Chemistry 1100 (EXAM 1) - Mizzou
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Matter
- Takes up space
- Has mass
- Either a Solid, Liquid, or Gas
Atoms
- Building Blocks of matter
- 118 (known) atoms
- Reactants > Compounds
The Periodic Table
Purpose: Organize elements by atomic number and by atomic mass.
- Rows are Periods
- Columns are Groups (share similar chemical properties)
periodic means repeating pattern
Group 1A Name:
Alkali Metals
Group 2A Name:
Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 5A Name:
Pnictogens
Group 6A Name:
Chalcogens
Group 7A Name:
Halogens
Group 8A Name:
Noble Gases
What kind of charge does a Proton have?
+1
What kind of charge does an Electron have?
-1
What kind of charge does an Neutron have?
0
Neutron
# of Protons = # of Electrons
What determines an elements identity?
The # of protons it has
Can an element contain a different # of electrons?
Yes. (Ions)
example: Na (11e-, 11p+) >(1e-) Na (10e-, 11p+)
Can an element contain a different # of neutrons?
Yes. (Isotopes)
example: 3 kinds of Carbon
6p, 6n, 6e - Carbon-12 (99% of all carbon)
6p, 7n, 6e - Carbon-13 (1% of all carbon)
6p, 8n, 6e - Carbon-14 (almost 0% of all carbon)
(radioactive)
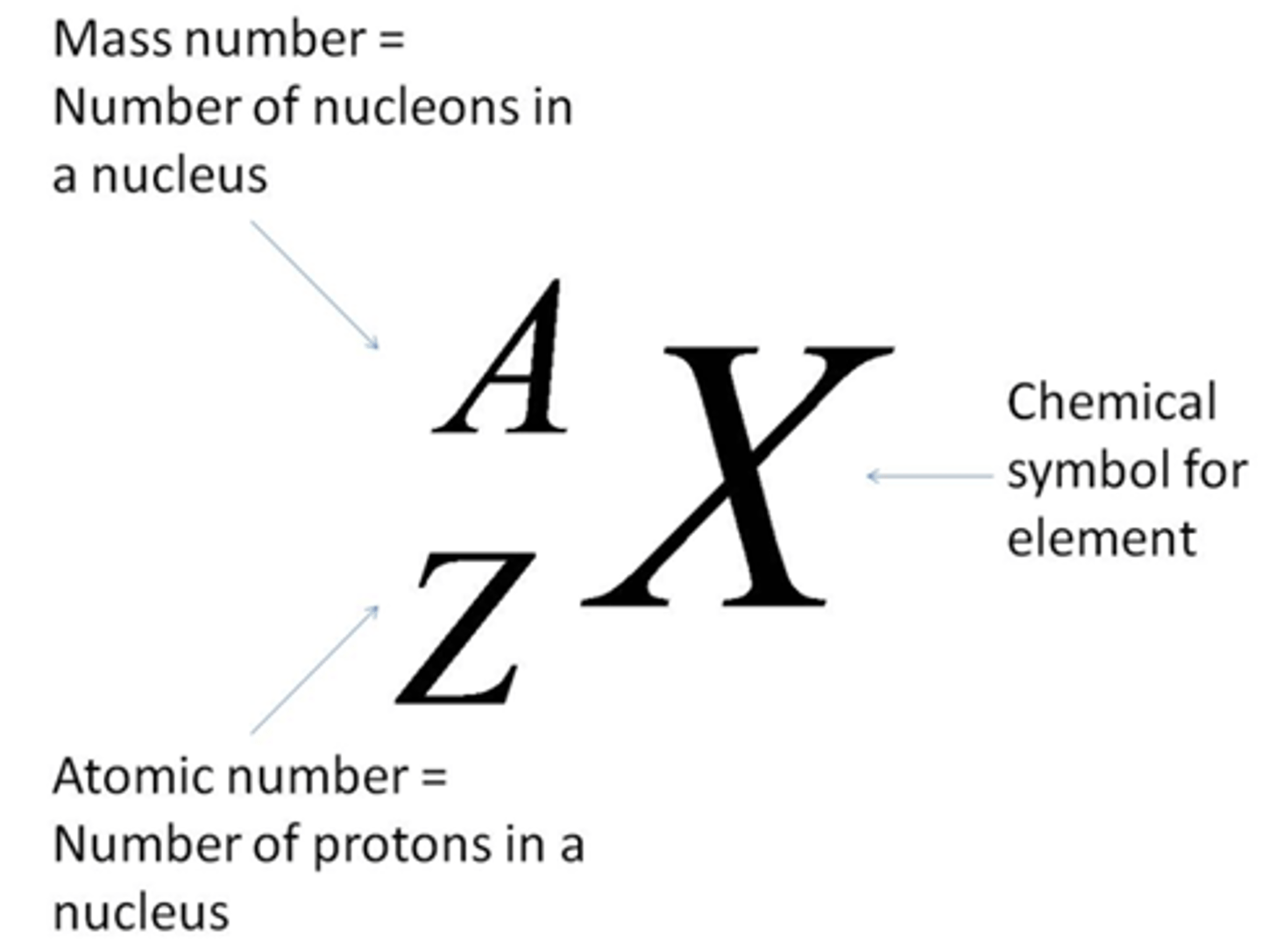
Atomic Number (Z)
# of protons in nucleus
Mass Number (A)
# of protons + number of neutrons = (Z) + # of neutrons
Isotopes:
same element (X) with different numbers of neutrons
How to write Mass Number/Atomic Number and Element
What happens if you change the # of protons in an element?
