L.10 Chromatin Stucture and DNA replication
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Chromatin is what?
Repeating stricte of DNA and proteins (histones)
Each histone has this structure
Octomeric core
2H2A
2H2B
2H4
Nucleosome structre
146 DNA base pairs wrapped around histone
Chromatin fiber structure
Nucleosomes (beads) and linker DNA (string)
How to release nucleosomes
Digest chromatin with nucleus
How to link nucleosomes
Histone H1
Structure of histone H1
Globular NH2-terminal domain and COOH-terminal “arm”
How does H1 Link nucleosomes
binds to nucleosomes via globular domain
COOH arm reach to next H1
H1 linking is the first step of?
Chromosomal condensation/compacting
Chromatin condensation needed for?
Packaging of metaphase chromosomes
4 levels of condensation
11-nm chromatin fibre (DNA with meleosomes)
30-nm histone H1 pulls closer
300-nm 10 fold packing of looped/ folded part of chromosome
700-nm looped area get 20 loop (visible in metaphase)
Types of chromosomes, how many, and how to number
22 autosomal
2 sex
Numbered by length
G-banding karotype analysis
Classic giemsa staining allows to see dark bands (heterochromatin)
Normal (____ploid) karyotype for females
euploid
46, XX
Karyotype of male with Down syndrome
(47, XY, +21)
Philadelphia chromosome is example of _____ explain
oncogenic translocation
T(9;22) chromosome translocation forms new. (BCR/ABL) fusion gene
Burkitts lymphoma
t(8;14 translocation
Move proto-oncogene (c-myc) to enhancer of heavy gene → fires to much
_____ are readily seen with major chromosome abreirations
DNA instability syndromes
Mouse chromosome centromere location vs humans, but they have high ___ with people
Mouse - aeroccntric (at end)
Human - metacentric (centre)
Synteny (gene order)
Types of aberrations
aneuploidy (too many)
Segregation
Centromere loss
Fusion
Breakage
Structural elements of chromosome maitenee/replication
Telomere (caps ends to keep enzymes from destroying)
Organs of replication (inflation* points during S phase)
Kineochore (after nuclear breakdown, chromosomes segregated by kinelochore, formed at centromere
DNA replication begins at?
Origins of replication
Direction of DNA synthesis
Both directions form initiation complexes
What occurs when synthesis complexes meet
Strands lighted/joines to form daughter DNA
DNA polymerases synthesize in this direction, therefore stands are _____
5’ → 3’
Antiparallel
Leading strand process
5‘ → 3’ using 1 polymerase somplex
Lagging strand process
many proteins
Single strand binding proteins (keep strands apart)
Primate to “prime” DNA synthesis with RNA
Synthesis from RNA stands creat Okazaki fragments
Legate together
DNA pol III direction, how it works on leading strand
5’ → 3’ (created
Continuous replication
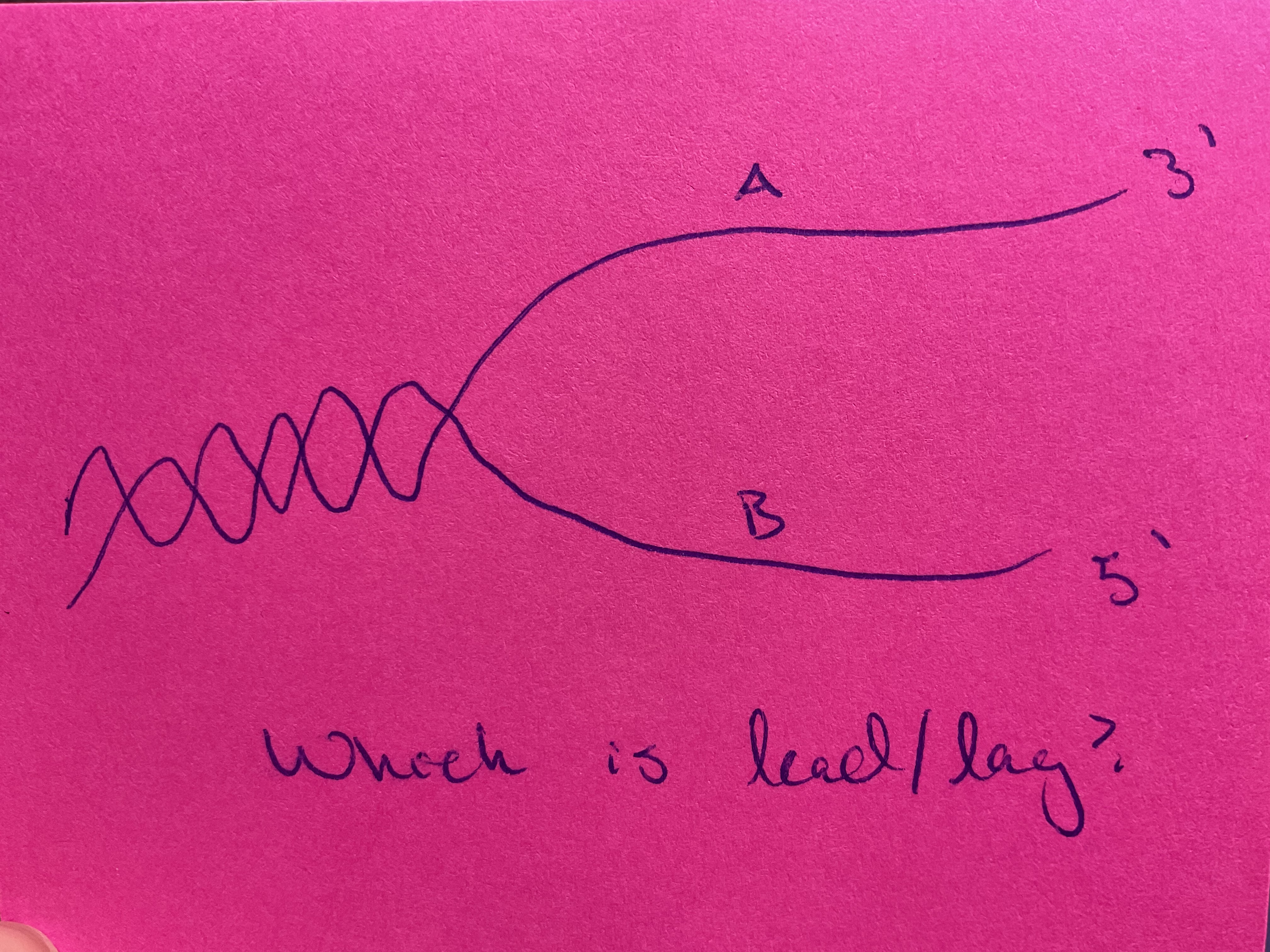
A = leading
B = lagging
Lagging strands requires ____ synthesis, where ____ templates made to prime ____ of _____ fragments, which are lighted together
discontinuous
Short RNA
DNA synthesis
Okazaki
Synthesis of both strands occurs ___, as what also occurs, forming this structure in the DNA
simultaneously
Chromosome unzipped form origin (DNA)
Replication fork
All steps of DNA replication
Replication origins recruit mutation complexes*
DNA unwound by toposiomerelase And helicases
Single strands stabilized by binding proteins
Leading synthesised by DNA pol III
Lagging synthesized by RNA primer and DNA primate to make Okazaki fragments with DNA pol I, DNA ligaments fuses
Example lagging strand with enzymes
RNA primer and DNA primate discontinuously
Okazaki fragments synthesized by DNA pol I
DNA ligaments fuses fragments together