chapter 42: Neural Regulation and Drug Effects on the Nervous System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Nervous system
receive information: environmental stimuli (internal/external)
translate information: evaluate stimuli
send response: initiate and send to effector, coordinate rapid, immediate responses
Nerve nets
interconnected neurons, no central control point
movement and response to stimuli
response from multiple directions, bidirectional
animals with nerve nets
clade radiata, phylum cnidaria (jellyfish)
-slow net: coordinates tentacles; fast net: coordinates swimming
clade bilateria, phylum echinodermata (starfish)
-radial nervous system: coordinates tube feet and arm movement
Bilateral nervous systems
structure: control point (ganglia/brain), interconnected neurons
function: integration (stimulus, intensity, direction), coordination of movement and response
response: localization of stimulus, unidirectional neurons (absolute refractory period), separation of function
animals with bilateral nervous system
platyhelminthes, annelida, arthropoda, cephalopoda
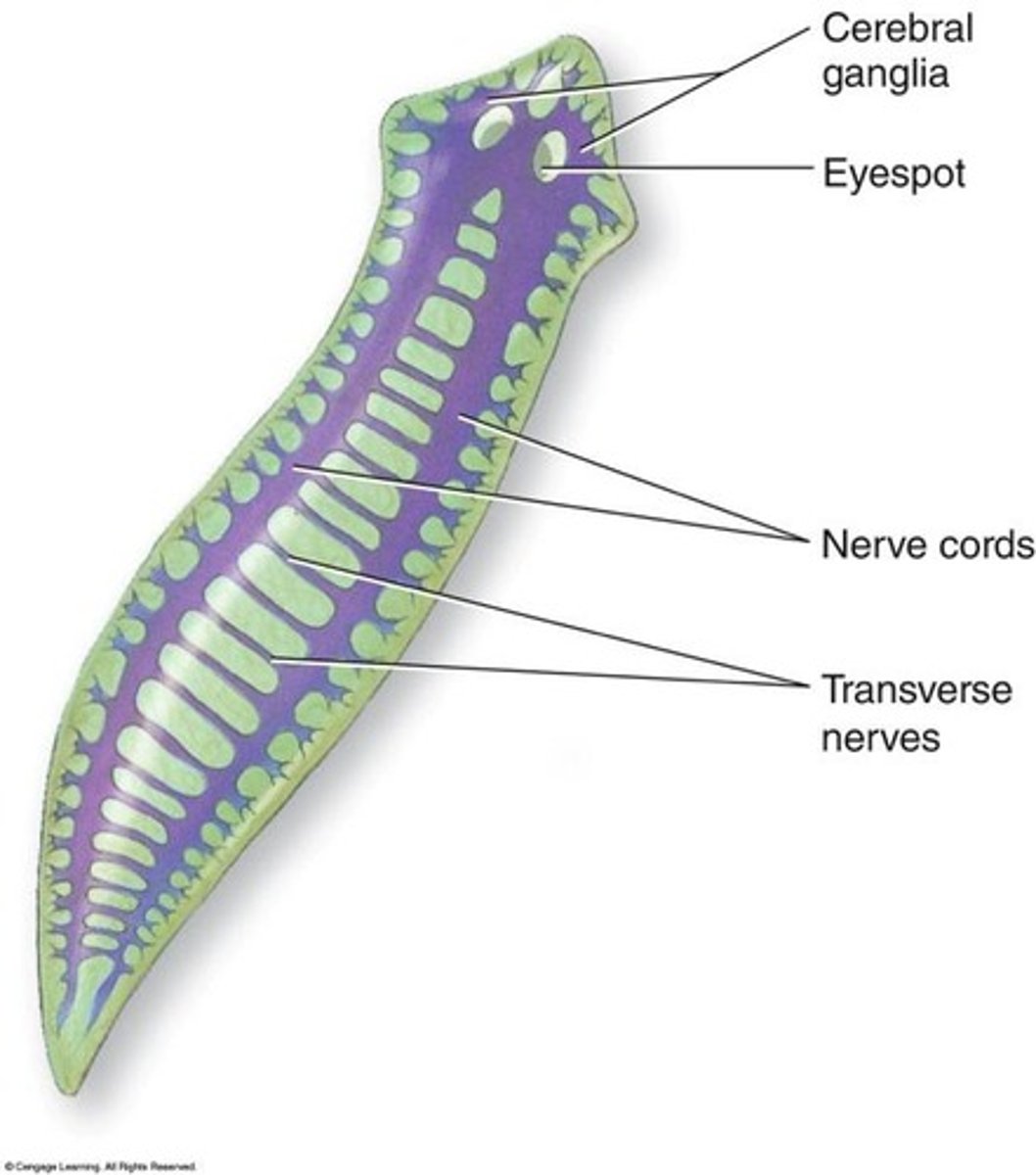
platyhelminthes nervous system
cerebral ganglia, primitive brain
nerve cords: two solid, ventral, longitudinal
neuron types: all 3 types
behavior: many senses, learning, directed movement (taxis)
