ACS and Anticoagulants
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
how can coronary heart disease present?
- wide spectrum (stable angina like chronic angina pectoris)
- ACS (unstable angina and MIs like STEMI and NSTEMI)
what is the etiology of angina?
atherosclerotic plaque in vessel wall
- limited blood flow to the heart so less O2 to the myocardium → coronary artery ischemia
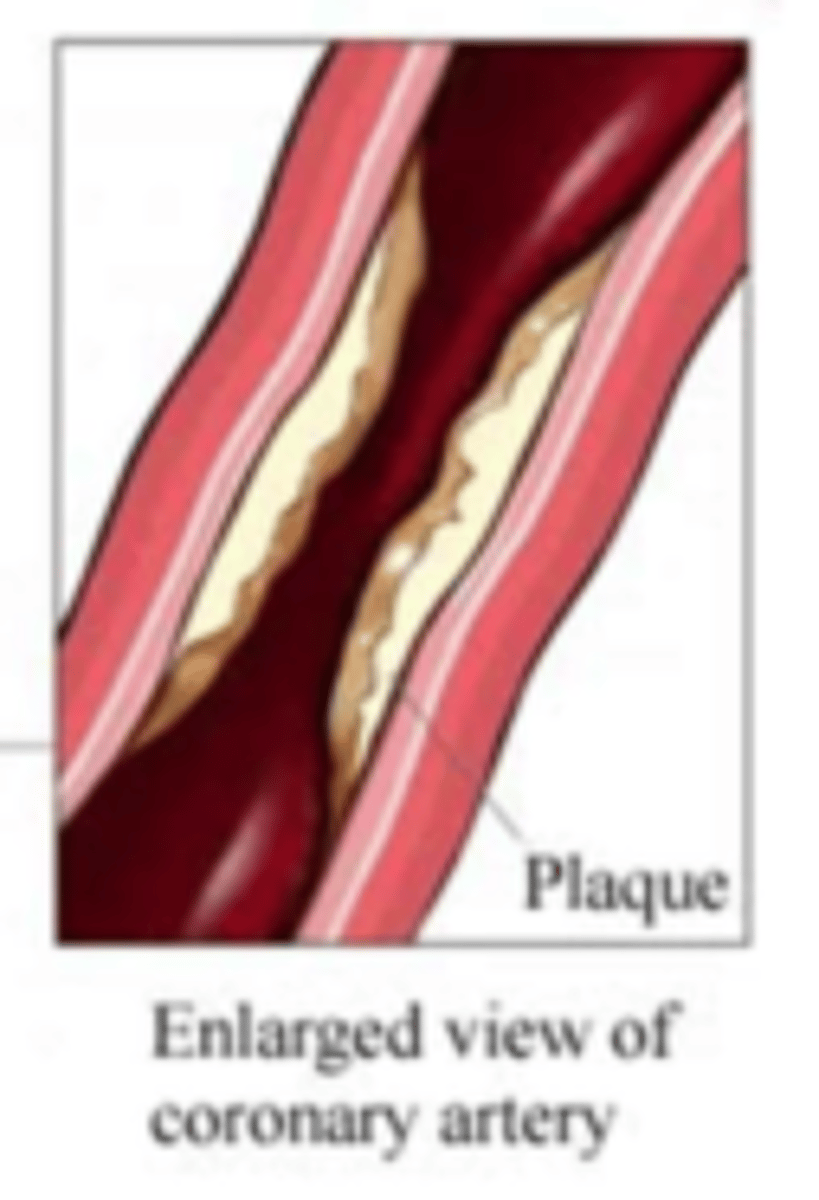
inadequate blood flow can cause...
