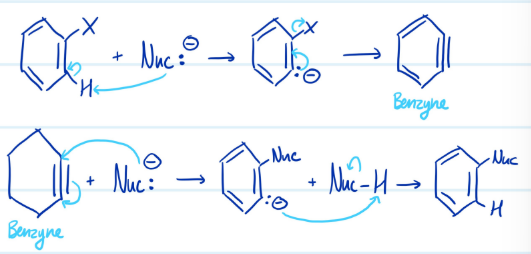
Mechanism
Elimination-Addition: Benzyne
1) Nucleophile deprotonates benzene > carbanion > benzyne
2) Nucleophile attacks benzyne > carbanion > protonate
Steps for Elimination-Addition: Benzyne
Conditions for Elimination-Addition: Benzyne
Requires benzene with no strong electron withdrawing groups
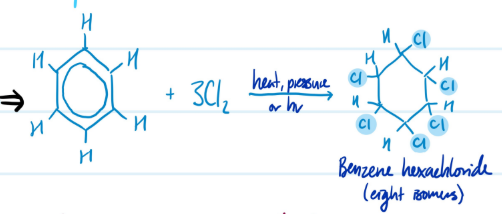
Mechanism
(Total) Chlorination of Benzene
1) Add 3Cl2
2) Add heat, pressure, or hv
Steps for (Total) Chlorination of Benzene
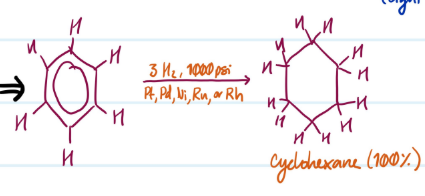
Mechanism
Catalytic Hydrogenation
1) Add 3H2, 1000 psi
2) Add Pt, Pd, Ni, Ru, or Rh
Steps for Catalytic Hydrogenation
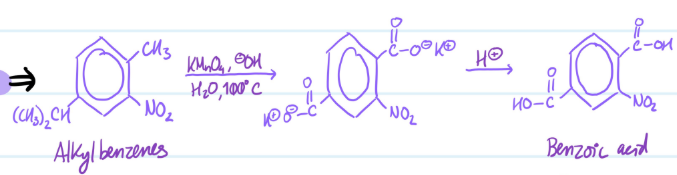
Mechanism
Permanganate Oxidation
1) Add hot KMnO4 and H2O
2) Protonate
Steps for Permanganate Oxidation
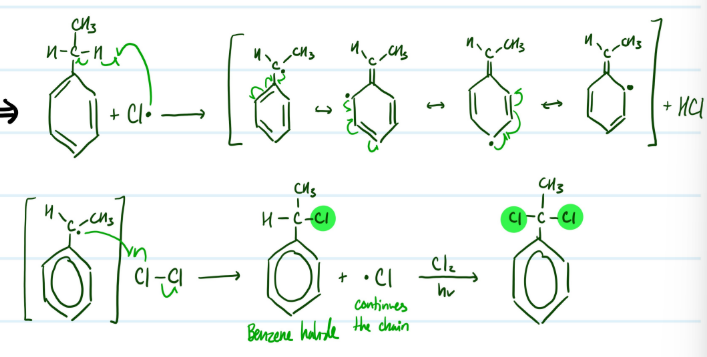
Mechanism
Side-Chain Chlorination
1) Add Cl radical, resonance
2) Add Cl-Cl to form benzene halide
Steps for Side-Chain Chlorination
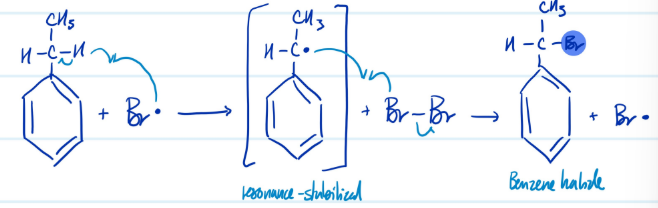
Mechanism