annelida nervous system
brain(coordinated, adaptive response), ganglion (segmented control)
nerve cord: solid, ventral
behavior: forward movement with segments, elongating and shortening at times
arthropoda nervous system
insects have the largest brain in phylum
have more neurons for learning, memory olfactory processing (foraging ants)
cephalopods nervous system
brain has lobes and intricate folds, regions well developed for specific functions
senses well developed
octopus
phylum cephalopoda
greatest brain size
significant ability to learn, perform difficult tasks
color, skin, shape changes
afferent nervous system
sensory
efferent nervous system
motor
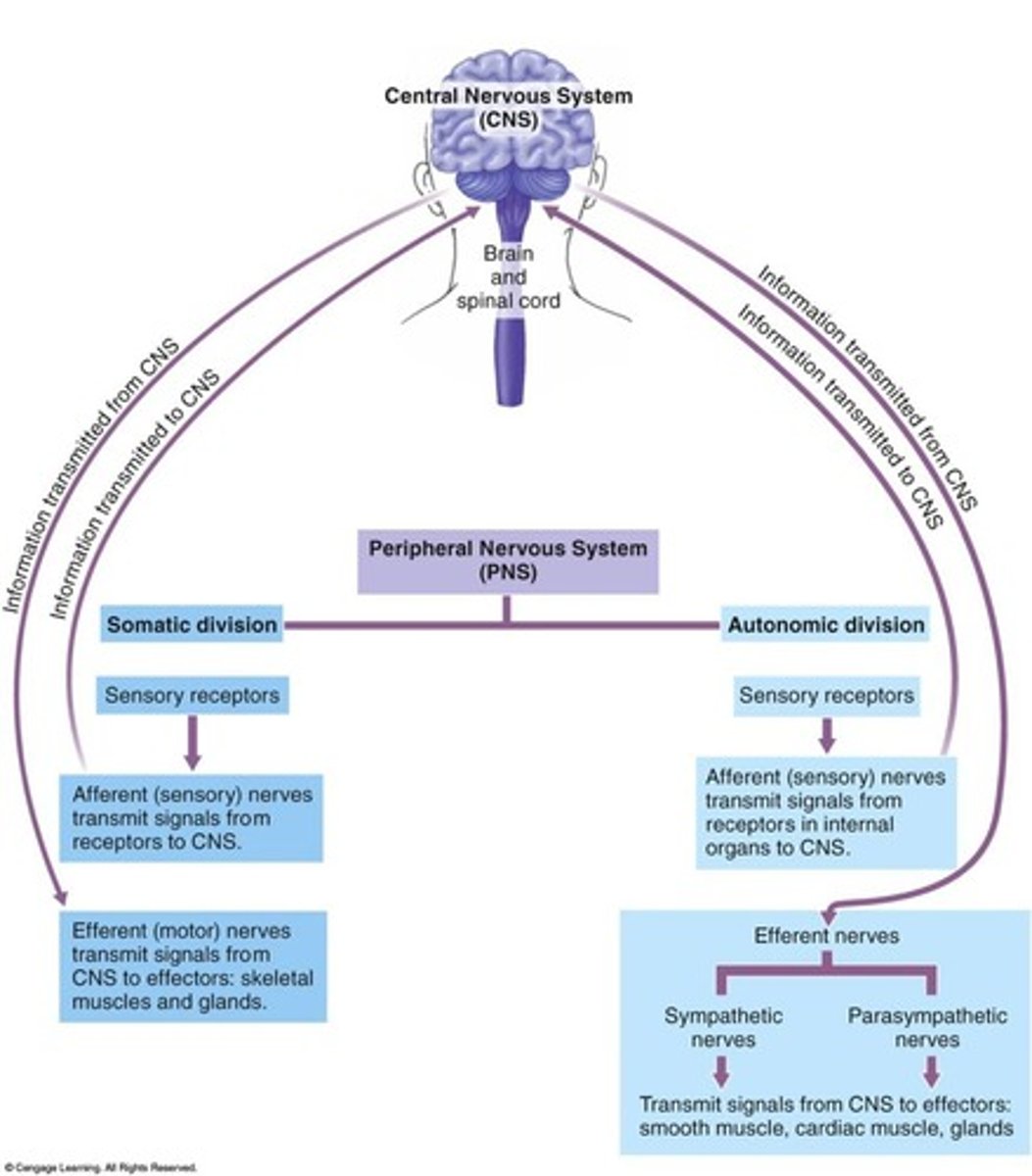
CNS
integrates information and sends responses
brain (cranium) and spinal cord
12 pairs of cranial nerves and 32 pairs of spinal nerves
nerves function to connect to periphery
PNS
connects to but lies outside of brain and spinal cord
carry information to and from body parts and regions
divisions: somatic and autonomic (parasympathetic and sympathetic)
somatic nervous system
part of PNS
skeletal muscle and skin
voluntary muscle movement - conscious activities
autonomic nervous system
part of PNS
involuntary response
controls internal organs
divides into parasympathetic and sympathetic
parasympathetic nervous system