- formation of thrombi (blood clots)
- coronary vasospasm
symptom of angina
heavy weight/pressure in chest
what is stable angina?
chronic angina pectoris
- similar characteristics and occurs each time under same circumstances
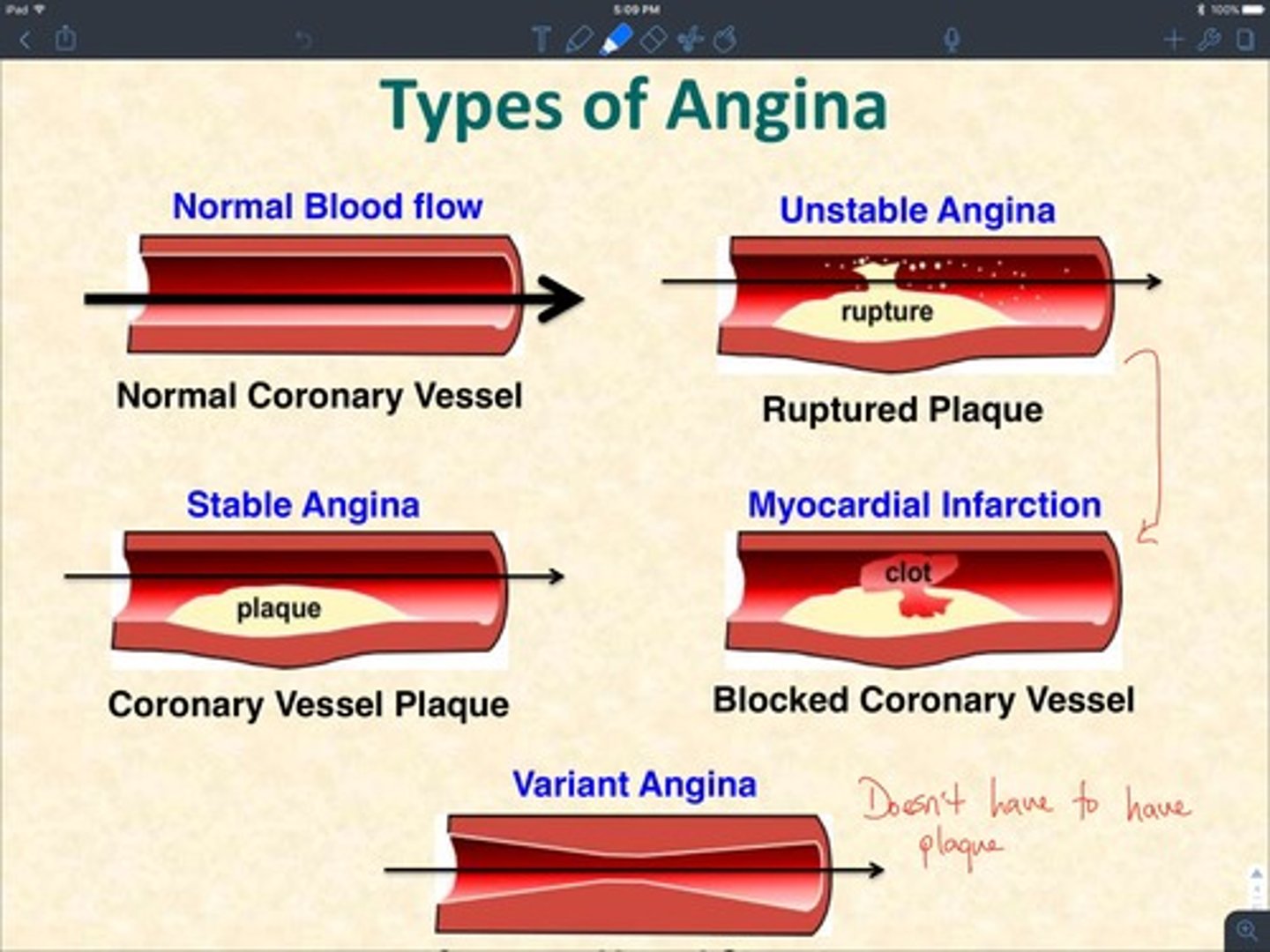
what is unstable angina?
