Umich EEB 390 Exam 1
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
First started natural phenomenon ideas
The early greeks (change over time/not static, fossils and extinction, hypothesis testing
Carolus Linneas
father of taxonomy, defined species w/ hierarchy of groups
Jean-Bapiste Lamarck
inheritance of characteristics acquired in lifetime (opposed Darwin's idea of natural selection) and gradual change towards ideal form
Charles Lyell
idea that landscapes had been created by a series of many small changes
Charles Darwin @ South America
Galapagos finches (beak size) and created natural selection. Learned that everything is related, the earth is very old, extinction is common, and there is extreme morphology
Requirements for natural selection
variation, heritability, selection
Alfred Wallace
came to Darwin about similar ideas of evolution; their work was published together by a friend
Origin of Species
made by Darwin; variation in phenotypes come from a common ancestor, variation is continuous and heritable, survival of the fittest, natural selection = how things change, laws of variation (later solved with genetics)
Problems with Origin of
Species
absence of transitional forms and sterile animals (haplodiploidy)
What Darwin was right about
natural selection and idea of a common ancestor
What Darwin was wrong about
inheritance, origin of variation, mass extinctions, structural constraint
what does natural selection act on
a phenotype
how is mutation affected by selection
mutation works independent of selection - they occur randomly
fitness
differential effect of a trait on reproductive success (variation always has fitness consequences)
Trade-Off
larger offspring survives with higher probability but need more resources so only a few large offspring can be produced
genetics of domestication
Siberian fox experiment of selective breeding for non-aggression but this lead to certain characteristics that followed along (floppy ears, curly tail, barking)
Darwin's framework for change over time
species diversity and descent with modification (all is still controversial b/c selection is too slow and there is an incongruence with the fossil record)
Neo-Lamarckism
inheritance of characteristics acquired in response to environmental conditions during a lifetime (alternative to Darwin)
orthogenesis
variation moves toward a specific goal (alternative to Darwin)
Mutationism
mutations lead to new species (alternative to Darwin)
theistic evolution
change is directed by god - proved false by end of 1800 (alternative to Darwin)
Genetics
the study of heredity - started by Mendel and Thomas Morgan
Modern synthesis
theory of evolution that incorporates genetics, systematics, selection, and other things - started by Haldane, Fisher, and Wright
population genetics
Study of allele frequency distribution and change under the influence of evolutionary processes -- consistent with natural selection
Ronald Fisher
provided statistical basis of inheritance (heterozygote advantage, large populations have more variance)
John Haldane
math to trace gene frequencies (rule of hybrid sterility, factors for evolutionary resistance)
Sewall Wright
inbreeding, drift, adaptation, adaptive landscapes
T. Dobzhansky
fruit flies and chromosomal changes (natural selection maintains diversity in wild populations)
Ernst Mayr
biological species concept, naturalist, evolution from geographic separation
Simpson
fossils and population genetics - disagreed with Mayr on speciation
post-synthesis controversy
later arguments different from what modern synthesis said. Also a public disconnect (debate of evolution ended for scientists but never fully for the public - creationism too high)
Synthesis controversy over units of selection and speed of change
Synthesis said selection acts on individuals or populations and change is slow. Later people said selection acts on higher species and speed is punctuated equilibrium
Punctuated equilibrium
evolutionary theory proposing that species experience long periods of stability (stasis) interrupted by shortbursts of significant evolutionary change (alternative to gradualism; fossil record shows both)
molecular biology data proves modern synthesis and evolution
nucleic Acids=variation, chromosome=inheritance, theory of gene=unit of selection, central dogma=DNA sequencing
Phylogeny
visual representation of relationships between entities with some metric of time included; need data and models (key = variation)
node
hypothetical ancestor (MRCA)
branch
evolution lineage
tip/taxa
species or individual entity
OTU
technical term for tip of the tree
topology
arrangement of branches
phylogeny as a hypothesis
there is always some uncertainty; it is a reconstruction of a phenomenon that you can't directly observe and never a "true" or "correct" tree
clade
group that includes an ancestor (most recent common ancestor) and its descendants - can only be monophyletic
monophyletic group
ALL descendants came from one common ancestor
paraphyletic group
Pertaining to a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, descendants
polyphyletic group
an unnatural group that does not include the most recent common ancestor and is disjointed taxa
polytomy
when a node is split into more than two descendants
soft polytomy
uncertainty in a phylogeny that can be resolved with more data
hard polytomy
very rapid divergence that creates uncertainty that cannot be resolved by adding more data
rooting
node that connects all the tips (can put this anywhere)
ingroup
A species or group of species whose evolutionary relationships we seek to determine
outgroup
one or more species included to provide direction or a comparison in a phylogeny
character vs. state trait
character=idea, state=thing you see (phenotype)
ancestral traits vs. derived traits
ancestral=from ancestral population, derived=trait in a changed state from when it was an ancestral form
homologous vs analogous traits
homologous=inherited and in all species, analogous=not because of ancestry
parsimony
to minimize the number of changes/steps to get to an observed tip (helps infer ancestral traits)
how can traits reverse back?