relaxing system
maintain minimal energy levels
resting and digesting
sympathetic nervous system
alert system
mobilize energy, decrease non vital functions
stimulate adrenal gland to release epinephrine
fight or flight
Vertebrate nervous system
Includes the CNS and PNS
Reflexes
protective function
innate behavior
PNS connects to CNS
involve cranial or spinal pathways
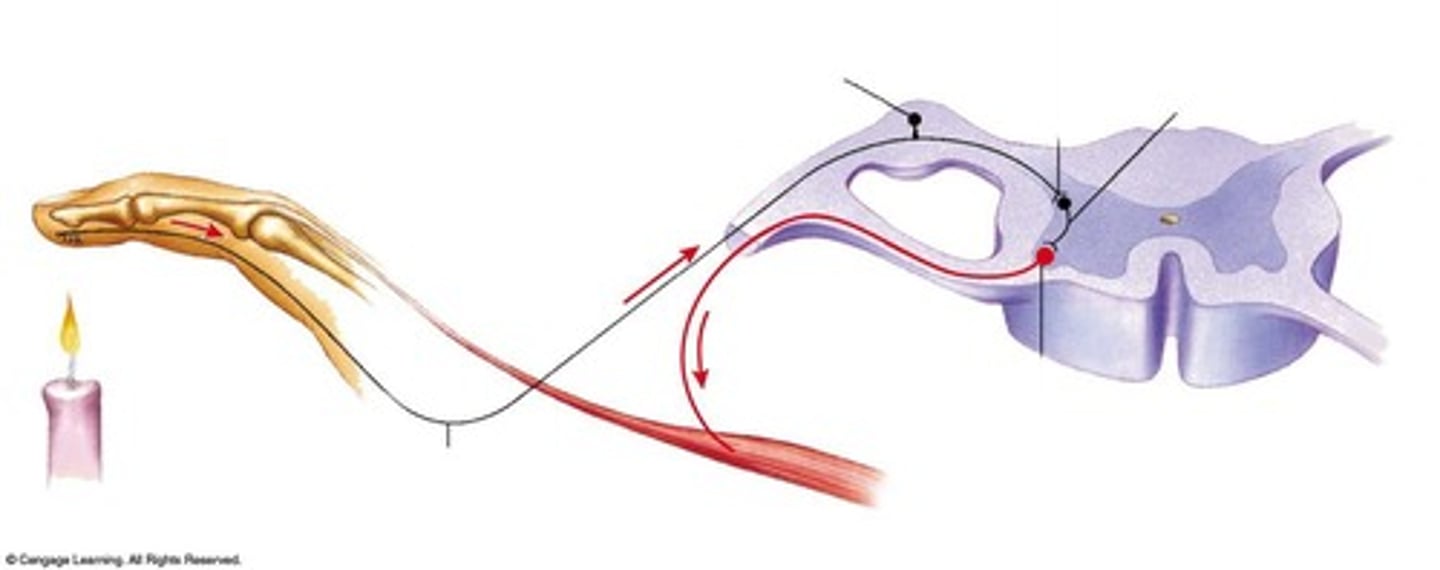
Muscle spindle reflex (glogi tendon stretch reflex)
spinal reflex
monosynaptic, unisegmental, ipsilateral (all on one side), reciprocal innervation (opposing muscle groups)
contraction opposite to the stretch initiator
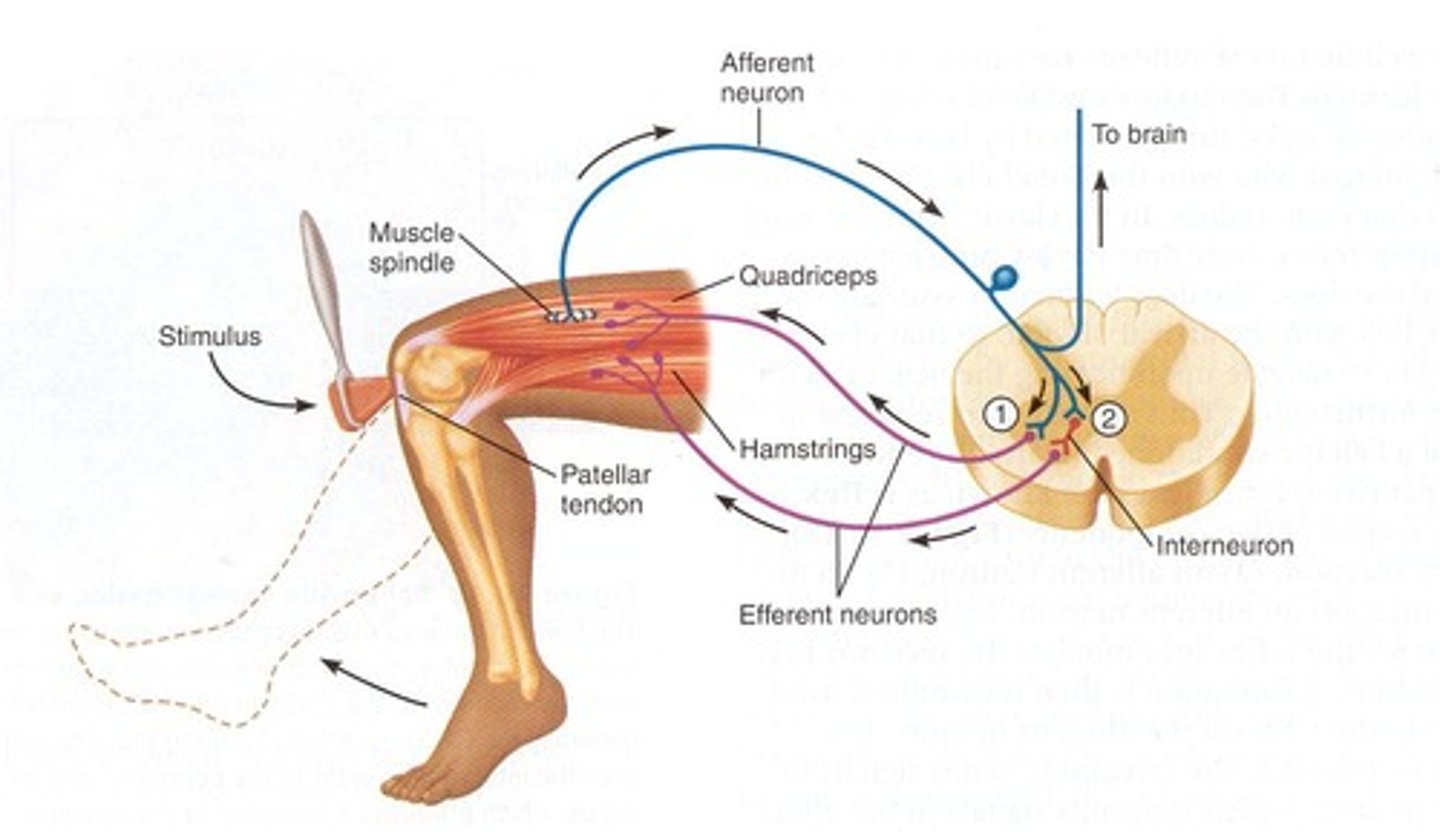
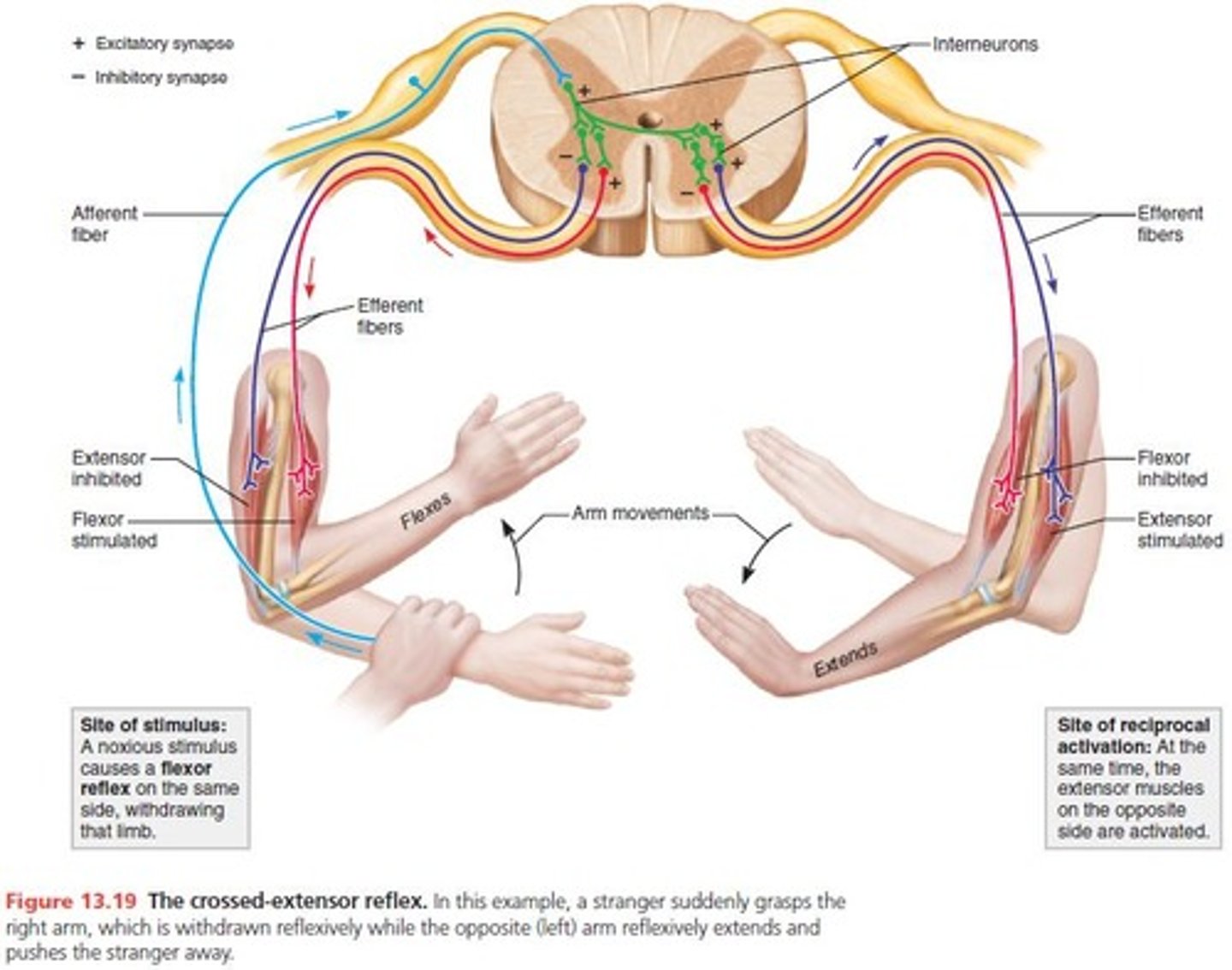
Withdrawal reflex
spinal reflex
excitatory and inhibitory interneuron
withdraw on stimulated side of body (ipsilateral), extension on opposite side of body (contralateral)
intersegmental response (both sides of cord)
same input- both side effected
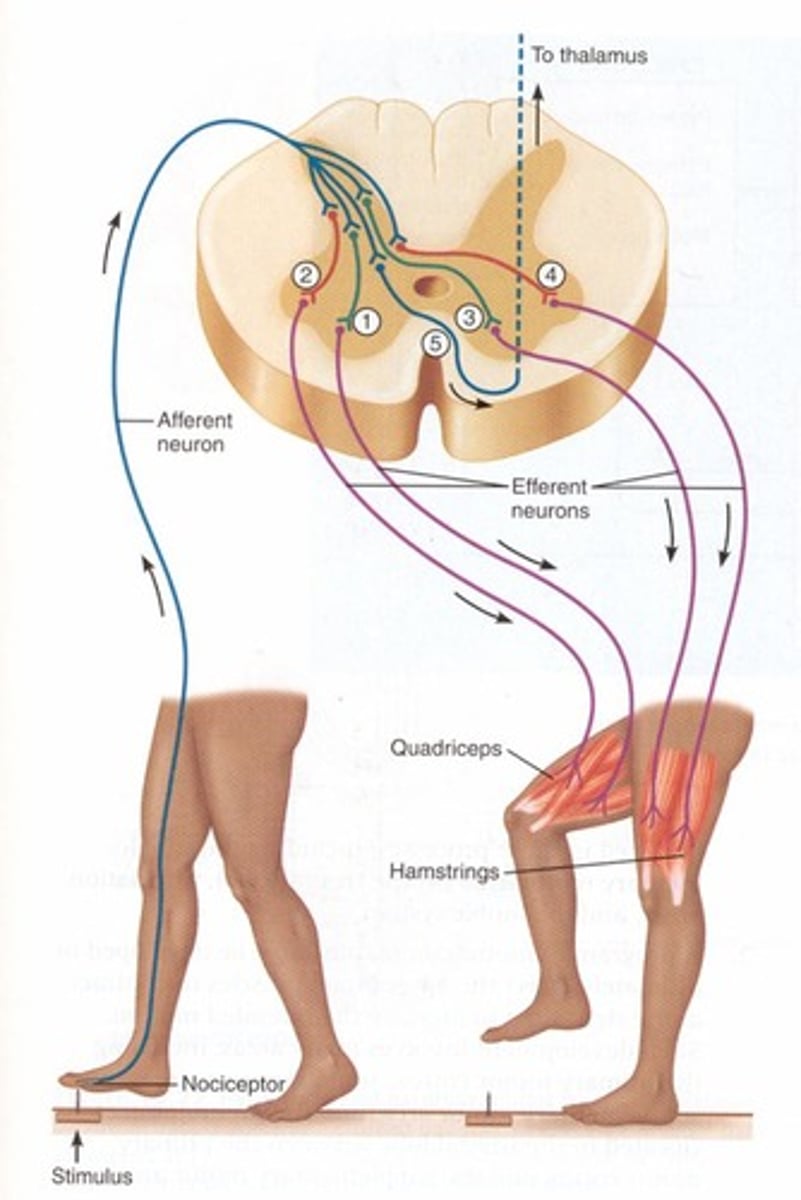
Cross extensor reflex
When one limb is withdrawn, the opposing limb extends to support the body
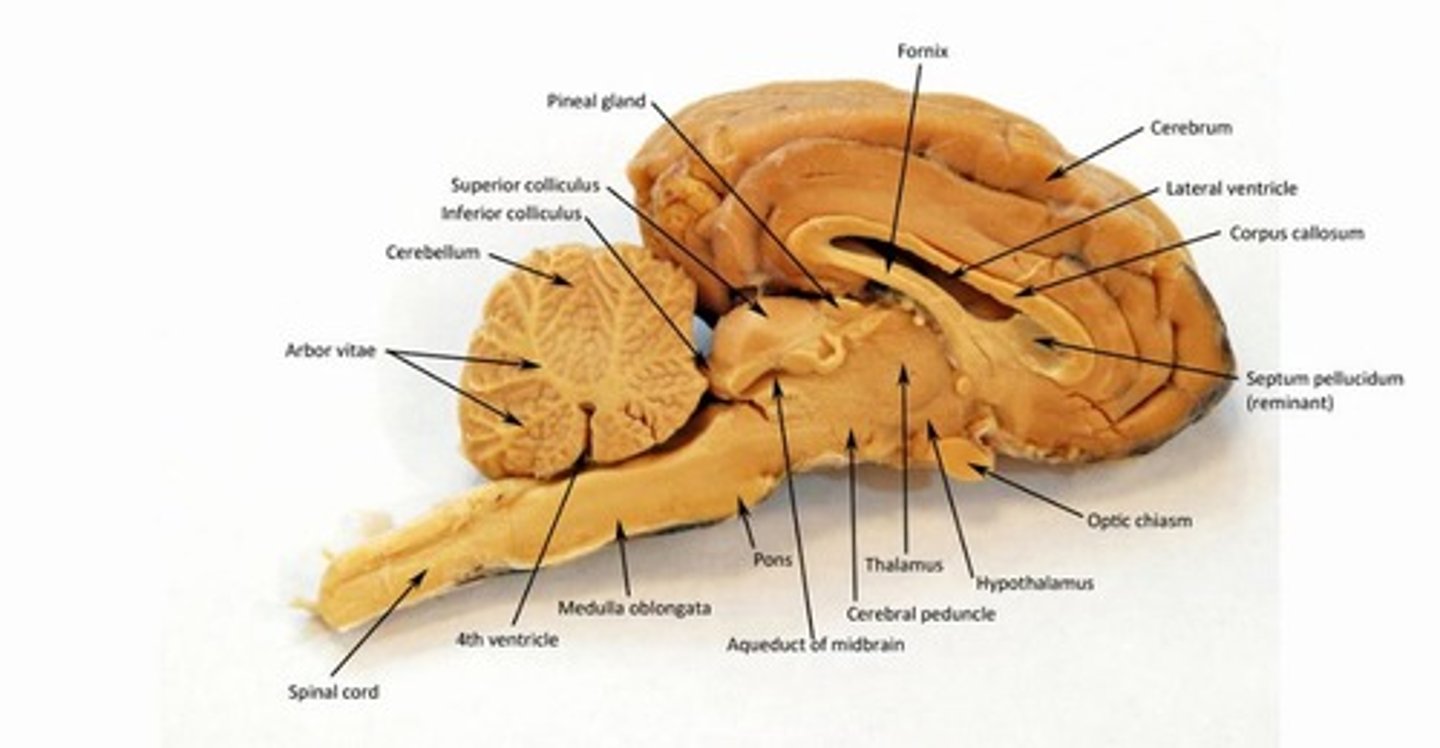
Cerebrum
most superior part and largest brain mass
second largest surface area
cortex: grey matter, cell bodies and dendrites, information processing