frequency and severity of attacks increase over time
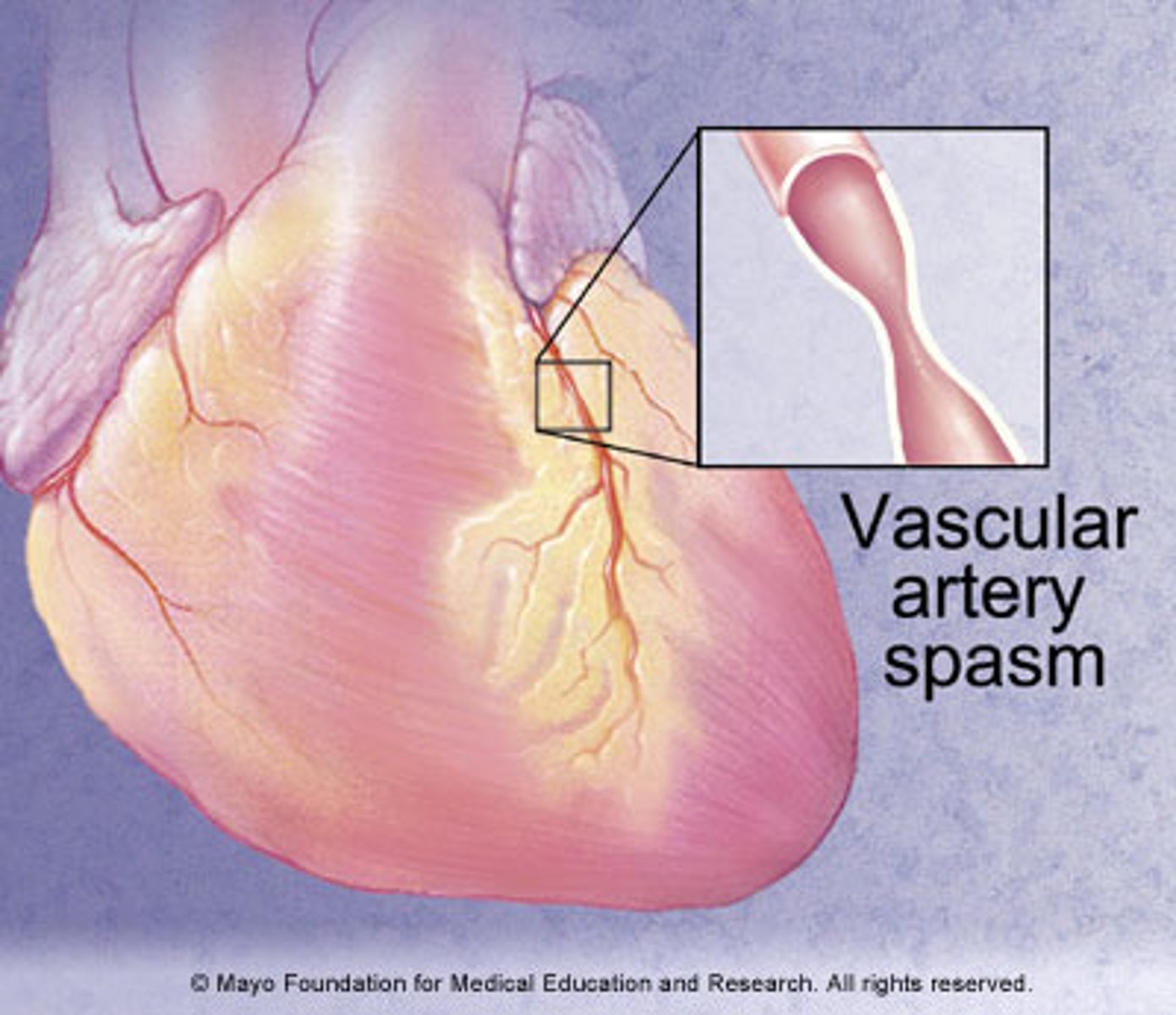
what is variant angina (Prinzmetal's angina)?
due to acute coronary vasospasm
- occurs at rest or sleep
- treated with vasodilators, not anticoagulants
what is the main principle of antianginal therapy?
oxygen supply = oxygen demand
to prevent or counteract ischemia, you should...
increase exercise tolerance and reduce frequency of attacks
what medications so we use to change oxygen supply and oxygen demand?
nitrates, CCBs, beta blockers
how do nitrates work?