when a deeply nested clade does not have a derived trait (clade in another clade)
homoplasy
the evolution of similar traits or structures in different species that aren't due to a recent common ancestor (ex. eye)
Synapomorphy
a shared, derived character trait inherited from a common ancestor, used to define a group
Plesiomorphy
an ancestral trait shared by members of a clade that was inherited from a distant common ancestor
Symplesiomorphy
a shared ancestral trait shared between two or more taxa, such as the backbone in all mammals
cautions of phylogenys
always some uncertainty!!
Coelacanths
ancient group of fish related to the lobe-finned fish ancestors of the amphibians. Most recent fossil is 70-80 mill y/a but in 1938 they found another
Sister taxa
Groups of organisms that share an immediate common ancestor and hence are each other's closest relatives
Vestigial traits
those that have no current function but were important in the past
critics of Darwin and variation
critics said variation should run out eventually, but this is false and it is continuous
Mendel breeding experiments
used peas and artificially pollinated flowers - created hybrid species and concluded: heredity is not blending but a combination of discrete factors from parents
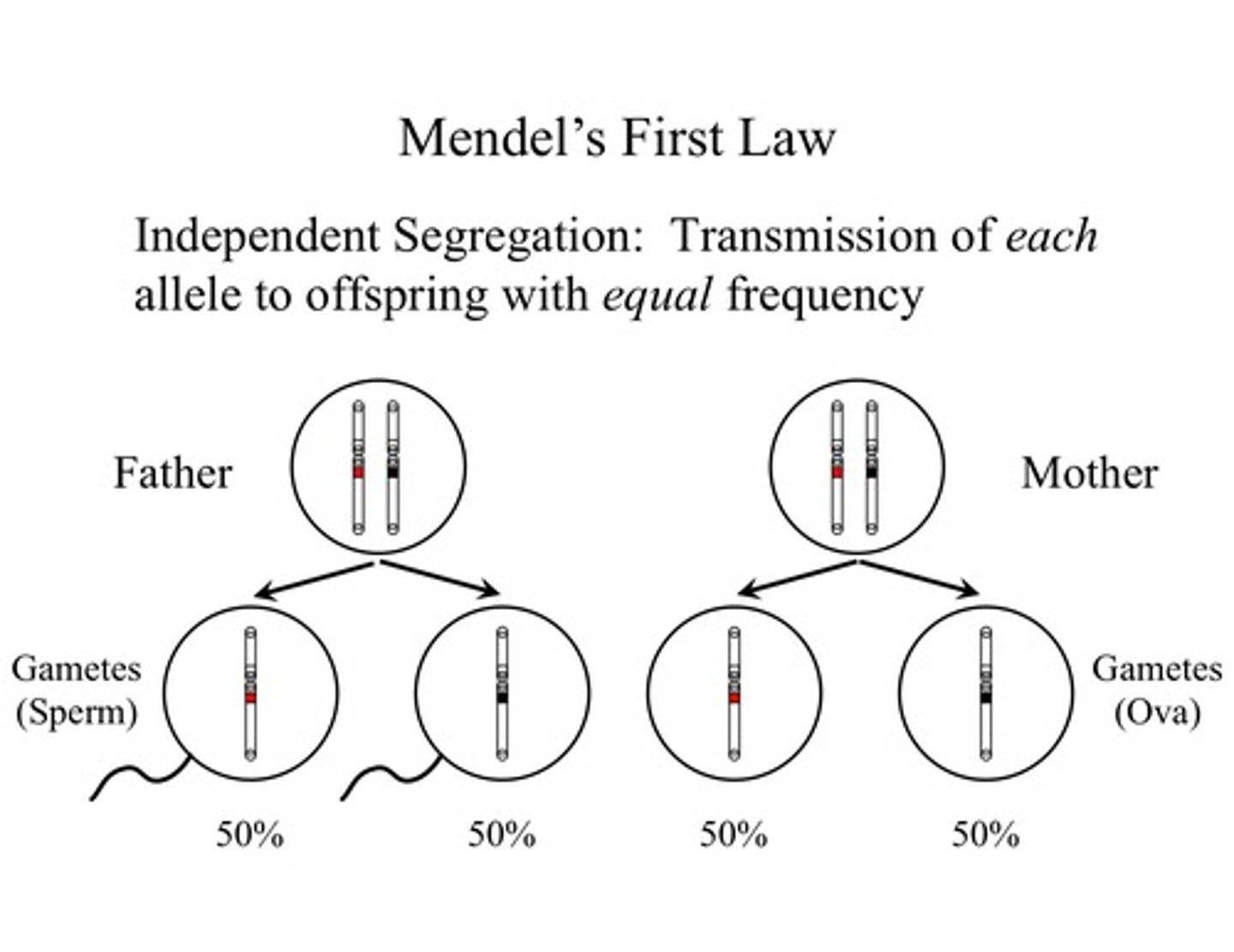
Law of Segregation
Mendel's law that states that the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis so that only one chromosome from each pair is present in each gamete
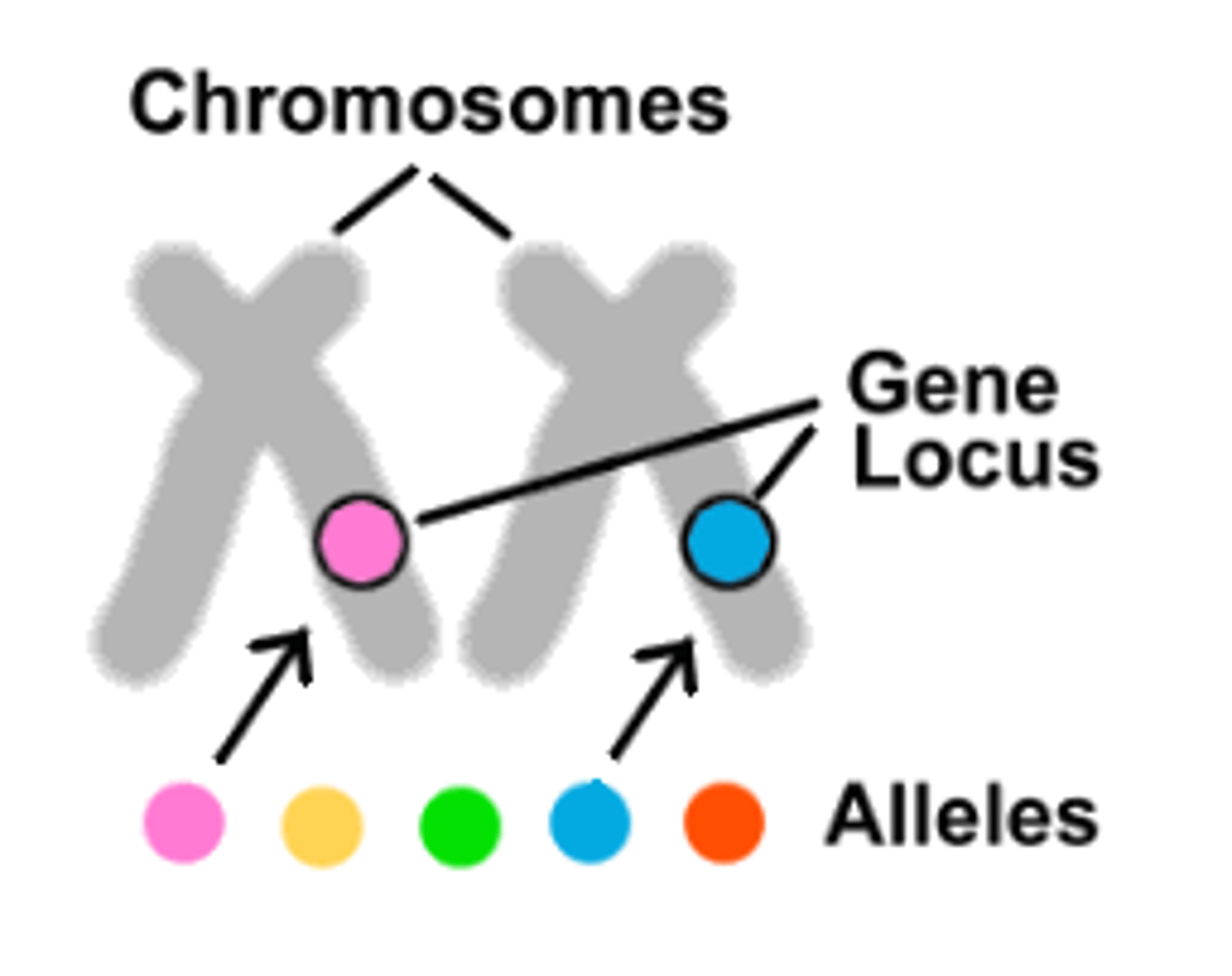
locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome
homozygote
organism that inherits two alleles of the same type for a given gene (AA or aa)
heterozygote
organism that inherits two different alleles for a given gene (Aa)
dominant
heterozygote has phenotype of the allele
recessive
phenotype is not expressed in heterozygote
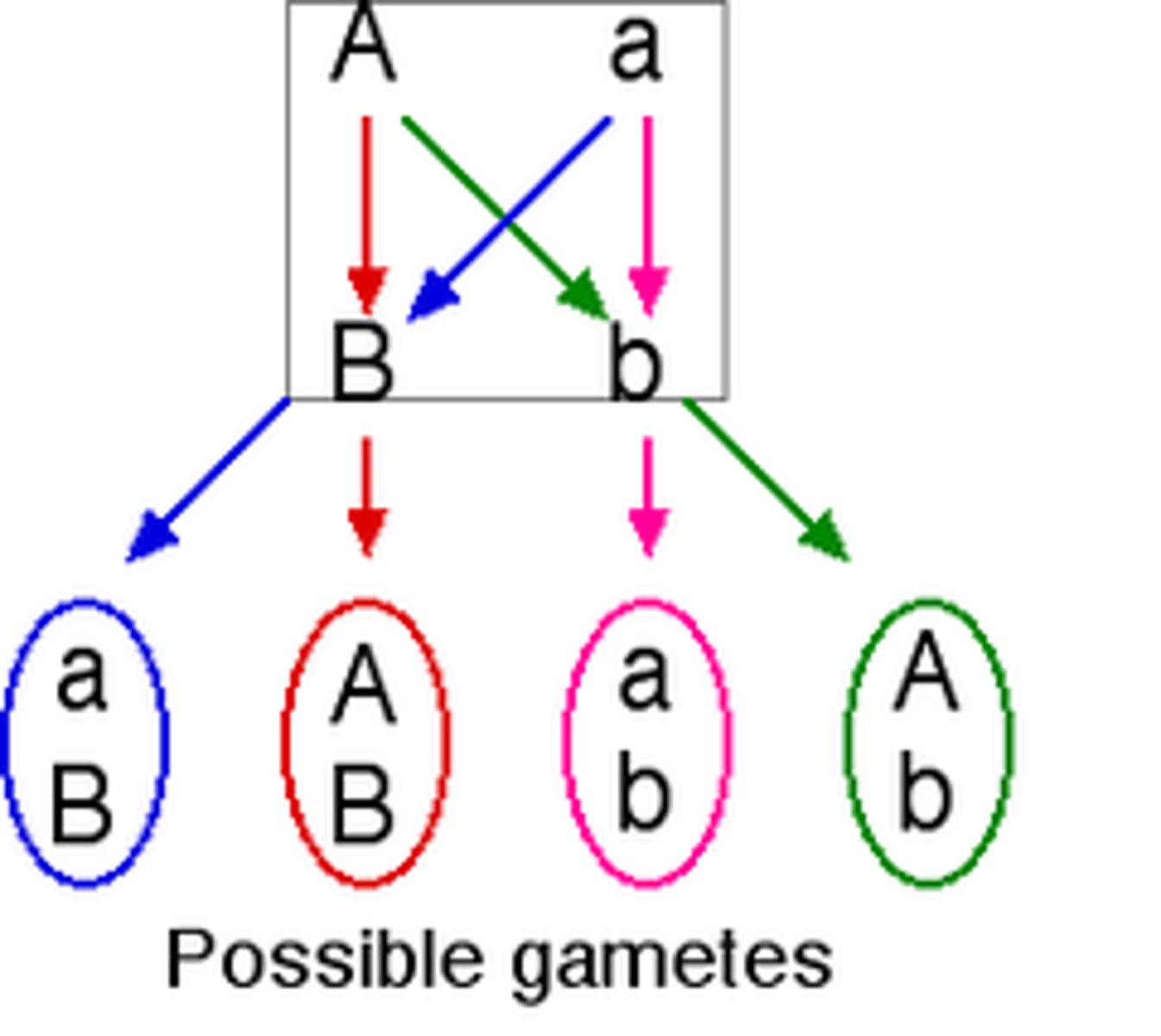
law of independent assortment
mendel's law that states that genes separate independently of one another in meiosis because they are not physically linked
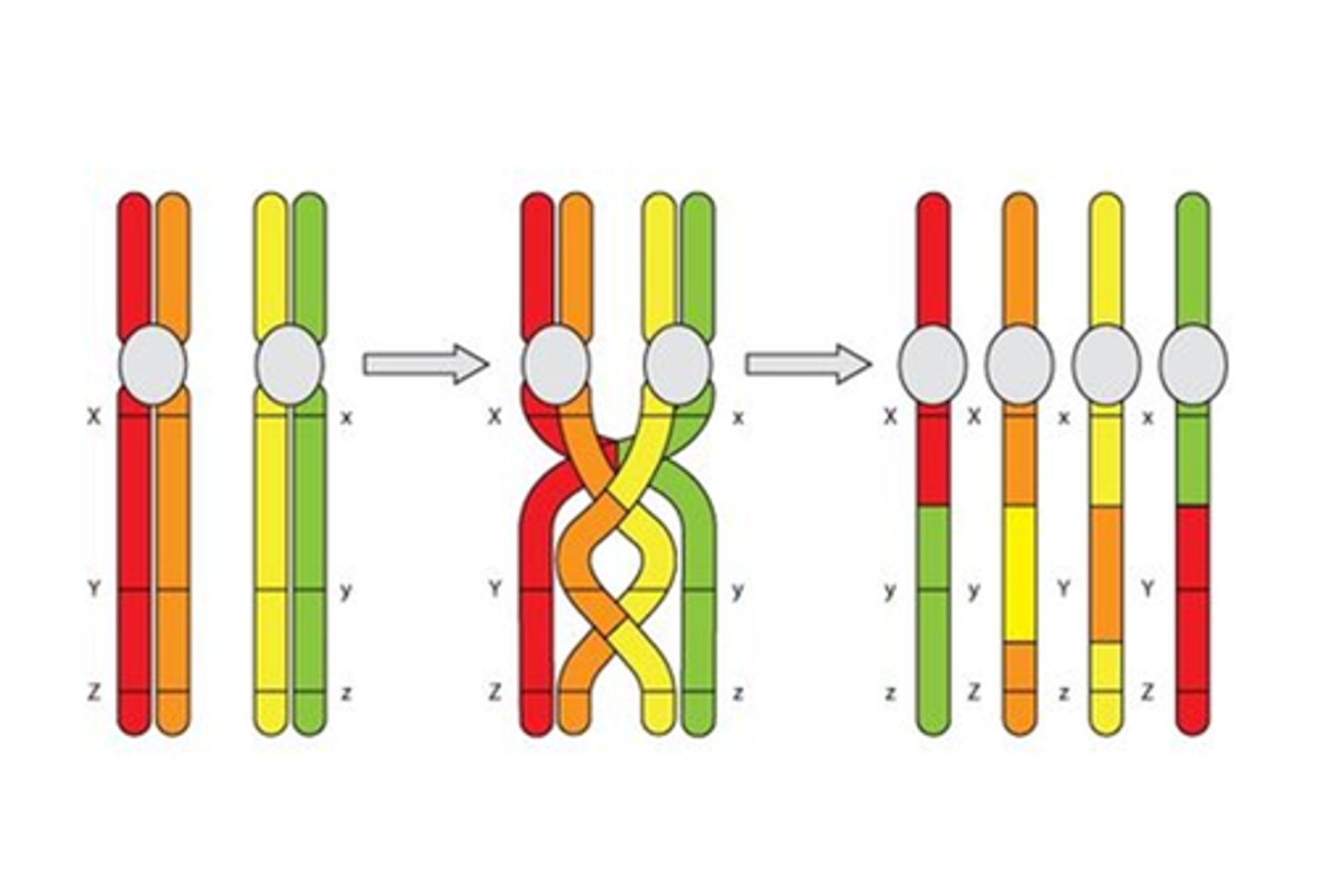
recombination