Side-Chain Bromination
1) Add Br radical, resonance
2) Add Br-Br to form benzene halide
Steps for Side-Chain Bromination
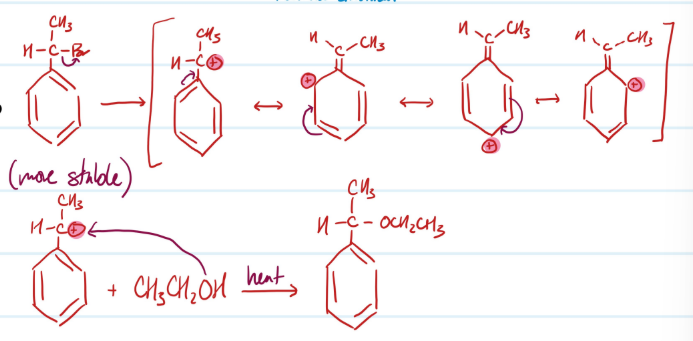
Mechanism
SN1: Benzylic Halides

Mechanism
SN2: Benzylic Halides
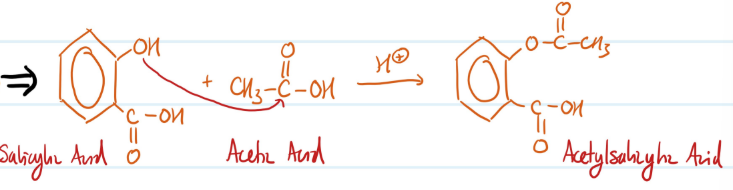
Mechanism
Acylation of Phenols
1) Phenol + Acetic Acid = Ester
Steps for Acylation of Phenols
Mechanism
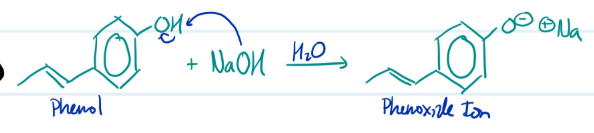
Formation of Phenoxide Ions
1) Phenol + NaOH = Phenoxide Ion
Steps for Formation of Phenoxide Ion
Mechanism
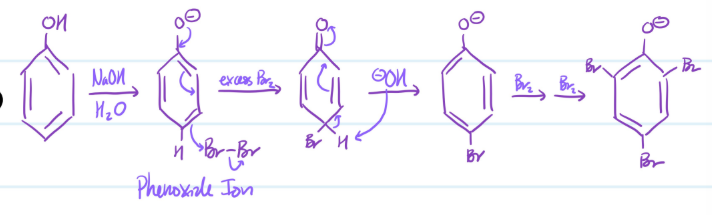
Phenol Substitution
1) Phenol + NaOH = Phenoxide Ion
2) Phenoxide Ion + excess Br2
3) -OH attacks H
4) Use Br2 to add more bromines
Steps for Phenol Substitution
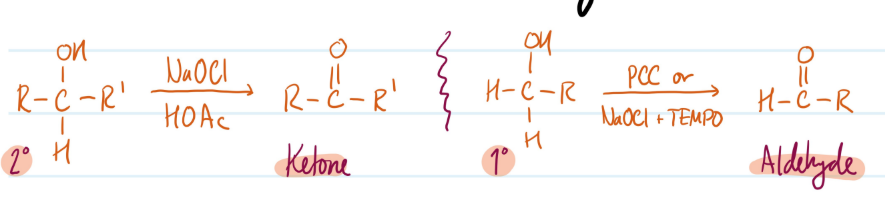
Mechanism
Oxidation of Alcohols (into Ketones & Aldehydes)
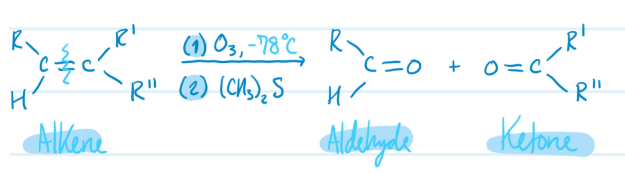
Mechanism
Ozonolysis (Alkene into Ketones & Aldehydes)
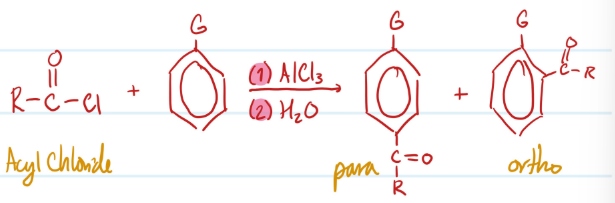
Mechanism
Friedel-Crafts Acylation (forms ketones)
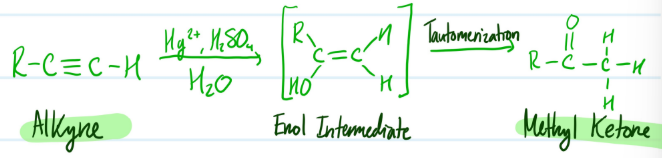