↑ NO = vasodilation, relieve MI symptoms
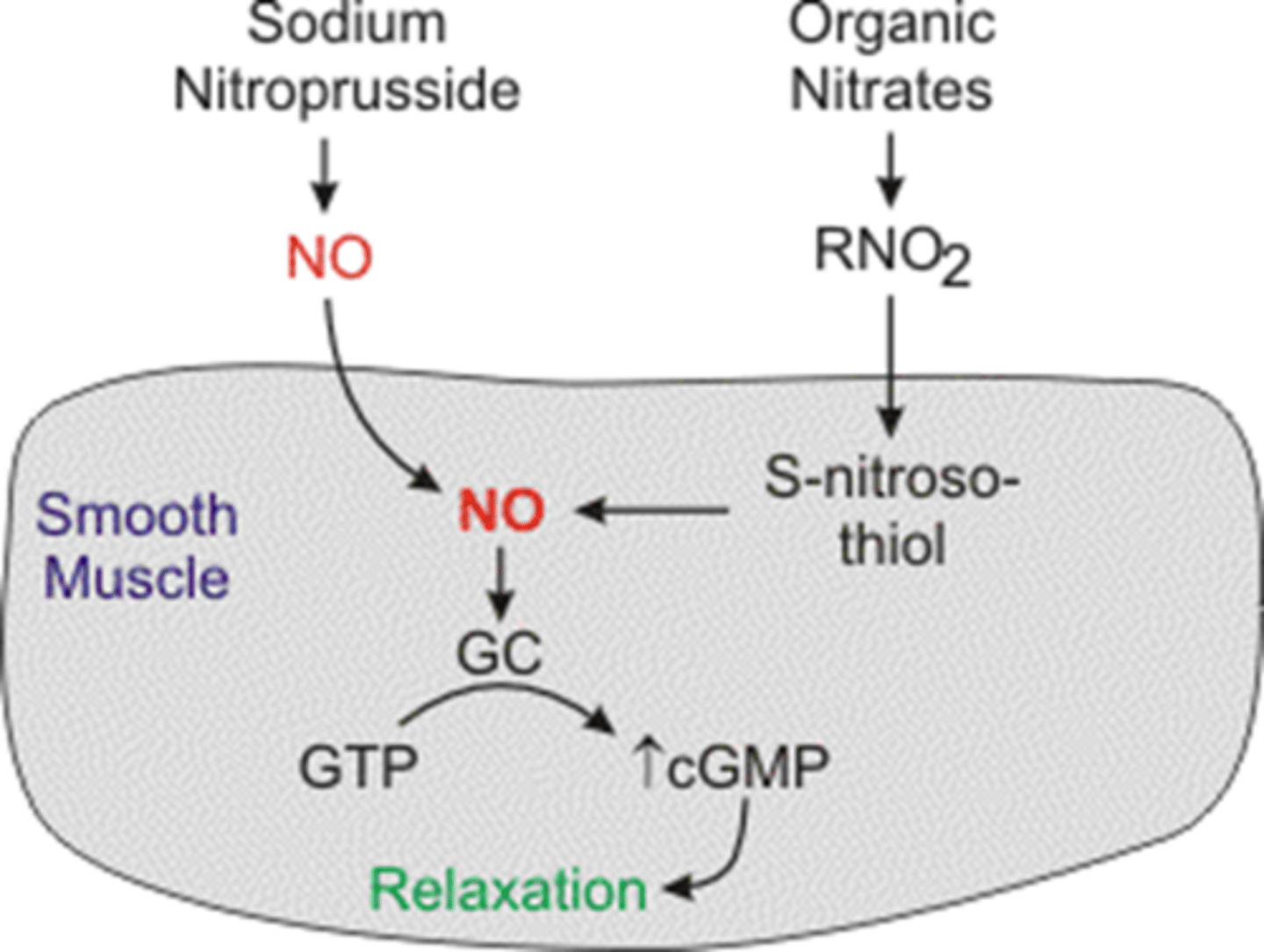
nitrate effects on arterial vasodilation and venodilation, respectively?
arterial vasodilation = ↓ BP
venodilation = ↓ O2 demand of myocardium, preload
contraindication of nitrates?