inner portion: mostly white matter, axons that connect various parts of brain
CNS protective barriers
The protective barriers of the central nervous system.
Receptor site
The location where drugs exert their effects.
Receptor affinity
The strength of the binding between a drug and its receptor.
Intracellular drug
A drug that works within cells.
Extracellular drug
A drug that works outside of cells.
Resistance
The reduction in effectiveness of a drug in curing a disease or condition.
Brain
a centralized control/integration point of the nervous system
Contralateral
when sensory and motor neurons enter and exit on opposite sides of the spinal cord, integration happens in the cord during the crossover to the other side
Decussation
crossing over of spinal nerve tracts that occurs in the medulla
Ganglion
a group of nerve cell bodies, in the vertebrate CNS they are located peripherally
Gray matter
nervous tissue that contains only unmyelinated axons, cell bodies, and support cells
Gyrus
the convoluted brain tissue of the cerebrum
Hemisphere
one half (left or right) of the cerebrum
Ipsilateral
when sensory, integration and motor neurons connect on one side of the spinal cord
Sulcus
furrows (dips between the gyri) that run throughout the cerebrum
Cerebral ganglia
concentration of nerve cell bodies; primitive brain - control system
Cerebellum
located dorsal to pons and medulla; second largest mass of the brain, involved in hand-eye coordination, balance, and posture
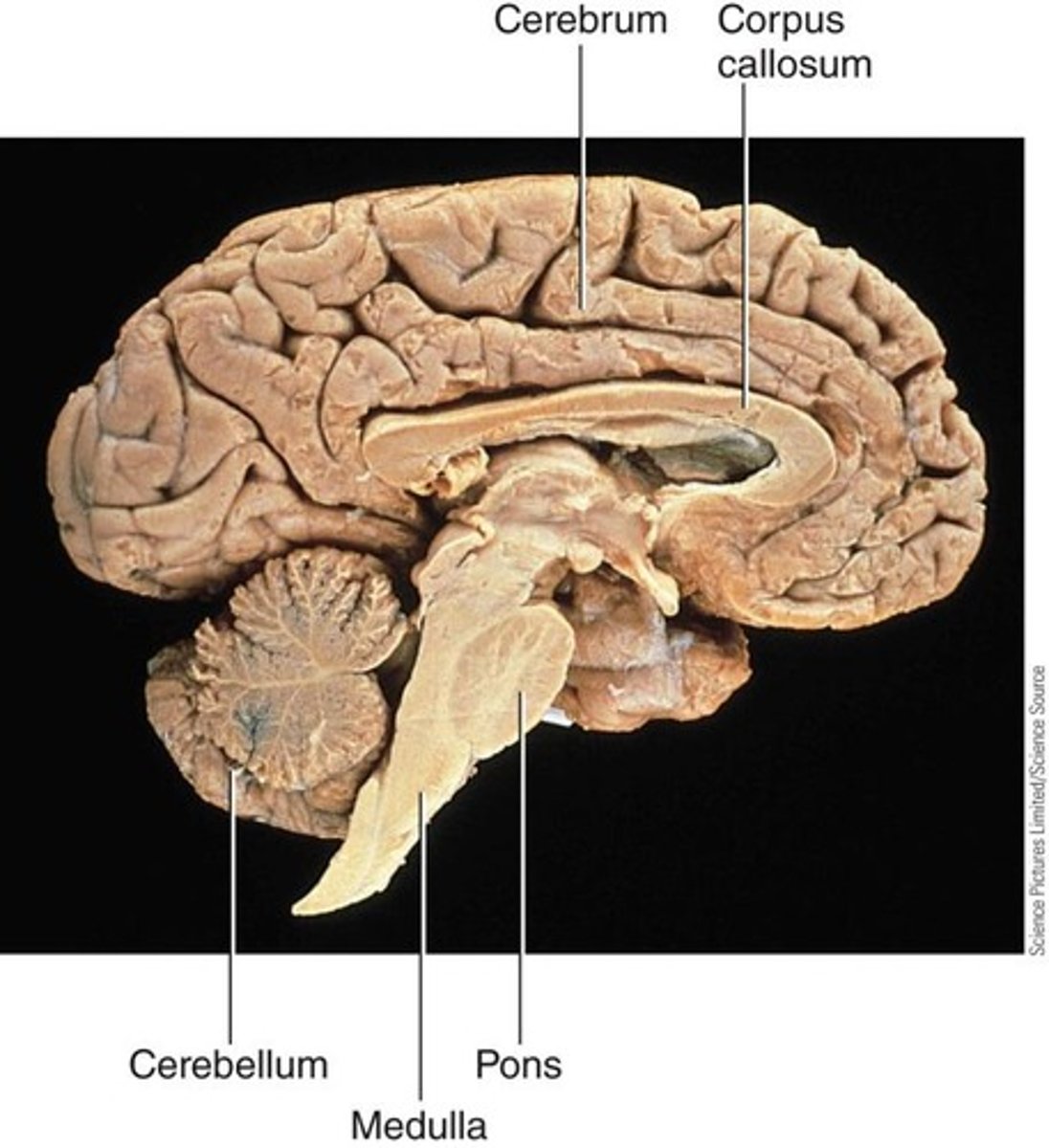
Medulla
part of both hindbrain and brain stem; regulates life-sustaining functions such as heart rate and respiration
Pons
lies superior to medulla and anterior to cerebellum; connects higher brain centers with the cord
helps regulate respiration
Midbrain
lies superior to pons; involved in motor movement of eyes and auditory processing
forebrain
at top of brain stem and includes thalamic structures: cerebral hemispheres and limbic system
Thalamus
has motor and sensory connections with the cerebral cortex; filters and sorts stimuli
crude sense of stimuli
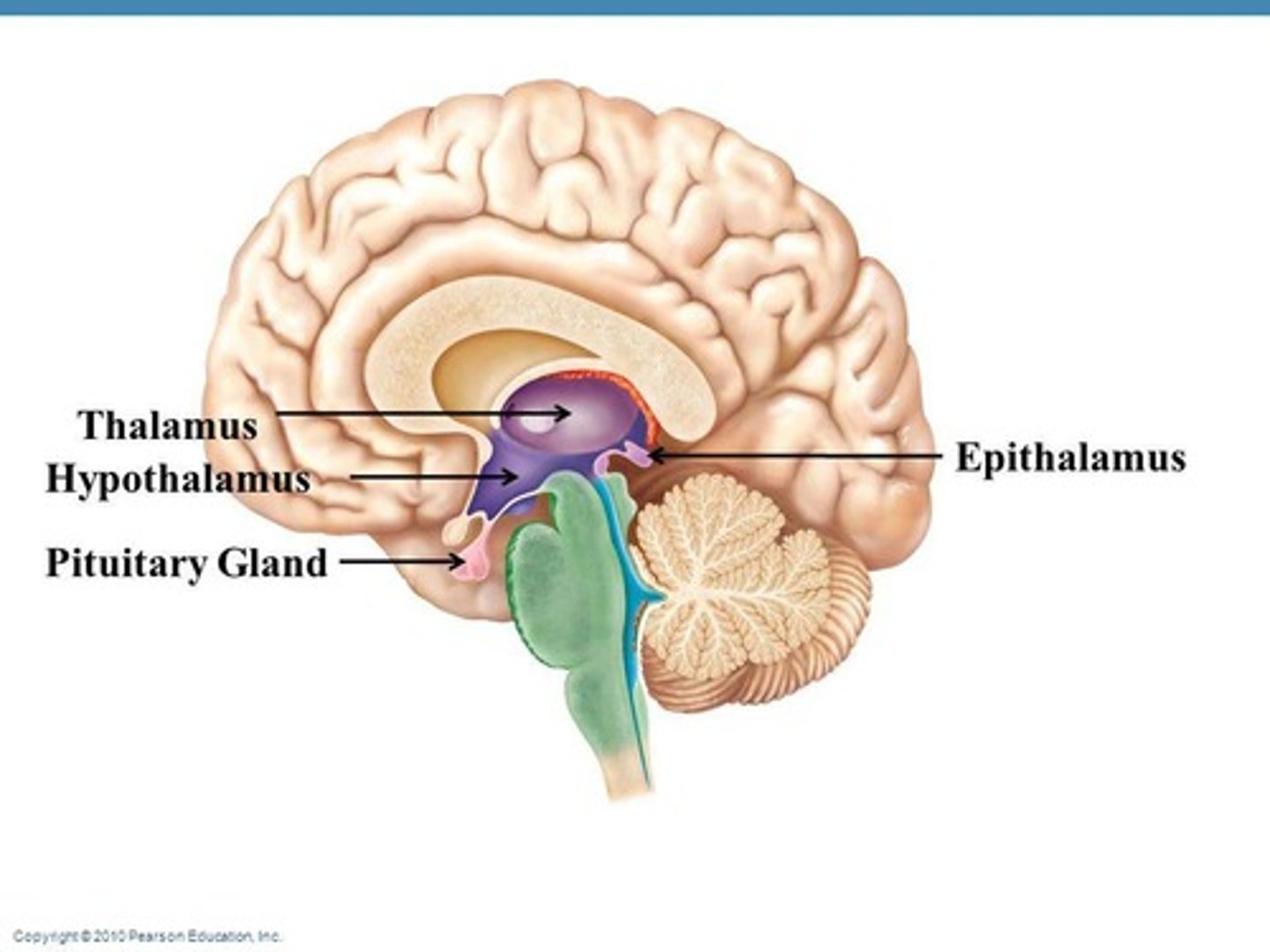
Hypothalamus
regulates autonomic and somatic responses; controls emotions and produces hormones; regulation of endocrine functions; regulation of body temps; hunger and thirst center
epithalamus
regulates sleep-wake cycle and emotions
right hemisphere
emotional processing
visual-spatial tasks - facial recognition
left hemisphere
controls language, decision making, fact recovering
Corpus callosum
large band of white matter forming roof of lateral ventricles; connects the two cerebral hemispheres
Wernicke's area