Mechanism
Hydration of Alkynes
1) Alkyne + Hg2+, H2SO4, H2O = Enol Intermediate (Markovnikov)
2) Enol Intermediate + Tautomerization = Methyl Ketone
Steps for Hydration of Alkynes
Mechanism
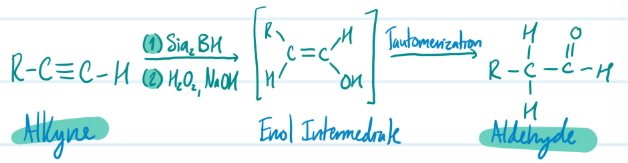
Hydroboration of Alkynes
1) Alkyne + Sia2BH + H2O2, NaOH = Enol Intermediate (Anti-Markovnikov)
2) Enol Intermediate + Tautomerization = Aldehyde
Steps for Hydroboration of Alkynes
Mechanism
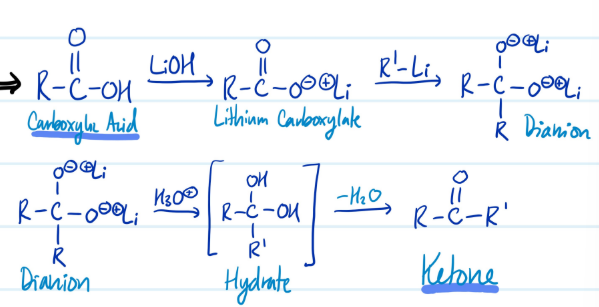
Carboxylic Acids into Ketones
1) Carboxylic Acid + LiOH = Lithium Carboxylate + R’-Li = Dianion
2) Dianion + H3O+ = Hydrate - H2O = Ketone
Steps for Carboxylic Acids into Ketones
Mechanism
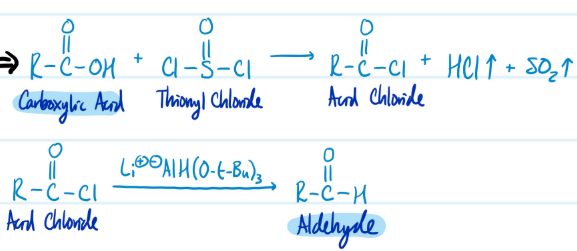
Carboxylic Acids into Aldehydes
1) Carboxylic Acid + SOCl2 = Acid Chloride
2) Acid Chloride + LiAlH(O-t-Bu)3 = Aldehyde
Steps for Carboxylic Acids into Aldehydes
Mechanism
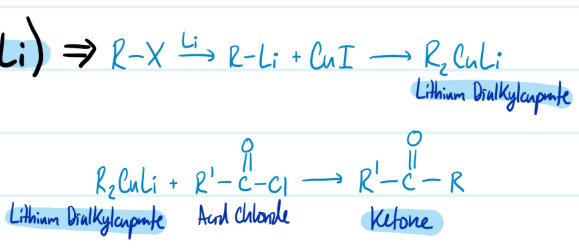
Carboxylic Acids into Ketones with R2CuLi
Pre) Carboxylic Acid + SOCl2 = Acid Chloride
1) R-X + Li = R-Li + CuI = R2CuLi