PDE inhibitors use (↓ BP, stroke)
what is nitroglycerin used for?
- preventing and treating angina attacks
- relieves chest discomfort and pain
3 routes of administration for nitroglycerin?
- sublingual
- IV (used for MI)
- transdermal and ointment (delayed onset)
ADR of nitroglycerin?
- hypotension (avoid if SBP<90 mmHg)
- flushing
- peripheral edema
- headaches
- dizziness
NG caveats for patients?
- keep meds in original, tightly closed container
- if anginal chest pain is unresolved in 15 mins → seek emergency medical help
- gradually decrease dose in pts using NG with prolonged use → avoid withdrawal reaction (chest pain)
2 related formulations of nitroglycerin?
- Isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN)
- Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN)
how are ISDN and ISMN administered?
SL and orally
ISDN/ISMN has a (slower/longer) onset of action and (shorter/longer) duration compared to NG
slower onset of action, longer duration of action
ISDN is converted to?
ISMN
- but they are available as a separate formulation
when using nitrates, especially ISDN and ISMN, what do you need to be conscious of?
tolerance
what should you do to prevent nitrate tolerance?
examples?
nitrate-free interval = (space out the administration where you don't give any nitrates, 10-12 hours/day)
- skin patch removed for 10 hours
- long acting oral meds given once (or twice) a day
- Ismo tablet given 2x a day 7 hours apart (i.e. 8 am and 3pm)
how does ranolazine work?
- antianginal and anti-ischemic effect without changing hemodynamic parameters (heart rate or blood pressure)
- reduces intracellular Na (less Ca++ via Na/Ca exchanger) = ↓ Ca in cell, ↓ ventricular tension and O2 consumption of heart
3 categories of ACS and their pathophysiology?
1. asymptomatic = decr. O2 supply (flow limiting stenosis, anemia, plaque rupture/clot, increased O2 demand)
2. angina = O2 supply/demand mismatch → ischemia
3. Myocardial infarction = myocardial ischemia → necrosis
clinical signs of unstable angina
thrombus?
ECG?
Cardiac enzymes?
- non-occlusive thrombus
- non-specific ECG
- normal cardiac enzymes
clinical signs of Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
thrombus?
ECG?
Cardiac enzymes?
- non-occlusive thrombus sufficient to cause tissue damage and mild myocardial necrosis
- ST depression +/- T wave inversion on ECG
- elevated cardiac enzymes
clinical signs of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
thrombus?
ECG?
Cardiac enzymes?
- complete thrombus occlusion
- ST elevations or new LBBB (left bundle block) on ECG
- elevated cardiac enzymes
- more severe symptoms
which of the cardiac enzymes are the most specific?
troponins
why do you retest cardiac enzymes if a pt. presents with chest pain in ED?
troponins take 3-4 hours to show up so you have to make sure you don't do them too early
how long do the troponin enzymes last in blood?
7-10 /7-14 days
(up to 2 weeks)
ACS symptoms
- midline anterior anginal chest pain
- severe new-onset angina
- increasing angina > 20 mins
- pain may radiate to left arm, jaw, back
- nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, SOB
what 3 populations may have atypical or no symptoms for ACS?
- women
- diabetics
- elderly patients
what does MONA stand for?
Morphine (PRN)
Oxygen
Nitroglycerin (SL or IV)
Aspirin
who do we give MONA to?
both STEMI and NSTEMI
what do we give to a pt with STEMI?
- MONA
- beta blocker (or Ca channel blocker)
- antiplatelet therapy
- parenteral anticoagulant
- PCI (preferred) or fibrinolytics
what is a form of antiplatelet therapy?