integrative speech area located in the left temporal lobe; responsible for understanding language
Broca's area
located in the frontal lobe of the dominant hemisphere; involved in the ability to produce clear speech
Frontal lobe
most anterior lobe and the largest; involved in planning and executing movement and complex functions
Parietal lobe
integrates sensory input; identifies objects and spatial relationships
Temporal lobe
functions include short term memory, speech, and musical rhythm
Occipital lobe
houses the primary visual center; processes and integrates visual signals
Cerebral cortex
functionally divided into sensory areas, motor areas, and association areas
Central sulcus
lies between frontal and parietal lobes; boundary of somatosensory and somatomotor cortex
Primary motor cortex
runs anterior to precentral gyrus; controls voluntary movement
Primary sensory cortex
runs posterior to precentral gyrus; receives information from sensory structures
non-surface lobe
insula lobe
functions: emotions, visceral response
limbic system
ring of forebrain structures surrounding the brain stem
behavioral and emotional response, motivation (dopamine stimulates motivation)
Spinal cord
Location: inside vertebrae - from base of brain, foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebrae
Spinal cord function
Connect periphery and brain (afferent and efferent)
Structure of spinal cord
Central canal surrounded by H shaped gray matter - reaches dorsal surface
White matter
Surrounds gray matter and conducts impulses to and from brain
myelinated
Tract
Collection of axons with a common origin and destination
Ascending tracts
Tracts that carry impulses up to the brain
Descending tracts
Tracts that carry impulses down from the brain
CNS protection
Bone and three connective tissue layers (Meninges): Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, Pia mater
Cerebral-spinal fluid
Produced by choroid plexus and circulates in subarachnoid space, central canal of cord, and ventricles in brain
Blood-brain barrier
Tight junctions between capillaries regulate exchange between blood and CNS
Drug defined
Substance that has a physiological or psychological effect when ingested
Prescribed drugs
~25% of prescribed drugs alter psychological conditions
Drug actions
Receptor site: drugs act at specific locations
Agonist
Binding causes effect in target similar to the normal activating molecule
Antagonist
Binding blocks binding of normal effector molecule
Length of effect
Depends on reception affinity and circulation concentration of drug
Physical dependence
Drugs cause physiological changes that result in withdrawal symptoms when drug use is discontinued
Drug addiction
Compulsive use of a drug despite negative effects
Tolerance
Occurs when body's response decreases and greater amounts may be needed to obtain the same effect
Atropine
Cold medications - reduces secretions, dilates pupils, low dose slows heartbeat, high dose treats slow heartbeat (brachycardia)
Digitalis
Stimulates heart contractions and cardiac output - used for congestive heart failure
Paregoric
From podium poppy, used to treat diarrhea
Cocaine's action
Stimulates reward pathway but can also cause physical effects such as fast heart rate and sweating
Myasthenia gravis
Autoimmune disease causing muscle weakness due to antibodies attacking acetylcholine receptors
strychnine
binds post synaptic receptor
pest poisons
blocks normal IPSP transmutation
muscle spasm, convulsions death
tetanus
prevents presynaptic relase of inhibitory neurotransmitters
Continued stimulation
Effects like strychnine but different cause
lead
binds volage -gated Ca channels
Affects neurotransmitter release
venom
causes massive release of acetylcholine
Increases Ca increases release of neurotransmitter
Agonist for prolonged depolarization
Muscle paralysis - rigid paralysis
curare
binds postsynaptic receptors and blocks acetylcholine binding
Antagonist to neurotransmitter release
Muscle paralysis - depolarization blocked (flaccid paralysis)