It changes the identity of the element.
What happens if you change the # of neutrons in an element?
It changes it to an Isotope.
What happens if you change the # of electrons in an element?
It changes to an Ion
Classification of Matter
Gases, Liquids, Solids, Plasma = Matter
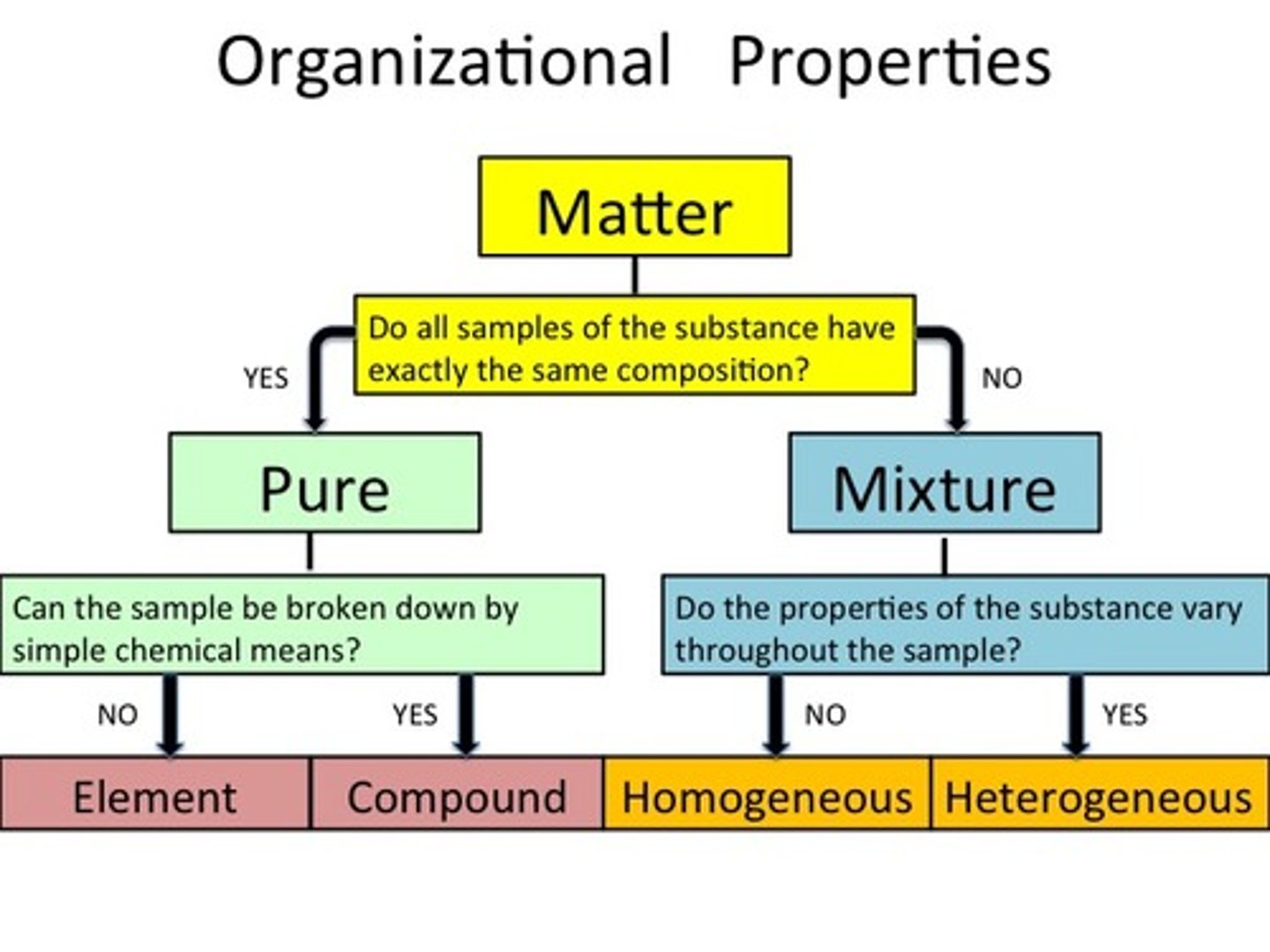
What are elements?
On the periodic table, expressed by a chemical formula
What are compounds?