P2Y12 antagonist
what are examples of parenteral anticoagulants?
- unfractionated heparin
- low molecular weight heparin
- fondaparinux
- direct thrombin inhibitors (bivalirudin)
when do you give fibrinolytics to a STEMI patient?
if symptoms within 12 hours of presentation
for STEMI pts, which is better in lowering mortality (PCI/fibrinolytics)?
PCI stands for percutaneous coronary intervention (like a stent)
PCI = opens arteries better
- reduces risk of major bleeding, intracranial hemorrhage (ICH)
- better side effect profile
what is the "door-to-balloon" time for PCI? how many minutes should it be?
time of hospital presentation to time occluded artery is opened
- should be < or = 90 mins
what do we give to pt with NSTEMI?
- MONA
- beta blocker (or Ca channel blocker)
- antiplatelet therapy
- parenteral anticoagulant
- PCI/G2b3a therapy based on TIMI score
what do we NEVER GIVE to a NSTEMI?
NEVER GIVE FIBRINOLYTIC THERAPY
the treatment of NSTEMI is based on...
TIMI score
- Thrombolytics In Myocardial Infarction
TIMI risk scores
low: 0-2
intermediate: 3-4
high risk: 5-7
*high risk pts go to cath lab
what is the difference in how you treat NSTEMI compared to STEMI?
for NSTEMI, give GPIIbIIIa receptor blockers in high-risk pts.
- NEVER give fibrinolytic therapy (contradicated)
what is morphine and how does it work?
- analgesia
- reduces pain/anxiety by ↓ sympathetic tone, SVR, and O2 demand
what conditions do you need to be careful with when using morphine (4)?
hypotension, hypovolemia, respiratory depression, alcohol consumption
how does O2 treatment work? why do we give it?
may limit ischemic myocardial damage by incr. O2 delivery/reduce ST elevation
- up to 70% of ACS pts demonstrate hypoxemia
how does nitroglycerin work?
- analgesia (given as a titrate infusion to keep pt pain free)
- dilates coronary vessels = ↑ bld flow
- ↓ SVR and ↓ preload
what conditions do you need to be careful with when using nitroglycerin (5)?
- recent erectile dysfunction meds
- hypotension
- bradycardia
- tachycardia
- right ventricular infarction
how does aspirin work?
- irreversible inhibition of platelet aggregation (platelets don't stick together)
- stabilizes plaque and arrests thrombus
what conditions do you need to be careful with when using aspirin (3)?
- active peptic ulcer disease
- hypersensitivity
- bleeding disorders
which is the only med in MONA that reduces mortality in STEMI pts?
aspirin
- as primary and secondary prevention!
who are nitrates given to?
both STE and NSTE ACS pts to relieve ischemic chest pain
do nitrates have any mortality benefit in acute MI?
no, just symptom relief
route of administration of nitrates?
- first given as a tablet
- if chest pain persists → IV
beta blockers should be given (early/late) to STEMI and NSTEMI patients if there are no contradictions
early!
- some contraindications are arrhythmias like bradyarrhythmia or AV block
do you take pt off beta blocker after they had a heart attack?
no, continue indefinitely
- quality care indicator for MI pts
why do we only give IV beta blockers to hemodynamically stable pts (with/without) signs of (compensated/decompensated) HF?
only give to pts without signs of decompensated HF because it incr. risk of cardiogenic shock!
when do we use Ca channel blockers instead of beta blockers?
in STEMI and NSTEMI when beta-blockers are contraindicated (pt responding poorly/ bad side effects)
how do Ca channel blockers work?
inhibit Ca influx to myocardial and vascular sm. cells → vasodilation
muscles can't constrict without Ca
non-dihydropyridines (Ca channel blockers, verapamil and diltiazem) have (more/less) anti-ischemic effects?
more = slow HR via AV node conduction
do CCB (ca channel blockers) have an effect on mortality?
no, just symptom relief
the (positive/negative) (inotropic/chronotropic) effects of CCB may worsen outcomes
negative inotropic effects may worsen outcomes
how do platelets turn into clots?