(crossing over) a combining of genes or characters different from what they were in the parents
molecular genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes
central dogma
DNA (genotype) -> RNA -> Protein (phenotype); many ways to alter this process and get variation
transcription
RNA polymerase reads coding sequence of DNA and produces complementary RNA called messenger RNA (mRNA)
translation
process where strand of mRNA is decoded by a ribosome to produce an amino acid sequence
codon
genetic code of a three nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid; lots of redundancy for codes
promotor
signals to begin transcription where RNA polymerase binds
introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
exons
expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein
expression of genes
how much gene product is made/the process of a gene being transformed into a product -- controls phenotype!!
epigenetic inheritance
Inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms not directly involving the nucleotide sequence (heritable changes in gene expression without changing DNA sequence) - basically irreversible
examples of epigenetics
x-inactivation, genomic imprinting, maternal effects
X inactivation in cat coats
one of two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated so only 1 active x-chromosome in female controls color
human height
overtime people are taller (changes over time) and height is highly heritable, can see based on slope of parent v offspring graph.
Polygenic trait
trait controlled by two or more genes at the same time
what mutations can affect
changes in protein structure, regulation/expression of the gene, silencing a gene, splicing of a gene → all lead to more variation
polymerase errors
DNA polymerase assembles the DNA nucleotides (building blocks)
hemoglobin mutation
mutated version of this allele leads to sickle cell anemia (problems for homozygotes); Β-globin allele is co-dominant and creates heterozygote advantage because it has malaria protection (common for Africans)
macromutations
Mutations with extensive and important phenotypic results ("hopeful monsters") - ex. colorful crest on a birds head
DFE of Mutation
requencies of mutations with various fitness consequences (distributions should be similar for species)
population level thinking
integrates selection with mendelian genetics
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
principle that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause the frequencies to change
Hardy-Weinberg null hypothesis
no relationship between variables, all variation is random (NO selection, NO migration, NO non-random mutating, NO mutation, and NO drift (population size = ∞)
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time (slope=0)
Hardy-Weinberg calculations
1) genotype frequencies (F[A,A], F[A,a], F[a,a])
2) allele frequencies (F[A] = p, F[a] = q
3) expected genotype frequencies (F[A,A] = p^2, F[A,a] = 2pq, F[a,a] = q^2)
4) do observed and expected genotype frequencies match? If yes, accept null and it is in equilibrium
H-W - relaxing selection
one allele favored over another