2) R2CuLi + Acid Chloride = Ketone
Steps for Carboxylic Acids into Ketones with R2CuLi
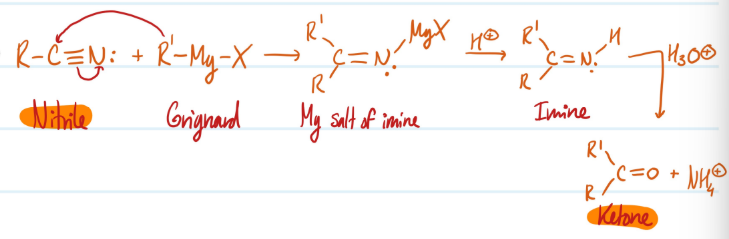
Mechanism
Nitriles into Ketones
1) Nitrile + R’-Mg-X = Mg salt of Imine + H+ = Imine
2) Imine + H3O+ = Ketone
Steps for Nitriles into Ketones
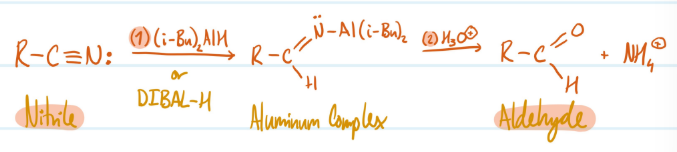
Mechanism
Nitriles into Aldehydes
1) Nitrile + DIBAL-H = Aluminum Complex
2) Aluminum Complex + H3O+ = Aldehyde
Steps for Nitriles into Aldehydes
Mechanism
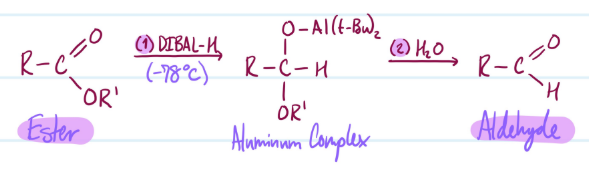
Esters into Aldehydes
1) Ester + DIBAL-H (-78°C) = Aluminum Complex
2) Aluminum Complex + H2O = Aldehyde
Steps for Esters into Aldehydes
Mechanism
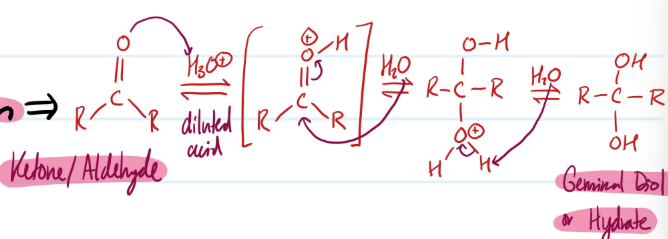
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
1) Protonate Ketone/Aldehyde
2) Water nucleophile attack on carbon, lose double bond
3) Deprotonate = Geminal Diol/Hydrate
Steps for Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
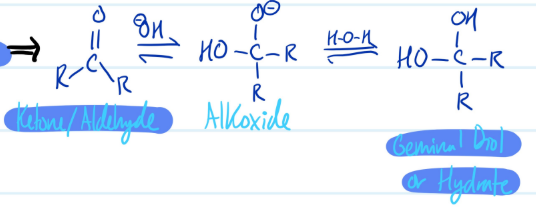
Mechanism
Base-Catalyzed Hydration
1) -OH nucleophile attacks carbon, forms alkoxide