1. adhesion = subendothelium is exposed so platelets stick there, releases TXA2 and ADP
2. recruitment and activation = more platelets come to the scene
3. aggregation = fibrin strand is formed between platelets forming a clot
what are the 5 P2Y12 Antagonists?
-Ticlopidine
-Clopidogrel
-Prasugrel
-Ticagrelor
-Cangrelor
what are the 3 glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inihibitors?
-Abciximab
-Tirofiban
-Eptifibatide
MOA of aspirin?
inhibits cyclooxygenase within platelets which ↓ thromboxane A2 production = ↓ platelet aggregation
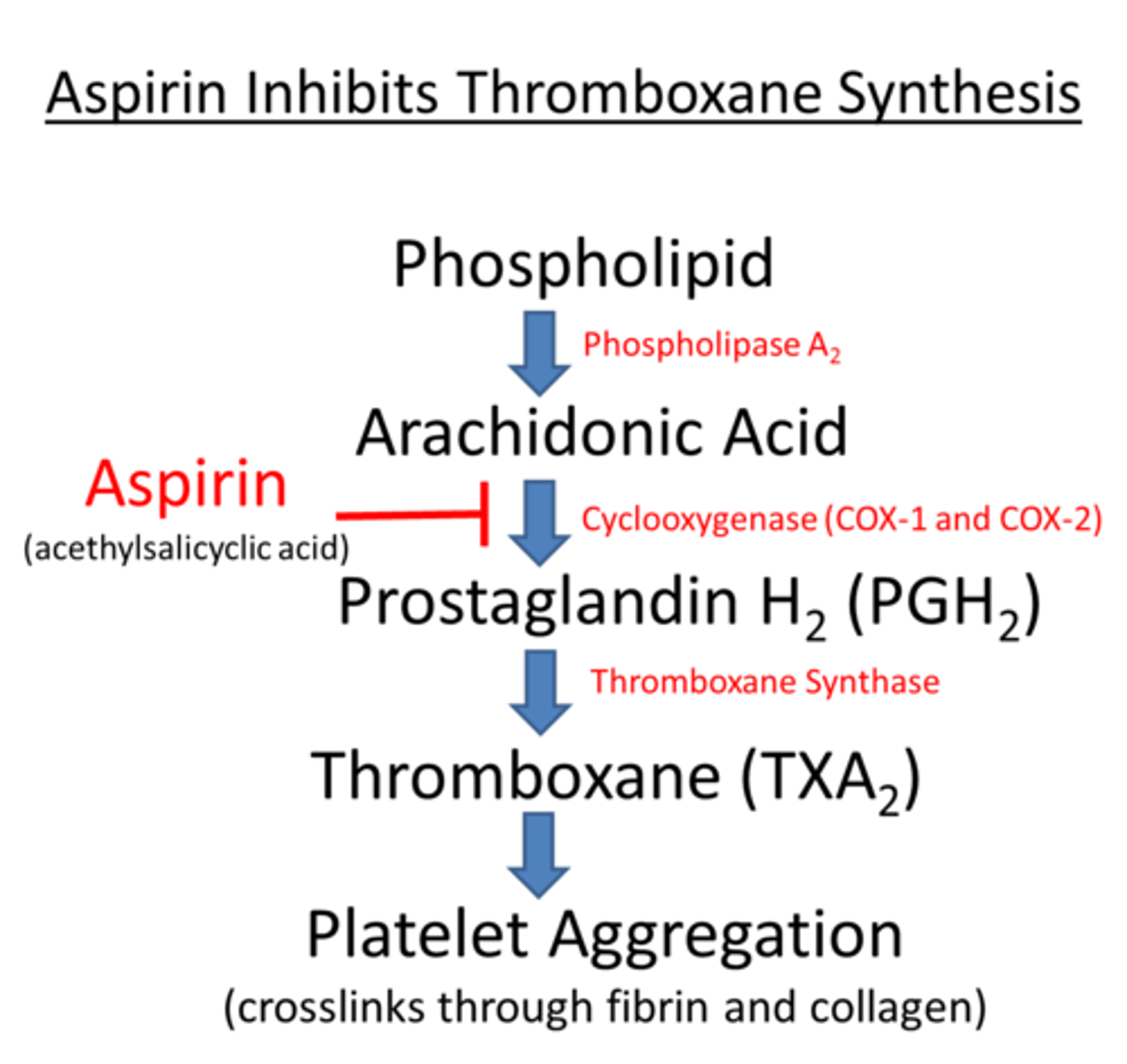
ADR of aspirin?
