Conceptual Problems
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
The current definition of the standard meter of length is based on
A. The distance between the earth and the sun
B. The length of a particular object kept in France
C. The distance traveled by light in a vacuum
D. The distance between the earth’s equator and north pole
C. The distance traveled by light in a vacuum
If an operatic aria lasts for 5.75 minutes, its length expressed in seconds is x seconds, where x is
A. Greater than 5.75
B. Less than 5.75
A. Greater than 5.75
Suppose that an object travels from one point in space to another. Make a comparison between the magnitude of the displacement and the distance traveled by this object.
A. The displacement is either greater than or equal to the distance traveled.
B. The displacement can be either greater than, smaller than, or equal to the distance traveled.
C. The displacement is always equal to the distance traveled.
D. The displacement is either less than or equal to the distance traveled.
D. The displacement is either less than or equal to the distance traveled.
Suppose that a car is traveling to the west begins to slow down as it approaches a traffic light. Which of the following statements about its acceleration is correct?
A. The acceleration is zero
B. The acceleration is towards the east
C. Since the car is slowing down, its acceleration must be negative
D. The acceleration is towards the west
B. The acceleration is towards the east
When a ball is thrown straight up with no air resistance, the acceleration at its highest point
A. reverses from upward to downward
B. is upward
C. is downward
D. reverses from downward to upward
E. is zero
C. is downward
An object is moving with constant non-zero acceleration in the +x direction. The position versus time graph of this object is
A. a horizontal straight line
B. a vertical straight line
C. a straight line making an angle with the time axis
D. a parabolic curve
D. a parabolic curve
Which of the following graphs represent an object at rest?
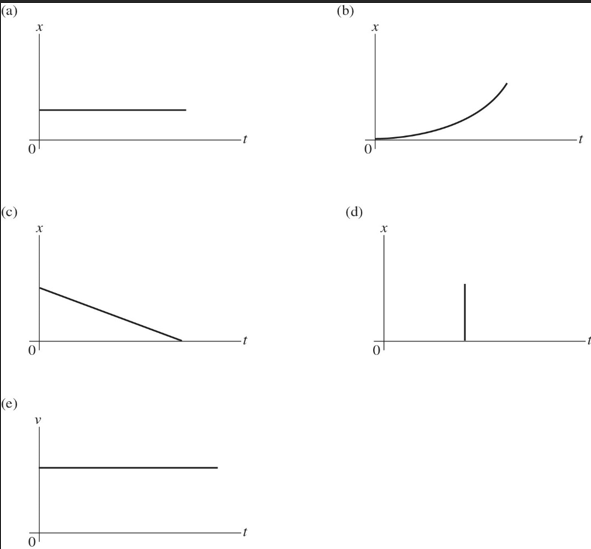
A. Graph a
B. Graph b
C. Graph c
D. Graph d
E. Graph e
A. Graph a
Two displacement vectors have magnitude of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. If these two vectors are added together the magnitude of the sum
A. Is equal to 8.6 m
B. Is equal to 2.0 m
C. Is equal to 12 m
D. Could be as small as 2.0 m or as large as 12 m
D. Could be as small as 2.0 m or as large as 12 m
A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a tower at the same time a stone is dropped vertically. Which object is traveling faster when it hits the ground below if neither of the, experiences air resistance?
A. It is impossible to tell because we do not know their masses
B. The ball
C. The stone
D. Both are traveling at the same speed
B. The ball
James and John dive from an overhang into the lake below. James simply drops straight down from the edge. John takes a running start and jumps with an initial horizontal velocity of 25 m/s. Compare the time it takes for each to reach the lake below if there is no air resistance.
a. Cannot be determined without knowing the weight of both James and John
b. Cannot be determined without knowing the masses of James and John
c. John reaches the surface of the lake first
d. James reached the surface of the lake first
e. James and John will reach the surface of the lake at the same time
e. James and John will reach the surface of the lake at the same time
In a collision between a huge SUV and a small hybrid car, the SUV exerts a larger force on the hybrid than the hybrid exerts on the SUV
a. True
b. False
c. It depends on whether the collision is a head-on collision or a rear-end collision
b. False
Bill and his daughter Susan are both standing on identical skateboards (with really good frictionless ball bearings), initially at rest. Bill weighs three times as much as Susan. Bill pushes horizontally on Susan’s back, causing Susan to start moving away from Bill. Just after Bill stops pushing
a. Susan and Bill are moving away from each other, with equal speeds
b. Susan and Bill are moving away from each other, and Susan’s speed is three times that of Bill
c. Susan and Bill are moving away from each other, and Susan’s speed is one-third that of Bill
d. Susan is moving away from Bill, and Bill is stationary.