2) Protonate = Geminal Diol/Hydrate
Steps for Base-Catalyzed Hydration
Mechanism
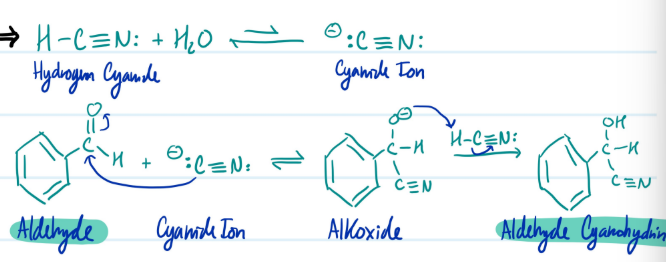
Cyanohydrin
1) HCN: + H2O = - :CN:
2) Aldehyde + - :CN: = Alkoxide + HCN: = Aldehyde Cyanohydrin
Steps for Cyanohydrin
Mechanism
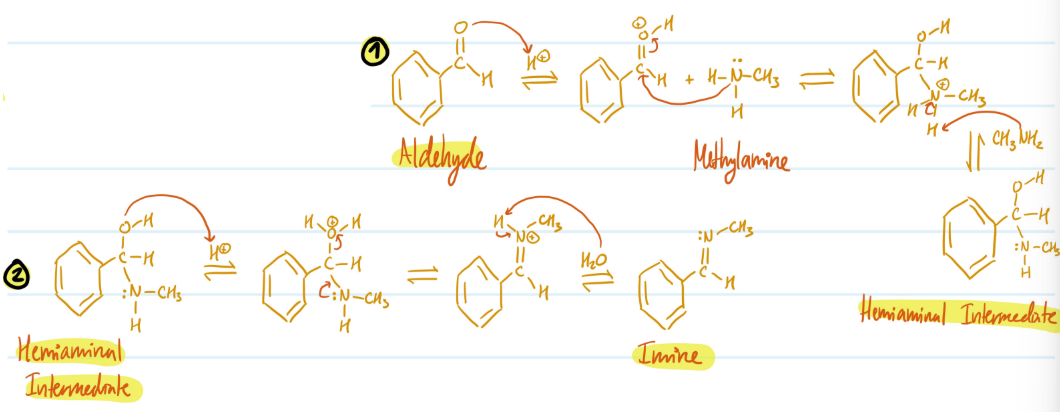
Imines
1) Protonate Aldehyde, NH2CH3 attacks carbon, lose double bond
2) Use NH2CH3 to deprotonate N = Hemiaminal Intermediate
3) Protonate OH to make good leaving group, N forms double bond
4) Deprotonate N = Imine
Steps for Imines
Mechanism
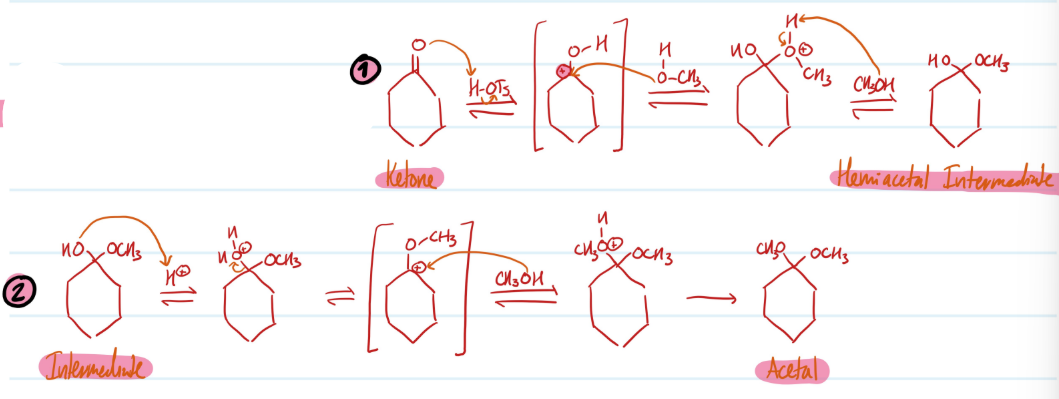
Acetals
1) Protonate Ketone using H-OTs, lose double bond, carbocation
2) CH3OH nucleophilic attack, deprotonate = Hemiacetal Intermediate
3) Protonate OH to make good leaving group, carbocation
4) CH3OH nucleophilic attack, deprotonate = Acetal
Steps for Acetals
Mechanism
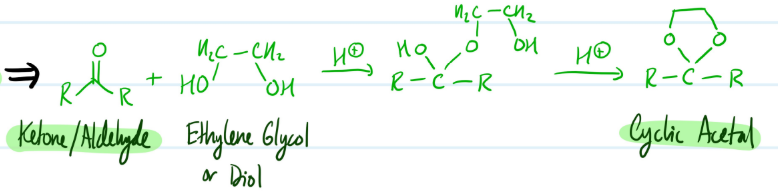
Cyclic Acetals
1) Ketone/Aldehyde + Ethylene Glycol/Diol
2) Add H+ = Cyclic Acetal
Steps for Cyclic Acetals
Purpose of Cyclic Acetals?