- GI distress to ulcers
- incr. bleeding risk
MOA of clopidogrel?
blocks the P2Y12 component of ADP receptors on the platelet surface, which prevents activation of the GPIIb/IIIa receptor complex = reducing platelet aggregation
when is clopidogrel often used?
pts undergoing PCI (stent surgery)
ADR for clopidogrel?
- bleeding
- GI distress
why is ticlopidine no longer preferred? when is it used?
- produces bad side effects (neutropenia, diarrhea)
- used in pts allergic to clopidogrel
how long is clopidogrel therapy?
sometimes indefinitely depending on the type of stent used
what is dual antiplatelet therapy?
aspirin + clopidogrel
MOA of prasugrel?
blocks ADP2Y12 receptors on platelets = prevents fibrin binding
in which pts should you have caution when using prasugrel?
- pts > 75 y/o
- pts weighing < 60 kg
which of the P2Y12 antagonists is weight-dependent?
prasugrel
- decrease the maintenance dose by 5 mg for pts <60 kg
which of the P2Y12 antagonists are prodrugs?
- clopidogrel
- prasugrel
which type of drugs should you not use with clopidogrel?
proton pump inhibitors
what are thienopyridines?
prodrugs that are metabolized in the liver into active metabolites
- clopidogrel
- prasugrel
similarities and differences of clopidogrel and prasugrel metabolism?
similar: prodrugs metabolized in liver that undergo cytochrome p450 oxidation
difference: many more steps that clopidogrel undergoes to metabolize, most of clopidogrel is in not active (only 15%)
why is it worse to use PPI with clopidogrel than with prasugrel?
PPI inhibit more of the pathway for clopidogrel
which CYP do PPI target for clopidogrel vs prasugrel?
Clopidogrel:
- 2C19
- 2B6
- 2C19
- 2C9
same one twice
Prasugrel
- 2C19
example of PPI?
omeprazole
drug-drug interaction for clopidogrel and omperazole?
omeprazole inhibits the CYP-2C19 pathway = reduces active metabolite so no effect of med
MOA for ticagrelor?
Reversibly and noncompetitively binds the adenosine diphosphate (ADP) P2Y12 receptor on the platelet surface
- reduces platelet aggregration
what medication must you limit the dose when taking ticagrelor?
limit concurrent ASA to no more than 150 mg daily
MOA for Cangrelor?
Direct P2Y12 platelet receptor inhibitor = blocks ADP-induced platelet activation and aggregation
when is cangrelor normally used?
before and during PCI surgeries
MOA of GP IIb/IIIa inhibtors?
Inhibits the binding of fibrinogen to the GP IIb/IIIa receptors of platelets = blocking the final step of platelet aggregation
prevents cross linking of platelets through inhibiting GP2b/3a receptors
route of administration for GP IIa/IIIb inhibitors?
IV
- with aspirin and IV heparin
caution when using GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors?
high risk of bleeding
GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors may help with...
early opening of coronary arteries
3 contradictions for GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors?
- active bleeding
- thrombocytopenia
- history of stroke
2 ADE of GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors?
- bleeding
- immune mediated thrombocytopenia
which medication is used as monoclonal antibody?
abciximab
when is abciximab used?
- PCI (stents)
- unstable angina (pt not responding to meds when PCI planned within 24 hours)
ADR for abciximab?
hypersensitivity reactions