b. Susan and Bill are moving away from each other, and Susan’s speed is three times that of Bill
A student of physics knows that Newton’s first law states:
A. An object in motion stays in motion, or an object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an outside force
B. F = ma
C. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
D. Physics is really hard
E. It’s Friday, please leave me alone
A. An object in motion stays in motion, or an object at rest stays at rest unless acted upon by an outside force
In everyday language, speed and velocity are synonyms, but in physics
A. velocity has only magnitude
B. speed has only direction
C. velocity has magnitude and direction
D. speed has magnitude and direction
E. velocity has only direction
C. velocity has magnitude and direction
The radius of a circle is tripled. By what factor is the area changed? (A = (pi)r²)
A. 3
B. 6
C. 9
D. 12
C. 9
Which of the following is not an SI base unit?
A. kelvin
B. kilogram
C. pound
D. second
E meter
C. pound
Consider a deer that runs from point A to point B. The distance the deer runs can be greater than the magnitude of its displacement, but the magnitude of the displacement can never be greater than the distance it runs.
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which of the following situations is impossible?
A. An object has constant non-zero velocity and changing acceleration.
B. An object has constant non-zero acceleration and changing velocity.
C. An object has zero velocity but non-zero acceleration.
D. An object has velocity directed east and acceleration directed west.
E. An object has velocity directed east and acceleration directed east.
A. An object has constant non-zero velocity and changing acceleration.
An object moves 15.0 m north and then 11.0 m south. Find both the distance it has traveled and the magnitude of its displacement.
A. 4.0 m, 26.0 m
B. 4.0 m, 4.0 m
C. 26.0 m, 26.0 m
D. 26.0 m, 4.0 m
D. 26.0 m, 4.0 m
A car accelerates from 5.0 m/s to 21 m/s at a constant rate of 3.0 m/s². How far does it travel while accelerating?
A. 117 m
B. 207 m
C. 69 m
D. 41 m
C. 69 m
A car is traveling at 26.0 m/s when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, causing the car to slow down with constant acceleration. The car comes to a stop in a distance of 120 m. How fast was the car moving when it was 60.0 m past the point where the brakes were applied?
A. 9.20 m/s
B. 15.0 m/s
C. 22.5 m/s
D. 12.1 m/s
E. 18.4 m/s
E. 18.4 m/s
Two displacement vectors have magnitudes of 5.0 m and 7.0 m, respectively. If these two vectors are added together, the magnitude of the sum
A. could be as small as 2.0 m or as large as 12 m.
B. is equal to 2.0 m.
C. is equal to 12 m.
D. is equal to 8.6 m.
A. could be as small as 2.0 m or as large as 12 m.
A boy jumps with a velocity of magnitude 20.0 m/s at an angle of 25.0° above the horizontal. What is the horizontal component of the boy's velocity?
A. 8.45 m/s
B. 15.6 m/s
C. 18.1 m/s
D. 12.6 m/s
E. 9.33 m/s
C. 18.1 m/s
A ball is thrown with an initial velocity of 20 m/s at an angle of 60° above the horizontal. If we can neglect air resistance, what is the horizontal component of its instantaneous velocity at the exact top of its trajectory?
A. 17 m/s
B. zero
C. 10 m/s
D. 20 m/s
C. 10 m/s
If you pound a feather with a hammer, which one feels a greater force?
A. If the feather moves, then it felt the greater force
B. Always the feather
C. The size of the force is always exactly the same on both of them
D. Always the hammer
C. The size of the force is always exactly the same on both of them
You are in a train on a horizontal track and notice that a piece of luggage starts to slide directly toward the front of the train. From this observation, you can conclude that this train is _____?
A. Speeding up
B. Slowing down and changing direction
C. Speeding up and changing direction
D. Its Friday and I don’t care
E. Slowing down
E. Slowing down
A 200-N sled slides down a frictionless hillside that rises at 37 above the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the force that the hill exerts on the sled parallel to the surface of the hill?
A. 200 N
B. 120 N
C. 160 N
D. 150 N
E. 0 N
E. 0 N