Protects ketones/aldehydes from unwanted reactions
Mechanism
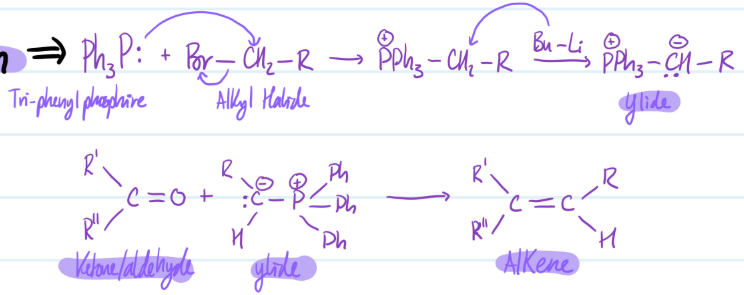
Wittig Reaction
1) Ph3P: + Br-CH2-R = +PPh3-CH2-R + Bu-Li = +PPh3- - :CH-R (Ylide)
2) Ketone/Aldehyde + Ylide = Alkene
Steps for Wittig Reaction
Mechanism
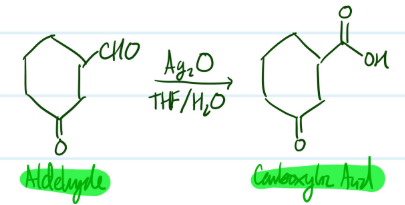
Oxidation of Aldehydes
1) Aldehyde + Ag2O, THF/H2O = Carboxylic Acid
(Can use Na2Cr2O7 with H2SO4 OR KMnO4 OR excess NaOCl/TEMPO)
Steps for Oxidation of Aldehydes
Mechanism
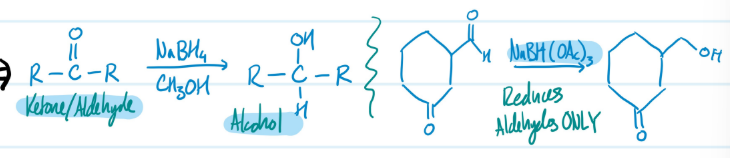
Hydride Reductions
1) Ketone/Aldehyde + NaBH4, CH3OH = Alcohol
> NaBH(OAc)3 reduces aldehydes ONLY
Steps for Hydride Reductions
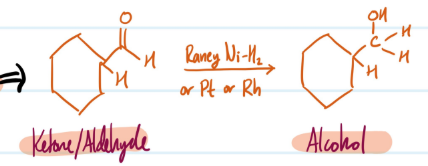
Mechanism
Catalytic Hydrogenation (of Ketone/Aldehyde)
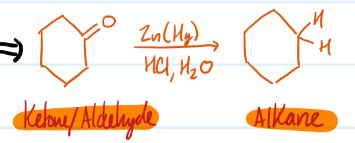
Mechanism
Clemmensen Reduction (of Ketone/Aldehyde)
Basicity of Amines
Ammonia < 3 < 1 < 2
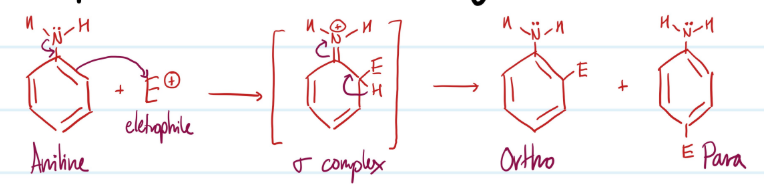
Mechanism
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Arylamines
1) Aniline ring attacks electrophile, N forms double bond, sigma complex
2) Ortho and Para addition of electrophile
Steps for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Arylamines
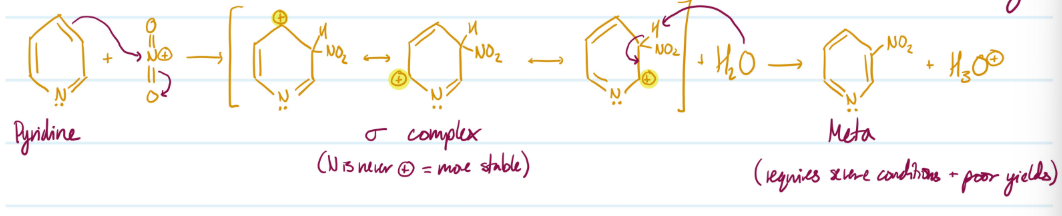
Mechanism
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Pyridine
1) Pyridine ring attacks NO2, meta addition (Nitrogen heteroatom = deactivating)
2) sigma complex (N is never positive = more stable)
3) H2O removes H, aromaticity regained
Steps for Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Pyridine
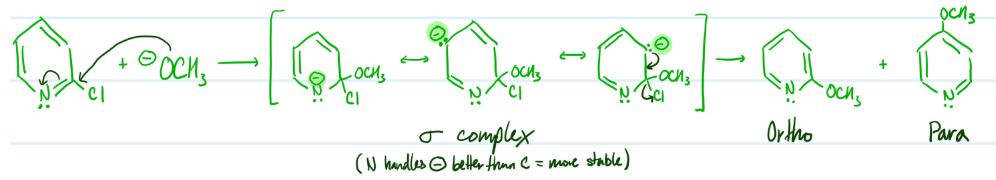
Mechanism
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution of Pyridine